CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Test Paper 1
Multiple Choice Question Type (1 mark)
Choose the correct answers:
1. Expenditure of revenue nature which gives benefit for more than one accounting period is classified as __________.
a) Capital Expenditure
b) Revenue expenditure
c) Deferred Revenue Expenditure
d) None of these
2. An amount of ₹10,00,000 spent on purchasing a building is _____.
a) Revenue Expenditure
b) Capital Revenue
c) Deferred Expenditure
d) Capital Expenditure
3. Sale of goods is a_________.
a) Revenue receipt
b) Capital receipt
c) Deferred revenue expenditure
d) revenue expenditure
4. Depreciation will be charged on which of the following?
a) Wages
b) Sales
c) Capital
d) Plant & machinery
5. For charging depreciation on an asset ___________.
a) Installation charges are deducted and scrap value is added to cost
b) Installation charges and scrap value are added to its cost
c) Installation charges are added and scrap value is deducted from the cost
d) Installation charges and scrap value are deducted from its cost
6. On 1st October, 2021 X Ltd. purchased a building costing ₹600000. Depreciation is to be charged @10% p.a. by straight line method. What amount of depreciation will be charged for the year ending March 31, 2023?
a) ₹30000
b) ₹60000
c) ₹54000
d) ₹57000
7. A new machine was imported by Rahul Ltd from Japan for ₹9,00,000 on 1st April, 2021
and 20% p.a. depreciation is charged as per written down value method. What will be the book value of the machine on 31 March, 2023?
a) ₹7,20,000
b) ₹3,24,000
c) ₹5,40,000
d) ₹5,76,000
8. ___________ is not a cause of depreciation.
a) Obsolescence
b) Wear & tear
c) Fluctuation in prices
d) Efflux of time
9. Under straight line method of charging depreciation, the amount of depreciation charged every year _______.
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Remains same
d) May increase or decrease
10. Statement I: When Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared with Credit balance as per Cash book; the balance derived will be only Debit balance as per Cash Book.
Statement II: Bank reconciliation statement is prepared by Bank.
a) Both the statements are false
b) Both the statements are true
c) Only Statement II is true
d) Only Statement I is true
11. Which of the following transactions will be shown as less item while preparing Bank Reconciliation Statement with balance as per Pass Book given?
a) Interest on investment collected by Bank
b) Bank charges charged by bank
c) Cheque deposited in the Bank not yet cleared
d) Bills paid by bank on standing instruction
12. A Bill dated 1st January, 2023 is paid three months after date. The maturity date of the bill
will be _____.
a) 5th April, 2023
b) 4thApril, 2023
c) 3rd April, 2023
d) 10th April, 2023
13. Maker of the bill is also known as _______.
a) Bill Receivable
b) Drawer
c) Drawee
d) Reserve
14. Credit balance as per Pass Book is ₹40,000. Cheques deposited but not yet collected were
₹ 14,000. What will be the resulting balance after preparing Bank Reconciliation Statement?
a) Debit Balance as per Cash Book ₹26,000.
b) Debit balance as per Cash Book ₹54,000
c) Credit balance as per Cash Book ₹26,000
d) Credit balance as per Cash Book ₹54,000
15. Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared to reconcile ____________.
a) Difference in the balance of Pass Book and Cash Book.
b) Difference in the cash and the bank balance
c) Difference in the Cash book in the beginning and at the end
d) None of the above
16. Gross profit of the firm was ₹5,60,000. There were indirect expenses of ₹1,50,000 and indirect income of ₹40,000. Then the final result will be ___________?
a) Net profit of ₹4,20,000
b) Net loss of ₹2,80,000
c) Net profit of ₹4,50,000
d) Net loss of ₹4,20,000
17. When Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared with Debit balance as per Cash Book, the balance derived will be ______.
a) Credit balance as per Pass Book
b) Debit balance as per Pass Book
c) Debit balance as per Cash Book
d) Either (a) or (b) is possible
18. The acceptor of the bill of exchange is known as __________.
a) Drawer
b) Drawee
c) Bank
d) Endorsee
19. From incomplete records, it is possible to prepare _____.
a) Trial balance
b) Statement of affairs
c) Ledger accounts
d) None of the above
20. While preparing Statement of affairs, total of asset side was ₹6,20,000, sundry creditors amounted to ₹100,000 and bills payable of ₹30,000
as on 31st March, 2023. The capital as on 31st March,2023 will be _________.
a) ₹7,50,000
b) ₹4,90,000
c) ₹5,20,000
d) ₹6,90,000
21. Capital of the firm is increased by________.
a) Loss
b) Profit
c) Drawings
d) Expense
22. Interest received from Bank is shown in _____________.
a) Debit side of Trading account
b) Credit side of profit & Loss account
c) Liabilities side of Balance Sheet
d) Asset side of Balance Sheet
23. Carriage inward is shown in ___________.
a) Debit side of Trading account
b) Debit side of Profit & Loss account
c) Credit side of Profit & Loss account
d) Credit side of Trading account
24. Which of the following is not a financial statement prepared by a sole trader?
a) Balance sheet
b) Bank reconciliation Statement
c) Trading account
d) Profit & Loss account
Short Questions (3 Marks)
1. State any three points of distinction between capital and Revenue expenditure.
2. Riya incurred the following expenditure on various items during the year ended 31st March, 2023:
Furniture ₹ 2,00,000
Salaries ₹ 40,000
Advertisement on launching new products ₹ 70,000
Carriage outward ₹ 2,000
Identify the items of capital expenditure, revenue expenditure and deferred revenue expenditure from the above.
3. Distinguish between straight line method and Diminishing Balance method on any three basis.
4. On 20th July, 2022, Rakesh sold goods to Amit for ₹40,000 and issued upon him a bill for 3 months. Amit accepted the bill and returned it to Rakesh. The bill was met on due date. Pass entries in the books of Rakesh.
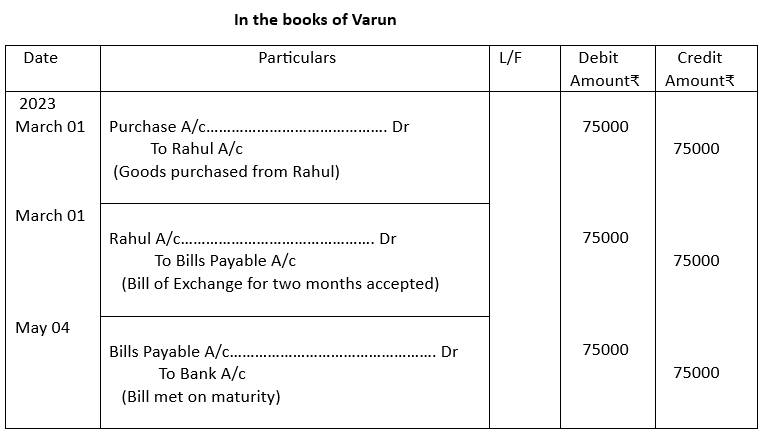
5. On 1st March, 2023, Varun purchased goods from Rahul of ₹75,000 and accepted a bill for two months. The bill was met on due date. Pass entries in the books of Varun.
Short Questions (4 marks)
1. Kamal received from Rohan an acceptance for ₹ 60,000 on 1st June, 2022 at 4 months. Kamal got this acceptance discounted @12% p.a. at his bank. On the due date, Rohan paid the required amount. Give the journal entries in the books of Kamal and Rohan.
2. From the following information, prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 31st March, 2023:
a) Cash Book showed a balance of ₹52,000.
b) Cheques issued but not yet presented for payment amounted to ₹3,000.
c) Bank charges debited by Bank but not recorded in cash Book amounted to ₹950.
d) Cheques deposited in Bank and cleared but omitted to be entered in Cash Book amounted to ₹2,000.
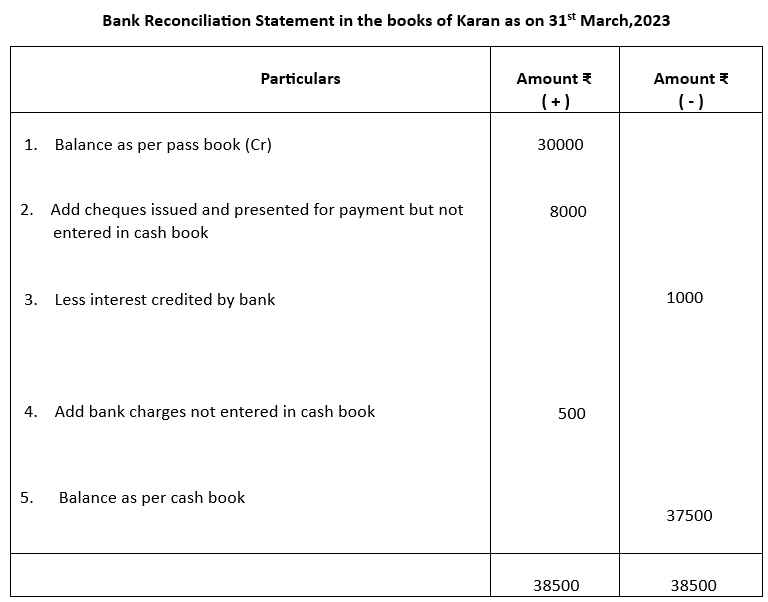
3. Prepare bank Reconciliation Statement of Karan as on 31st March, 2023:
a) Pass Book showed a credit balance as on date is ₹30,000
b) Cheques issued and presented for payment for ₹8,000 but omitted to be entered in Cash book.
c) Interest credited to Bank amounted to ₹1000
d) Bank charges amounted to ₹500 were not credited to Cash book
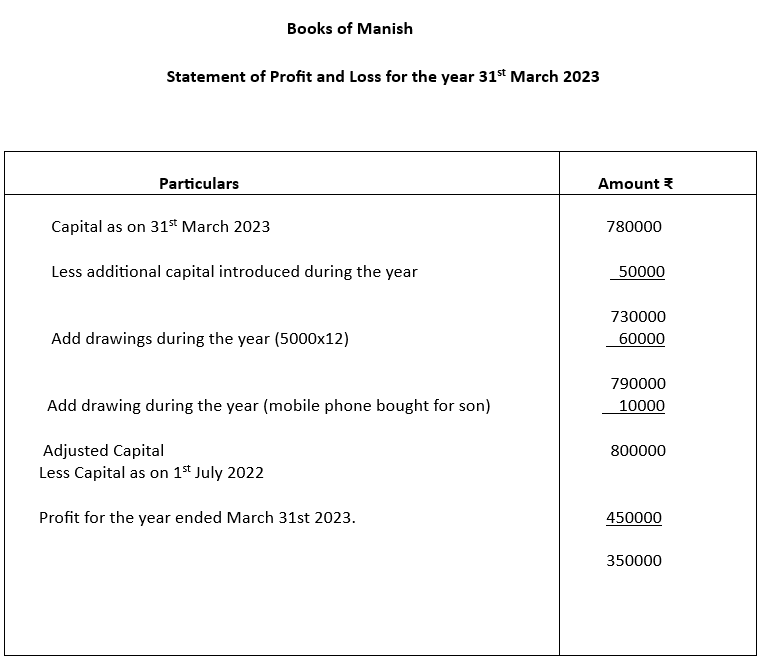
4. Manish started business with capital of ₹4,50,000 on 1stJuly,2022. He introduced additional capital of ₹50,000 on 31st October,2022 and withdrew ₹5,000 per month for personal use. He also spent ₹10,000 from the business to buy mobile phone for his son. If the capital as on 31st March, 2023 was ₹7,80,000, calculate Profit & Loss for the year March 31st 2023.
5. Differentiate between Trading Account and Profit & Loss account.
6. Differentiate between direct expense and indirect expense.
Long Question (6 Marks)
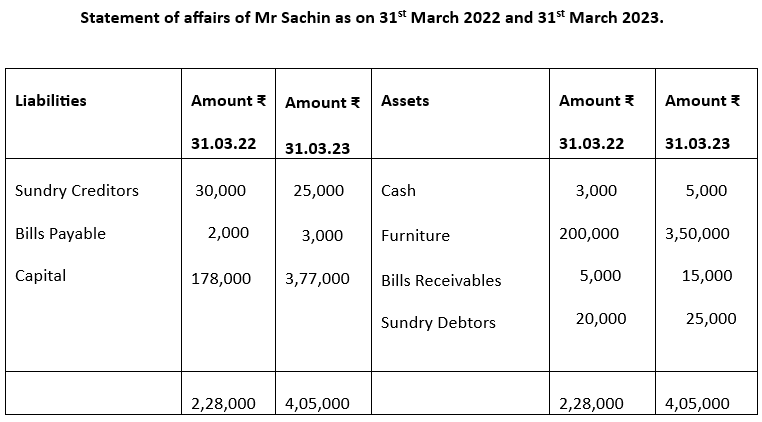
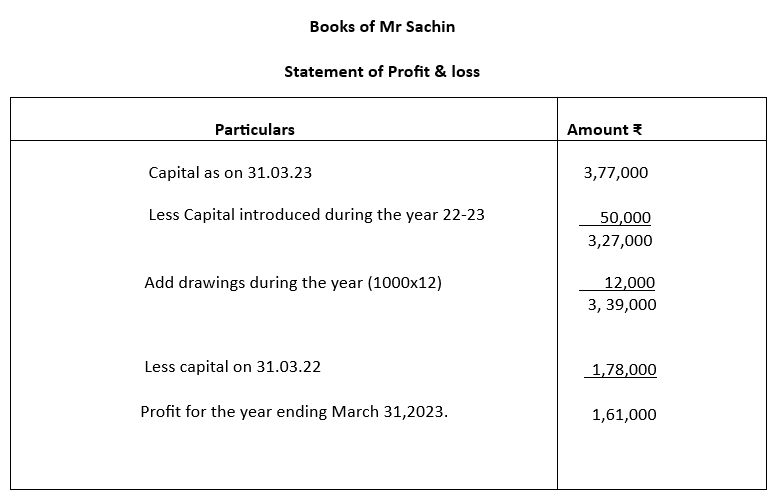
1. Following is the position statement of Mr Sachin (who maintains his accounts in incomplete system) as on 31st March 2022 and 31st March 2023.
| Particulars | 31st March 2022 | 31st March 2023 |
| Amount in ₹ | Amount in ₹ | |
| Cash | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| Furniture | 2,00,000 | 3,50,000 |
| Sundry Creditors | 30,000 | 25,000 |
| Bills Receivables | 5,000 | 15,000 |
| Sundry Debtors | 20,000 | 25,000 |
| Bills Payables | 2,000 | 3,000 |
During the year 2022-2023, he introduced ₹50,000 as additional capital and withdrew ₹1,000 per month for his personal use. Ascertain his profit for the year ending March 31, 2023.
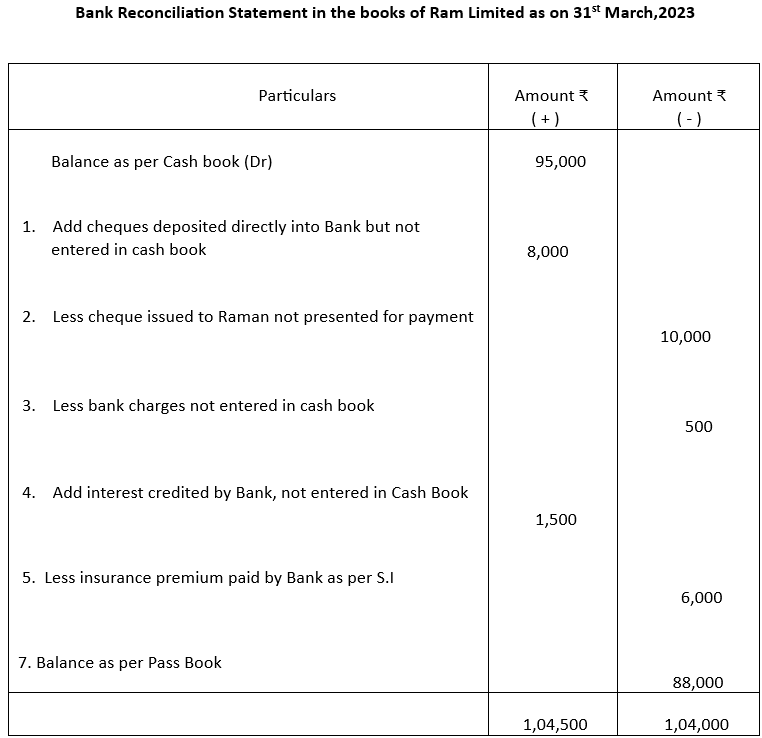
2. Debit balance shown by the Cash Book of Ram Limited is ₹95,000. Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as on31st march 2023:
a) Cheque deposited of ₹8000 directly into Bank.
b) Cheque issued for ₹!0,000 to Raman was not presented for payment.
c) Bank charges debited ₹500
d) Bank had credited ₹1,500 as interest which was not recorded in Cash Book
e) Insurance premium of ₹6,000 paid by bank directly as per standing instruction, not recorded in cash book.
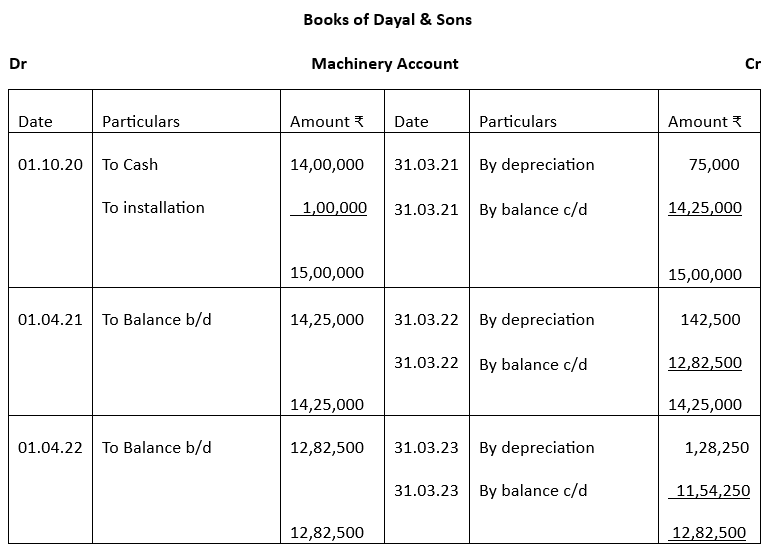
3. Dayal & Sons purchased a machinery for ₹14,00,000 on 1st October 2020 and spent ₹1,00,000 on installation. Depreciation was to be provided @10% by written down value method. Prepare machinery account for 3 years assuming the books are closed on March 31st every year.
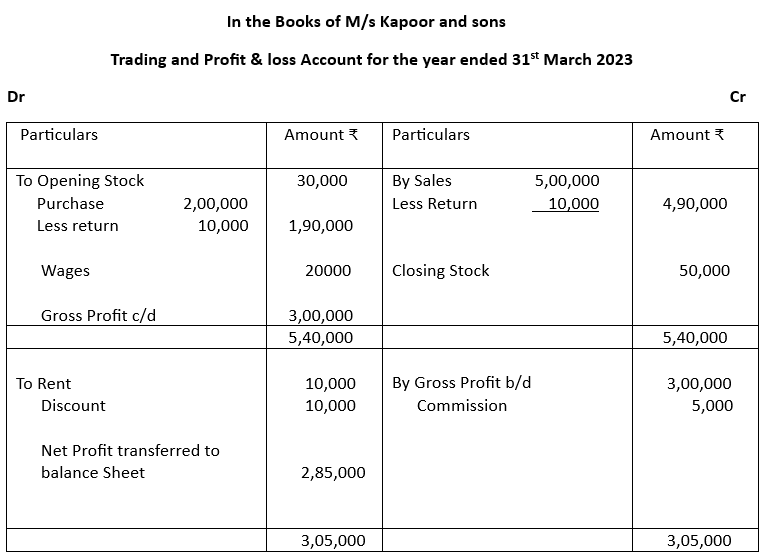
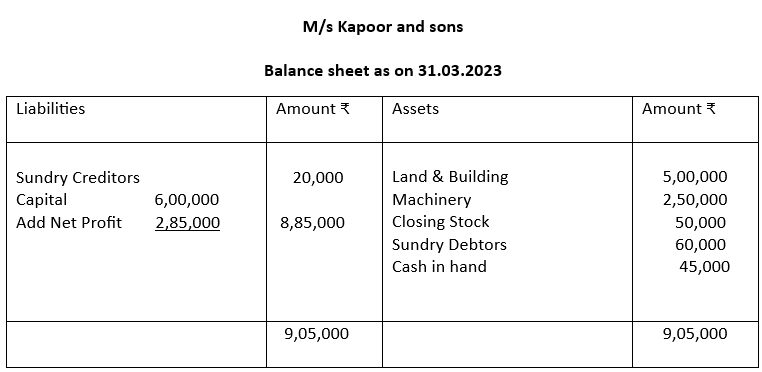
4. Prepare Trading Account, Profit & Loss Account and Balance sheet for M/s Kapoor and sons from the following information for the year ending 31st March 2023 when closing stock is valued at
₹50,000.
Trial balance as on 31.3.23
| Name of the Account | Debit Balance (₹) | Credit balance (₹) |
| Opening Stock | 30,000 | |
| Purchase and Sales | 2,00,000 | 5,00,000 |
| Returns | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| Debtors & Creditors | 60,000 | 0,000 |
| Land & Building | 5,00,000 | |
| Wages | 20,000 | |
| Rent | 10,000 | |
| Capital | 6,00,000 | |
| Cash in Hand | 45,000 | |
| Machinery | 2,50,000 | |
| Commission | 5,000 | |
| Discount | 10,000 | |
| 11,35,000 | 11,35,000 |
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Test Paper 1 Solutions
Answers to MCQ questions (1 Mark)
1. c) Deferred Revenue Expenditure
2. d) Capital Expenditure
3. a) Revenue receipt
4. d) Plant & machinery
5. c) Installation charges are added and scrap value is deducted from the cost
6. b) ₹60000
7. d) ₹5,76,000
8. c) Fluctuation in prices
9. c) Remains same
10. a) Both the statements are false
11. a) Interest on investment collected by Bank
12. b) 4thApril, 2023
13. b) Drawer
14. b) Debit balance as per Cash Book ₹54,000
15. a) Difference in the balance of Pass Book and Cash Book.
16. c) Net profit of ₹4,50,000
17. a) Credit balance as per Pass Book
18. b) Drawee
19. b) Statement of affairs
20. b) ₹4,90,000
21. b) Profit
22. b) Credit side of profit & Loss account
23. a) Debit side of Trading account
24. a) Balance sheet
Answers to Short Questions (3 Marks)
1.
| Capital Expenditure | Revenue Expenditure |
| Capital expenditure increases earning capacity of the business. | Revenue Expenditure is incurred to maintain the earning capacity of the business. |
| Capital expenditure is incurred to acquire Fixed assets for operation of the business | Revenue Expenditure is incurred to meet day to day expenses of the business |
| Capital expenditure is non-recurring in nature. | Revenue Expenditure is generally recurring in nature. |
2.
Capital expenditure: Furniture ₹2,00,000
Revenue expenditure: Salary ₹40,000
Carriage Outward ₹2000
Deferred Revenue Expenditure: Advertisement ₹70,000
3.
| Points of difference | Straight Line Method | Diminishing Balance method |
| 1. Basis of charging depreciation | Original Cost of the asset | Book Value i.e. original cost less depreciation charged till date or net Book value at the beginning of the year |
| 2. Annual depreciation charge | Fixed every year | Declines year after year |
| 3. Total depreciation charge against profit & loss account | Increases in the later years with rising repair expenses | Almost equal every year as declining depreciation cost is balanced with rising repair expenses |
4.
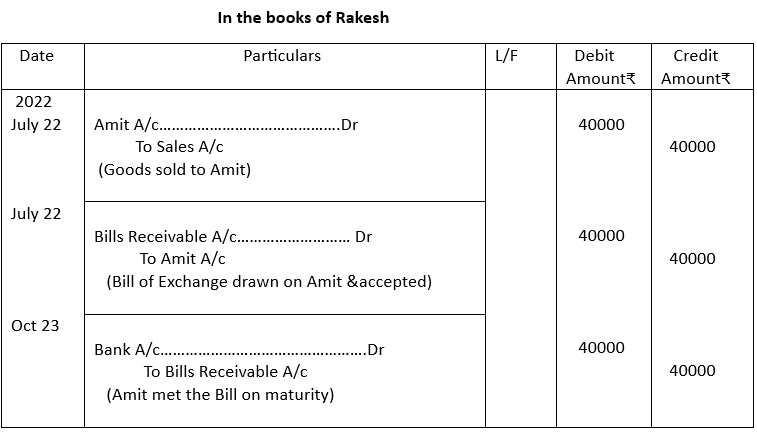
5.
Answers to Short Questions (4 Marks)
1.
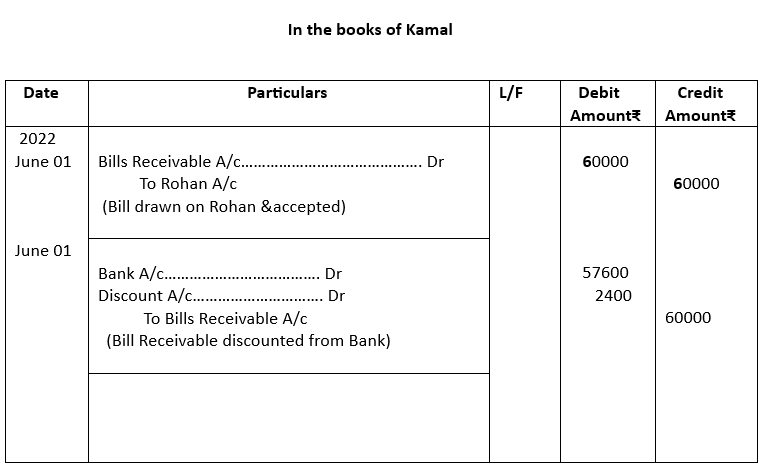
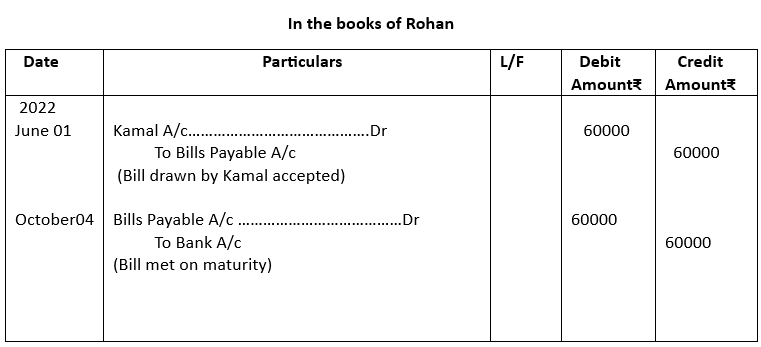
2.

3.
4.
5.
| Trading account | Profit & loss Account |
| 1. All expenses directly related to production process i.e. purchases, wages, electricity are shown in Trading Account. | 1. All indirect expenses like salaries, rent, taxes, depreciation are debited to Profit & Loss Account. |
| 2. Trading Account arrives at Gross Profit of a concern. | 2. Profit & loss Account shows Net profit of a business concern. |
| 3. Opening Stock and Closing stock figures are shown in Trading account. | 3. Profit & Loss Account does include any stock amount. |
| 4. Gross profit shown in Trading account is carried over to Profit & Loss Account | 4. Net Profit/Loss as calculated in Profit & Loss account is transferred to Balance Sheet. |
6.
| Direct Expenses | Indirect Expenses |
| 1. Direct expenses are costs that are directly related to the production of goods. For example, purchase of raw materials, wages, electricity etc. | 1. Indirect expenses do not relate directly to the production activity, but cover other costs of running the business, for example, administrative expenses, staff salaries, taxes, advertisement, depreciation etc. They are also called overhead expenses. |
| 2. Direct expenses are accounted for in Trading Account to find out Gross Profit. | 2. Indirect expenses are deducted In Profit & loss Account to arrive at Net Profit. |
| 3. Direct expenses varies with the volume of production. | 3. Indirect or overhead expenses are usually fixed and do not vary with the volume of production. |
| 4. Direct expenses are related to cost of goods (Purchase + direct expense – Closing Stock = Cost of Goods) | 4. Indirect expenses are related to Cost of Goods sold (Cost of Goods + Indirect expense = Cost of Goods Sold) |
Answers to Long Question (6 Marks)
2.
3.
4.
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Test Paper 1 – Completed
Related Links:
Unit 1: Capital and Revenue
Unit 2: Depreciation
Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement
Unit 4: Bills of Exchange
Unit 5: Final Accounts
Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete records
Test Paper 1
Test Paper 2


