CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Test Paper 2
Multiple Choice Question (1 mark each)
1. Which of the following is a Capital Receipt?
a) Rent Received
b) Sale of services
c) Loan received by the business
d) Salary received
2. Which of the following is revenue expenditure?
a) White wash expense
b) Trade Mark purchase
c) Expenses incurred to get manager’s office air-conditioned
d) Goodwill purchased
3. Capital Receipts and Revenue Receipts _________.
a) are different
b) are not different
c) may or may not be distinguished
d) must not be distinguished
4. A machinery was purchased for ₹800000 on 1st October, 2021. Depreciation was to be charged @ 10% p.a.by straight line method. What will be the book value of machinery on 31st, March, 2022?
a) ₹760000
b) ₹720000
c) ₹700000
d) ₹800000
5. A firm purchased furniture of ₹500000 on 1stApril, 2020.Depreciation was to be charged @5% p.a. on Written Down Value method. What will be the book value of the machinery on 31st March, 2022?
a) ₹457250
b) ₹451250
c) ₹450000
d) ₹451000
6. On 1st April, 2019 B Ltd. Purchased machinery of ₹800000. Depreciation was to be charged @10% p.a. by Fixed Instalment system. On the same day Ram Ltd. Also purchased machinery of the same amount and charged depreciation @ 10% p.a.by Reducing Instalment method. On 31stMarch, 2021 which of the following statements holds good?
a) Book value of machinery of both the firms will remain the same
b) Book value of machinery of Ram Ltd. Will be ₹8000 more than B Ltd
c) Book value of machinery in B Ltd. Will be ₹8000 more than Ram Ltd.
d) Book value of machinery in B Ltd. Will be ₹10000 less than Ram Ltd.
7. Depreciation Account is closed at the end of the year by transferring its balance to specific account. Which of the following is a name of this Account?
a) Fixed Asset Account
b) General Reserve Account
c) Profit and Loss Account
d) Capital Account
8. Assertion (A): Under written down value method, the amount of depreciation decreases every year.
Reason (R): In written down value method, the book value of asset will never become zero.
a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
c) (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect
d) (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct
9. Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared _______
a) to know the payment made through cheque
b) to know the errors in bank pass book
c) to compare the cash book balance with bank pass book balance and ascertain the difference
d) to balance pass book
10. Bank Reconciliation statement is ________.
a) a part of double entry system
b) not a part of double entry system
c) a part of single entry system
d) a part of cash balances of the cash book
11. Statement -1:
When Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared with overdraft balance as per pass book, the balance derived will be only balance as per Bank Pass Book
Statement-2: Bank Reconciliation statement is prepared by Account holder.
a) Both the statements are false
b) Both the statements are true
c) Only Statement 1 is true
d) Only statement 2 is true
12. A business receives its bank statement showing the closing balance as ₹8500 overdrawn. It is found that there were unpresented cheques of ₹2000 and uncredited deposits of ₹1500. Overdraft as per cash book will be __________.
a) ₹5000
b) ₹8000
c) ₹9000
d) ₹12000
13. Cash Book shows ₹1000 as overdrawn. When bank statement is received it was identified that one of the debtors has deposited ₹400 into the account and bank charges of ₹20 had been debited to the account. Bank statement balance is __________.
a) ₹1420 (Dr)
b) ₹ 620 (Dr)
c) ₹4300 (Dr)
d) ₹1700 (Dr)
14. Assertion (A) : A bill of exchange must be unconditional
Reason (R): A bill of exchange must specify the date by which the amount should be paid
a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of A
b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
c) (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect
d) (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct
15. A bill of exchange facilitates credit purchase. A bill of exchange has _________.
a) two parties
b) three parties
c) four parties
d) seven parties
16. On 1st January, 2022 Jishu issued a bill on John for 4 months. What will be the maturity date of
the bill?
a) 3rd May, 2022
b) 4th May, 2022
c) 5th May, 2022
d) 10th May, 2022
17. On 1st April, 2021, Ram sold goods to Mohan for ₹50000. On the same date, Mohan accepted a bill drawn upon him by Ram, at 3 months for ₹50000. On due date the bill was met. Who is the drawer of the bill in the above situation?
a) Ram
b) Mohan
c) Bank
d) Government
18. Loss on sale of an old car is debited to _________.
a) Profit and Loss Account
b) Car Account
c) Depreciation Account
d) Trading Account
19. While preparing Trading Account return inward is deducted from ___________.
a) Purchases
b) Sales
c) Return Outward
d) Gross Profit
20. Gross profit of a firm was ₹400000. Which of the following will reduce the amount of net profit?
a) Rent received
b) Depreciation
c) Interest received
d) Discount received
21. Which statement shows financial position of the business?
a) Trading Account
b) Profit and Loss Account
c) Balance Sheet
d) Trial Balance
22. Which of the following is not shown in the Balance Sheet?
a) Opening Stock
b) Closing Stock
c) Patents
d) Debtors
23. Statement 1
Statement of Profit and Loss is not prepared by owner in case of ‘incomplete records’
Statement 2
Single entry system is an incomplete double entry system varying with circumstances
a) Both the statements are false
b) Both the statements are true
c) Only statement 1 is true
d) Only statement 2 is true
24. While preparing Statement of Affairs, total of asset side was ₹600000, Loan ₹100000. Here, the balancing figure of ₹500000 will be known as ______.
a) Loss
b) Profit
c) Capital
d) Creditors
25. From incomplete records it is possible to prepare _______.
a) Ledger Accounts
b) Trial Balance
c) Statement of Affairs
d) Profit and Loss Account
Short Questions (3 mark)
1. Hira started a business with a capital of ₹500000. She purchased furniture of ₹75000 and shop for ₹175000. During the year 2021-22 she paid salaries of ₹50000. She also spent ₹30000 on advertisement for launching her business which is assumed to provide benefit for more than one financial year. On the basis of the above information, calculate the following:
a) Total Revenue Expenditure
b) Total Capital Expenditure
c) Total Deferred Revenue Expenditure
2. State the three points of difference between Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure
3. State any three merits of ‘Straight Line Method ‘of charging depreciation.
4. On 10th March, 2022, A sold goods to B for ₹20000. A drew on B a bill at 3 months for ₹20000 which B accepted immediately and returned it to A. The bill was met on the due date. Give necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of A.
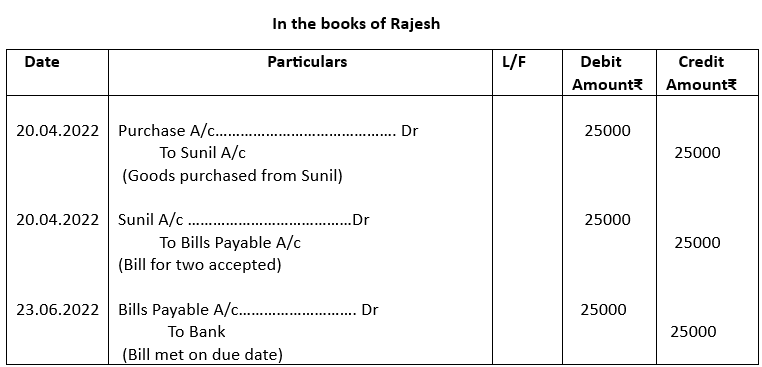
5. On 20th April, 2022 Rajesh purchased goods from Sunil worth ₹25000 and accepted a bill for two months. The bill was met on due date. Pass necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of Rajesh.
Short Question (4 mark each)
1. On 31st March, 2022, Cash Book of Rahul showed a bank balance of ₹7800. On comparing the Cash Book with Pass Book, the following discrepancies were noted:
a) Cheque deposited in bank not credited ₹3000
b) Cheque issued but not yet presented for payment ₹1500
c) Insurance premium paid by the bank ₹2000
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement
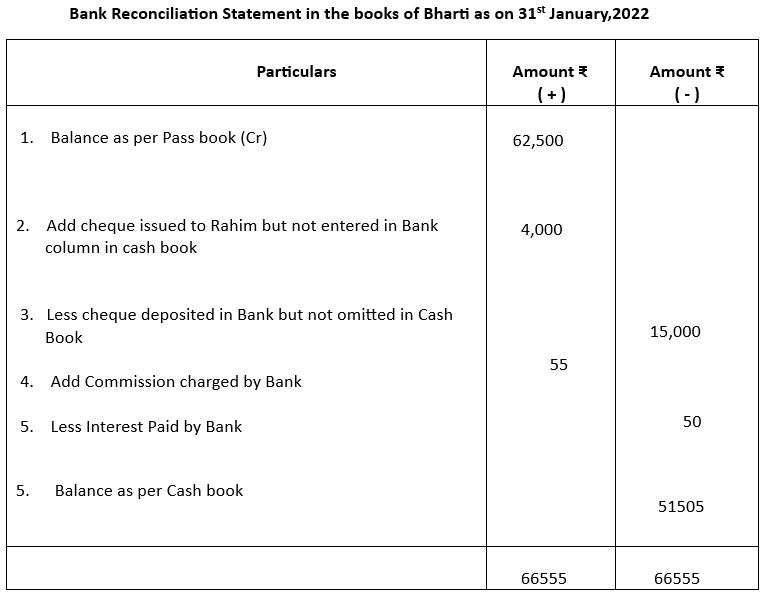
2. Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement of Bharti as on 31.1.2022. Balance as per Pass Book as on 31.1.2022 was ₹62500.
i) A cheque of ₹4000 issued to Rahim was taken in the cash column
ii) A cheque of ₹15000 was paid into Bank but was omitted to be entered in Cash Book
iii) The bank has charged ₹55 as its commission and has allowed interest ₹50.
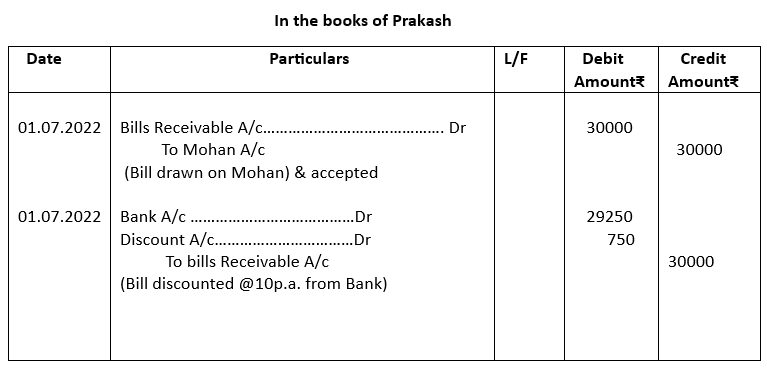
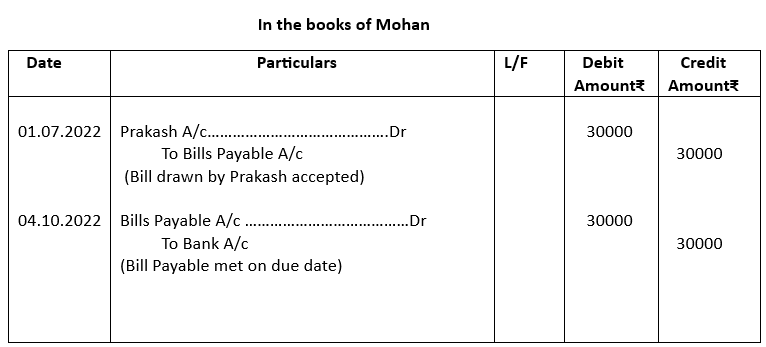
3. Prakash received from Mohan an acceptance for ₹30000 on 1st July, 2022 at 3 months. Prakash got this bill acceptance discounted at 10% p.a. from his bank. On the due date, Mohun paid the required amount. Give the necessary Journal Entries for the above transactions in the books of Prakash and Mohan.
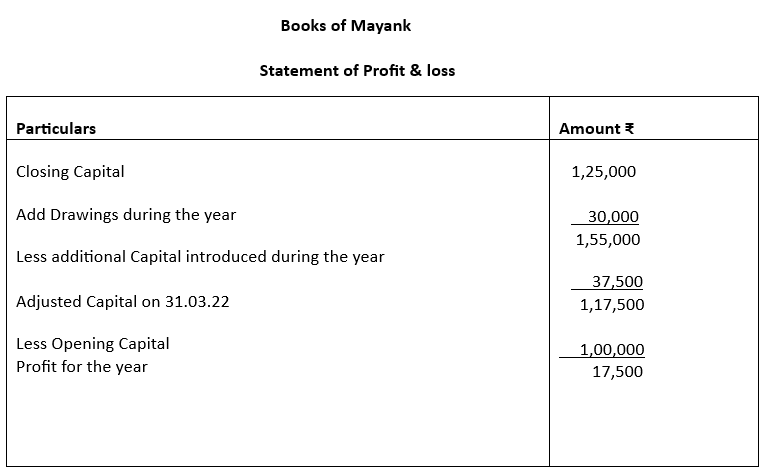
4. Mayank does not keep proper records of his business. He gives you the following information:
Opening Capital ₹100000
Closing Capital ₹125000
Drawings made ₹ 30000
Additional Capital
introduced during the year ₹ 37500
Calculate profit or loss for the year.
Long Question (6 mark each)
1. On 1st January, 2020, a company purchased second hand machinery for ₹ 96000 and spent ₹24000 on its erection. Prepare the Machinery Account for three years. The rate of depreciation is 10% p.a. The accounts are closed on 31st December. Depreciation was charged on the basis of Straight-Line Method.
2. Sudhir was running a business of medicine and was having bank account with HDFC Bank. His accountant went on leave and when he came back, he found that the cash book balance was not tallying with pass book balance as on 31st August, 2022. Upon enquiry the following points were found to be the reasons of disagreement:
i) Cheque deposited into the Bank but no entry was passed in the Cash Book ₹500
ii) Cheque received and entered in the Cash Book but not sent to Bank ₹1200
III) Credit side of the Cash Book bank column was cast short by ₹200
iv) Insurance premium paid directly by the bank under the standing advice ₹600
v) Bank charges ₹20 were entered twice in the Cash Book
From the above hypothetical case study, answer the following questions
a) Name the statement to be prepared by Ramesh for finding out the reasons for the disagreement
in the Cash Book and Pass Book balances
b) If the balance as per Cash Book is the starting balance for preparing the statement then how will
you treat item (i)?
c) If balance as per Pass Book is starting balance for preparing the statement the how will you treat
item (ii)?
d) If balance as per cash Book is starting balance for preparing the statement then how will you treat
item (iii)?
e) if balance as per Pass Book is the starting balance then how will you treat item (iv)?
f) If balance as per Cash Book is starting balance for preparing the statement, how will you treat
item (v)?
3. Following is the position statement of Ramji as on 31-3-2020 and 31-3-21. He maintains
incomplete accounts. During 2020-21 he introduced ₹10000 as additional capital. He withdrew ₹3000 every month for his personal use. Ascertain his profit for the year ended 31st March, 2021.
| Particulars | 31-03-20 ₹ | 31-03-21 ₹ |
| Cash | 1000 | 900 |
| Sundry Debtors | 39000 | 45000 |
| Stock | 34000 | 32000 |
| Plant and Machinery | 60000 | 80000 |
| Sundry creditors | 30000 | 14900 |
| Bills Payable | 50000 |
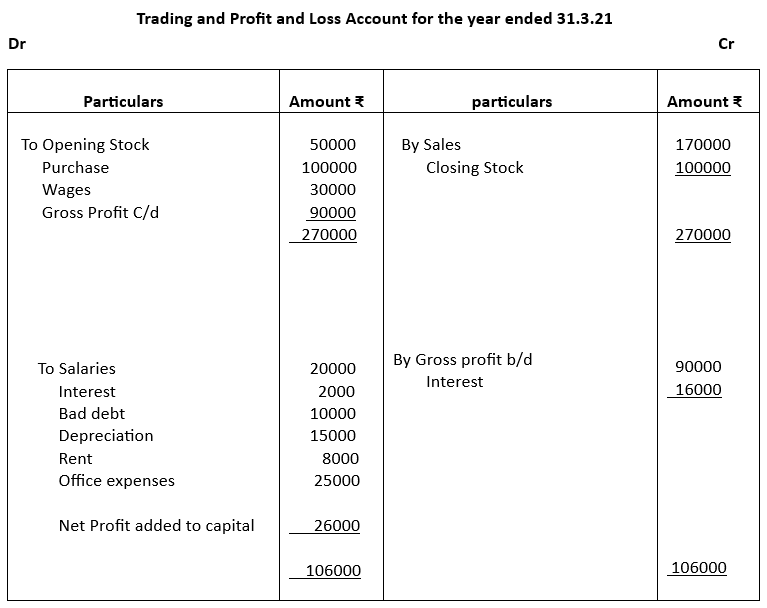
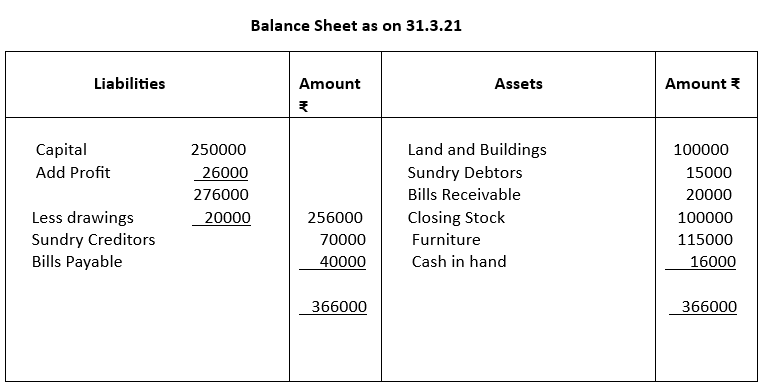
4. From the following trial Balance prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Accounts for the year ended 31.03.2021
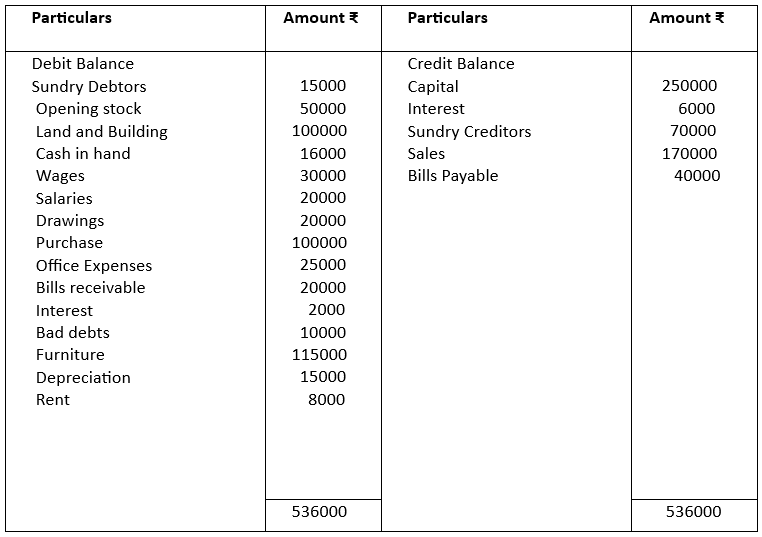
The closing stock was valued at ₹100000
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Test Paper 2 Solutions
Answer to MCQ questions (1 Mark)
1. c) Loan received by the business
2. a) White wash expense
3. a) are different
4. a) ₹760000
5. b) ₹451250
6. c) Book value of machinery in B Ltd. Will be ₹8000 more than Ram Ltd.
7. c) Profit and Loss Account
8. a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
9. c) to compare the cash book balance with bank pass book balance and ascertain the difference
10. b) not a part of double entry system
11. d) Only statement 2 is true
12. a) ₹5000
13. b) ₹ 620 (Dr)
14. a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of A
15. b) three parties
16. b) 4th May, 2022
17. a) Ram
18. a) Profit and Loss Account
19. b) Sales
20. b) Depreciation
21. c) Balance Sheet
22. a) Opening Stock
23. d) Only statement 2 is true
24. c) Capital
25. c) Statement of Affairs
Answers to Short Questions (3 mark)
1. a) Total Revenue Expenditure ₹50,000
b) Total Capital Expenditure ₹2,50,000
c) Total Deferred Revenue Expenditure ₹30000
2.
| Capital Expenditure | Revenue Expenditure |
| 1. Capital Expenditure increases earning capacity of business. | 1. Revenue Expenditure is incurred to maintain earning capacity. |
| 2. Capital Expenditure is incurred to acquire fixed assets of the business. | 2. Revenue Expenditure is incurred to meet day to day expenses. |
| 3. Capital Expenditure is non-recurring in nature. | 3. Revenue Expenditure is generally recurring in nature. |
3. Three merits of ‘Straight Line Method ‘of charging depreciation are:
(i) It is very simple to understand and apply.
(ii) Assets can be depreciated up to Net Asset Value or scrap value. Therefore, this method makes it possible to distribute full depreciable cost over useful life of the asset.
(iii) Every year same amount is charged as depreciation in the Profit & Loss account. This makes comparison of profits of different years easy and realistic.
4.
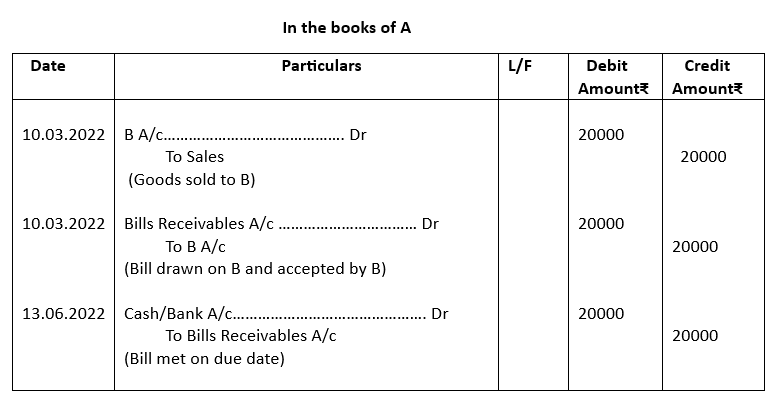
5.
Answers to Short Questions (4 mark)
1.
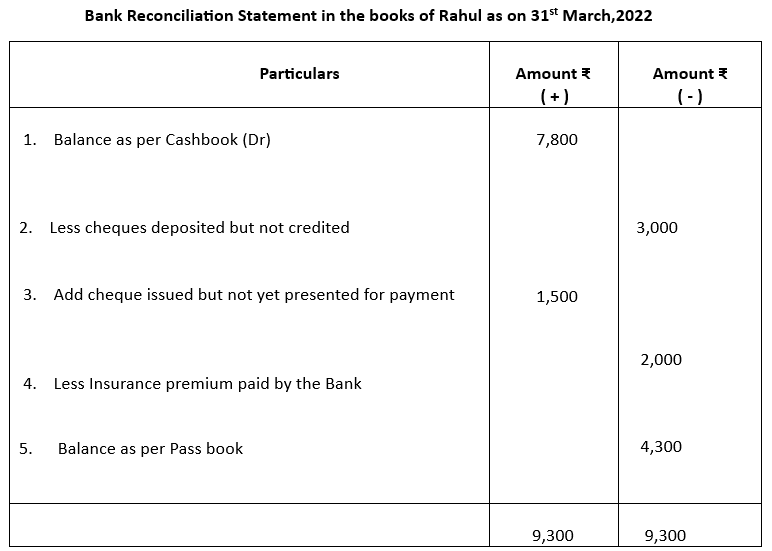
2.
3.
4.
Answers to Long Question (6 mark each)
1.
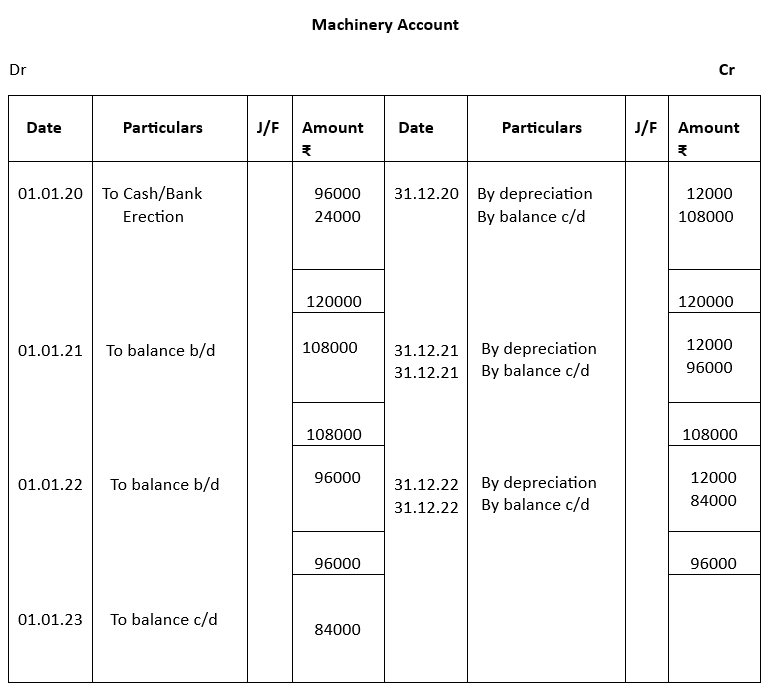
2.
(a) Bank Reconciliation Statement
(b) No entry was made in the cash book for cheque deposited into bank for ₹500. So, this amount has to be added to cash book balance.
(c) Cheque received was entered in the Cash Book but was not sent to bank. The cheque amount of ₹1200 has to be added to Pass book balance.
(d) Cash Book balance was undercast by ₹200, so ₹200 has to be added to Cash Book balance.
(e) The Bank has paid the insurance premium reducing the balance. Starting with Pass Book balance it has to be added back to make it reconcile with Cash Book balance.
(f) Bank charges entered twice in Cash Book, So, ₹20 has to be added to cash book balance.
3.
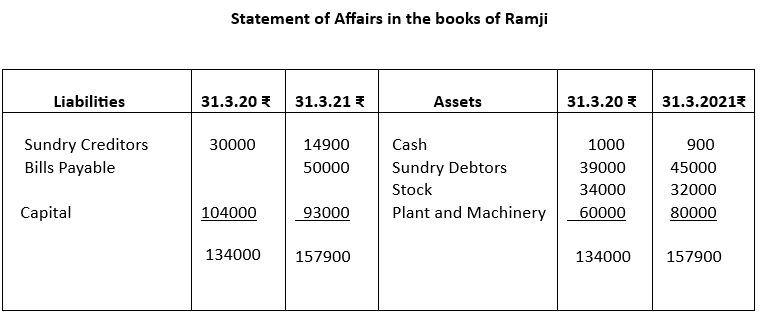
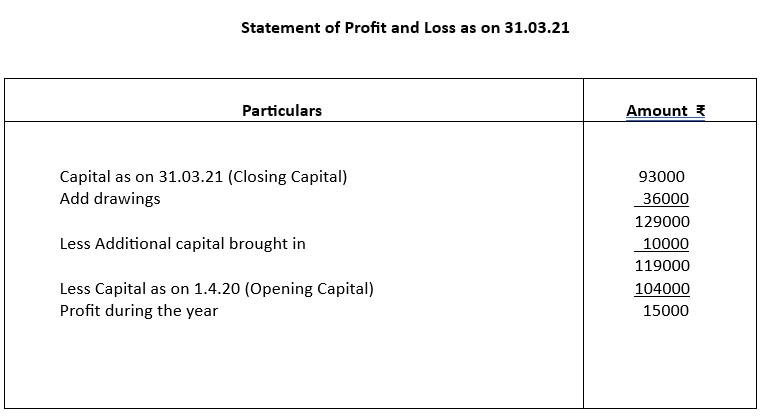
4.
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Test Paper 2 Solutions – Completed
Related Links:
Unit 1: Capital and Revenue
Unit 2: Depreciation
Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement
Unit 4: Bills of Exchange
Unit 5: Final Accounts
Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete records
Test Paper 1
Test Paper 2


