Content:
Meaning of Bank Reconciliation Statement
Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement with given pass book/cash book balance
Learning Outcomes:
Understanding the concept of Bank Reconciliation Statement
Appreciating the need for preparing bank reconciliation statement
Developing the skill of preparing bank reconciliation statement
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement
Meaning of Bank Reconciliation Statement
We know that every business organisation maintains cash book to record all cash and bank transactions and both these accounts are balanced at the end of a period.
Once the cash book has been balanced it is customary to check the detail of the firm’s bank transactions as recorded by the bank in the pass book. To do this one has to ensure that the cash book is up to date and the latest bank pass book /statement has been obtained from the bank. The balance shown in the pass book should tally with the balance shown in the cash book.
But, in actual practice this seldom happens. Generally, the balance shown in the bank statement will differ from the one showed by cash book. To keep the records straight this anomaly has to be rectified. This is done by ascertaining the causes of difference and then making adjustments in a statement called Bank Reconciliation Statement to reconcile the balances shown in the cash book and the bank pass book/ statement.
It is a statement prepared by the account holder who is the bank’s client. The bank provides only the pass book record or bank statement to facilitate the reconciliation process.
Need for Bank Reconciliation Statement
Sometimes difference between the cash book and pass book/Bank statement may arise due to accounting errors like wrong recording of transactions relating to cheques issued or cheques deposited. There can be omission or wrong recording of transactions, wrong totalling etc. Such
mistakes will cause difference in cash book balance and balance as per bank pass book/statement, hence the need for Bank reconciliation statement. Reasons for discrepancy between Cash Book Balance and Passbook Balance:
a) Timing difference on recording of the transactions because the business and its bankers do not record the transactions at the same time.
b) Accounting errors made by the business or by the bank.
Causes of Timing difference:
i) Cheques issued but not presented for payment: Cheques issued to creditors may not be presented by them immediately for payment. The bank will debit the party’s account only when the cheque is presented for payment provided there is sufficient balance. This time lag will cause a mismatch of balances between cash book and bank pass book/statement.
ii) Cheques paid into bank but not yet collected yet: When a firm receives cheques from customers (debtors) it is recorded in the debit side of the cash book increasing the bank balance. However, the bank will credit the customer account when the amount of the cheque is actually realised. So, this time lag between cash book entry and the entry in bank’s ledger will cause a difference in balances.
iii) Bank charges: Banks often deduct service charges/interest on loan by debiting the customer account but the clients come to know about it only when they receive the bank statement. This time lag causes a mismatch between bank balance as shown in cash book and the balance shown in bank ledger. The same thing happens when there is a standing instruction to deduct certain expenses.
iv) Direct payments in bank account: Sometimes a party may directly deposit money in bank account of a creditor. This will only show in clients account with the bank but the client will come to know about it when the statement of account is received from the bank. So, the bank balance in cashbook will differ from the balance shown in bank’s books.
v) Bank collections: Banks often collect interest or dividends on behalf of the customers which are immediately posted in the bank’s ledger. But due to communication gap such entries are posted in cash book at a later date. In the interim period the cash book balance and balance in bank’s ledger
will not match.
vi) Dishonoured cheques/Bills of exchange: When a cheque deposited by a firm is dishonoured or a bill of exchange discounted by the bank is dishonoured, the bank will immediately debit the client’s account. But the message in the form of bank statement will reach the client at a later
date. This will result in pass book/statement balance showing less amount than the cash book balance.
Preparation of the Bank Reconciliation Statement – starting point:
After the causes of difference have been identified, the bank reconciliation statement can be prepared in two ways:
a) Without adjusting cash book balance
b) By adjusting cash book balance
If we adopt option (a) balance as per Pass Book is the starting point.
If we take option (b) we have to start with balance as per Cash Book.
Understanding Preparation of Bank Reconciliation – Favourable and Unfavourable Balances
Debit balance as per cashbook means favourable balance held at the bank i.e. deposits are more than withdrawals and indicates favourable balance in cash book.
Credit balance as per pass book also means favourable balance as deposits by a client is credited in bank ledger.
Credit balance as per cash book means unfavourable balance or overdraft i.e. excess amount has been withdrawn over the amount deposited in the bank.
Debit balance as per bank pass book/statement will be overdraft or unfavourable balance i.e. excess amount is withdrawn from bank.
Situations for reconciliation:
There may be four different situations while preparing the bank reconciliation statement. These are:
1. When debit balance (favourable balance) as per cash book is given and the balance as per pass book is to be ascertained
2. When credit balance (favourable balance) as per pass book is given and the balance as per cash book is to be ascertained
3. When the credit balance (negative or unfavourable balance) as per cash book is given and the balance as per pass book is to be ascertained
4. When debit balance as per pass book (overdraft) is given and cash book balance has to be worked out.
Steps in Reconciliation process:
Assumption : Balance as per Cash Book:
i) The date of the statement to be written as header
ii) Start with ‘Balance as per cash book’
iii) Deduct (-) amount of cheque deposited but not collected
Reason: When the cheque was deposited it was entered in the cash book showing increased bank balance but the bank balance remained the same as the cheque was not collected. So, to restore parity cash book balance has to be reduced.
iv) Add (+) cheques issued but not presented for payment
Reason: When a cheque is issued cash book balance is reduced. Since it was not yet presented for payment, the bank balance remained the same, the cash book balance has to be increased by the cheque amount to achieve parity with bank balance.
v) Deduct (-) bank charges, interest on overdraft, standing instruction payments debited
Reason: The bank charges and interest on overdraft which were charged by the bank reduced the company’s bank balance. The cash book balance would however show higher balance which has to be reduced to match the bank statement.
vi) Add (+) dividends collected by bank or direct deposit by debtors in bank account.
Reason: The bank already collected the dividends and the deposits were made directly into bank account. Now, to achieve parity these amounts have to be added in cash book to be at par with the bank account.
vii) Less (-) Cheque deposited into bank returned dishonoured
Reason: When the cheque was deposited the amount was debited to cash book increasing the balance. It was not reflected in pass book because the cheque was dishonoured. So, to restore parity cash book balance has to be reduced.
viii) Now, the net balance has to be written as ‘Balance as per pass book’
If we are starting with Balance as per Pass book treatment of all the items noted above will be the reverse of the above to adjust parity with cash book :
Item (iii) listed above: Cheque deposited but not collected
Add Cheque amount to pass book balance as it has already been added in cash book when the cheque was issued.
Item (iv) as above: Cheque issued but not presented for payment
Deduct cheque amount from pass book balance as the amount of cheques issued has already been deducted in cash book.
Item (v) as above: Bank charges interest on overdraft charged by bank not entered in cash book Add bank charges, interest on overdraft to pass book balance as the same has not been deducted in cash book.
Item (vi): Dividend collected by bank and direct deposit by debtors not recorded in cash book.
Deduct dividend collected or direct bank deposit by debtors from pass book balance as the same are not yet recorded in cash book.
Item (vii): Cheque deposited in bank returned dishonoured
Add the amount of dishonoured cheque to pass book balance as cash book has already been debited as soon as the cheque was deposited and the dishonour of the cheque was not yet recorded.
viii) Now, the net balance has to be written as Balance as per cash book
Important point to remember: One must keep in mind whether one is starting with Cash book balance or Bank Pass Book balance /Statement
Usually, The Bank reconciliation statement can also be prepared with two amount columns one showing addition (+ column) and the other showing deduction (-column). The format will be as under:

Examples of Bank Reconciliation Statement with cash book or pass book both showing favourable or positive balance:
Example 1.
From the following particulars available from M/s Modern Industries prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement dt.31.03.2022:
1. Balance as per cash book ₹60000
2.Cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹8000
3.The bank had directly collected dividend of ₹8000 and credited to bank account but was not entered in cash book
4. Bank charges of ₹ 500 not entered in cash book
5. A cheque of ₹ 5000 was deposited but not collected by the bank.
Solution:
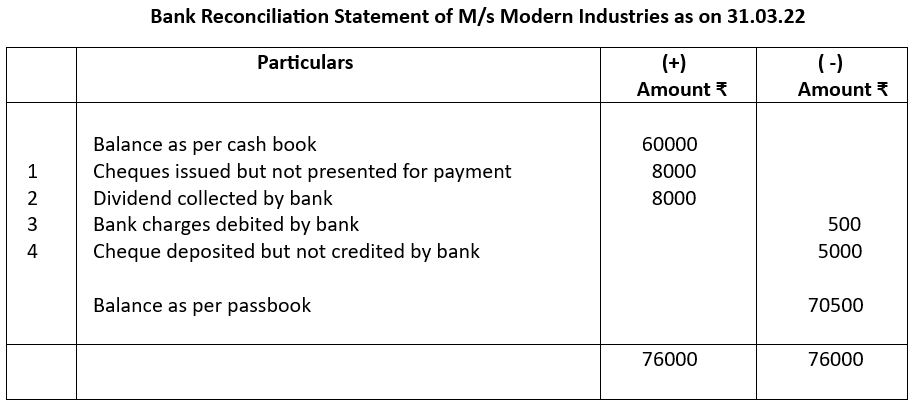
Notes:
Sl. no. 1 Cheque issued, cash book balance reduced but pass book balance remained the same since it was not presented for payment. So, cash book balance was increased
Sl. no. 2 Dividends collected by bank, pass book balance increased so, cash book balance had to be increased
Sl. no. 3 Bank charges deducted, so pass book balance was reduced, hence cash book balance had to be decreased as well
Sl. no. 4 Cheque deposited, thus cash book showed increased balance. It was not yet credited by bank. So, cash book balance has to be reduced to achieve parity with pass book balance.
Example 2
We will now adapt the same situations noted in example 1 by taking pass book balance as the starting point.
Solution:
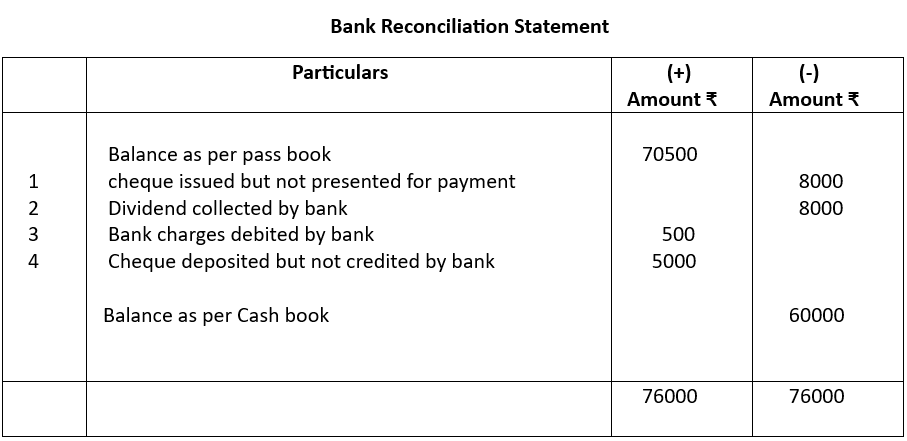
Note:
We see that when we are starting with balance as per pass book treatment of all the items shown in example 1 (balance as per cash book) has been reversed and quite logically so. In this way also we have reconciled the cash book and pass book balance.
Example 3
From the following particulars of Premji Bros. prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on 31.3.20
1. Balance as per cash book ₹65000
2. Cheques for ₹5000 deposited in the bank but not yet collected by them
3. Incidental charges ₹200 debited to Premji Bros. account which was not recorded in cash book
4. A cheque of ₹25000 issued by Premji & co. not presented for payment
Solution:
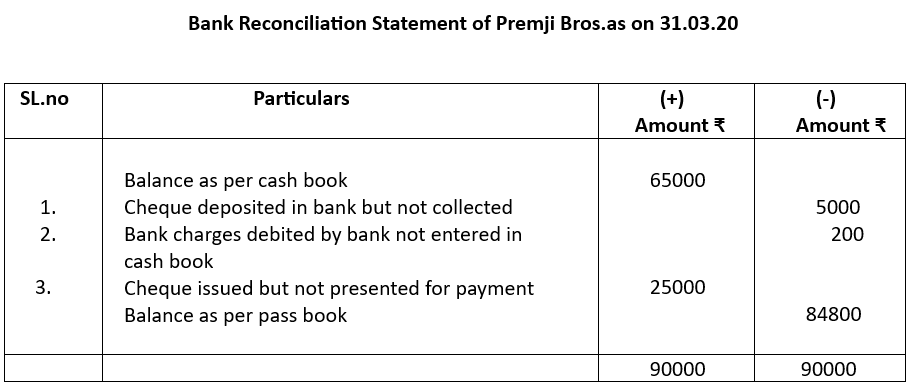
Reasons:
Sl.no. 1: Cheques deposited means higher cash book balance, no collection means lower pass book balance. So, cash book balance to be reduced
Sl.no. 2: Bank charges reduce bank balance, so cash book balance has to be reduced
Sl.no. 3: Cheque issued hence cash book balance was reduced. But it was not presented for payment and pass book balance remained the same, so cheque amount has to be added back
Example 4
The bank pass book of M/s Chaudhary Bros. showed a balance of ₹40000 as on 31.05.23. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement from the following particulars:
1. Cheques issued between 15.05,23 to 25.05.23 amounting ₹30000 were not presented for payment
2. Two cheques of ₹4500 and ₹3550 were deposited into the bank on May 30 the bank credited the same in June
3. A cheque amounting ₹2500 deposited earlier was dishonoured and debited by the bank
Solution:
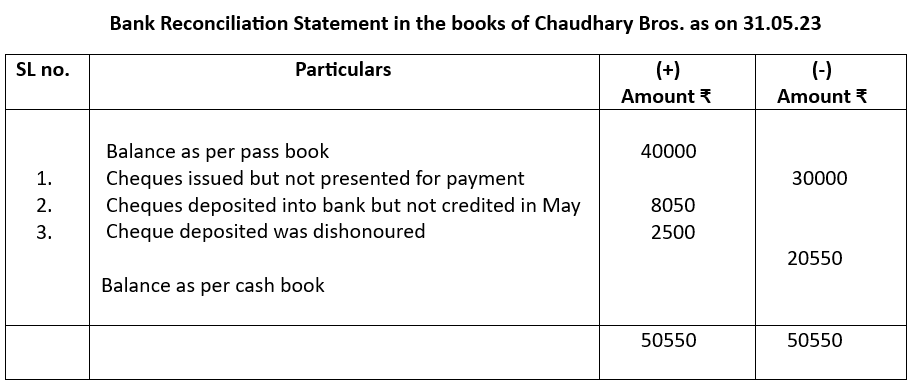
Notes:
1. Cheque issued but not presented for payment means cash book balance was reduced but pass book balance was not. So, pass book balance was to be reduced.
2. Cheques deposited means cash book was debited and balance increased but bank account was not credited till May, 31. So, the bank account or pass book balance has to be increased.
3. Cheque dishonoured was recorded in bank account but was not entered in cash book which included the cheque amount dishonoured. So, to restore parity the amount has to be added to pass book balance.
Overdraft – Reconciliation of unfavourable accounts
The above examples of reconciliation statements were all dealing with positive bank balances i.e. where the debit side total of cash book was higher than credit side which reflected in the bank pass book as well. But sometimes it might so happen that the credit side of cash book is more than debit side which shows the company has drawn more than its deposits turning it into an overdraft account. An overdraft is regarded as a negative balance in bank reconciliation statement with deposits reducing the balance and expenses increasing it. Credit balance in cashbook means debit balance in bank account.
Example 1
1. Nair & Co had an overdraft balance of ₹10000 on March 31, 2022 in cash book.
2. Cheque amounting to ₹4000 deposited but not collected by the bank
3. Issued cheques amounting₹2000 which was not presented for payment
4. Interest on overdraft charged by the bank ₹200 and bank charges ₹100
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement
Solution:

Important point:
The Overdraft account being a negative (-) balance account, any addition to overdraft amount will have to be entered on the negative (-) side. Conversely, to subtract the overdraft balance amounts should be entered on the positive (+) or favourable side. The reasons behind the above entries will explain this.
Sl. No.1. Cheque deposited means overdraft was reduced in cash book. As it was not collected by bank the OD balance remained same there. So, in cash book the overdraft balance has to be increased.
Sl. No.2. Cheque issued means OD balance in cash book got increased. It was not presented in bank for payment. So, OD in bank remained the same. To reconcile, the cheque amount credited earlier had to be reversed in cash book on the debit side.
Sl. No.3. Interest on OD Increased the OD balance in bank account, so in cash book also the balance has to be increased.
Sl. No.4. For bank charges, same treatment as 3
Example 2
From the following particulars of Tewari Bros. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement on 31.03.23
Overdraft as per pass book ₹50000
Cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 5000
Cheque deposited but not cleared ₹ 4000
Interest on overdraft ₹ 2000
Insurance premium paid by the bank ₹ 500
Wrongly debited by the bank ₹ 1000
Solution:
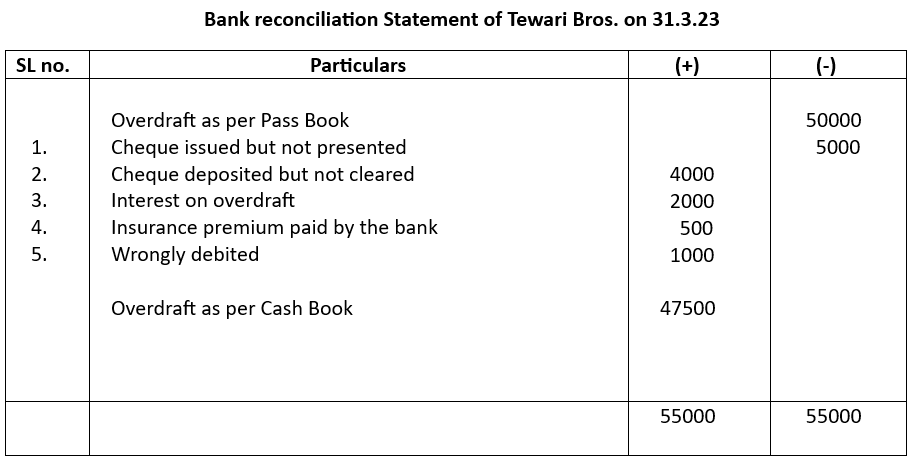
Reasons:
Sl. No. 1. When cheque was issued overdraft in cash book increased. As the cheque was not presented OD account in bank remained the same which has to be increased adding to overdraft (-) column.
Sl. No. 2. Cheque deposited but not collected means while cash book OD was reduced bank OD remained the same as it was not collected. So, Bank OD has to be reduced by adding to positive (+) balance.
Sl. No. 3. Interest on OD increased the overdraft balance which the cash book was not aware of. To restore parity the pass book OD has to be reduced which is done by placing it on the positive side (+)
of the statement
Sl. No. 4. Insurance premium paid by the bank has to be treated in the same way as 3 above
Sl. No. 5. Wrong debit in OD account by bank increased the overdraft amount which has to be reduced by recording on the (+) positive side of the statement
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement – Completed
We have completed the following topics in this unit:
Content:
Meaning of Bank Reconciliation Statement
Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement with given pass book/cash book balance
Learning Outcomes:
Understanding the concept of Bank Reconciliation Statement
Appreciating the need for preparing bank reconciliation statement
Developing the skill of preparing bank reconciliation statement
Related Links:
Unit 1: Capital and Revenue
Unit 2: Depreciation
Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement
Unit 4: Bills of Exchange
Unit 5: Final Accounts
Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete records
Test Paper 1
Test Paper 2


