Content:
Preparation of Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet of sole trader
Adjustment for Closing Stock with given amount
Learning Outcomes:
Meaning of financial statements and the purpose they serve to a sole proprietor
Developing the skill of preparing Trading Account and calculating gross profit
Developing the skill of preparing Profit and Loss Account and calculating the net profit
Explain the need for preparing Balance Sheet
Develop the understanding of simple adjustment for closing stock
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Unit 5: Final Accounts Notes
Financial Statements:
The most important part of accounting information is to meet diverse informational requirements of various users. As it is not possible to generate user-specific information for different interested groups, a set of financial statements which satisfies information needs of various users and present a true and fair view of the financial position of the business is prepared. These financial statements are:
a) Trading and Profit and Loss Account
b) Balance Sheet
The Trading and Profit and Loss Account also known as financial statements show the financial performance in the form of profit earned or loss sustained by a firm in an accounting period. Balance Sheet shows the position of the business from the standpoint of Assets, Liabilities and Capital. These are prepared on the basis of Trial Balance which is the summary of debit and credit balances recorded in the ledger. From the point of view of the sole proprietor, the financial statements satisfy the following information needs:
i) Profitability of the business
ii) Assets and Liabilities position
iii) Drawings in relation to capital
iv) Revenue growth through sales
vi) Stock position by turnover
vii) Income Tax assessment
Some Relevant Terms:
Direct Expenses:
Direct Expenses means all expenses directly connected with manufacturing of goods to make them sales ready. In other words, direct expenses turn raw-materials into finished products. Direct Expenses include:
1. Carriage Inwards (for purchases)
2. Freight inwards
3. Wages
4. Factory lighting
5. Coal, water and fuel
6. Royalty on production etc.
7. Packaging material cost
Indirect Expenses:
Indirect expenses are those which are not directly involved in production process but necessary for office maintenance and distribution of the finished goods in market. Some indirect expenses are:
1. Salaries
2. Rent
3. Office electricity
4. Commission
5. Office Expenses
6. Discounts
7. Printing and stationery
8. Interest allowed/received
Gross Profit/Loss:
Sales is the main source of revenue for a business. The excess of sales over purchases and direct expenses is called Gross Profit. If the amount of purchase and direct expenses is more than the sales revenue, the net result will be Gross Loss. Gross profit can be shown in the form of equation:
Gross Profit = Sales – (Purchase + Direct Expenses)
The Gross Profit or Gross Loss is transferred to Profit & Loss A/c from Trading A/c.
Net Profit/Loss:
From Trading A/c, the gross profit of the Trading A/c is transferred to the credit side of Profit & Loss A/c. All Revenue/Gains other than sales are also transferred. Now, all indirect expenses are entered on the debit side of the Profit & Loss A/c. If the credit side total is more than the debit side, the
difference is the Net Profit for the period for which it was prepared. On the other hand, if the debit side total is more than the credit side the difference is the Net Loss suffered by the business. The Net Profit can be shown in an equation form as follows:
Net Profit = Gross profit + Other incomes – indirect Expenses
The Net Profit or Net loss so computed is transferred to the capital account in the Balance Sheet. Net Profit is added to Capital and Net Loss is deducted from Capital.
Relevant items in Preparation of Trading and Profit and Loss A/c:
Items on the debit side of Trading Account:
1. Opening stock: This is the stock of goods which has been carried forward from the previous year and is a debit balance item in trial balance. In the trading account it appears on the debit side because it forms part of the cost of goods sold for the current accounting year.
2. Purchase less returns: Goods which are bought for resale or processing appears as purchases on the debit side. This includes goods purchased on cash or credit. Goods which are returned to suppliers are termed Purchase Return. It is shown by way of deduction from purchases.
3. Wages: Wages refer to remuneration paid to workers who are directly involved in manufacturing process and unloading of raw materials.
4. Carriage Inward/Freight Inward: These are expenses incurred in bringing materials purchased to the place of business, like transport costs, unloading charges.
5. Fuel/water/power /gas: These are input costs of manufacturing and hence part of direct expenses.
6. Packaging charges: Cost of packaging material and small packages used to pack individual product saleable is part of direct expenses. However, large containers used to transport goods to market are indirect expenses to be debited to profit and loss account.
Items on the debit side of Profit & Loss account
1. Salaries: These include salaries paid to administrative staff, godown and warehouse staff. Salaries include perks like medical facilities, rent free accommodation etc.
2. Rent: These include office and go down rent, municipal taxes.
3. Commission paid: Commission paid or payable on business transactions is an expense debited to Profit and Loss account
4. Repairs and renewals: Small repairs and renewals relating to plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures etc. for keeping them in working condition are included under this head and debited to Profit & loss account.
5. Miscellaneous expenses: These expenses can be classified under different heads some of which are small enough to be clubbed together as sundry expenses and debited to profit & loss account.
Items on the Credit side of Trading Account:
Sales less Returns: Sales account balance in trial balance shows gross sales both cash and credit. This item is shown on the credit side of Trading account. Goods returned by customers called Return Inwards and are deducted from total sales to arrive at net sales.
Items on the credit side of profit and loss account:
Gains and Incomes: Items such as interest received, dividend received, discount received,commission received are credited to profit and loss account.
Preparation of Trading and Profit & loss Account of a Sole Trader
The trading and profit and loss account present useful information about profitability from business operations. As an example, let us consider the following basic trading account.
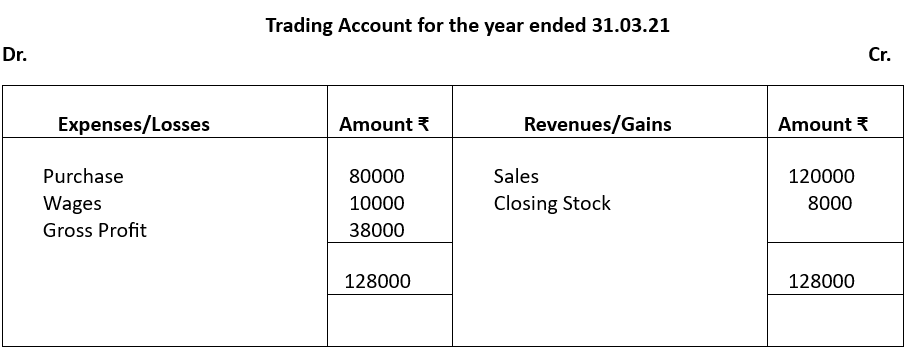
Illustration 1
Prepare a trading account of National Industries from the following particulars pertaining to the year 2021-22.
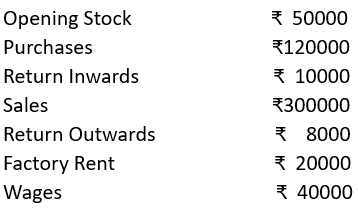
Solution:
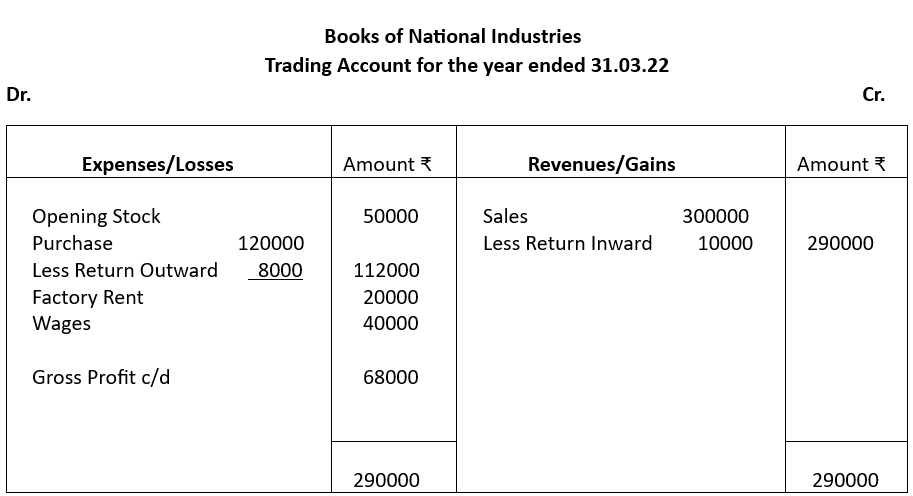
Illustration 2
Prepare a Trading Account in the books of Mitra Bros. for the year ended 31.3.2022.
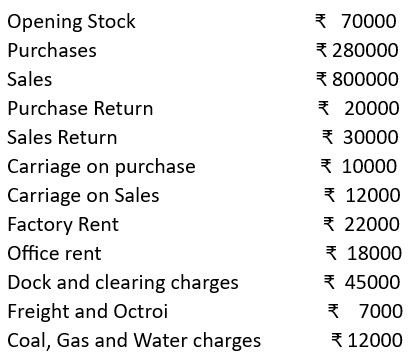
Solution:
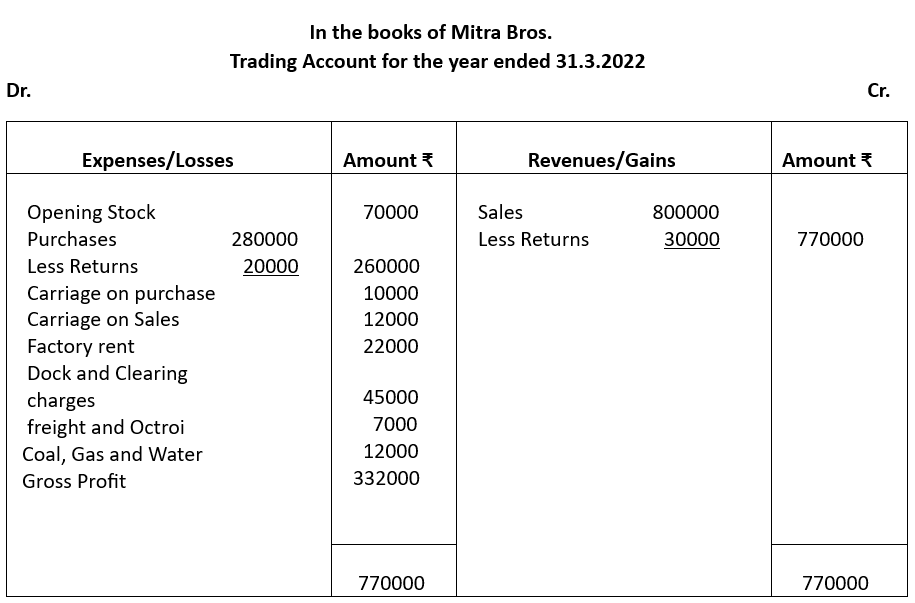
Illustration 3
From the following information, prepare a Profit and Loss Account for the year ending 31.03.21
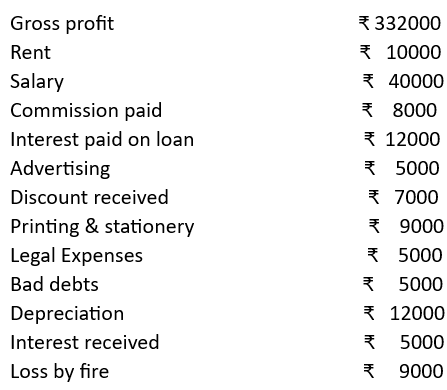
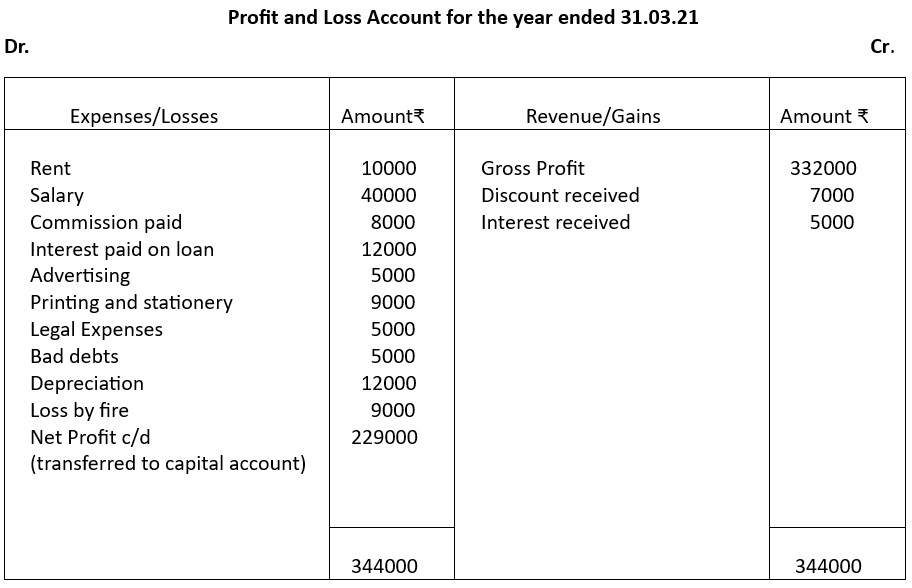
Adjustment for Closing Stock
If there is no closing stock or unsold stock it will be presumed that all the goods purchased have been sold. But, in actual practice there is some unsold stock at the end of the financial year. Now let us assume that all of the goods purchased were not sold and goods costing ₹8000 remained in hand. This is termed as closing stock.
Adjustment Entry for Closing Stock:
1. As closing stock does not normally form part of trial balance it is brought into the books with the help of the following journal entry:

2. The entry opens a new account of asset i.e. Closing stock A/c which is transferred to Balance Sheet
3. The Closing Stock of current year will be the Opening Stock for the next year
Illustration 4
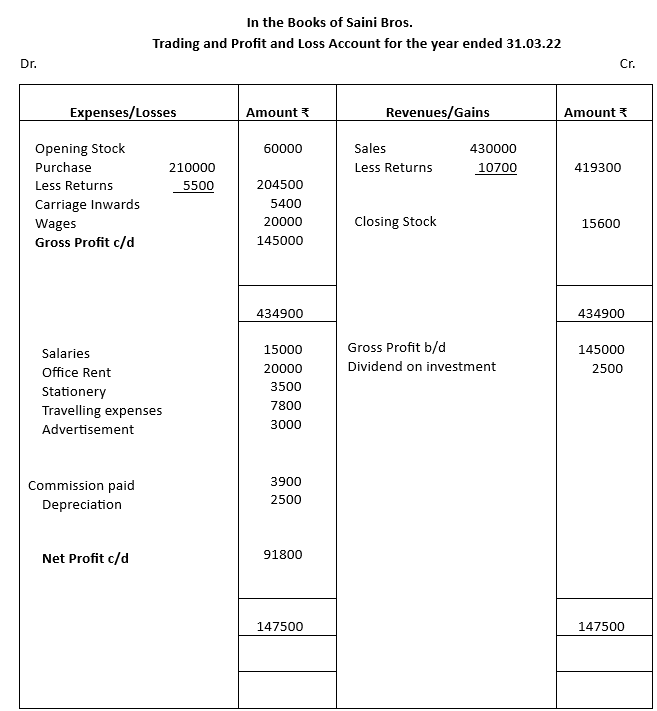
From the following balance extracted from the books of Saini Bros., ascertain the Gross Profit and Net Profit for the year ended 31.03.22:
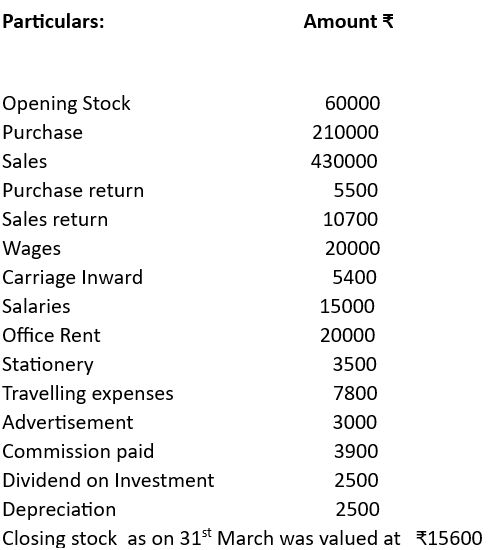
Solution:
Balance Sheet:
The Balance Sheet is a statement showing the financial position of the business, summarising all assets and liabilities on a given date. The assets reflect the debit balances and liabilities (including capital) reflect the credit balances. It is prepared at the end of the accounting period after the
trading and profit and loss account have been prepared. It is called balance sheet because it is a statement of balances of ledger accounts that have not been transferred to trading and profit and loss account. Balances appearing in the Balance sheet are carried forward to the next accounting year with the help of opening entries made in the journal at the beginning of the year.
Balance Sheet:
The Accounts of assets, liabilities and capital are shown in the Balance Sheet with capital and liabilities shown in the left hand side as liabilities with assets and other debit balances shown on the right side.
Items which are generally included in a balance sheet are as follows:
1. Current Assets:
Current assets are either in the form of cash, bank balance, bills receivable, closing stock, sundry debtors, investments, prepaid expenses etc.
2. Current Liabilities:
Examples of current liabilities are bank overdraft, bills payable, sundry creditors, loans and overdrafts, outstanding expenses etc.
3. Fixed Assets:
Fixed assets are those which are held on a long-term basis to bring prolonged benefits to a company and are not acquired for the purpose of resale. Examples are land and building, plant and machinery, furniture and fixture etc.
4. Intangible assets: Assets which cannot be seen or touched like goodwill, patents, trademarks are intangible assets.
5. Long term liabilities:
The important items of long-term liabilities are long term loans from banks or other financial Institutions.
6. Capital:
It is the excess of assets over liabilities due to outsiders/investors. It represents the amount originally contributed by the proprietor/partners/shareholders increased by profit and decreased by losses or drawings.
7. Drawings:
Amount withdrawn by proprietor for personal use is known as drawings. It is shown by way of deduction from capital.
Marshalling of Balance sheet:
In a Balance sheet assets and liabilities are arranged either on the basis of liquidity or permanence.
In case of permanence, the most permanent asset or liability is put on top of the items in Balance Sheet. In case of liquidity, the order is reversed and the most liquid assets or liabilities is placed at the top. A balance sheet in order of permanence is illustrated below:
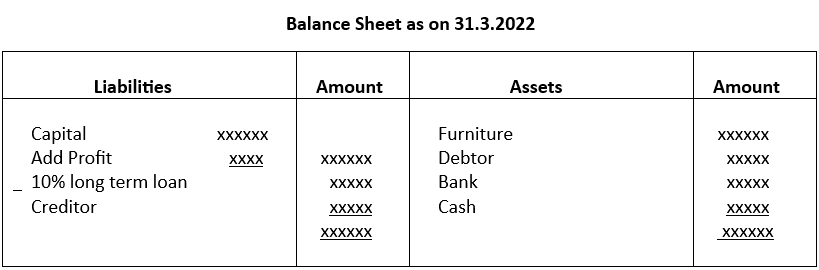
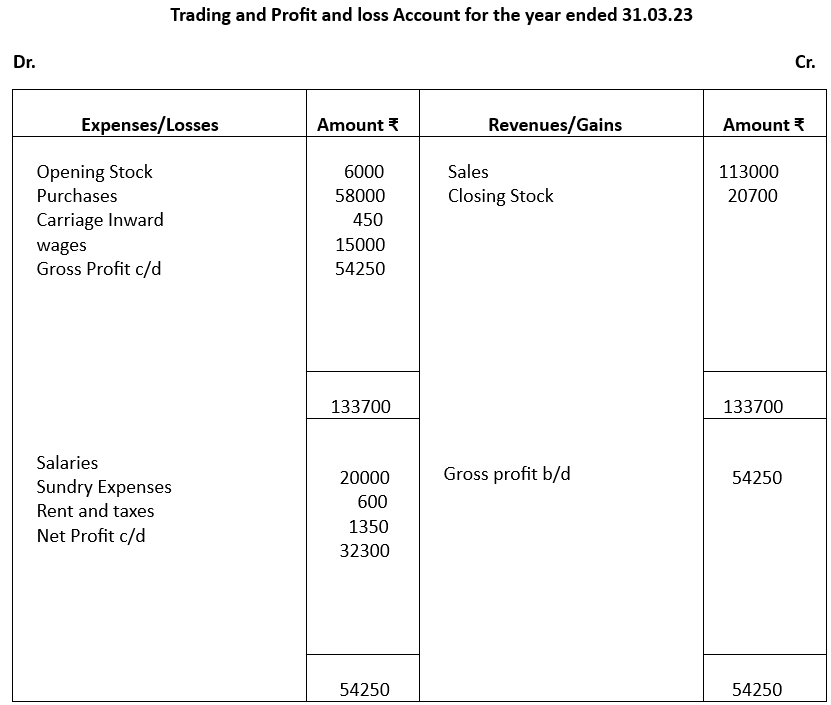
Illustration 5:
From the following trial balance prepare a Trading, Profit and Loss account and Balance Sheet as on 31.3.23
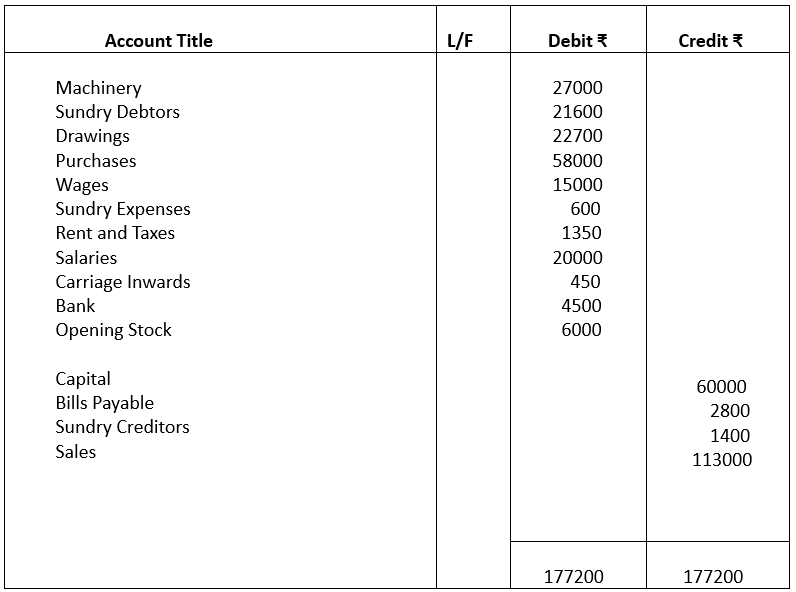
Closing Stock on 31st march, 23 ₹20700
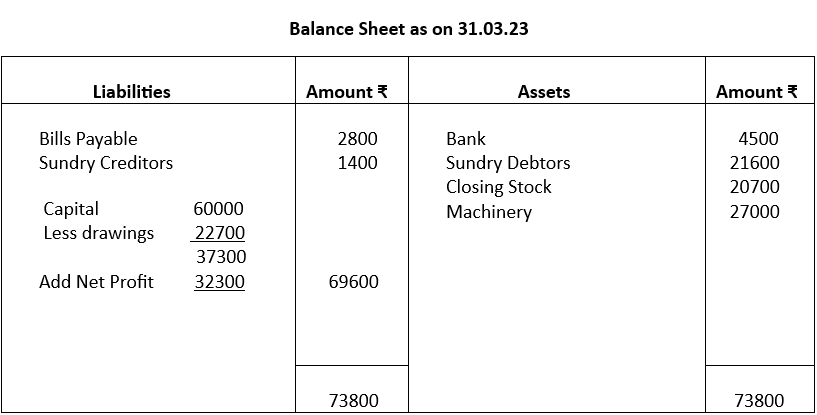
Notes:
1. Trading and Profit and Loss being accounts, Debit (Dr) and Credit (Cr) are written below the header.
2. Balance Sheet being a statement, no Dr or Cr is mentioned
3. Trading and Profit and Loss account header ends with the words “for the year ended…….”
4. Balance Sheet header ends with the words “as on……”
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Unit 5: Final Accounts – Completed
The following topics were covered in this unit:
Content:
Preparation of Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet of sole trader
Adjustment for Closing Stock with given amount
Learning Outcomes:
Meaning of financial statements and the purpose they serve to a sole proprietor
Developing the skill of preparing Trading Account and calculating gross profit
Developing the skill of preparing Profit and Loss Account and calculating the net profit
Explain the need for preparing Balance Sheet
Develop the understanding of simple adjustment for closing stock
Related Links:
Unit 1: Capital and Revenue
Unit 2: Depreciation
Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement
Unit 4: Bills of Exchange
Unit 5: Final Accounts
Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete records
Test Paper 1
Test Paper 2


