Content:
Meaning of Incomplete Records and accounting from Incomplete Records
Preparation of Statement of Profit
Statement of affairs method only
Learning Outcomes:
The learners would be able to:
State the meaning of incomplete records
Understand the uses and limitations of incomplete records
Develop the skill of computation of profit/loss by preparing the Statement of Profit
Develop the skill of preparing ‘Statement of Affairs’ and ascertain the position of the business on a particular date
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete records Notes
Meaning of incomplete records:
We have seen that modern and scientific accounting is about analysing every transaction on the basis double entry principle. The adoption of this method ensures accuracy and presents a reliable source of information about the financial position of a business. But maintaining the system requires fair amount of investment and professional help. For many small enterprises or family run businesses where the number of transactions is low, it is a burden.
The single-entry system of book keeping is a solution to this problem and a cost-effective way to keep financial records. It is also called accounting from incomplete records as it is not comprehensive and does not follow the traditional double entry system of accounting. It is a kind of hybrid system that adapts double entry for some items like cash receipts and payments, but employs the single-entry system to record purchases, sales, expenses and fixed assets.
Cash book is the most important book in single entry system that records most of the transactions. Personal accounts of debtors and creditors are maintained but there are no entries for bad debts or depreciation.
Thus, we see that accounting from incomplete records is a combination of double entry, single entry and no entry record of transactions. One can say it is an incomplete double entry system suitable for small time entrepreneurs who are interested in a simple but flexible accounting method that does not require too many books of accounts to be maintained.
Features of Incomplete Records:
1. It is an unsystematic method of accounting transactions.
2. Generally, it records cash transactions and maintains personal accounts. No information is given for revenues or gains, expenses or losses, assets or liabilities.
3. Drawings for personal use may be recorded.
4. Style of accounting differs in different businesses depending on suitability.
5. Original vouchers are only source of information to work out profit/loss.
6. Profit/loss can only be approximation without high degree of accuracy.
Uses of incomplete records:
In spite of its inherent weaknesses, the accounting under incomplete records has some uses:
1. Easy to use: Because of its simplicity and uncomplicated procedure, accounting of incomplete records is the preferred choice of many small businesses where there are mostly cash transactions.
2. Less expensive: As there are not too many books of accounts to be maintained the system is less expensive which can be written by non-technical persons as well. For some concerns double entry system is a luxury.
3. Quick cash book entries: Cash book is often called the mirror of a business. Under single entry or incomplete books system, cash book is the principal book of accounts and an entrepreneur can easily access the cash flow position and adjust his transactions accordingly.
4. Easy monitoring of accounts: As limited number of accounts are maintained in this system, so it is easy to monitor each account effectively.
Limitations of Incomplete Records:
1. Arithmetical Inaccuracy: All the accounts are not treated in double entry system and there is no trial balance to check the arithmetical accuracy of accounts. So, there can be a host of errors hidden in the accounts.
2. Miscalculation of Profit/loss: The system cannot produce an accurate estimation of profit/Loss. Only an approximation is possible and true position of business is only a guesswork.
3. Incomplete database: Since proper double entry system is not followed the database is inadequate and unclear for taxation purpose, specially from the point of view of GST.
4. Difficult to source finances: Since no clear profit and loss account or balance sheet is maintained, it is difficult to obtain loans from banks and financial institutions.
5. Information lag for legal remedies: Lack of detailed accounting record, non-availability of profit and loss account and balance sheet could pose serious problems in seeking legal redressal.
Ascertainment of Profit or Loss:
Every business wishes to ascertain the results of its operations, to assess its efficiency, success and failures. This is possible only through generating financial statements to disclose:
(a) The profit made or loss sustained by the firm during a given period
(b) the amount of assets and liabilities as at closing date of accounting period.
One has to utilise the available information in the incomplete records to determine the financial position of the business at the end of the year. This can be done in two steps:
1. Preparing the Statement of Affairs as the beginning and at the end of the financial period
2. Preparing a Statement of Profit and Loss
Statement of Affairs:
The Statement of Affairs under single entry is what Balance sheet is under double entry system. It is a compilation of assets and liabilities at the end of a year. The difference between the two sides (balancing figure) is the capital. There is no separate Capital account. Preparation of this statement is not based on scientific methods and except for cash book no other double entry record can be traced. Transaction amounts are sourced from bills/vouchers and informal records. So, Statement of affairs is more of an approximation rather than an accurate information. Though Statement of Affairs resembles Balance Sheet it is not called a Balance Sheet because the data is not based on ledger balances.
Difference between Statement of Affairs and Balance Sheet:
Both statement of affairs and balance sheet show the assets and liabilities of a business on a particular date. However, there are some fundamental differences between the two:
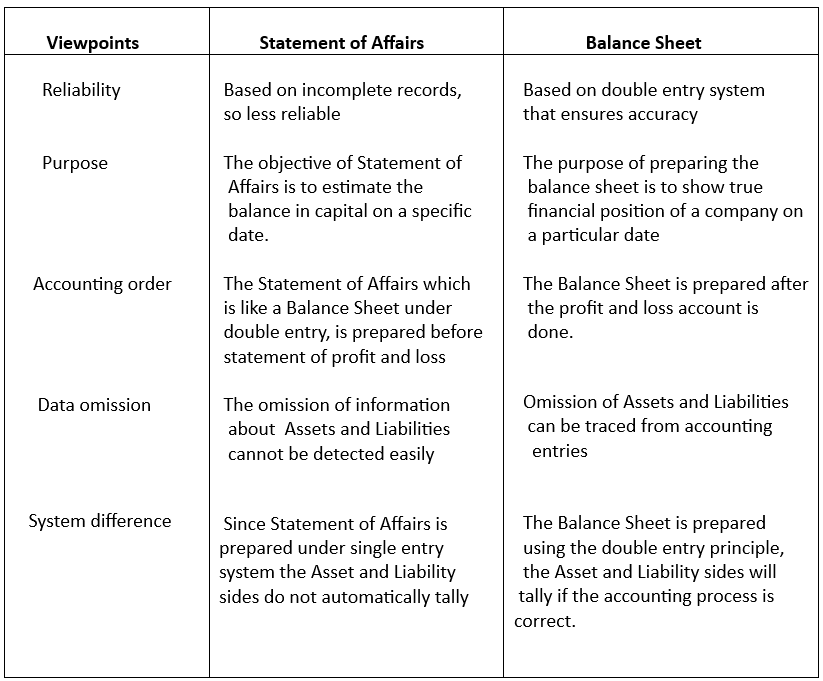
Illustration:
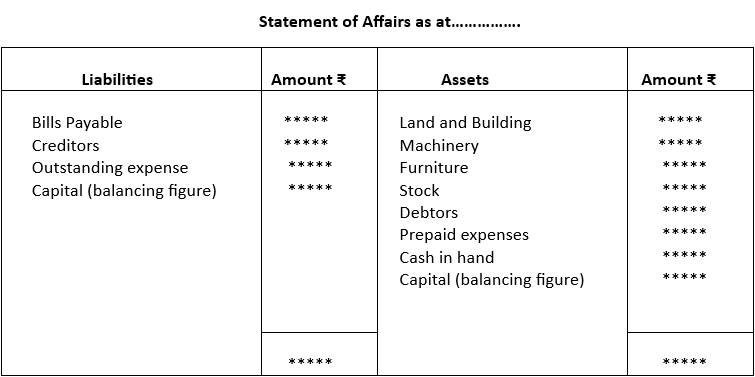
Note: Where the total liability side is more than total asset side, capital would be shown on the asset side and would represent debit balance of capital.
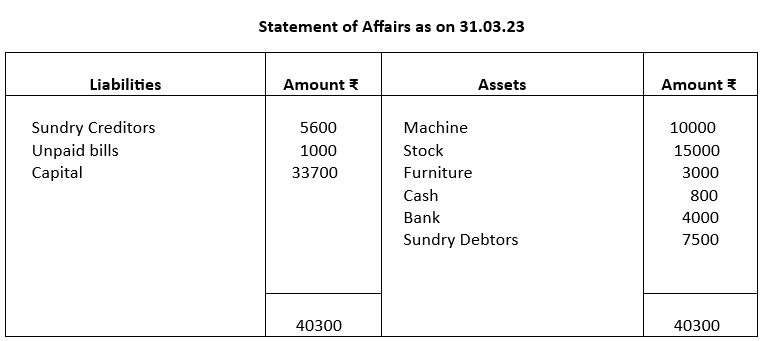
Example 1.
Sanjit, a small trader started his business with a capital of ₹10000 on 01.04.22. He had withdrawn ₹2000 every month but introduced further capital of ₹10000 during the year. Sanjit keeps accounts on single entry basis and on 31.03.23 he worked out the following balances:
Machine ₹10000
Stock ₹15000
Bank ₹ 4000
Cash ₹ 800
Sundry Debtors ₹ 7500
Unpaid bills ₹ 1000
Sundry Creditors ₹ 5600
Furniture ₹ 3000
Prepare a Statement of affairs as on 31.03.2023
Solution:
Statement of profit and loss:
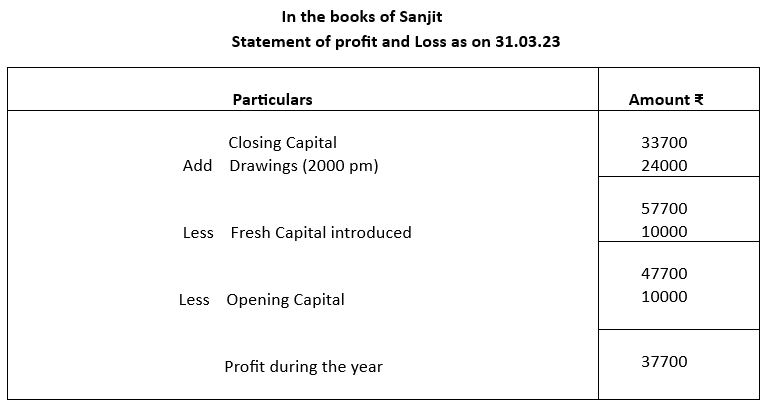
Calculation of profit and/or loss under single entry system is radically different from that of double entry system. Here, profit or loss is the difference between opening balance of capital and the closing balance after adjustment of drawings and introduction of fresh capital during the year. This is reflected in the Statement of Profit or Loss and involves the following steps:
1. Start with closing capital
2. Add back drawings during the year. This is necessary to find out true opening capital
3. Deduct amount of fresh capital introduced during the year to figure out exact opening capital
4. Deduct opening capital
5. Balance will be profit or loss during the year
Illustration:

Using the data from Example 1 above. Prepare a Statement of Profit and Loss as on 31.03.2023
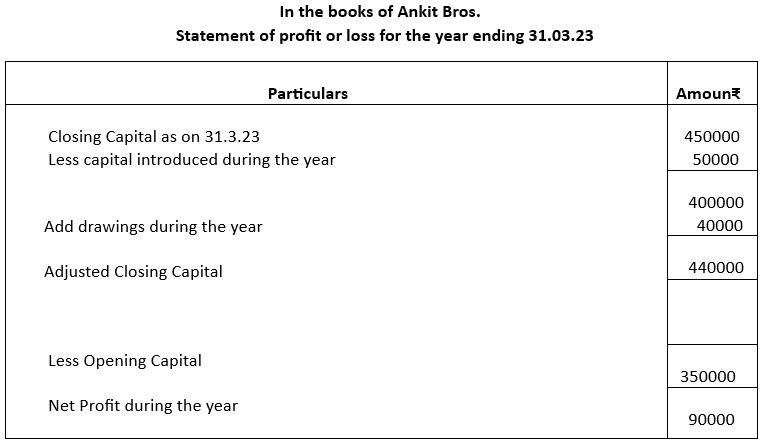
Example 2
M/s. Ankit Bros. keeps accounts under single entry system. From the following particulars furnished by them prepare a statement of profit/loss for the year 2022-23.
Capital on 1.4.2022 ₹350000
Capital introduced during the year ₹ 50000
Drawings during the year ₹ 40000
Capital as on 31.3.23 ₹450000
Solution:
Example 3
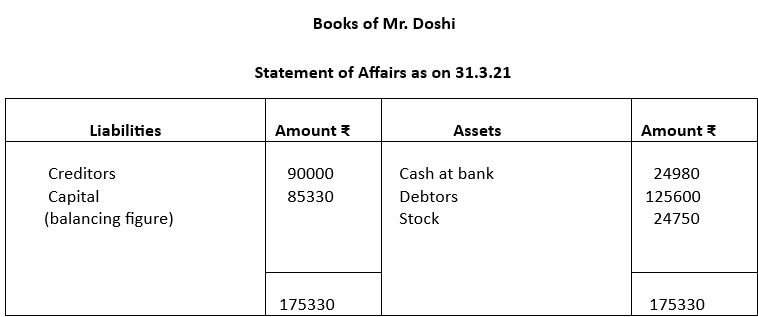
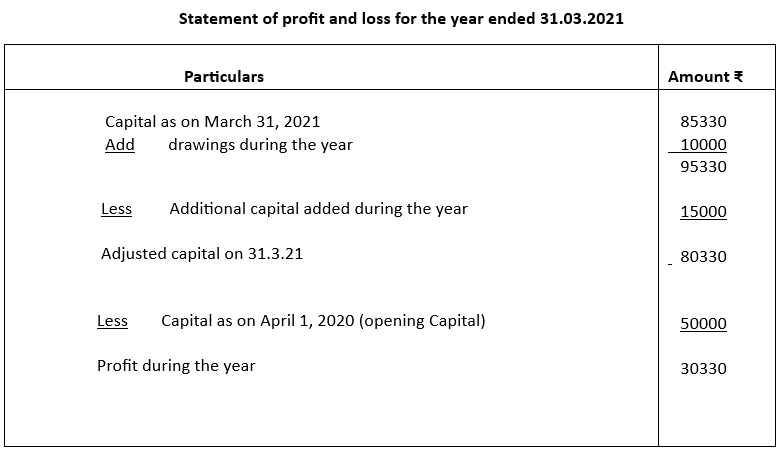
Mr. Doshi started a business on April 1, 2020 with a capital of ₹50000. He did not maintain his books as per double entry system. During the year he introduced fresh capital of ₹15000. He withdrew ₹10000 for personal use. On March 31, 2021 his assets and liabilities were as follows:
Creditors ₹90000
Debtors ₹125600
Stock ₹24750
Cash at bank ₹24980
Calculate profit or loss made by Mr. Doshi during the year
Solution:
CBSE Class 10 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete records – Completed
The following topics were completed in this unit:
Content:
Meaning of Incomplete Records and accounting from Incomplete Records
Preparation of Statement of Profit
Statement of affairs method only
Learning Outcomes:
The learners would be able to:
State the meaning of incomplete records
Understand the uses and limitations of incomplete records
Develop the skill of computation of profit/loss by preparing the Statement of Profit
Develop the skill of preparing ‘Statement of Affairs’ and ascertain the position of the business on a particular date
Related Links:
Unit 1: Capital and Revenue
Unit 2: Depreciation
Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement
Unit 4: Bills of Exchange
Unit 5: Final Accounts
Unit 6: Accounting from Incomplete records
Test Paper 1
Test Paper 2


