Test Paper 1
Multiple Choice Type Questions (MCQ)
Select the correct answer
1. Voucher is prepared for ___________.
a) Cash received and paid
b) Cash/credit sales
c) Cash/Credit purchase
d) All of the above
2. Business transactions are recorded _________.
a) In chronological order
b) on weekly basis
c) monthly
d) none of the above
3. Which of the following is not a business transaction?
a) Bought furniture
b) Paid wages
c) Appointed Brijesh as factory manager
d) Sold goods for cash
4. Find the correct answer
a) Credit is a decrease in asset
b) Credit is an increase in expense
c) Debit is an increase in revenue
d) Credit is the increase in capital
5. An Asset account is debited______.
a) when an order is placed for its purchase
b) when payment is made for it
c) when the delivery is taken on purchase
d) when enquiries regarding purchase are made
6. A debtor is a person _________.
a) To whom the company owes money
b) To whom goods are sold for cash
c) who owes money to a business
d) who collects debts from the market
7. Which account is to be debited when a table is purchased for personal use of by the proprietor?
a) Furniture Account
b) Fittings Account
c) Drawings Account
d) Office furniture Account
8. A Creditor is person _______.
a) who sells goods on credit
b) who owes money to a business
c) receives benefit from a business
d) None of the above
9. Which of the following cannot be recorded in the books of accounts?
a) Depreciation allowed on Machinery
b) Sale of old office equipment
c) Strike by employees
d) Wages outstanding
10. Purchase of furniture on credit will be recorded in _______.
a) Purchase book
b) Journal proper
c) Cash book
d) Sales book
11.Trial Balance is prepared_____.
a) to ascertain profit for a period
b) to ascertain the accuracy of the accounts
c) to ascertain cash balance
d) to find out financial position of the business
12. Salaries paid to staff will be debited to____.
a) Cash A/c
b) Salary A/c
c) Staff A/c
d) Expenses A/c
13.Goods returned by a customer will be entered in ______.
a) Purchase book
b) Purchase return book
c) Sales book
d) Sales return book
14. Purchase return is ___________.
a) Revenue expenditure
b) Capital gains
c) Revenue gain
d) Loss of revenue
15. A ledger account is prepared from ___________.
a) events
b) transactions
c) journal
d) None of the above
16. If the debit side of Cash book exceeds credit side it means ___________.
a) unfavourable balance
b) favourable balance
c) Excess expenditure
d) unfavourable bank balance
17. Business owes Profit to the proprietor due to ___________.
a) Entity aspect
b) Dual aspect
c) going concern aspect
d) Cost aspect
18. Which account is to be credited for salary outstanding but not paid ________.
a) Salary account
b) Cash account
c) Salary outstanding account
d) None of the above
19. When a firm maintains a cash book it need not maintain ___________.
a) Journal proper
b) purchase book
c) sales journal book
d) Bank and cash account in the ledger
20. Double column cash book records ___________.
a) All transactions
b) Cash and Bank transactions
c) Only cash transactions
d) Only credit transactions
21. Goods purchased in cash are recorded in the ______.
a) Purchase (journal)book
b) sales (journal) book
c) cash book
d) Purchase return book
22. Which document is mentioned in purchase journal _____.
a) Cash memo
b) Invoice
c) Debit Note
d) Folio no.
23. Depreciation is a ___________.
a) liability
b) Expense
c) Revenue
d) None of the above
24. Find the correct answer:
a) Debit the decrease in assets
b) Credit the increase in expense
c) Debit the increase in revenue
d) Credit the increase in capital
25. Trial Balance is prepared __________.
a) After preparation of financial statement
b) After recording transaction in subsidiary books
c) After posting to ledger is complete
d) After posting to ledger is complete and accounts have been balanced
Short Answer Type questions (3 mark each)
1. Give three points of difference between Book keeping and Accountancy.
2. What are the three objectives of Book keeping?
3. Give three advantages of Accounting.
4. Give any three uses of ledger.
5. Differentiate between Journal and ledger on the basis of three points.
6. Cash book is both a journal and ledger – explain.
7. What is the difference between Trade Discount and Cash Discount?
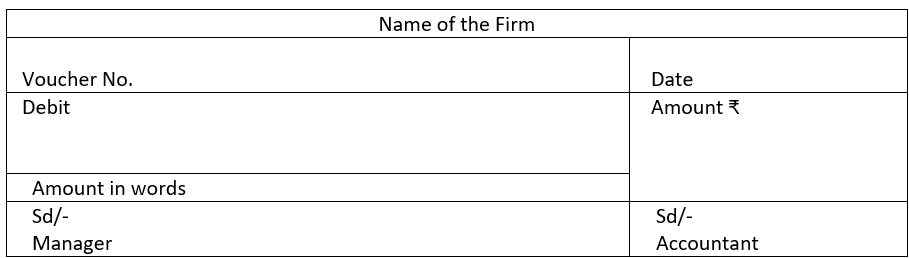
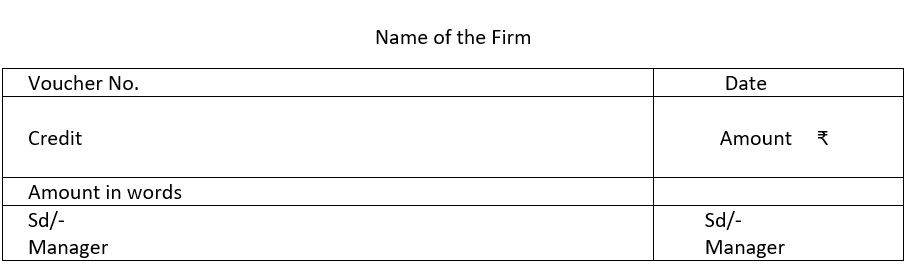
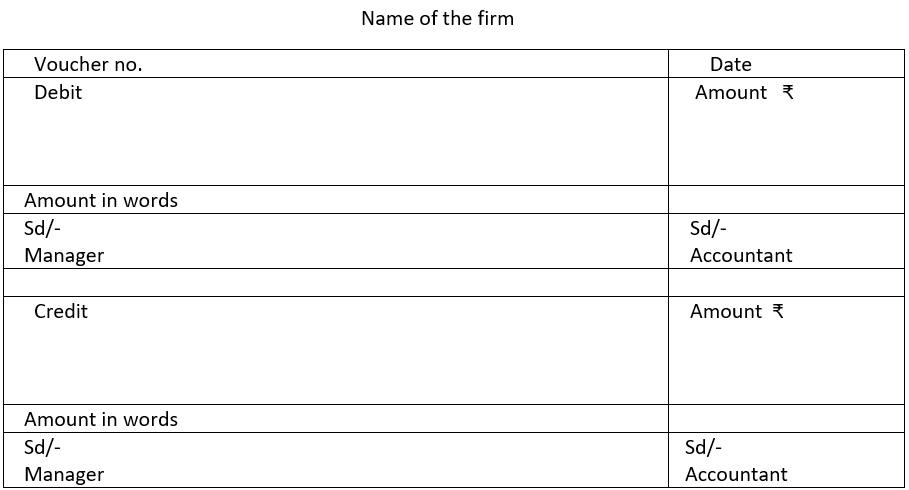
8. Give the format of debit voucher, credit voucher and transfer voucher
9. Write three fundamental steps in accounting process.
10. Write any three limitations of preparing a trial balance.
11. Why is capital a liability to business?
12 What is the purpose of contra entry?
Short Answer Type Questions (4 mark each):
1. What are the four modern rules of debiting and crediting various accounts?
2. Rearrange the following steps in preparing ledger
i) Enter the relevant amount in “amount” column
ii) Identify the ledger account in which the transactions are recorded
iii) Enter the date of transaction in the date column
iv) Record the page number of the journal
3. What entries, debit or credit, would you make to _______?
a) increase revenue
b) decrease expense
c) record drawing
d) record fresh capital introduced
4. Name the subsidiary book in which each of the following transactions will be recorded:
a) Cash purchase of goods
b) Credit purchase of goods
c) Cash sale of goods
d) Credit sale of office furniture
5. What is comparability of accounting information?
6. Trace the supporting documents for the following transactions:
a) Rent paid to the landlord
b) Cash deposited into Bank
c) Goods purchased on credit from Gupta Bros.
d) A cheque issued to a supplier
7. Cash book is both a journalised ledger – explain
8. Give four examples of entries which appear in journal Proper
Application Based Questions (6 mark each)
1. Insert the following in Tabular Petty Cash Book. On 1st May,2024, based on an imprest cash of ₹800 on a monthly basis
| April 2024 | Transactions | Amount ₹ |
| 2 | stationery | 80 |
| 5 | Metro fare | 50 |
| 8 | Tea | 30 |
| 18 | Postage | 50 |
| 24 | Metro fare | 40 |
| 30 | Printing | 100 |
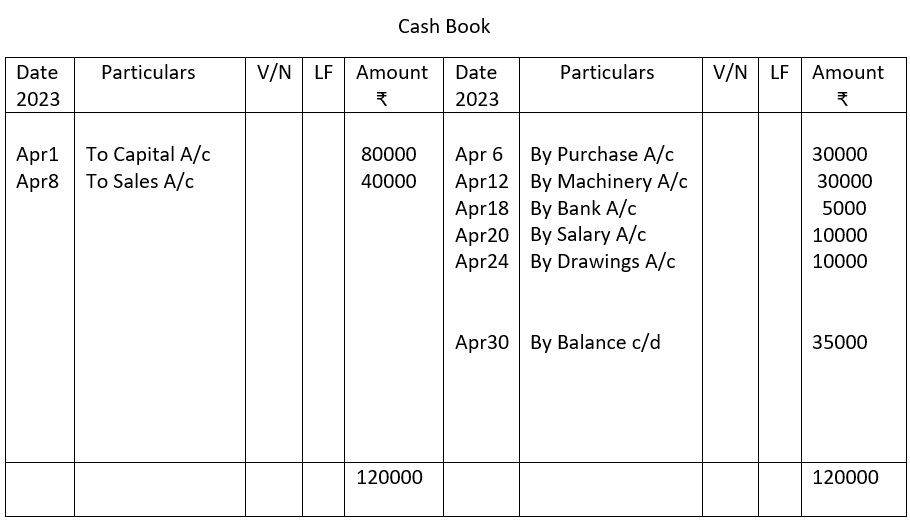
2. From the following single column Cash Book show postings in the ledger.
3. From the following information draw up a Trial Balance in the books of Rajinder Goel as on 31.3.23.
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| Capital | 200000 | Sale | 90000 |
| Purchases | 70000 | Sundry creditors | 10000 |
| Cash in hand | 10000 | Rent | 5000 |
| Cash at Bank | 8500 | Furniture | 15000 |
| Electricity Stationery | 4800 800 | Bank loan Investment Outstanding expenses | 10000 5000 1200 |
| Office Equipment | 4400 | Commission paid | 1050 |
| Sundry debtors | 9200 | Opening stock | 4500 |
| Machinery | 160000 | Commission received | 1200 |
| Salaries | 13300 | Postage | 850 |
| Closing Stock | 5000 |
4. Prepare the Accounting Equation from the following transactions:

5. Give business transactions for each of the following records
(a) Increase one asset and decrease another asset
(b) Increase one asset and increase the liabilities
(c) Increase the assets and increase the capital
(d) Decrease the asset and decrease the capital
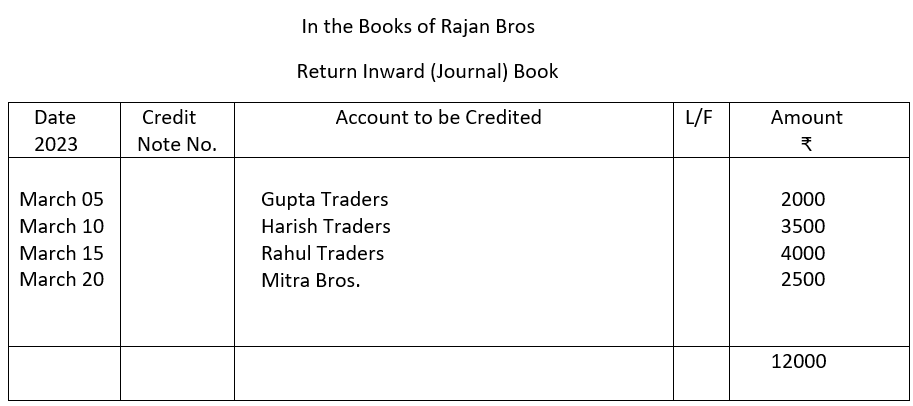
6. (a) Which source document is used to record Return Inward of goods?
(b) Prepare a Return Inward Journal Book from the following transactions in the books of Rajan Bros.

Solutions – Test Paper 1
Answers to Multiple Choice Type Questions– 1 mark each
1. (d) is correct
2. (a) is correct
3. (c) is correct
4. (a) is correct
5. (c) is correct
6. (c) is correct
7. (c) is correct
8. (a) is correct
9. (c) is correct
10. (a) is correct.
11. (b) is correct
12. (b) is correct
13. (d) is correct
14. (b) is correct hint. Less amount to be paid to creditor
15. (c) is correct
16. (b) is correct
17. (a) is correct hint. Business is a distinct entity owing profit to owner
18. (c) is correct
19. (d) is correct
20. (b) is correct
21. (c) is correct
22. (b) is correct
23. (b) is correct
24. (d) is correct
25. (d) is correct
Answers to Short Answer Type questions (3 mark each)
1. a) Accountancy starts where book keeping ends.
b) Book keeping is concerned with systematic recording of transactions like journalising and ledger posting. Accountancy is about analysis of the recorded data which results in profit and loss account and balance sheet.
c) Book keeping work is done on a daily basis as the transactions take place. Accounting work is undertaken at year ending.
2. The three objectives of Book-Keeping are:
a) Identification of business transactions and events
b) Classification of transactions in journal and ledger
c) Summarising of the classified data in trial balance
3. The three advantages of Accounting are:
a) It helps the management in decision making and planning.
b) It helps calculating tax liability.
c) It helps knowing the financial position of the business at a point of time.
4. The three uses of ledger are:
a) Ledger provides complete information about all accounts in one book.
b) It facilitates the preparation of final accounts i.e., Trading, Profit & loss Account and balance sheet.
c) It enables to ascertain the main items of revenues expenses, assets and liabilities.
5. The differences between journal and ledger can be listed as follows:
| Journal | Ledger |
| 1. It is a book of primary entry and is based on transactions. | 1. It is a book of final entry based on journal entries. |
| 2. Journal is the book of chronological or date wise record. | 2. Ledger is an analytical record. |
| 3. The journal has greater importance in legal evidence. | 3. Ledger is more concerned with profit and loss of business. |
6.The Cash Book is a book of original entry since transactions are recorded here for the first time from source documents. This is a feature of journal. Then again Cash book is a ledger in the sense that its format is that of a ledger account where cash receipts are posted on the debit side and Cash payments are posted on the credit side. Thus, Cash Book is both a journal and a ledger, so it is often called a journalised ledger.
7. Trade discount is the deduction of agreed percentage on list price offered to customers by manufacturers / whole-sellers of goods to buyers or retailers. Cash discount is the deduction of certain percentage on invoice value allowed to debtors for payment within the stipulated time frame. Trade discount is a regular business practice while cash discount is discretionary.
8. (a) Debit Voucher:
(b) Credit Voucher:
(C) Transfer voucher
9. The three fundamental steps in accounting process are:
(a) Identification of economic transaction
(b) Recording of transaction
(c) Communication
10. A Trial Balance is not a conclusive proof of accuracy of the books of accounts since certain types of errors remain even when the Trial Balance agrees. The limitations of trial balance are as follows:
a) Error of principle
b) Errors of complete omission
c) Compensating error
The above errors do not affect the Trial balance at all.
11. Amount invested by the owner of a firm is known as capital. It may be brought in the form of cash or assets. For the business entity capital is an obligation and a claim on the assets of the business. Capital is, therefore, shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
12. When cash is deposited in the bank or when cash is withdrawn from the bank, both the entries are recorded in the cash book.
When cash is paid into bank the amount deposited is written on the left side of the bank column and at the same time this amount is written on the right side of the cash column.
The reverse entry is passed when cash is withdrawn from the bank. Against such entries the word “C” or Contra is written in the L.F. It signifies that such entries need not be posted to the ledger accounts.
Answers to Short Answer Type questions (4 mark each)
1. The four modern rules of debit and credit are as under:
For Assets:
Debit – Increase in Assets
Credit – Decrease in Assets
For Liabilities and Capital:
Debit – Decrease in Liabilities and Capital
Credit – Increase in Liabilities and Capital
For Expenses and Losses:
Debit – Increase in Expenses and losses
Credit – Decrease in Expenses and Losses
For Incomes and Gains:
Debit – Decrease in Incomes or Gains
Credit – Increase in Incomes and Gains
2. ii) Identify the ledger account in which the transactions are recorded
iii) Enter the date of the transaction in the date column
iv) Record the page number of the journal
i) Enter the relevant amount in the amount column
3. a) To increase revenue:
Debit Cash account
Credit Sales account
b) To decrease expenses:
Debit Creditor account
Credit Return Outward account
c) To record drawing:
Debit Drawings account
Credit Cash account
d) To record fresh capital introduced:
Debit Cash account
Credit Capital account
4.
a. Cash Book
b. Purchase Book
c. Cash Book
d. Journal Proper
5. It is not sufficient that financial information is relevant and reliable at a particular time for a business entity. But it is equally important that users of the general-purpose financial accounting reports are able to compare various aspects of an entity with other entities. To be comparable, accounting reports must belong to a common period and use the common unit of measurement and formal reporting.
6.
(a) Rent receipt
(b) Bank pay-in-slip
(c) Invoice
(d) Bank cheque book
7. The Cash book is a book of original entry since transactions are recorded here for the first time from source documents. This is a feature of journal. The Cash Book is a ledger in the sense that it is designed in the form of a Cash Account and records cash receipts on the debit side and cash
payments on the credit side like a ledger account. Thus, Cash Book is both a journal and ledger and is often called a journalised ledger.
8. Examples of entries recorded in Journal Proper are:
a) Debtor account debit
Old furniture account credit
(Old furniture sold on credit)
b) Drawings account debit
Goods account credit
(withdrawn goods by owner for personal use)
c) Debit Advertising account
Credit Purchase account
(Sample distributed free of cost)
d) Debit Office Equipment
Credit party/creditor
(Office equipment purchased on credit)
Answers to Application Based Questions (6 mark each)
1.
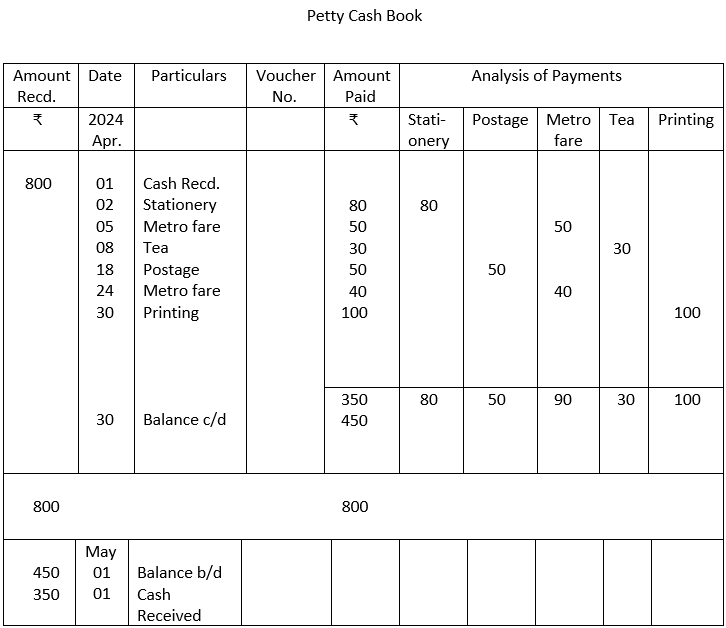
2.
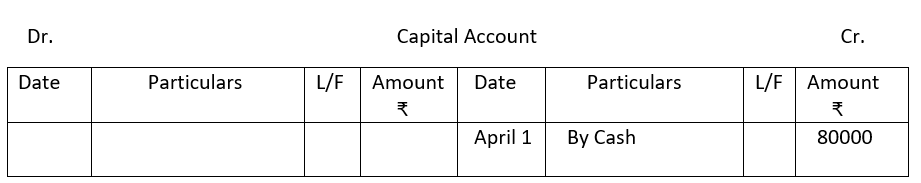
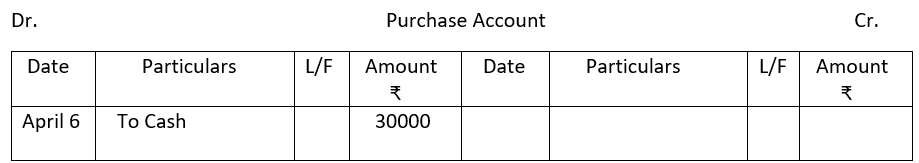
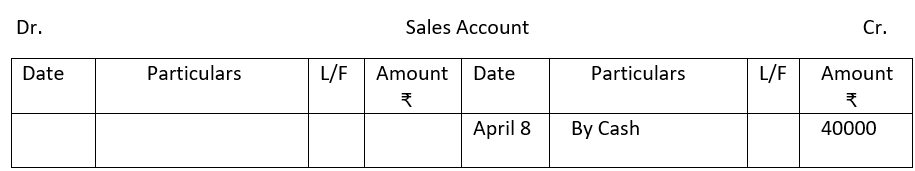
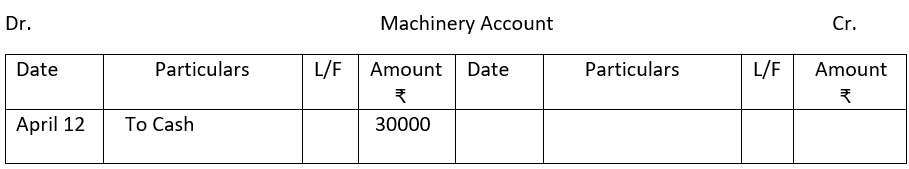
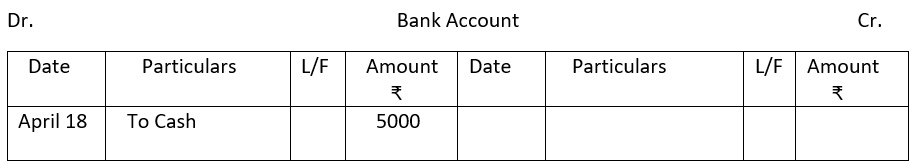
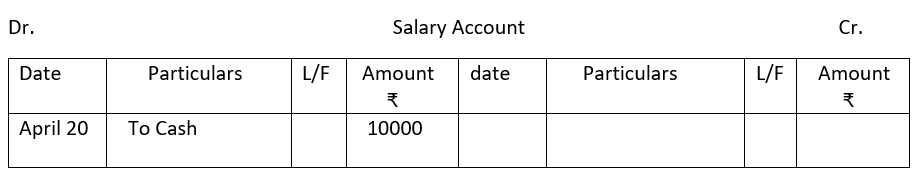
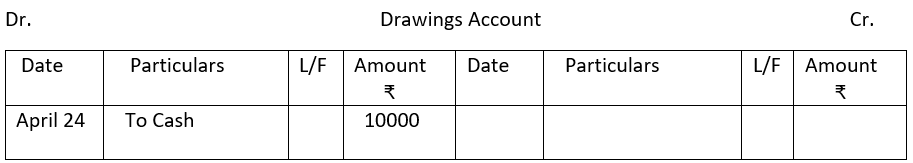
3.
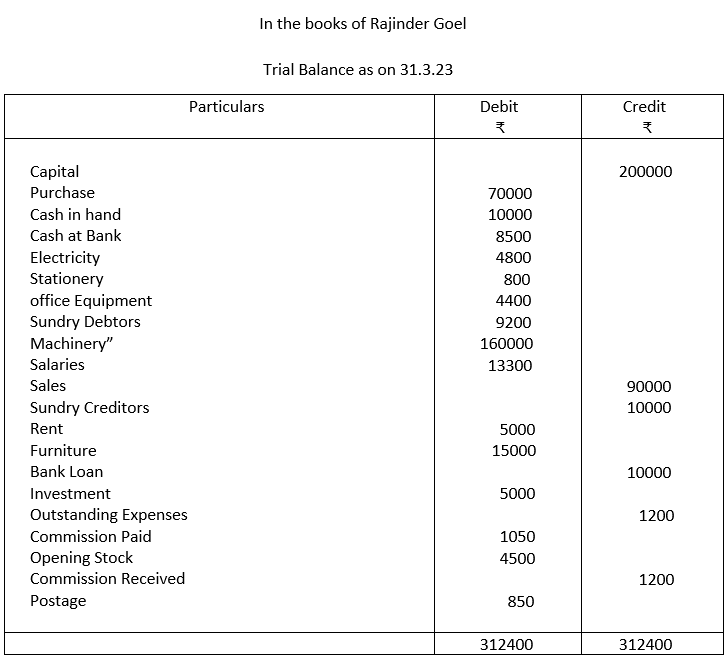
Note: Closing stock is not taken into account in Trial Balance
4.
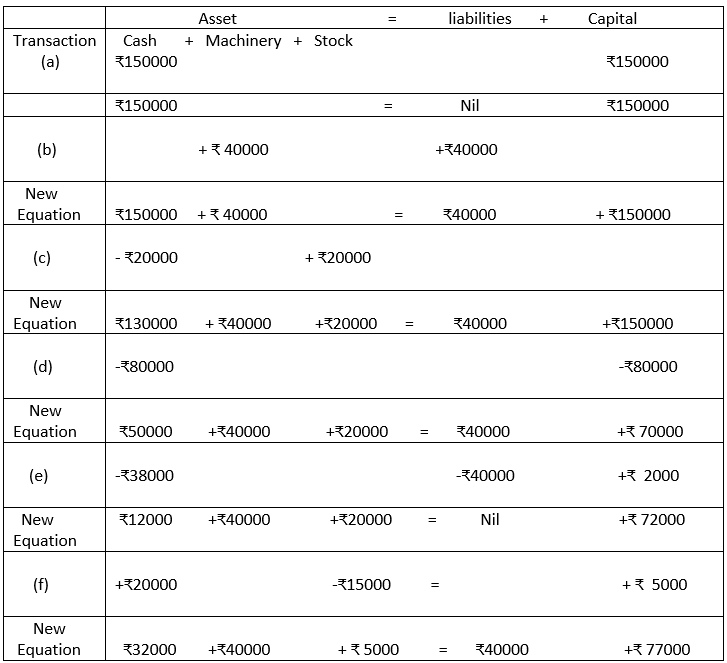
Analysis:
a) Cash introduced in business, Capital created
b) Asset (Machinery) created, Liabilities (Creditor) created
c) Asset (cash) increased and stock reduced
d) Asset (cash) reduced and Capital reduced as drawings effected
e) ₹ 38000 paid to creditor in full settlement of ₹ 4000 which means that ₹ 2000 is gained and added to capital as profit.
f) Asset (cash) added by ₹20000 (stock) reduced by ₹15000 and the difference ₹5000 is added to capital as profit
5. a) Purchase of Machinery for cash
This will decrease Cash A/c (Asset) and increase Machinery A/c (Asset)
b) Received Bank loan
This will increase Bank balance (Asset) and increase Bank loan A/c (Liability)
c) Fresh Capital introduced
This will increase Cash A/c (Asset) and increase Capital A/c
d) Depreciation on fixed Asset
This will decrease the fixed Asset and decrease Capital when the amount of depreciation is deducted
6. a) Credit Note
b)
CBSE Class 9 Elements of Book-Keeping and Accountancy – Test Paper 1 – Completed


