11. Complete Activity 3.11 (Page 44).
- Collect all the metal samples except sodium and potassium again. If the samples are tarnished, rub them clean with sand paper. CAUTION: Do not take sodium and potassium as they react vigorously even with cold water.
- Put the samples separately in test tubes containing dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Suspend thermometers in the test tubes, so that their bulbs are dipped in the acid.
- Observe the rate of formation of bubbles carefully.
- Which metals reacted vigorously with dilute hydrochloric acid?
- With which metal did you record the highest temperature?
- Arrange the metals in the decreasing order of reactivity with dilute acids
Answer:
Aim: To test the reaction of the samples with dilute hydrochloric acid and conclude based on the observations.
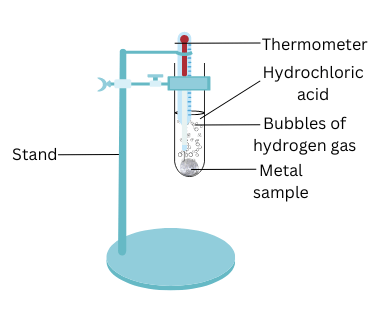
Materials Required: Magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, copper, lead, sand paper, 6 test tubes, 6 thermometers, dilute hydrochloric acid.
Procedure:
(i) Pour dilute hydrochloric acid in the 6 test tubes.
(ii) Put the samples of magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, copper, lead separately in 6 test tubes containing dilute HCl.
(iii) Suspend the thermometers in the test tubes by attaching them to the stand. Ensure that their bulbs are dipped in the acid.
(iv) Observe the rate of formation of bubbles and the increase in temperature in each test tube.
(v) Based on the observations, arrange the metals in the decreasing order of reactivity with dilute acids
Observations:
The rate of formation of bubbles was fastest and the increase in temperature was highest in case of magnesium, followed by aluminium, zinc, iron in that order. In case of copper and lead no reaction was seen and the temperature also remained unchanged.
Conclusions:
- The metals arranged in decreasing order of reactivity with dilute acids are Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu, Pb.
- The reactions of magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron with dilute hydrochloric acid are as follows:
Magnesium: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Aluminum: 2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2(g)
Zinc: Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Iron: Fe(s) + 2HCl → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
“Complete Activity 3.11 (Page 44).
- Collect all the metal samples except sodium and potassium again. If the samples are tarnished, rub them clean with sand paper. CAUTION: Do not take sodium and potassium as they react vigorously even with cold water.
- Put the samples separately in test tubes containing dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Suspend thermometers in the test tubes, so that their bulbs are dipped in the acid.
- Observe the rate of formation of bubbles carefully.
- Which metals reacted vigorously with dilute hydrochloric acid?
- With which metal did you record the highest temperature?
- Arrange the metals in the decreasing order of reactivity with dilute acids” – Solved.
Related Links:
Solution to Activity 3.1
Solution to Activity 3.2
Solution to Activity 3.3
Solution to Activity 3.4
Solution to Activity 3.5
Solution to Activity 3.6
Solution to Activity 3.7
Solution to Activity 3.8
Solution to Activity 3.9
Solution to Activity 3.10
Solution to Activity 3.11
Solution to Activity 3.12
Solution to Activity 3.13
Solution to Activity 3.14


