3. Complete Activity 4.3 (Page 41).
Collect some China rose (Gudhal) petals and place them in a beaker. Add some warm water. Keep the mixture for some time till water becomes coloured. Use the coloured water as an indicator. Add five drops of the indicator to each of the solutions given in Table 4.4. What is the effect of the indicator on acidic, basic and neutral solutions?
Answer: The activity is described below:
Aim: To test the given solutions using China rose indicator.
Materials Required: Shampoo (dilute solution), lemon juice, soda water, sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, vinegar, sugar solution, common salt solution, China rose petals, warm water, beaker.
Procedure:
(i) Soak some China rose (Gudhal) petals in warm water in a beaker until the water becomes coloured.
(ii) The coloured water is the indicator which you will use to identify the solutions listed in Table 4.4. Add five drops of the indicator to each of the solutions.
Observation:
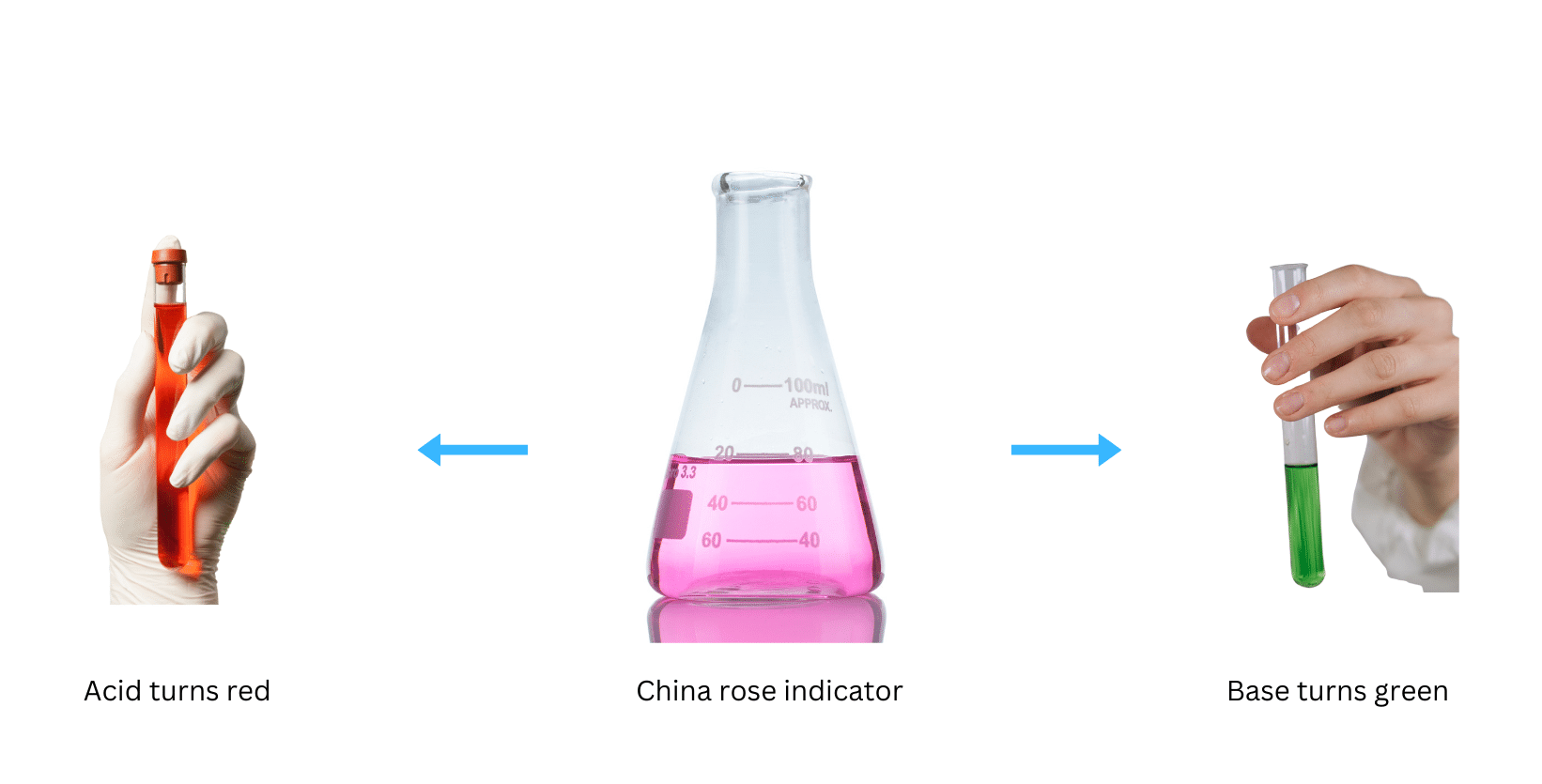
China rose indicator turns acids to dark pink and basic solutions to green.
The completed Table 4.4 is shown below:
| S. No. | Test Solution | Initial Colour | Final Colour |
| 1. | Shampoo (dilute solution) | White | Green |
| 2. | Lemon juice | White | Dark pink |
| 3. | Soda water | White | Green |
| 4. | Sodium hydrogencarbonate solution | White | Green |
| 5. | Vinegar | White | Dark pink |
| 6. | Sugar solution | Colourless | Colourless |
| 7. | Common salt solution | Colourless | Colourless |
Conclusions: China rose solution turns acids into dark pink and basic solutions to green. Therefore, it can be used to distinguish between acidic and basic solutions.
“3. Complete Activity 4.3 (Page 41).
Collect some China rose (Gudhal) petals and place them in a beaker. Add some warm water. Keep the mixture for some time till water becomes coloured. Use the coloured water as an indicator. Add five drops of the indicator to each of the solutions given in Table 4.4. What is the effect of the indicator on acidic, basic and neutral solutions?” – Solved.
Related Links:
Solution to Extended Learning Question 1
Solution to Extended Learning Question 2
Solution to Extended Learning Question 3
Solution to Extended Learning Question 4
Solution to Activity 4.1
Solution to Activity 4.2
Solution to Activity 4.4
Solution to Chapter 4 Acids, Bases and Salts


