9. Complete Activity 3.9 (Page 41).
CAUTION: The following activity needs the teacher’s assistance. It would be better if students wear eye protection.
- Hold any of the samples taken above with a pair of tongs and try burning over a flame. Repeat with the other metal samples.
- Collect the product if formed.
- Let the products and the metal surface cool down.
- Which metals burn easily?
- What flame colour did you observe when the metal burnt?
- How does the metal surface appear after burning?
- Arrange the metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity towards oxygen.
- Are the products soluble in water?
Answer:
Aim: To burn the metal samples in oxygen and answer the questions given based on the observations.
Materials Required: Sodium, magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, copper, lead, tongs, burner, water.
Procedure:
(i) Hold each of the samples over the burner with a pair of tongs.
(ii) Collect the product if formed in each case.
(iii) Let the products and the metal surface cool down.
(iv) Identify the metals which burn easily.
(v) Identify the flame colour observed when the metal is burnt.
(vi) Comment on the appearance of the metal surface after burning.
(vii) Arrange the metals in decreasing order of their reactivity towards oxygen.
(viii) Check whether the products are soluble in water.
Observations:
Which metals burn easily?
- Sodium and magnesium burn easily. Sodium burns more easily than magnesium.
- Aluminium, zinc, iron, copper, lead burn less easily. It is hard to say which of these are more reactive and which are less reactive when burning in oxygen.
What flame colour did you observe when the metal burnt?
- Sodium burns with a bright yellow flame.
- Magnesium burns with a bright white flame.
- Aluminium burns with a bright white flame, through less bright than magnesium.
- Zinc burns with a blue-green flame.
- Iron burns with bright yellow-orange sparks.
- Copper burns with a green flame.
- Lead shows no distinct flame colour.
How does the metal surface appear after burning?
- Sodium, magnesium and aluminium form a white powder after burning.
- Zinc produces a white powder on cooling after burning.
- Iron forms a black powder.
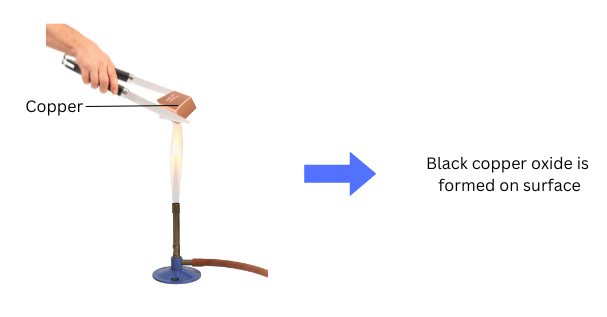
- Copper forms a black layer.
- Lead forms a yellow layer.
Reactivity towards oxygen (decreasing order):
- Sodium is the most reactive followed by magnesium and then aluminium.
- It was not possible to decide about the reactivity of zinc, iron, copper, lead
Solubility of the products in water:
- The product resulting from burning of sodium is soluble in water.
- The product resulting from burning of magnesium is soluble in water.
- The products resulting from burning of aluminium, zinc, iron, copper, lead are insoluble in water.
Conclusions:
- All metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxides. For example, on heating sodium combines with oxygen to form sodium oxide (Na2O).
- Most metal oxides are insoluble in water.
- The activity proves that sodium is the mist reactive of the samples of metal taken, followed by magnesium. It was not possible to decide about the reactivities of aluminium, zinc, iron, copper, lead by burning in oxygen only. Further testing needs to be done.
“9. Complete Activity 3.9 (Page 41).
CAUTION: The following activity needs the teacher’s assistance. It would be better if students wear eye protection.
- Hold any of the samples taken above with a pair of tongs and try burning over a flame. Repeat with the other metal samples.
- Collect the product if formed.
- Let the products and the metal surface cool down.
- Which metals burn easily?
- What flame colour did you observe when the metal burnt?
- How does the metal surface appear after burning?
- Arrange the metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity towards oxygen.
- Are the products soluble in water?” – Solved.
Related Links:
Solution to Activity 3.1
Solution to Activity 3.2
Solution to Activity 3.3
Solution to Activity 3.4
Solution to Activity 3.5
Solution to Activity 3.6
Solution to Activity 3.7
Solution to Activity 3.8
Solution to Activity 3.9
Solution to Activity 3.10
Solution to Activity 3.11
Solution to Activity 3.12
Solution to Activity 3.13
Solution to Activity 3.14


