Hello folks! Find below solutions to the questions posed at the end of this chapter, the in-text questions and a variety of extra questions of many formats for practice. We advise that you work out the problems yourselves alongside studying them. This will boost your understanding and retention.
Find solutions to NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 5 ‘Water’ here:
1. Answer the following questions:
(i) What is precipitation?
Answer:
Precipitation is caused by the condensation of water vapour into tiny droplets of water which float in the air as clouds. When the clouds become too heavy to remain suspended in air they fall to the ground as rain, snow, sleet or hail.
(ii) What is the water cycle?
Answer:
The water cycle is the process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land.
(iii) What are the factors affecting the height of the waves?
Answer:
The factors affecting the height of the waves are the speed and strength of winds, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or underwater landslides. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger are the waves.
(iv) Which factors affect the movement of ocean water?
Answer:
The factors affecting the movement of ocean water are:
- Temperature
- The gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface
- Warm and cold ocean currents
- Wind
(v) What are tides and how are they caused?
Answer:
The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water, twice in a day, is called a tide. Tides are caused by the strong gravitational force exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface.
(vi) What are ocean currents?
Answer:
Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. The ocean currents may be warm or cold.
2. Give reasons.
(i) Ocean water is salty.
Answer:
Ocean water is salty because it contains a large amount of salt dissolved in it. The salt present in ocean water is mostly sodium chloride or the common salt that we consume.
(ii) The quality of water is deteriorating.
Answer:
The quality of water is deteriorating because of irresponsible human activities like deforestation which affects the water cycle, indiscriminate dumping of garbage and untreated toxic wastes in water bodies, increased use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides, and release of hazardous chemicals from industries into ponds, canals and rivers.
3. Tick the correct answer.
(i) The process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land.
(a) Water cycle
(b) Tides
(c) Ocean current
Answer:
(a) Water cycle
(ii) Generally, the warm ocean currents originate near
(a) Poles
(b) Equator
c) None of these
Answer:
(b) Equator
(iii) The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called
(a) Tide
(b) Ocean current
(c) Wave
Answer:
(a) Tide
4. Match the following:
| (i) Caspian Sea | (a) Largest Lake |
| (ii)Tide | (b) Periodic rise and fall of water |
| (iii) Tsunami | (c) Strong seismic waves |
| (iv)Ocean currents | (d) Streams of water moving along definite paths |
| (e) Water cycle |
Answer:
| (i) Caspian Sea | (a) Largest Lake |
| (ii)Tide | (b) Periodic rise and fall of water |
| (iii) Tsunami | (c) Strong seismic waves |
| (iv)Ocean currents | (d) Streams of water moving along definite paths |
5. For fun
Be a detective
(i) The name of one river is hidden in each of the sentences below. Spot it. Example: Mandira, Vijayalakshmi and Surinder are my best friends
Answer:
Ravi
(a) The snake charmer’s bustee, stables where horses are housed, and the piles of wood, all caught fire accidentally. (Hint: Another name for River Brahmaputra)
(b) The conference manager put pad, material for reading and a pencil for each participant. (Hint: A distributary on the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta)
(c) Either jealousy or anger cause a person’s fall (Hint: Name of a juicy fruit!)
(d) Bhavani germinated the seeds in a pot (Hint: Look for her in West Africa)
(e) “I am a zonal champion now” declared the excited athletic. (Hint: The river that has the biggest basin in the world)
(f) The tiffin box rolled down and all the food fell in dusty potholes. (Hint: Rises in India and journeys through Pakistan)
(g) Malini leaned against the pole when she felt that she was going to faint. (Hint: Her delta in Egypt is famous)
(h) Samantha mesmerised everybody with her magic tricks. (Hint: London is situated on her estuary)
(i) “In this neighbourhood, please don’t yell! Owners of these houses like to. have peace”. Warned my father when. we moved into our new flat”. (Hint: colour!)
(j) ‘Write the following words, Marc!’ “On”, “go”, “in” said the teacher to the little boy in KG Class. (Hint: Rhymes with ‘bongo’). Now make some more on your own and ask your classmates to spot the hidden name. You can do this with any name: that of a lake, mountains, trees, fruits, school items, etc.
Answer:
(a) Teesta
(b) Padma
(c) Orange
(d) Niger
(e) Amazon
(f) Indus
(g) Nile
(h) Thames
(i) Yellow
(j) Congo
Carry on Detective
(ii) With the help of an atlas, draw each river which you discovered in For Fun (i) on an outline map of the world.
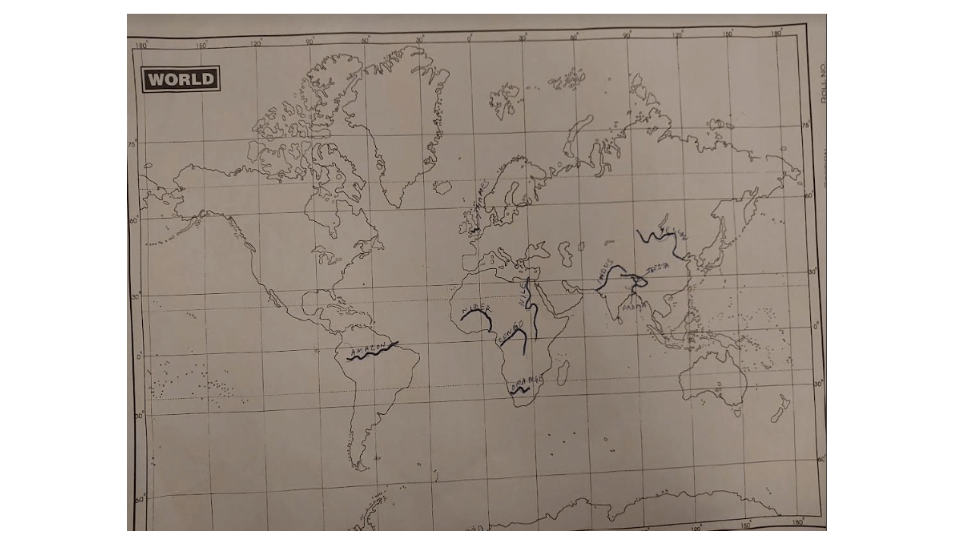
Solutions for In-text questions of NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 5 “Water”
Text book page no 30
Activity
Make your own terrarium.

Aim: To build a terrarium
Materials Required: A large glass Jar, soil, humus water indoor plants
Procedure:
(i) Fill one fourth of the jar with soil and press down.
(ii) Spread a thin layer of humus on top of the soil layer.
(iii) Plant the largest plant in the centre and plant the smaller ones around it.
(iv) Spray the plants with water and close the jar.
Observations:
- After a while we see a light mist covering the inner walls of the glass jar.
- Gradually water droplets are observed on the walls of the jar.
- Then the water droplets trickle down walls of the jar to moisten the soil.
Conclusions:
The water vapour that is released by the plants during transpiration condenses to form water which in turn sustains the plants.
The earth is like a huge terrarium. The sun’s heat causes the water from the rivers, lakes, seas and oceans to evaporate and rise up. When the water vapour cools down, it condenses to form clouds. And then it falls down as rain, snow or sleet. The continuous process by which water continually changes form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land is known as the water cycle.
Activity (Page 32)
Take 2 litres of water. Let it represent the total water on the surface of the earth. Measure out 12 spoons of water from this vessel into another bowl. The water that is left behind in the vessel represents the salty water found in oceans and seas. It is saline (contains salts).
The 12 spoons of water that was taken in a bowl is the total amount of fresh water on earth. The figure shows us the distribution of this fresh water. See for yourself how much water can actually be used by you.
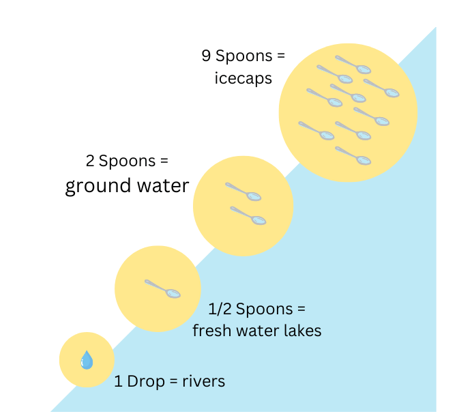
This diagram shows us how precious this life-supporting resource is and should make us conscious of the need to preserve fresh water without which no living organism can survive.
Text book page no 33
1. Why water is important for us?
Answer:
Water is indispensable for life on earth to exist. Without water all living creatures would perish and plants would disappear from the face of the earth. Water is a precious resource which is useful in many ways. We require water for drinking, cleaning, washing, cooking, bathing, for agriculture, gardening. Industries too need water to function. Therefore, we must use water judiciously and conserve it.
2. Suggest some ways in which water can be conserved in your home and in your school.
Answer:
Some ways in which water can be conserved in our home and in our school are:
- We should not waste water, but use only the amount of water required.
- We should close taps after use. We should repair the leaky taps.
- We should try to minimise the wastage of water by turning off the tap while brushing our teeth or shaving.
- Rainwater harvesting techniques should be applied.
- We should not pollute water by dumping garbage
- Water recycling should be done.
Extra Questions NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 5 ‘Water”
A. Multiple Choice type Questions (MCQ)
1. What is the percentage of salt water on earth?
(i) 02.0%
(ii) 97.3%
(iii) 0.0019%
(iv) 0.68%
2. What fraction of the earth’s surface is covered by water?
(i) one-fourth
(ii) one-third
(iii) half
(iv) three-fourth
3. When is World Water Day celebrated?
(i) 22nd May
(ii) 22nd March
(iii) 24th March
(iv) 28th July
4. Which of the following is an artificial enclosure for keeping small house plants?
(i) terrace
(ii) terrain
(iii) territory
(iv) terrarium
5. What percentage of the earth’s water flow down our rivers?
(i)0.00010%
(ii) 0.1%
(iii) 0.0001%
(iv) None of the above
6. A tidal wave is also called a __________.
(i) a Tsunami
(ii) a tide
(iii) a giant wave
(iv) none of the above
7. The movement of ocean water is called________.
(i) wave
(ii)tide
(iii)current
(iv) All of the above
8. The size of the waves depends on the________
(i) gravitational pull of the sun and moon
(ii) the heat of the sun
(iii)the strength of the wind
(iv) all the above
9. Which of the following currents is a cold current?
(i) The Labrador current
(ii)The Gulf stream current
(iii)The Kuroshio current
(iv) North Equatorial current
10. How are high tides helpful?
(i) they help in navigation
(ii) they help in fishing
(iii) they help generate electricity
(iv) All of the above
Answer:
1. (ii) 97.3%
2. (iv) three-fourth
3. (ii) 22nd March
4. (iv) terrarium
5. (iii) 0.0001%
6. (i) a Tsunami
7. (iv) All of the above
8. (iii)the strength of the wind
9. (i) The Labrador current
10. (iv) All of the above
B. Fill in the blanks with suitable words to complete the following sentences:
1.The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called ______.
2. The stronger the wind blows, the __________ the waves becomes.
3.The sun’s heat causes ___________of water into water vapour.
4. _________ or harbour wave struck destruction in the Indian Ocean on 26 December 2004.
5. When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternatively, They are called ___________.
Answer:
1.The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called tide.
2.The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the waves becomes.
3. The sun’s heat causes evaporation of water into water vapour.
4. Tsunami or harbour wave struck destruction in the Indian Ocean on 26 December 2004.
5. When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternatively, They are called waves.
C. Match the words in column A with those in column B
| A | B |
| Neap tides | cause evaporation of water |
| Sun’s rays | salinity level of more than 340gms per litre of water |
| Precipitation | fresh water |
| Dead sea | condensation of water vapour |
| glaciers | Low tides |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Neap tides | Low tides |
| Sun’s rays | cause evaporation of water |
| Precipitation | condensation of water vapour |
| Dead sea | salinity level of more than 340gms per litre of water |
| glaciers | fresh water |
D. State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE:
1. The largest tsunami waves travel at a speed of more than 700km per hour.
2. Neap tides occur when the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same line on full moon and mew moon days.
3. Indira Point in the Andaman and Nicobar islands that marked the southernmost point of India got submerged completely during the tsunami of 26 December 2004.
4. The areas where the warm and cold currents meet provide the best fishing grounds of the world.
5. Salinity is the amount of salt in grams present in 100 grams of water.
Answers:
1. True
2. False – When the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same line on full moon and new moon days, the tides are highest and are known as Spring tides.
3. True
4. True
5. False- Salinity is the amount of salt in grams present in 1000 grams of water. The average salinity of the oceans is 35 parts per thousand.
E. Very Short Answer type Questions:
1. What are the major sources of fresh water?
Answer:
The major sources of fresh water are the rivers, ponds, springs and glaciers.
2. Which is the largest lake?
Answer:
The Caspian sea is the largest lake.
3. What is the percentage of ground water present on earth?
Answer:
Ground water constitutes only 0.68% of the total water on earth.
4. When are the tides highest?
Answer:
Tides are highest on full moon and new moon days.
5. In which direction do cold currents move?
Answer:
Cold currents carry water from polar or higher latitudes to tropical or lower latitudes.
6. Where was the epicentre of the earthquake of 26th December, 2004?
Answer:
Sumatra was the epicentre of the earthquake of 26th December, 2004.
7. Where are the best fishing grounds in the world?
Answer:
The areas where the warm and cold currents meet provide the best fishing grounds, such as the seas around eastern coast of North America and Japan.
8. Why is it possible to float in the Dead Sea??
Answer:
The Dead Sea has a salinity level of 340 grams per litre of water which makes it very dense enabling swimmers to float easily.
9. What are waves?
Answer:
The water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately to form waves.
10. What causes tides?
Answer:
The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface cause tides.
11. What is the significance of World Water Day?
Answer:
On the occasion of World Water Day (22nd March) awareness is raised about the need to conserve water in different ways.
12. What happens during high tide?
Answer:
During high tide, waves rise high and water covers much of the shore.
13. What is a Tsunami?
Answer:
Tsunami is a Japanese word that means ‘Harbour Waves’ because the harbors get destroyed whenever there is a Tsunami.
14. What is a terrarium?
Answer:
It is an artificial enclosure for keeping small house plants. .
15. What is the average salinity of the oceans?
Answer: The average salinity of the oceans is 35 parts per thousand.
F. Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is the first indication of a tsunami? What mistake did people of the coastal areas make which resulted in the loss of many lives in 2004?
Answer:
The first indication of an approaching tsunami is the rapid withdrawal of water from the coastal region followed by a destructive wave. When this happened in 2004, instead of seeking refuge on higher ground, people thronged the coast to view the miraculous event. As a consequence, there was a large casualty of curious onlookers when the tsunami struck the Indian coast.
2. How are tides caused? What do you understand by high tide and low tide?
Answer:
The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called a tide. The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface causes the tides. The water of the earth closer to the moon gets pulled under the influence of the moon’s gravitational force and causes high tide.
It is high tide when water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level. It is low tide when water falls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore.
3. Distinguish between spring tide and neap tide?
Answer:
Spring tides occur during the full moon and new moon days, when the sun, the earth and the moon are in the same line and the tides are at their highest level. These tides are called spring tides.
Neap tides occur when the moon is in its first and last quarter, then the ocean water gets drawn in diagonally opposite directions by the gravitational pull of sun and earth resulting in low tides.
4. In what ways are high tides beneficial?
Answer:
High tides are important for various reasons:
(i) They help in navigation.
(ii) They raise the water level close to the shores. This helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
(iii) The high tides also help in fishing. Much more fish come closer to the shore during the high tide. This enables the fisherman to get a plentiful catch.
(iv) The rise and fall of water due to tides is being used to generate electricity in some places.
5. What are the waves? Write a short note on it.
Answer:
The water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately to form waves. Waves are formed when winds scrape across the ocean surface. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the wave becomes. During a storm, the winds blow at very high speed and therefore huge waves are formed. These waves are very strong, hence very destructive.
6. What do you know about Tsunami?
Answer:
Tsunami is a Japanese word meaning ‘Harbour waves’ as the harbours get destroyed during a tsunami. It is a seismic wave created by underwater disturbance such as an earthquake, landslide, or volcanic eruption which can shift large amounts of ocean water. As a result enormous waves called tsunami as high as 15 metres are formed. The tsunami of 2004 struck havoc in the Indian ocean on 26 December 2004. It was caused by an earthquake measuring 9.0 on the Richter scale. It caused death and destruction in the coastal areas of India. The Indira Point in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands got submerged after the tsunami.
7. Describe the water cycle.
Answer:
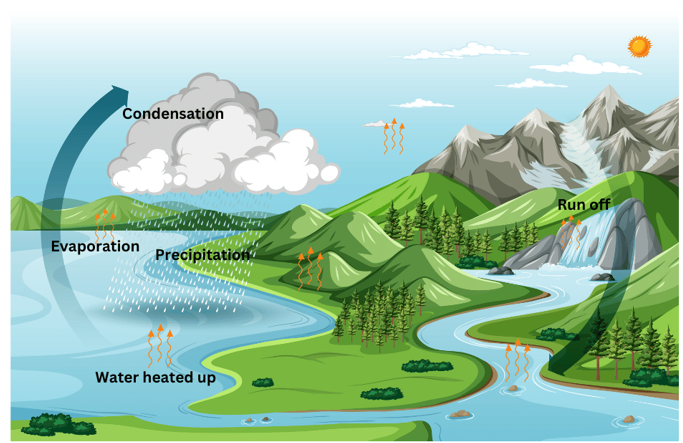
The process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere, and land is known as the water cycle.
The cycle starts with the evaporation of water from rivers, lakes, ponds and seas due to the heat of the sun. Evaporation causes water vapour to rise into the atmosphere. There it cools down through a process called condensation into tiny droplets of water which form clouds.
When the clouds become too heavy to float, the phase of precipitation begins as they start falling to earth in the form of rain, snow, hail or sleet.
Thus we see that the water cycle has three distinct phases – evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
8. Differentiate between warm ocean current and cold ocean current.
Answer:
Difference between warm ocean currents and cold ocean currents are as follows:
| Warm ocean currents | Cold ocean currents |
| Warm currents generally originate near the equator and move towards the poles. | Cold currents carry water from the polar or higher latitudes to tropical or lower latitudes. |
| Warm currents bring warm temperatures over land surfaces | Cold currents bring down the temperature over land surfaces. |
| Example of a warm current is the Gulf Stream current | Example of a cold current is the Labrador current. |
9. List the differences between between waves and tides.
Answer:
The differences between waves and tides are as follows:
| Waves | Tides |
| Waves rise and fall alternately all day long. | Tides occur twice in a day. |
| Waves are caused when winds scrape across the surface of seas and oceans. | The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface causes tides. |
G. Long answer Type Questions
1. What are the different movements of ocean water? How are they caused?
Answer:
The important movements that occur in oceans can be classified as waves, tides and currents:
- Waves occur when the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternatively. Waves are formed when winds scrape across the ocean surface. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the waves become.
- Tides are the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day. High tide occurs when water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level. Low tide occurs, when water falls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore. The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface causes the tides.
- Ocean Currents are the streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. The ocean currents may be warm or cold. Normally, the warm ocean currents originate near the equator and move towards the poles. The cold currents carry water from polar or higher latitudes to tropical or lower latitudes. The Labrador Ocean current is cold current while the Gulf Stream is a warm current.
The areas where the warm and cold currents meet provide the best fishing ground of the world. For example, seas around Japan and the Eastern Coast of North America. The areas where the warm and cold currents meet also experience foggy weather making navigation difficult.
2. What is Tsunami? What are the causes of Tsunami? Cite an example to explain the damages caused by Tsunamis.
Answer:
Tsunami is a Japanese word which means ‘Harbour waves’ as the harbours get destroyed whenever there is a tsunami.
A volcanic eruption, an earthquake or underwater landslides can displace large amounts of ocean water.
The first indication that tsunami is approaching is the rapid withdrawal of water from the coastal region.
Next, a huge tidal wave known as tsunami which may be as high as 15 m is formed. The largest tsunami ever measured was 150 m high. These waves travel at a speed of more than 700 km per hour.
The tsunami of 2004 caused devastating and disastrous damage in the coastal areas of India. The Indira Point in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands got submerged after the tsunami. More than 10000 people were killed and more than a lakh of houses were damaged.
These damages caused to life and property are due to the lack of monitoring, lack of the early warning systems and knowledge among the coast dwellers.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 5 ‘Water’
These solutions and extra material have been designed by an expert team of Indian and foreign-educated teachers. They have designed them logically and scientifically to ensure maximum learning and retention. All the phenomena you need to know are explained with attractive figures wherever necessary. You will find similar concepts and questions in your exams, so practise them on your own as well. We suggest that you refer to maps and diagrams whenever you study this lesson so that you form a clear idea of the material covered which will remain in your memory forever.
The free PDFs of the solutions are available for download anytime! If you like our material and want plenty more from us, keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list. We will send all the latest study material and other resources that you need straight to your inbox!
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Water Cycle
Distribution of Water Bodies
Ocean Circulation
Ocean Currents
What do you mean by salinity?
What is a Tsunami?
What happens during high tide?
How do spring and neap tides occur?
In what way are high tides important?
Write a note on the importance of water.
Explain the water cycle with a neat and labelled diagram.
Give an account of ocean currents.
How are waves formed?
Yes, certainly. Our team of competent subject teachers have carefully anticipated all the queries you may have about the lesson and crafted these excellent solutions which draw your attention to every detail and also explain the essence of the chapter.
We suggest that at first you read the lesson closely and then read the solutions taking in all the details. Refer closely to the diagrams and maps while preparing the lesson. This will engage your visual memory and help you understand better.
Our seasoned subject experts have painstakingly provided many extra questions which are similar to exam questions and are designed to give you sufficient practice.
Go through the solutions before the exam and practise writing out some answers within a specified time period. This is an important step which should not be skipped because practice not only makes perfect, but also boosts your self-confidence. You will be well-equipped to take on any challenge that your examiner may pose! Good luck!
Need us to coach you and prepare you for your exams? Our expert teachers look forward to teaching bright young students like you and will go the extra mile to help you succeed. Feel free to contact us with your requirements anytime and we’ll be happy to help you out! We provide on-demand one-to-one coaching, based on your convenience and your needs – have it completely your way! Book any number of online appointments now!


