Hello students! Find below our excellent solutions to the exercise text questions, the in-text questions and a variety of extra questions in many formats designed to test your preparedness. As usual the solutions prepared by our team of subject experts trained both in India and abroad are the best place to begin your study. We advise you to read the lesson attentively and then attempt to answer the questions in your own words after reading our solutions. This will boost your understanding and retention.
Find NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Studies Geography Our Environment Chapter 7 ‘Life in the Deserts’, here.
1. Answer the following questions.
(a) What are the two types of deserts found in the world?
Answer:
There are two types of deserts in the world depending on the temperature:
- Hot Desert
- Cold Desert
Example: The Sahara in Africa is a hot desert and Ladakh in India is a cold desert.
(b) In which continent is the Sahara Desert located?
Answer:
The Sahara Desert is located in the continent of Africa. It stretches across a large part of North Africa touching eleven countries. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Red Sea to the east.
(c) What are the climatic conditions of the Ladakh desert?
Answer:
The climate of Ladakh is extremely cold and dry owing to its altitude which ranges from 3000m in Kargil to 8000m in the Karakoram. The air is so thin that the heat of the sun is intensely felt. Day temperatures in summer are just above zero degree, whereas the temperatures dip at night to below -300C. It is freezing cold in winters with temperatures below – 400C for most of the time. Rainfall is very scarce, about 10cm every year as the region lies in the rainshadow of the Himalayas. The region experiences freezing winds and burning hot sunlight putting people at risk of heat strokes and frostbite simultaneously.
(d) What mainly attracts tourists to Ladakh?
Answer:
Tourists from India and abroad visit Ladakh every year drawn by the Buddhist monasteries like Hemis, Thiksey, Shey and Lamayaru as well as the traditional gomphas which dot the landscape. Others are lured by glaciers, snow-capped mountains and lakes. Many come to attend the colourful ceremonies and festivities of Ladakh such as the Hemis Tsechu and Losar.
(e) What type of clothes do the people of the Sahara Desert wear?
Answer:
The people of the Sahara Desert wear heavy robes with head gear as protection against dust storms and hot winds in the desert. These heavy robes also insulate them against the burning heat of the day and freezing cold at night.
(f) Name the trees that grow in Ladakh.
Answer:
Groves of willows and poplars are seen in the valleys. Trees like apple, apricot and walnut bear fruit during the summer season in Ladakh. Other than that, there are scanty patches of shrubs and grass for animals to graze. Due to the cold climate, there is not much fauna in this region.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Sahara is located in which part of Africa?
(a) Eastern
(b) Northern
(c) Western
Answer:
(b) Northern
(ii) Sahara is what type of desert?
(a) Cold
(b) Hot
(c) Mild
Answer:
(b) Hot
(iii) The Ladakh desert is mainly inhabited by
(a) Christians and Muslims
(b) Buddhists and Muslims
(c) Christians and Buddhists
Answer:
(b) Buddhists and Muslims
(iv) Deserts are characterised by
(a) Scanty vegetation
(b) Heavy precipitation
(c) Low evaporation
Answer:
(a) Scanty vegetation
(v) Hemis in the Ladakh is a famous
(a) Temple
(b) Church
(c) Monastery
Answer:
(c) Monastery
(vi) Egypt is famous for growing
(a) Wheat
(b) Maize
(c) Cotton
Answer:
(c) Cotton
3. Match the following.
| (i) oasis | (a) Libya |
| (ii) Bedouins | (b) monastery |
| (iii) Oil | (c ) glacier |
| (iv) Gangri | (d) depressions with water |
| (v) Lamayuru | (e ) cold desert |
| (f ) Sahara |
Answer:
| (i) oasis | (d) Depressions with water |
| (ii) Bedouins | (f) Sahara |
| (iii) oil | (a) Libya |
| (iv) Gangri | (c) Glacier |
| (v) Lamayuru | (b) Monastery |
4. Give reasons.
(i) There is scanty vegetation in the deserts.
Answer:
The climate of the deserts is unsuitable for vegetation because it is either very hot and dry, or very cold and dry. Either way the extreme temperatures coupled with low rainfall are not favourable for the growth of plants. Hence there is scanty vegetation in deserts.
(ii) People of the Sahara Desert wear heavy robes.
Answer:
People in the Sahara Desert wear heavy robes to protect themselves from the dust storms and scorching dry winds. The heavy robes insulate them against the burning heat during the day and the freezing cold temperatures at night.
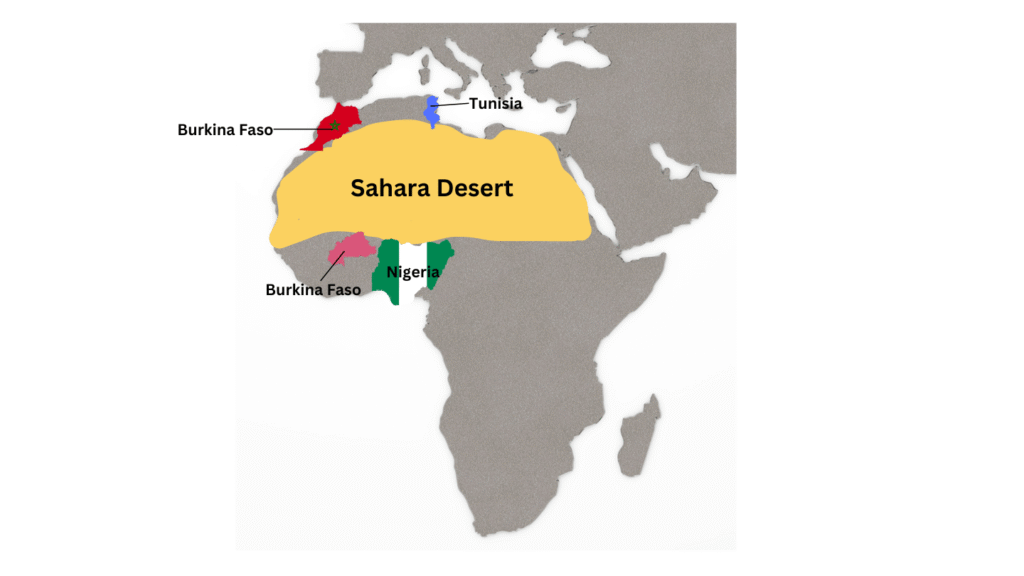
5. Map Skills
(i) On the outline map of Africa, mark the Sahara Desert and any four countries around it.
Answer:
(ii) On the outline map of India, mark the Karakoram Range, Zanskar Range, Ladakh and Zoji La pass.
Answer:
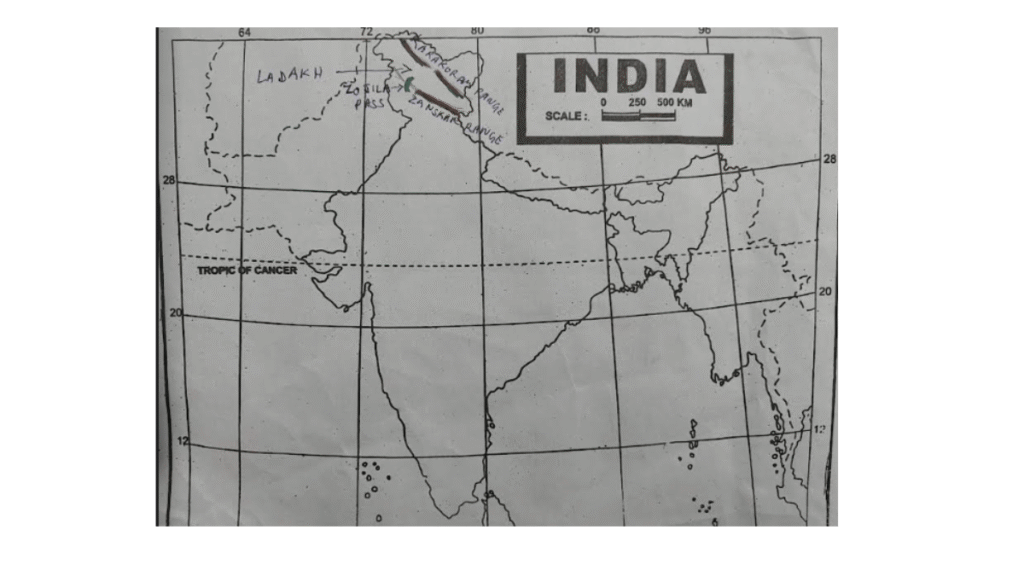
6. For Fun
Desert Game
This is a class room activity involving all the students. The teacher will create a list of desert creatures. The number of the creatures should be same as the number of students in the class. The creatures can be picked up from the categories of mammals, birds and reptiles. Mammals can include – camel, yak, fox, sheep, goat, antelope…
Birds – raven, eagle, vulture, turkey…
Reptiles – snakes …
Assign one desert creature to each student. Ask the student to write three characteristics of the creature on plain sheet of paper. (students can use index cards of size 10 cm × 15 cm). Questions such as – in what type of deserts it is found? Major adaptation? Use to man?
These characteristics will be used as clues in the guessing game. On the board make three columns – mammals, birds and reptiles. Paste a sheet of paper in the column under the particular category. The class can be divided in three to four groups. They will compete against each other in the ‘desert game’. Each group now takes turn in guessing the correct answer. Explain to the class that they have to guess what animal matches the characteristics listed on the paper.
For example:
• Animal of hot desert
• Has double set of eyelashes to keep away the sand
• The hide is used for making water bottles
The correct answer is ‘camel’. Within the group there will be a student who has prepared the card. That student should not answer. Ten points are awarded for the correct answer.
This game will enable students to understand the desert. You can play the same game by taking different types of fruits, flora and the clothes the people wear.
Answer:
Prepare the cards in this manner, a few samples are provided for your reference:
Yak – Found in the cold desert of Ladakh
reared for its milk
Its milk is used to make cheese and butter
Sheep – found in both Sahara desert and the cold desert of Ladakh
reared for meat
The fleece is used for making woollens.
Robin – It has a dull reddish breast
Found in the cold regions of Ladakh
they roost in flocks together to conserve energy and stay warm
Raven- very intelligent bird
It is black
lives in the cold desert of Ladakh
Hoopoe- colorful bird with distinct crown of feathers
enjoys taking dust and sand baths
Considered sacred in ancient Egypt
Scorpion –lives in the hot Sahara Desert
has a pair of grasping pincers
carries its tail which ends in a stinger in a forward curve over the back
Solutions for In-text questions of NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 7 “Life in the Deserts”
Text book Page no 51
1. Scientists have actually found skeletons of fish in this desert. What could have happened?
Answer:
The fish bones found by scientists point to the existence of former waterbodies in place of the desert now. Cave paintings in the Sahara Desert show that there used to be rivers with crocodiles. So, we may assume that long term climate change has transformed what was once a lush green plain to an arid desert.
Text book Page no 53
2. Do you find any resemblance between the people of Ladakh and the inhabitants of Tibet and Central Asia?
Answer:
The people of Ladakh are either Muslims or Buddhists, so their culture resembles both the inhabitants of Central Asia and those of Tibet. Ladakh is sometimes called “Little Tibet” in light of the strong influence of Tibetan culture. Buddhist influence is profound and clearly evident. Every village or town has a temple or monastery whether small or large.
3. Can you name some more mountain passes in the Himalayas?
Answer:
Some of the important mountain passes in the Himalayas are:
Karakoram Pass
Zoji La Pass
Khardung La Pass
Rohtang Pass
Banihal Pass
Diphu Pass
Nathu La Pass
Extra Questions NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 7 “Life in the Deserts”
A. Multiple Choice type Questions (MCQ)
1. What are the features you would see in the Sahara desert?
(i) sand
(ii) gravel plains
(iii) elevated plateaus with bare rocky surfaces
(iv) All of the above
2. Which place recorded the highest temperature of 57.70C in 1922?
(i) Tripoli
(ii) Cairo
(iii) Al Azizia
(iv) None of the above
3. Which animals would you not find in the Sahara desert?
(i) camels
(ii) Yaks
(iii) jackals
(iv) hyenas
4. Which of these countries is not touched by the Sahara desert?
(i) Algeria
(ii) Libya
(iii) Nigeria
(iv) None of the above
5. Which trees is found in the Sahara?
(i) apricot tree
(ii) apple tree
(iii) date palm
(iv) None of the above
6. What is Egypt famous for?
(i) Wheat
(ii) barley
(iii) cotton
(iv) beans
7. Why is there low precipitation in Ladakh?
(i) The moisture evaporates faster then it accumulates
(ii) The air is thin so the sun shines very intensely.
(iii) It lies in the rainshadow of the Himalayas.
(iv) None of the above
8. Which monastery is not in Ladakh?
(i) Lamayaru
(ii) Pemayangstse
(iii) Hemis
(iv) Thiksey
9. The National Highway 1A connects Leh to Kashmir through _________pass.
(i) Rohtang Pass
(ii) Banihal Pass
(iii) Khardung La Pass
(iv) Zoji La Pass
10. In which countries in the Sahara was oil discovered?
(i) Libya
(ii) Algeria
(iii) Egypt
(iv) all of the above
Answer:
1. (iv) All of the above
2. (iii) Al Azizia
3. (ii) Yaks
4. (iii) Nigeria
5. (iii) date palm
6. (iii) cotton
7. (iii) It lies in the rainshadow of the Himalayas.
8. (ii) Pemayangstse
9. (iv) Zoji La Pass
10. (iv) all of the above
B. Fill in the blanks with suitable words from the box to complete the following sentences:
1. The Sahara desert despite its harsh climate has been inhabited by nomadic tribes like the ___________ and the _______.
2. The ________ in the Sahara and the ______ Valley in Egypt supports settled population.
3. The minerals of importance found In the Sahara include iron, phosphorus, manganese and __________.
4. Ladakh is a _________ desert lying in the Great Himalayas. In winter the climate is so harsh that people keep themselves engaged in festivities and ________.
5. The people of Ladakh have over the centuries learned to live in balance and harmony with
___________.
Answer:
1. The Sahara desert despite its harsh climate has been inhabited by nomadic tribes like the Bedouins and the Tuaregs.
2. The oasis in the Sahara and the Nile Valley in Egypt supports settled population.
3. The minerals of importance found In the Sahara include iron, phosphorus, manganese and uranium.
4.Ladakh is a cold desert lying in the Great Himalayas. In winter the climate in Ladakh is so harsh that people keep themselves engaged in festivities and ceremonies.
5. The people of Ladakh have over the centuries learned to live in balance and harmony with nature .
C. Match the words in column A with those in column B
| A | B |
| Lungalacha La | Ladakh |
| Kharpa-chan | Sahara desert |
| Gangri | shahtoosh |
| scorpions | Manali- Leh highway |
| Chiru or Tibetan antelope | glacier |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Lungalacha La | Manali- Leh highway |
| Kharpa-chan | Ladakh |
| Gangri | glacier |
| scorpions | Sahara desert |
| Chiru or Tibetan antelope | shahtoosh |
D. State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE:
1. The finest cricket bats are made from oak wood.
2. Due to aridity in Ladakh, the vegetation is sparse. There are scanty patches of grasses and shrubs for animals to graze.
3. The climate of Sahara is scorching hot and parch dry. It has a short rainy season.
4. There is little rainfall in Ladakh as it lies in the rainshadow of the Karakoram.
5. Drass, in Ladakh, is one of the coldest inhabited places on earth.
Answer:
1. False – The finest cricket bats are made from the wood of willow trees.
2. True
3. True
4. False – There is little rainfall in Ladakh as it lies in the rainshadow of the Himalayas.
5. True
E. Very Short Answer type Questions:
1. What do you mean by desert?
Answer:
Desert is an arid region marked by extremely high or low temperatures and has scarce vegetation due to very low rainfall.
2. Name the countries which are touched by the Sahara Desert?.
Answer:
The Sahara Desert touches eleven countries, namely Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
3. Which are the most well-known monasteries of Ladakh?
Answer:
The major and famous monasteries of Ladakh are Hemis, Thiksey, Lamayuru, and Shey.

4. Name the capital of Ladakh.
Answer:
The capital of Ladakh is Leh.
5. What is replacing camels in the salt trade?
Answer:
Trucks are replacing camels in the salt trade.
6. What lies in the north of Ladakh?
Answer:
The Karakoram range lies in the north of Ladakh.
7. Which trees bloom in summer in Ladakh?
Answer:
In summer apple, apricot and walnut trees bloom in Ladakh.
8. What are the hair of sheep and goats used for by the Ladakhis?
Answer:
The Ladakhis use the hair of sheep and goats to make woollens.
9. Which animals are reared by the Bedouins and Tuaregs.
Answer:
Goats, sheep, camels and horses are reared by the Bedouins and Tuaregs.
10. Which are the four passes that Manali – Leh highway crosses?
Answer:
The Manali- Leh highway crosses four passes: Rohtang la, Baralacha la, Lungalacha la and Tanglang la.
11. Why is the Chiru or Tibetan antelope hunted?
Answer:
People hunt the Chiru or Tibetan antelope for its wool known as Shahtoosh.
12. What is the meaning of the word Ladakh?
Answer:
‘Ladakh’ is made up of two words -”la’ meaning ‘mountain pass’ and “Dak” meaning country.
13. How much rainfall does Ladakh get?
Answer:
Ladakh gets little rainfall, as low as 10 cm every year because it lies in the rainshadow area of the Himalayas.
14. Name two fruits which grow in the Sahara Desert.
Answer:
Dates and cactus fruit grow in the Sahara Desert.
15. What is the area of the Sahara desert?
Answer:
The Sahara desert covers an area of around 8.54 million sq. km.
F. Short Answer Type Questions:
1. How do people live in the arid deserts?
Answer:
People find places where little water is available for agriculture in the desert and live there, for example in oases in the Sahara, or near streams which are formed from melting snow in the cold desert of Ladakh.
2. What is an oasis? Name a large oasis.
Answer:
An oasis is formed in the desert when the wind blows away the sands and depressions are formed where underground water reaches the surface. These areas are fertile and people settle down around these waterbodies. They grow date palms and other crops. Some oases are abnormally large. Tafilalet Oasis in Morocco is a large oasis covering an area of about 13000 sq.km.

3. Describe the Climate of the Sahara Desert.
Answer:
The climate of the Sahara Desert is scorching hot and parch dry. The rainy season is very short lived. The sky is cloudless and clear. Days are unbearably hot. The temperatures during the day may rise as high as 50°C. The nights may be freezing cold with temperatures nearing zero degrees.
4. Why do the nomadic tribes of Sahara Desert rear livestock?
Answer:
The nomadic tribes of the Sahara Desert rear livestock such as sheep, goats, camels, and horses which are very useful. These animals provide them with milk and meat. The leather from animal hides is fashioned into objects of practical use like belts, slippers, water bottles. The animal hair is also used for making mats, carpets, clothes and blankets. Camels also provide a safe and sure means of transport in the sandy desert.
5. What do cave paintings found in the Sahara Desert tell us about the region?
Answer:
Cave paintings found in the Sahara Desert depict that Sahara once used to be a lush green plain. There were flowing rivers with crocodiles. A variety of animals were found such as elephants, lions, giraffes, ostriches, sheep, cattle and goats. Due to the change in climate, it has transformed into a very hot and dry region.
6. Describe the flora and fauna found in the Sahara Desert.
Answer:
The Sahara Desert has vegetation such as cactus, date palms and acacia. In some places there are oases which are like green islands with date palms. Since water is available in oases and in the Nile valley, crops such as rice, wheat, barley and beans are also grown. Long-stapled cotton grown in Egypt is known all over the world.
The animals found in the Sahara Desert are camels, hyenas, jackals, foxes, scorpions, several varieties of snakes and lizards.
7. Describe the location and physical features of Ladakh.
Answer:
Ladakh is a cold desert lying in the Great Himalayas on the eastern side of Jammu and Kashmir. It is enclosed by the Karakoram Range in the north, and the Zanskar mountains in the south. Many rivers flow through Ladakh and Indus is the most important amongst them. The rivers form deep valleys and gorges. Several glaciers are found in Ladakh like the Gangri and Siachen glaciers. The altitude in Ladakh varies from 3000m in Kargil to 8000m in the Karakoram
8. What are the summer and winter activities of the people of the Ladakh desert?
Answer:
In the summer season the people of the Ladakh desert are busy cultivating barley, potatoes, peas, beans and turnip. During winters due to the freezing temperatures no outdoor work is possible, so they keep themselves engaged in festivities and ceremonies. The hardworking women manage the house and fields with great skill. They also manage small businesses and shops. One of the important occupations is weaving. Pashmina shawls are woven from the wool of the chiru antelope. Carpets and rugs from the sheep.
9. Describe the climatic conditions of the Ladakh desert.
Answer:
Ladakh is a cold desert that lies in the Great Himalayas. The altitude of Ladakh varies from 3000m to 8000m, because of which the climate is very cold and dry. The air at this altitude is so thin that the heat of the sun can be felt very intensely. The temperature in winter is less than –40°C, and the day temperature in summer is just above zero degrees with night temperatures dropping well below – 300C. As it lies in the rain shadow of the Himalayas, there is very little rainfall, not more than 10cm every year. Ladakh experiences freezing winds and burning hot sunlight.

G. Long answer Type Questions
1. Describe in brief the flora and fauna of Ladakh.
Answer:
Flora:
Vegetation is sparse in the Ladakh desert due to high aridity. There are scanty patches of grasses and shrubs for animals to graze. Groves of willows and poplars are seen in the valleys. During the summers, fruit trees such as apples, apricots and walnuts bloom.
Fauna:
Many bird species are sighted in Ladakh. Common birds like Tibetan snow cock, robins, raven, redstarts and hoopoe are found here. Some of them are migratory birds. The animals which are found in Ladakh are wild goats, wild sheep, yak and special kinds of dogs. Some Bactrian camels are also found in Ladakh. Animals are reared for their milk, meat and hides.
2. What do you know about the people who inhabit the Sahara Desert? Also write about their activities.
Answer:
In spite of the scorching heat and inhospitable climate of the Sahara Desert, tribes of people like the Bedouins and Tuaregs live here.
They are nomadic tribes who pursue different activities. They rear animals such as goats, sheep, camels and horses to obtain milk, meat and hides. They prepare leather from hides. This leather is used in making belts, slippers, water bottles. They use the hair of these animals in making mats, carpets, clothes and blankets. The people of the Sahara Desert wear heavy robes to protect themselves from the dust storms and hot winds.
The oases in the Sahara Desert and the Nile valley in Egypt have a settled population. Since water is available, people grow date palms. They also grow rice, wheat, barley and beans. The Nile valley is famous for cultivation of fine long-stapled Egyptian cotton.
The discovery of oil in Algeria, Libya and Egypt has led to a transformation in the activities of the people. More and more nomadic herdsmen are taking to city life as they find jobs in the oil and gas operations. Trucks are replacing camels in the salt trade. Tuareg tribesmen are taking up jobs as guides to foreign tourists.
The Sahara is undergoing change with fast speed. Tuaregs, the nomadic tribe, are now acting as guides to foreign tourists. More and more nomadic herdsmen are migrating to cities in search of jobs in oil and gas operations.
3. What are the differences between the deserts of Sahara and Ladakh?
Answer:
| Sahara | Ladakh |
| The Sahara is a hot desert. | Ladakh is a cold desert. |
| It is located in North Africa. | It is located in the northern Himalayas in India. |
| The climate is extremely hot and parched dry. | The climate is extremely cold and dry. |
| It attracts fewer tourists | It attracts tourists because of the beauty of the meadows and glaciers, and its festivities and different ceremonies. |
| It is inhabited by nomadic tribes mainly. In the oases and the Nile valley there are settlers. | The people are either Muslims or Buddhists. |
| Few plants grow such as cactus, date, palm and acacia | Fruits trees such as apples, apricots bloom in the summer. Trees such as poplar, willows, etc. also grow in the valleys. |
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 7 “Life in the Deserts”
Our team of competent subject experts educated both in India and overseas have crafted these accurate solutions taking into account every detail and presenting them in the most easy-to-understand way possible. Every single aspect of the lesson has been explained in a clear and lucid manner. We recommend that you go through them in detail because they will help to clear your concepts.
Feel free to download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime! There’s plenty more helpful study material and other resources on the way – so keep visiting our website and join our email list to get free access to them!
The topics discussed in this chapter are as follows:
(i) The Hot Sahara Desert
– Climate
-Flora and Fauna
-People
(ii) The Cold Desert – Ladakh
– Location andClimate
– Flora and Fauna
– People
What are the two characteristic features of a desert?
How many countries are touched by the Sahara Desert? Name them.
Describe the Climate of the Sahara Desert.
Mention the summer and winter activities of the people of the Ladakh desert.
Describe the people of the Sahara Desert. Also write about their activities.
Describe the flora and fauna found in the Ladakh desert.
How are things changing in the Sahara Desert?
Why is Ladakh a popular tourist destination?
Yes, certainly. Our team of competent subject teachers have thoughtfully anticipated all the queries you may have about the lesson and crafted these excellent solutions which draw your attention to every detail in the lesson and also explain the essence of the chapter.
We suggest that at first you read the lesson closely and then read the solutions taking in all the details.
Our seasoned subject experts have painstakingly provided many extra questions which are similar to exam questions and are designed to give you sufficient practice.
Go through the solutions before the exam and practice writing out some answers within a specified time period. This is an important step which should not be skipped because practice not only makes perfect, but also boosts your self-confidence. You will be well-equipped to take on any challenge that your examiner may pose! Good luck!
Need us to coach you and prepare you for your exams? Our expert teachers look forward to teaching bright young students like you and will go the extra mile to help you succeed. Feel free to contact us with your requirements anytime and we’ll be happy to help you out! We provide on-demand one-to-one coaching, based on your convenience and your needs – have it completely your way! Book your appointment now!


