We have prepared top-quality solutions to NCERT Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures for you, along with additional questions keeping in mind students’ and NCERT’s requirements. The additional questions include very short answer type, short-answer type, long-answer type, fill in the blanks and match and pair type questions and provide a wealth of practice.
Solutions to ‘Let us enhance our learning’ (Page No 227) of NCERT Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
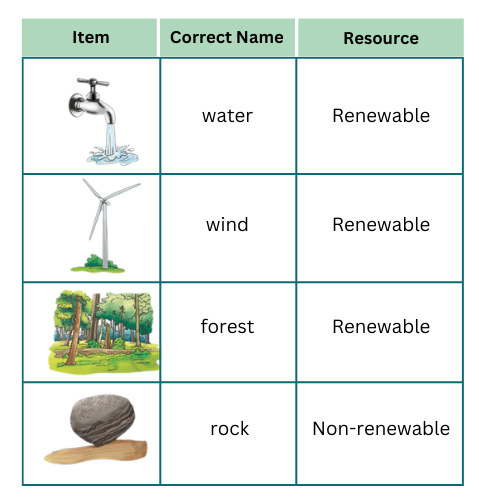
1. Fig. 11.9 shows items related to natural resources. Match them with their jumbled up names. Make another table and write the names of these resources. Classify these resources as renewable or non-renewable.
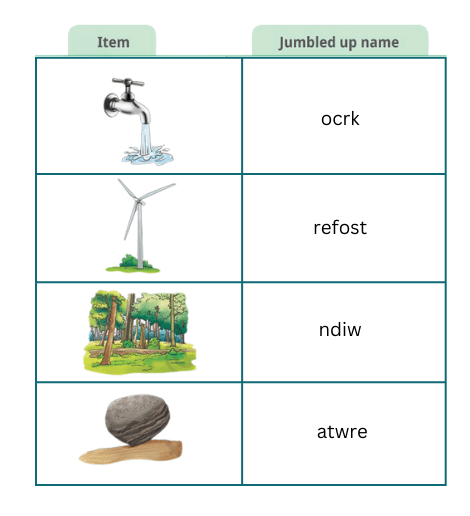
Solution:
2. State whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F]. If False, correct them.
(i) Nature has all the resources to meet human needs. [ ]
(ii) Machines are a resource found in nature. [ ]
(iii) Natural gas is a non-renewable resource. [ ]
(iv) Air is a renewable resource. [ ]
Solution:
(i) Nature has all the resources to meet human needs. [ ]
True [T].
(ii) Machines are a resource found in nature. [ ]
False [F]. Machines are man-made resources.
(iii) Natural gas is a non-renewable resource. [ ]
True [T].
(iv) Air is a renewable resource. [ ]
True [T].
3. Fill in the blanks using the most appropriate option—
(i) A fuel that is commonly used in two wheelers like scooters or bikes is………
(a) Kerosene
(b) Petrol
(c) Diesel
(d) LPG
Solution:
(b) Petrol
(ii) An example of a renewable resource is ………………
(a) Coal
(b) Water
(c) Natural gas
(d) Petrol
Solution:
(b) Water
4. Classify the following as renewable or non-renewable resources—coal, natural gas, forests and minerals.
Solution:
Coal – Non-renewable
Natural gas – Non-renewable
Forests – Renewable
Minerals – Non-renewable
5. Why do we say that petroleum is a non-renewable resource?
Solution:
Fossil fuels like petroleum are formed from the remains of microorganisms and plants that got buried deep inside the earth under intense pressure for millions of years. Since it takes a very long time for petroleum to form, it is not replenishable. Hence, it is a non-renewable resource.
6. It is difficult to regrow forests. Justify this statement.
Solution:
It is difficult to regrow forests because seeds take a long time to grow into trees. Due to absence of trees, soil erosion occurs and the soil loses its nutrients, making it difficult for new trees to grow. The microorganisms in the soil which are essential in the growth of trees also get destroyed, further hindering the growth of trees. It is also difficult to stop the construction of roads, buildings and highways, due to which forests in many places are cleared.
7. Make a list of five daily activities in which you use natural resources. Suggest ways by which you can reduce their use.
Solution:
Daily Activities and Ways to Reduce Natural Resource Use
(i) Water Usage:
Natural Resource Used: Water
Activities: Water is used for drinking, bathing, cooking, watering plants etc.
Ways to Reduce Use:
- Reduce the number and duration of showers.
- Call the plumber to fix leaky taps and pipes.
- Practice rain water harvesting.
(ii) Electricity Usage:
Natural Resource Used: Coal, natural gas
Activities: Lighting, heating/cooling, using appliances such as TV, AC etc.
Ways to Reduce Use:
- Turn off the lights before leaving the house. Encourage community members to do the same.
- Use energy-efficient LED bulbs and appliances.
(iii) Fuel Usage:
Natural Resource Used: Petroleum, diesel
Activities: Driving a car, cooking.
Ways to Reduce Use:
- Use public transportation or bicycles.
- Use electric cars.
- Use solar powered cookers for cooking.
(iv) Paper Usage:
Natural Resource Used: Trees
Activities: Writing, packaging
Ways to Reduce Use:
- Use paper judiciously.
- Use digital alternatives for note-taking
- Recycle paper and encourage the community to do the same.
- Use reusable bags made of material such as jute instead of paper bags.
(v) Plastic Usage:
Natural Resource Used: Petroleum
Activities: For carrying food and other materials.
Ways to Reduce Use:
- Use reusable cloth bags.
- Recycle plastic.
8. List four activities that are possible due to the presence of air.
Solution:
Four activities that are possible due to the presence of air are:
- Breathing
- Operating wind mills
- Using fans for cooling
- Inflating a balloon
9. How can you contribute towards enhancing the green cover of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken.
Solution:
You can contribute towards enhancing the green cover of your locality in the following ways:
Planting Trees: You should seek permission from the local municipality for planting trees in open spaces and if possible, even in urbanised areas.
Raising Awareness: You should encourage your community to plant trees by participating in awareness campaigns. You can even request the media to cover and broadcast your work.
Maintaining Existing Green Spaces: Participate in or organize clean-up and maintenance activities for local parks and gardens.
Reducing Waste and Recycle Paper and Plastic: Using resources such as paper judiciously and recycling paper and plastic will go a long way in preserving trees.
Advocate for Green Policies: Lobbying the government to introduce green policies will go a long way in protecting trees.
10. In the given illustration, we see that food is being cooked.

Answer the following questions—
(i) What type of energy is being used for cooking?
(ii) Name one benefit and one drawback of using this type of energy for cooking.
Solution:
(i) Solar energy is being used for cooking in the illustration.
(ii) Benefit: Using a renewable energy source like solar energy for cooking conserves fossil fuels and reduces pollution.
Drawback: The initial cost of purchasing and setting up solar cooking equipment can be relatively high.
11. Cutting down trees on a large scale impacts the quality of the soil. Why do you think it is so?
Solution:
Cutting down trees on a large scale impacts the quality of the soil because without roots of trees to bind the soil, soil erosion happens. Along with soil erosion, nutrients present in the soil are also lost. Dead and decaying organic matter such as leaves and dead animals decompose and release vital nutrients and minerals into the soil. Hence, due to the absence of trees the nutrients in the soil are not replenished.
12. Explain two ways in which human activities pollute the air. Propose one action which can help in reducing air pollution.
Solution:
Two ways in which human activities pollute the air are:
(i) Industrial Emissions: Emissions from large scale industries are a major cause of air pollution.
(ii) Vehicular Emissions: Pollution from the large number of vehicles nowadays pollute the air.
To reduce air pollution, clean energy sources such as solar power, wind power, should be used.
13. A family uses solar panels to generate electricity, a gas stove to cook food and a windmill for pumping water from a well. What would happen if there were no sunlight for a week?
Solution:
If there is no sunlight for a week, the family’s solar panels would not work and electricity would not be generated. Their cooking would not be affected since the gas stove does not depend on solar energy. Their water supply would also not be affected as long as there is sufficient wind for the windmill to operate.
14. Fill up the blanks using the following terms—
(fossil fuels, forest, air, petroleum, coal, water and non renewable resource)
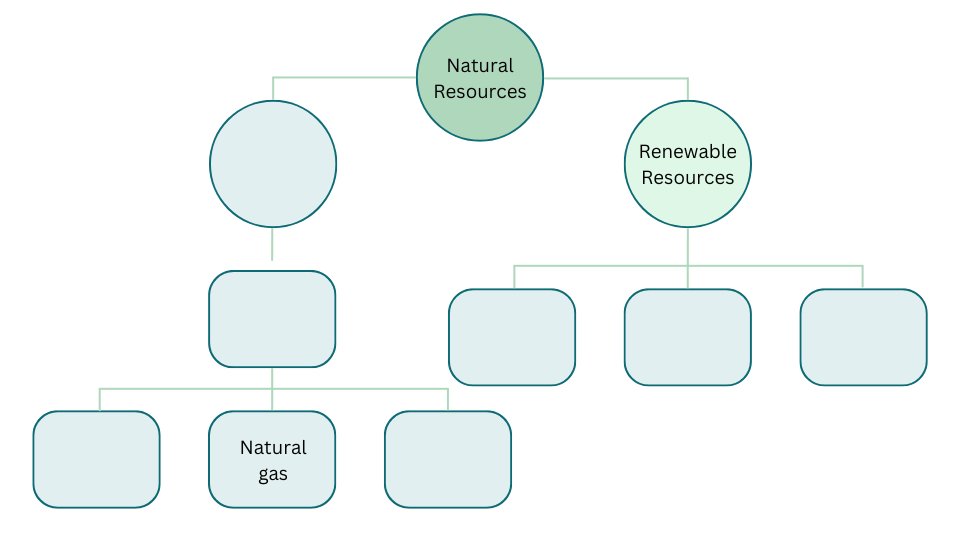
Solution:
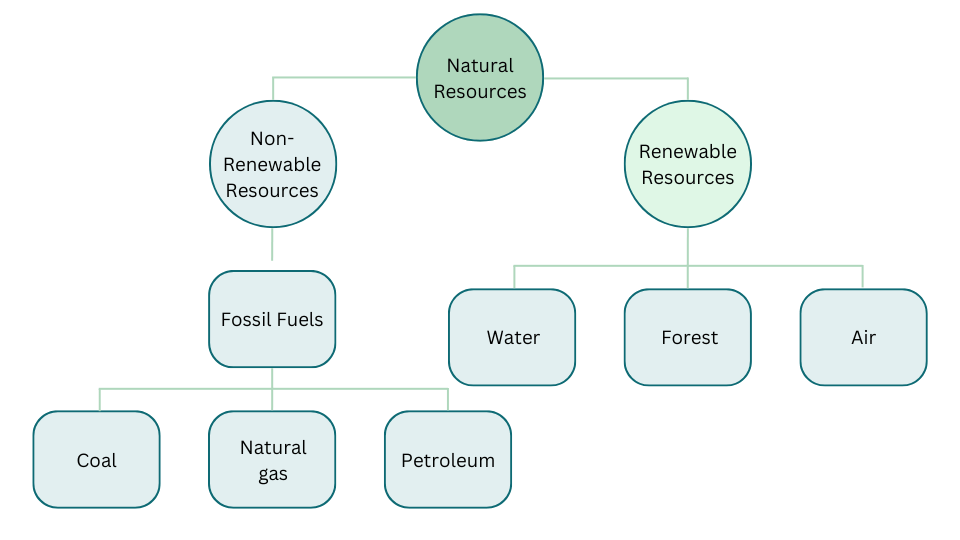
15. There is an increasing demand of trees to meet the requirements of industries and for housing. Therefore, trees are being felled. Is it justified? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Solution:
The felling of trees is not justified because of the following reasons:
(i) Loss of Biodiversity and Disruption of Food Chain: Large-scale cutting down of forests leads to loss of habitat for many species. These species move elsewhere in search food, thereby disrupting the existing food chain in that region. Due to these reasons, many species can also become extinct.
(ii) Climate Change and Pollution: Trees absorb excess carbon dioxide and other harmful gases from the atmosphere and give out oxygen, which we breathe. Large-scale tree felling increases the amounts of harmful gases in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming, climate change and increases pollution levels.
(iii) Soil Erosion: The roots of trees bind the soil together and prevent it from eroding away. If they are cut down, soil erosion will occur and the top layer of soil will lose its fertility.
(iv) Flash floods: Forests facilitate water infiltration into the soil, replenishing groundwater. Due to soil erosion, the soil loses its water holding capacity. This results in water suddenly flowing over the land surface during heavy rainfall, causing flash floods.
(v) Water Cycle Disruption: Forests bring about rainfall through transpiration and also play a critical role in maintaining groundwater levels. Therefore, the absence of forests will disrupt the water cycle.
(vi) Disruption of Livelihoods: Many indigenous and local communities depend on forests for their livelihoods. Deforestation can displace these communities and destroy their cultural heritage.
For building of industries and housing, the following practices should be followed:
(i) Using previously developed land that is not in use.
(ii) Repurposing existing buildings.
(iii) Considering vertical expansion instead of spreading outwards, especially in heavily forested areas.
Therefore, we can see that efficient urban planning strategies are required to preserve the green wealth of our nation.
16. Propose a plan to use less water in your school. What steps would you take to make this plan happen and how would it help the environment?
Solution:
Plan for Using Less Water in School:
- Install water-saving equipment such as low-flow taps and dual-flush toilets.
- Install rainwater harvesting units at strategic locations such as on the school terrace.
- Detect and fix leaks to prevent water draining out from defective and broken equipment.
- Use water-efficient cleaning practices and equipment.
- Decorate your school with plants that require less water to thrive.
Implementation of the Plan:
- Form a team to assess the usage of water throughout the school such as bathrooms, kitchens etc.
- Appeal to the school administration to install the aforementioned water-saving equipment.
- Encourage students, teachers and staff to immediately detect and report leaky equipment. Have the contact number of a local plumber handy, in case of emergencies.
- Encourage cleaning staff to minimize the usage of water while cleaning and use equipment such as mops, which require minimal water.
- Identify plants with low water requirements and seek permission from the school administration to grow these instead.
- Form a student group to monitor and enforce the implementation of the plan.
Benefits for the Environment:
- Reduces the dependence on the municipal/panchayat water supply system.
- Reduces the energy required to pump, treat and heat water, thereby helping the environment by reducing emissions.
- The water that is saved can be used for other purposes.
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
1. (Page 215) According to you, whose statement is correct and why?
Solution:
The final statement is correct because the cow gets its energy indirectly from the Sun. Grass uses sunlight to perform photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight into chemical energy which is stored in the form of starch. When the cow eats the grass, it consumes this stored chemical energy. Hence, the ultimate source of energy is the Sun.
2. (Page 216) What will happen if the Sun is not visible for a few days?
1. We may have to depend on artificial lighting during day time also.
2. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
3. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Solution:
1. We may have to depend on artificial lighting during day time also.
2. The temperature will drop, as there is no Sun to heat up the Earth.
3. Plants will not be able to produce food and the leaves will wilt.
3. (Page 217) What are the consequences of cutting a large forest area? Make a presentation or do a role play, or write a story or a poem that shows what could happen if we continue to cut down trees in our forests.
Solution:
“Once Upon A time in North America”
Once upon a time in North America, the native people of the land were in love with the serene beauty of their forests. They depended on it for their food, both for themselves and their cattle. They could not even imagine hurting the forest and refused to pluck fruits from trees, only helping themselves to the tasty treats they found on the forest floor. Their children frolicked amidst the woods, playing games such as “Hide and Seek” and singing soulful songs. They helped the adults in planting new trees and were in love with the forest as much as the adults were. Really, the native Americans were deeply in love with the green wealth they were blessed with.
Then one day, they came. Despite the protests of the elders and the whispers of the forest, which seemed to grow more urgent and sorrowful, the outsiders began their work. Trees, that had stood for centuries like fortresses of goodness, were felled, and the forest that once teemed with life started to disappear. Huge patches of land became barren. The water in the rivers and streams became muddy and eventually dried up. The native Americans lost their food and their only source of livelihood to the outsiders. They mourned the loss of their forests and vowed to bring them back.
One day, the outsiders left as suddenly as they had appeared. The native Americans toiled, day in and day out. They planted seeds and watered them. They planted medicinal herbs known only to them, much like their ancestors have done throughout the ages. They prayed and performed rituals for the well-being of the forest. Years passed, and slowly but surely, the forest began to recover. The new trees grew tall and strong, the streams cleared, and the animals began to return. The lush greenery which had sustained them for centuries came back. The native Americans celebrated and called it, “The Old Faithful”. And the children played in the forest and sang songs once again.
Moral of the Story: Protect your forests. They will bring you happiness and wealth, in more ways than one.
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 11 Nature’s treasures
Very Short Answer Type:
1. How is air essential for our survival?
Answer:
The air living beings breathe contains oxygen which is essential for the body to perform its functions.
2. Can you name some gases which are present in the air?
Answer:
Some gases which are present in air are nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide and other gases in small quantities.
3. Which gas is present in air in the largest quantity?
Answer:
Nitrogen (78 %)
4. What is the percentage of oxygen present in air?
Answer:
The percentage of oxygen present in air in 21 %.
5. Name one way in which carbon dioxide in air is used beneficially by nature.
Answer:
Plants use carbon dioxide during photosynthesis to give out oxygen, which we breathe.
6. What is the ultimate source of all energy on Earth?
Answer:
The Sun is the ultimate source of all energy on Earth.
7. When is World Water Day observed?
Answer:
World Water Day is observed on 22nd March every year.
8. Why are soil samples collected from different places of different colours?
Answer:
Soil samples from different places are made of different materials, hence they are of different colours.
9. Name two instruments that were made of rocks since ancient times.
Answer:
Hand axes and arrowheads.
10. What are rocks made up of?
Answer:
Rocks are made up of minerals.
11. Name some important metals which are extracted from minerals.
Answer:
Aluminium, gold, copper and iron.
12. Name some minerals that are used to make mobile phones.
Answer:
Some minerals that are used to make mobile phones are gold, silver, copper, cobalt.
13. Why are rocks a non-renewable resource?
Answer:
It takes thousands to millions of years to form rocks and hence they cannot be replenished easily. Hence, rocks are a precious non-renewable resource.
14. Name a precious metal that is also a mineral.
Answer:
Gold is a precious metal that is also a mineral.
15. Name two types of fuels used in vehicles.
Answer:
Petrol and diesel are two types of fuels used in vehicles.
16. Burning of which fossil fuel releases the least amounts of pollutants?
Answer:
Natural gas.
17. Give one way in which seed dispersal takes place.
Answer:
Animals and birds eat fruits and release droppings containing seeds in many places. This is one way in which seed dispersal takes place.
18. Give examples of renewable natural resources.
Answer:
Air, water and forest are some of the examples of renewable natural resources.
19. Give examples of non-renewable natural resources.
Answer:
Examples of non-renewable natural resources are minerals, soil, rocks, coal, petroleum and natural gas.
20. You are given a choice between coal, wood, dung cakes, natural gas, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) to be used as fuel for domestic fuel. Which of these would you choose and why?
Answer:
Natural gas and Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) should be chosen because they are cleaner fuels (much less polluting).
Short Answer Type:
1. Name three functions of windmills.
Answer:
Windmills can be used to run flour mills, to pull up water from a well and to generate electricity.
2. Name three leading wind farms in our country.
Answer:
Muppandal Wind Farm in Tamil Nadu, Jaisalmer Wind Park in Rajasthan and Brahmanvel Wind Farm in Maharashtra are some of the leading windmill farms in our country.
3. Name some uses of water in daily life.
Answer:
We need water for many daily activities such as drinking, cooking, bathing, washing, cleaning and gardening. It is also used in agriculture for growing crops and for industrial purposes.
4. Why is freshwater scarce?
Answer:
Most of the water on Earth is found in oceans and seas. However, this water is saline or salty. This saline water is not fit for domestic, agricultural and industrial use. Freshwater present in ice sheets and snow, or underground water is difficult to access. Hence, we have to rely on freshwater from ponds, rivers, lakes and wells. However, a very small fraction of the freshwater present in ponds, rivers, lakes and wells is easily accessible. Due to these reasons, freshwater is scarce and precious.
5. Name two ways in which water is wasted in daily activities.
Answer:
Two ways in which water is wasted in daily activities are:
(i) Leaving the taps around the house open.
(ii) Excess use of water during watering of plants in the garden.
6. How do we extract groundwater?
Answer:
We extract groundwater by the following ways:
(i) Ground water is the source of many lakes. Therefore, we can get the water from there.
(ii) Groundwater is also drawn by a handpump or a tubewell.
7. Describe the water harvesting system of stepwells.
Answer:
Stepwells store not only rainwater but also water seeping from nearby lakes, ponds and rivers. The walls of the trenches (long deep holes dug in the ground) are lined with blocks of stones that allow seepage of water from outside sources into the wells.
8. When is Van Mahotsav held? What is the aim of Van Mahotsav?
Answer:
Van Mahotsav is a week-long event celebrated across the country during the month of July. The aim of Van Mahotsav is to increase the green cover by planting trees and raise awareness about respecting and preserving forests.
9. How do trees in forests obtain nutrients in order to grow?
Answer:
The leaves that fall from the trees and dead animals and microorganisms decay and enrich the soil with nutrients. This soil is used by new plants and trees to grow.
10. How do earthworms indirectly help the growth of plants?
Answer:
Earthworms are natural agents that help in turning and loosening the soil. This helps air to enter the soil, so that the roots of plants can breathe. It also provides space for the roots to grow easily. In this way earthworms indirectly help the growth of plants.
11. Is soil a renewable or non-renewable resource? Explain.
Answer:
Soil is formed by the disintegration of rocks by actions of the Sun, water and living organisms over a period of thousands of years. Since it takes such a long time to produce soil, it cannot be replenished easily. Hence, soil is a precious non-renewable resource.
12. Name some uses of minerals.
Answer:
Important metals, such as aluminium, gold, copper and iron are extracted from minerals. Minerals are used in the manufacturing of airplanes, cars, jewellery, cosmetics, and electrical and electronic equipment.
13. What are fossil fuels? Are they renewable or non-renewable?
Answer:
Petroleum along with natural gas and coal are commonly called fossil fuels. They are formed from the remains of microorganisms and plants that got buried deep inside the earth, and were converted to petroleum, natural gas and coal under intense heat and pressure. It takes millions of years for these fuels to form and hence they are non-renewable.
14. Which are the major coal producing states in the country?
Answer:
The major coal producing states in the country are Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Telangana.
15. Give two reasons as to why the use of fossil fuels should be limited.
Answer:
Fossil fuels are present in limited quantities and are non-renewable, hence we must preserve them. Also, when fossil fuels are burnt, smoke and carbon dioxide gas are produced which causes large scale air pollution. For these reasons, we should limit the use of fossil fuels.
Long Answer Type:
1. Identify human activities that lead to water pollution.
Answer:
The human activities that lead to water pollution are:
(i) Improper disposal of household waste and sewage.
(ii) Dumping industrial waste into rivers, lakes, and oceans pollute the water bodies.
(iii) Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture can contaminate water.
(iv) Deforestation leads to soil erosion, which in turn causes sediments to accumulate in water bodies.
(v) Oil spills from ships pollute the seas and oceans.
2. How can water pollution be reduced?
Answer:
Water pollution can be reduced in the following ways:
(i) Domestic and industrial waste should be treated before being discharged into water bodies.
(ii) Biodegradable detergents, soaps, etc should be used to minimize the release of harmful chemicals into the water system.
(iii) Reforestation, afforestation and soil conservation efforts would minimize soil erosion and hence sedimentation in the water bodies.
(iv) Sewage containing human waste should be properly treated before being released into the environment.
(v) Organic farming practices should be taken up, which would reduce the need for harmful fertilizers and pesticides, thereby reducing water pollution.
(vi) Public awareness campaigns should be conducted to educate people about the scarcity of freshwater and the importance of its conservation.
3. In what ways can you conserve water?
Answer:
You can conserve water in the following ways:
(i) Practicing rainwater harvesting in your home. Installation of rooftops tanks, stepwells etc would go a long way in storing rainwater for later use.
(ii) Reducing domestic wastage of water by fixing leaks from faucets, using water-efficient appliances like dishwashers, washing machines, and low-flow showerheads.
(iii) Practising water-efficient irrigation systems such as drip irrigation.
(iv) Reusing greywater (water from sinks, showers, and washing machines) for gardening or flushing toilets.
4. What are some of the activities for which we need heat and light of the Sun?
Answer:
(i) Plants use sunlight to make food using photosynthesis.
(ii) Sunlight helps in drying clothes quickly and naturally.
(iii) Sunlight is essential for growth of crops in agriculture.
(iv) Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of energy. Sunlight is harnessed to generate solar power.
(v) Sunlight warms up the planet, which is essential for supporting life.
(vi) Sunlight provides us with natural light, which is essential for supporting life.
(vii) Exposure to sunlight helps our bodies produce Vitamin D, which is essential for bone health.
Fill in the Blanks:
electricity, coal, slate, petroleum, deforestation, laterite, wind
(a) When air moves, it is called _________.
(b) Solar panels are used to generate _________.
(c) Over the years, the forest cover has been decreasing, mainly due to human activities like _________.
(d) _________ is a type of rock that is used for building roofs.
(e) _________ is a type of rock that is used for making bricks.
(f) Petrol, diesel and kerosene are obtained from _________.
(g) ________ is mainly used for the production of electricity.
Answers:
(a) When air moves, it is called wind.
(b) Solar panels are used to generate electricity.
(c) Over the years, the forest cover has been decreasing, mainly due to human activities like deforestation.
(d) Slate is a type of rock that is used for building roofs.
(e) Laterite is a type of rock that is used for making bricks.
(f) Petrol, diesel and kerosene are obtained from petroleum.
(g) Coal is mainly used for the production of electricity.
Match and Pair:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Windmill | (a) Uttarakhand |
| (ii) Chipko movement | (b) Minerals |
| (iii) Rocks | (c) Fuel |
| (iv) CNG | (d) Stepwell |
| (v) Bawadi | (e) Electricity |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Windmill | (e) Electricity |
| (ii) Chipko movement | (a) Uttarakhand |
| (iii) Rocks | (b) Minerals |
| (iv) CNG | (c) Fuel |
| (v) Bawadi | (d) Stepwell |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
Our experts have covered the chapter comprehensively through the ‘Let us enhance your learning’ solutions and extra material. These will give you a clear understanding of the chapter and the associated concepts.
Feel free to download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime! We are preparing lots more helpful materials, so keep visiting our website and join our email list to get early access to all the latest goodies!
The following topics are covered:
11.1 Air
11.2 Water
11.3 Energy from the Sun
11.4 Forests
11.5 Soil, Rocks and Minerals
11.6 Fossil Fuels
11.7 Natural Resources: Renewable and Non-renewable
11.8 Resources We use
Of course! We have provided a free PDF of NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures for you to download! The PDF contains the entire material we have prepared for you, including the extra question set! Please look towards the top of the page!
Understand natural and human-made resources. Understand which of these are renewable and which are non-renewable. It is important that you study this chapter in detail, as you see detailed questions from this chapter in your exams. Our extra question set covers all the details in the chapter, so study it thoroughly.
If you need top-quality coaching, our expert teacher-mentors are there for you anytime you need them! Feel free to reach out to us anytime and let us help you out!
Need us to teach you from scratch? Need us to guide you in the right way? Get in touch with us anytime. Our expert teachers will train you and guide you to achieve success in life! We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs- have it completely your way! Let us help you out – book an appointment now!


