Hello students! We have prepared excellent Solutions to NCERT Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World right here. All ‘Let us enhance our learning’ questions have been answered accurately along with a plethora of additional questions, keeping in mind students’ and NCERT’s requirements. We advise that you take your time to study all of them in detail and understand the material instead of just memorising.
Solutions to ‘Let us enhance our learning’ (Page No 31) of NCERT Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
1. Here are two types of seeds. What differences do you find among the roots and leaf venation of their plants?

Answer:
Differences in Roots:
(a) Wheat: Wheat seeds are monocot seeds. Therefore, the plants possess fibrous roots. The fibrous roots of this plant appear as a bunch of similar-sized thin roots spreading outwards from the base of the stem. No branching is observed.
(b) Kidney beans: Kidney beans are dicot seeds. Therefore, the plants possess taproots. The tap roots of this plant consist of one main root and small side roots arising from it, forming a branched structure.
Differences in Leaf Venation:
(a) Wheat: Wheat seeds are monocot seeds. Hence, the leaves of wheat plant have parallel venation. The veins run parallel to each other.
(b) Kidney beans: Kidney beans are dicot seeds. Hence, the leaves of the plants exhibit reticulate venation. The veins form a net-like pattern on both sides of the thick middle vein.
2. Names of some animals are given below. Group them based on their habitats. Write the names of aquatic animals in the area marked ‘A’ and terrestrial animals in the area marked ‘B’. Enter the names of animals living in both habitats in part ‘C’.
Horse, Dolphin, Frog, Sheep, Crocodile, Squirrel, Whale, Earthworm, Pigeon, Tortoise
Answer:
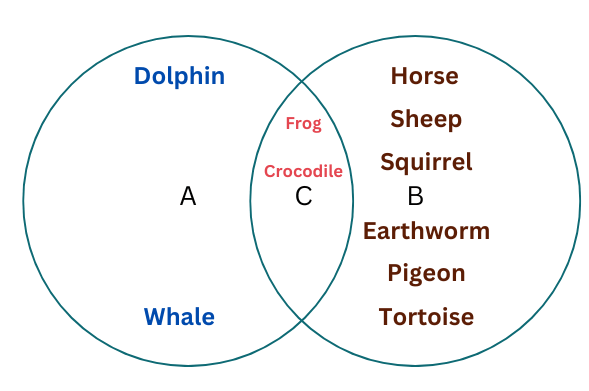
A – Aquatic Animals: Dolphin, whale
B – Terrestrial animals: Horse, sheep, squirrel, earthworm, pigeon, tortoise
C – Animals living in both habitats: Frog, crocodile
Note: A tortoise is a terrestrial animal. However, a turtle is an amphibian because it lives in both habitats, land and water.
3. Manu’s mother maintains a kitchen garden. One day, she was digging out radish from the soil. She told Manu that radish is a kind of root. Examine a radish and write what type of root it is. What type of venation would you observe in the leaves of radish plant?
Answer:
Examine each radish in the image below:

It is easy to see that each radish has a tap root system consisting of one main root and small side roots arising from it.
Examine the leaves of a red radish below:

It is easy to see that the leaves of the radish plant branch out on both sides of the thick middle vein forming a net-like pattern. Therefore, the leaves have reticulate venation.
4. Look at the image of a mountain goat and a goat found in the plains. Point out the similarities and differences between them. What are the reasons for these differences?

Answer:
Similarities:
- They belong to the same family.
- They have hooves and horns.
- Their bodies are covered with fur.
- The females of both give milk.
- They are both herbivores.
- They both live in herds.
Differences:
| Mountain goat | Goat found in the plains | |
| Habitat | Found in the mountains at high elevations. | Found in rolling landscapes, such as grasslands and agricultural areas. |
| Fur | The mountain goat has thicker fur which protects it from the harsh cold in the mountains. | In contrast, the shorter fur of the goat found in the plains helps it cope with the hotter climate in the plains. |
| Build | Tend to be stockier and more robust which helps to navigate the difficult terrain. | Have a leaner build compared to mountain goats. |
| Legs | Have muscular legs which helps in jumping and climbing up steep slopes. | Have thinner legs which help them move on flat ground. |
| Hooves | Their hooves are specialized for gripping which helps in climbing rocky mountain slopes. | They do not have specialized hooves because they move on flat, grassy surfaces. |
| Horns | Have shorter, straighter and pointier horns which enables them to fight off predators. | Their horns curve backward because they use speed to outrun their predators. |
5. Group the following animals into two groups based on any feature other than those discussed in the chapter— cow, cockroach, pigeon, bat, tortoise, whale, fish, grasshopper, lizard.
Answer:
We can classify the animals based on their mode of breathing.
Group 1: Animals that Breathe through Lungs
- Cow
- Pigeon
- Bat
- Tortoise
- Whale
- Lizard
Group 2: Animals that do Not Breathe through Lungs
- Cockroach
- Grasshopper
- Fish
We can also classify the animals based on whether they have a backbone or not.
Group 1: Animals that have a Backbone
- Cow
- Pigeon
- Bat
- Tortoise
- Whale
- Fish
- Lizard
Group 1: Animals that do not have a Backbone
- Cockroach
- Grasshopper
6. As the population grows and people want more comfortable lives, forests are being cut down to meet various needs. How can this affect our surroundings? How do you think we can address this challenge?
Answer:
Deforestation can affect our surroundings in the following ways:
Climate Change and Global Warming: Forests work to absorb excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. If forests are cut down, carbon dioxide will build up in the atmosphere and the planet will heat up causing global warming and climate change.
Loss of Biodiversity: Cutting of trees will result in plants, animals, insects and microorganisms losing their food and natural habitats. Gradually they will become extinct, leasing to a loss in biodiversity.
Disruption of Food Chain: As animals lose their natural habitats, they will migrate to other places in search of food and the food chain will get disrupted.
Soil Erosion: The roots of plants penetrate and anchor the soil. Without trees to bind the soil it will erode away.
Floods: Without adequate soil due to erosion, rain water cannot seep into the soil which causes floods. This also leads to depleted groundwater levels.
Water Cycle Disruption: Forests are critical in bringing about rainfall. Without forests there would be changes in weather patterns all over the planet.
Pollution: Forests absorb pollutants from the atmosphere and therefore deforestation would lead to increased pollution levels.
Impact on Indigenous Communities: Many indigenous communities rely on forests for their livelihoods, culture, and traditions. Deforestation can displace these communities and erode their way of life.
We can address the challenge of deforestation in the following ways:
Forest Conversation: Strict laws and regulations should be introduced to prevent illegal cutting of trees and illegal hunting activities. This would protect our existing forests from being depleted.
Building Nature Reserves and Wildlife Sanctuaries: This would allow diverse plant and animals a safe habitat in which they would thrive. These newly built forests would also contribute positively to our climate, control floods etc.
Reforestation and Afforestation: Reforestation restores existing forests in which the number of trees has been steadily decreasing. Afforestation means growing new forests by planting of trees. These combined efforts would play a huge role in preserving and expanding our forests.

Education and Awareness: We should educate the population at large about the dangers that come with forest depletion. Public service ads and mass media would be an excellent way to broadcast this news and encourage people to take action. Local communities should be engaged in the conservation efforts.
Preventing Climate Change: Forests are affected by changing climatic conditions. Therefore, we should work to reduce harmful gas emissions which cause climate change and use clean energy sources instead.
Reducing Consumption: Reducing the demand for products such as timber that drive deforestation would go a long way in protecting our forests.
If the above steps are followed then our forests will be preserved and the planet will be a healthier place to live in.
7. Analyse the flowchart. What can be examples of ‘A’ and ‘B’?
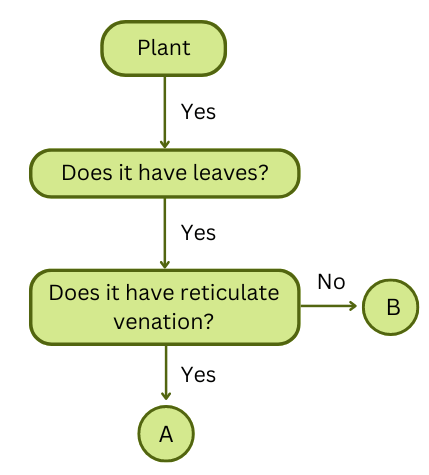
Answer:
Examples of A: The followingplants have reticulate venation: Hibiscus, chickpea, tulsi.
Examples of B: The following plants do not have reticulate venation (i.e. they have parallel venation): Banana, grass, lemongrass, wheat, maize.
8. Raj argues with his friend Sanjay that “Gudhal (hibiscus) plant is a shrub”. What questions can Sanjay ask for clarification?
Answer:
Sanjay can ask the following questions for clarification:
- What is the height of the Gudhal plant? Is it of medium height?
- What is the nature of the stem? Is it hard and thin? It is woody?
- What are the branches like? Do they originate from close to the ground?
- What is the colour of the stem? Is it brown in colour?
9. Based on the information in the table, find out examples of these plants for each group.
| Group | Type of seed | Type of root | Examples |
| A | Dicot | Tap roots | |
| B | Monocot | Fibrous roots |
(a) What other similarity do plants of group A have?
(b) What other similarity do plants of group B have?
Answer:
Group A Examples: Hibiscus, chickpea, tulsi.
Group B Examples: Banana, grass, lemongrass, wheat, maize.
(a) Plants of Group A are dicots and have leaves with reticulate venation.
(b) Plants of Group B are monocots and have leaves with parallel venation.
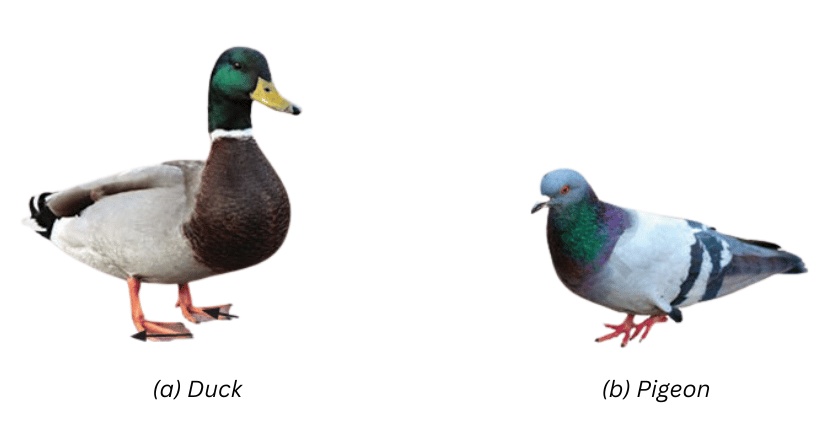
10. Observe the labelled part of a duck in the picture given below. What differences do you observe in the feet of the duck compared to the other birds? Which activity would the duck be able to perform using this part?
Answer:
First Part – Differences in the Feet:
The duck has webbed feet in which the toes are joined together. In contrast, the pigeon has feet with separate toes.
Second Part – Main Activity the Duck can Perform using Webbed Feet:
The webbed feet of the duck enable it to effortlessly glide through water while swimming. The webbing acts like a paddle, providing a larger surface area to push against the water.
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Do the same kinds of animals and plants live in all habitats?
Answer:
No,different kinds of animals and plants live in different habitats.
2. How do animals and plants in a marine habitat survive?
Answer:
Animals and plants survive by using oxygen dissolved in water.
3. What is the habitat of plants and animals that live on land called?
Answer:
The habitat of plants and animals that live on land is called terrestrial habitat.
4. What are examples of terrestrial habitats?
Answer:
Some examples of terrestrial habitats are forests, grasslands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions.
5. What is the habitat of plants and animals that live in water called?
Answer:
The habitat of plants and animals that live in water is called aquatic habitat.
6. What are examples of aquatic habitats?
Answer:
Some examples of aquatic habitats are lakes, rivers and oceans.
7. What are the biotic components of a habitat?
Answer:
The biotic components of a habitat are the living organisms, both plants and animals.
8. What are the abiotic components of a habitat?
Answer:
The abiotic components of a habitat are the non-living things like rocks, soil, air and water.
9. Are sunlight and heat biotic or abiotic components?
Answer:
Sunlight and heat are non-living, so they are abiotic components.
10. What is germination?
Answer:
When a seed turns into a sprout it is known as germination.
11. What happens to organisms who cannot adapt to their surroundings?
Answer:
Organisms who cannot adapt to their surroundings die.12. Name a type of plant that grows in the desert.
Answer:
A type of plant that growsin the desert is called cactus.
13. What kind of a habitat does a yak live in?
Answer:
The yak lives in a mountain habitat.
14. Are microorganisms biotic or abiotic?
Answer:
Microorganisms are biotic components of the environment.
15. Name one abiotic component which is missing in deep oceans?
Answer:
Sunlight is one abiotic component which is missing.
16. Name a habitat that is made artificially.
Answer:
The zoo is a habitat made artificially.
17. Name two things organisms cannot live without.
Answer:
Two things organisms cannot live without are respiration and food.
18. What is the process elimination of wastes from the body called?
Answer:
The elimination of wastes from the body is called excretion.
19. Do animals reproduce their own kind?
Answer:
Animals reproduce their own kind.
20. What is the process by which living things give birth called?
Answer:
The process by whichliving things give birth is called reproduction.
21. Do non-living things react to stimuli?
Answer:
Non-living things do not react to stimuli.
22. You are given a plant which is medium sized with branches rising from the base of the stem. What kind of a plant is it?
Answer:
It is a shrub.
23. Name an adaptation by which desert plants survive in the desert.
Answer:
Desert plants have fleshy stems that can store water and help them tolerate the hot conditions in these places.
24. Name an adaptation by which deodar trees survive in cold mountainous regions.
Answer:
The conical shapes branches of deodar trees enable them to let the snow slide off easily after snowfall in the mountains.
25. Name two adaptations by which rhododendrons survive in cold mountainous regions.
Answer:
Rhododendrons are of shorter height and have smaller leaves to survive through the heavy winds on mountain tops.
Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is biodiversity? Why does it vary from region to region?
Answer:
The variety of plants, animals, microorganisms etc found in a particular region is called the biodiversity of that region. It varies from region to region because of different environmental conditions.
2. What are creepers? Give examples.
Answer:
Creepers are plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright and grow and spread along the ground. Two examples of creepers are watermelon and pumpkin.
3. What are climbers? Give examples.
Answer:
Climbers are plants with weak stems that climb up using support. Two examples are grapevine and gourd.
4. What is the midrib of a leaf? What are veins?
Answer:
The prominent line in the middle of a leaf is called the midrib. The lines on the leaf around the midrib are called veins.5. If a plant has fibrous root, what type of venation do its leaves have?
Answer:
If a plant has fibrous root, the leaves will have parallel venation where the veins are parallel to each other. Wheat and maize are examples of such plants.
6. If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Answer:
If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, it will have a tap root. Carrot and rose are examples of such plants.
7. Is it possible for you to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Answer:
Yes, it is possible to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper. If the impression of the leaf has parallel venation, the plant will have fibrous root. If the impression of the leaf has reticulate venation, the plant will have tap root.
8. What is the difference between tap roots and fibrous roots?
Answer:
Tap roots have a main root with smaller roots called laterals roots.Plants which do not have a main root and in which all roots are similar are called fibrous roots.
9. What are some of the roots that we eat and why?
Answer:
Some of the roots that we eat are carrot, radish, sweet potato, turnip and tapioca. The food prepared by the leaves is conducted by the stem and is stored in different parts of the plant – one of these parts is the root.
10. What is adaptation?
Answer:
The presence of certain features or certain habits which enable an organism to live naturally in a place is called adaptation. Adaptation differs depending on the environment in which the organism lives. Without the necessary adaptation, the organism would not survive. For example, a fish cannot live out of water and a camel cannot live in the sea.
11. Which seed germinates better?
(a) Seeds soaked in water and kept in a sunny room.
(b) Seeds soaked in water and kept in a dark cupboard.
(c) Seeds soaked in water kept in a refrigerator.
Answer:
Abiotic factors like air, light, heat and water are needed for germination. Seeds kept in sunny room fulfils all the criteria of air, heat and water and therefore they will germinate. If seeds are soaked in water and kept in a dark cupboard, they will still germinate because light is not necessary for seed germination. Seeds kept in a refrigerator will not germinate because of the absence of heat.
Therefore, the correct answer is (a) and (b).
12. How long does adaptation take and why?
Answer:
Adaptation takes a long time. The abiotic factors of a region change very slowly, therefore adaptation also happens very slowly.
13. How do desert animals like rats and snakes adapt to survive in the desert?
Answer:
Although rats and snakes do not have long legs like a camel, they stay away from the heat of the sand by digging burrows deep in the sand. They come out only during the night when its cooler.
14. Name one way in which desert plants adapt to survive in desert conditions.
Answer:
Desert plants have adapted to lose very little water through transpiration. Some have no leaves; others have small leaves or they are in the form of spines. The stems have a thick waxy layer to retain water in the tissues and the roots go deep into the soil for absorbing water.
15. How have trees adapted to mountain climate?
Answer:
Trees in mountain regions are cone shaped, have sloping branches and have needle-like leaves. This enables rainwater and snow to slide off easily – thereby keeping the trees healthy.
16. How have animals adapted to mountainous regions? Explain with examples.
Answer:
Animals living in mountain regions have thick skin or fur for protection from the cold.
Examples: Yaks have long hair to keep them warm. The snow leopard has thick fur on its body including feet and toes for protection from the snow. The mountain goat has strong hooves which enable it to run up rocky slopes of mountains.
17. What kind of adaptations would an animal need in order to live in water?
Answer:
The adaptations an animal would need in order to live in water:
(i) Streamlined body to help in swimming.
(ii) Gills which enable most aquatic animals breathe in oxygen dissolved in water.
(iii) Fins to change directions and keep balance.
18. What kind of adaptations does the lion have to live in the grasslands?
Answer:
The lion has the following adaptations to live in the grasslands:
(i) Lions have long claws in their front legs which helps them to hunt.
(ii) Its light brown colour helps it to camouflage itself in the dry grasslands, so it can effectively hunt for prey.
(iii) It has eyes in front of the face which allow it to have a correct idea about the location of its prey.
19. Describe the adaptation of frogs.
Answer:
Frogs live on land as well as in water. To live on land, they have developed strong back legs which help them in leaping and catching prey. To live in water, they have webbed feet to help them swim.
20. Name one living thing that looks like a non-living thing. Why does it seem so?
Answer:
Plants are living things but do not move like a human or an animal. They also seem like they don’t take in food to get energy like animals do – but they do make food using photosynthesis and store it. They do not seem like they are breathing also, but they do take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide during respiration.
21. Name one non-living thing that looks like a living thing. Why does it seem so?
Answer:
Clouds are one living thing that move in the sky like a living thing would. Clouds also grow in size and give out water, which might make it seem that its alive.
22. What are stimuli?
Answer:
Changes in our surroundings that make us react or respond to them are called stimuli. All of us respond immediately to these changes. For example, if we suddenly step on a sharp object like a thorn, we wince. This is a reaction to an external stimulus.
23. What do plants do with waste products?
Answer:
Inplants the waste products are:
(i) Stored within their parts in a way that does not damage the plant.
(ii) Removed as secretions.
24. Do all animals reproduce the same way?
Answer:
Different animals reproduce in different ways:
(i) Some animals for e.g. hens, turtles, snakes and fish produce their young through eggs.
(ii) Mammals give birth to their young ones.
25. Talk about some kinds of movements that happen in plants.
Answer:
The following kinds of movements happen in plants:
(i) Water, minerals and the food synthesized by plants move from one part of the plant to another.
(ii) Flowers open and close in plants.
(iii) Parts of plants also move in response to external stimuli for e.g. leaves of the Mimosa plant recoil when being touched.
(iv) Plants kept in the shade turn towards sunlight.
Long Answer Type Questions:
1. How do camels survive in desert conditions?
Answer:
The camel survives in desert conditions because of the following adaptations:
(i) The body structure of the camel is designed in a way such that it has long legs to keep their bodies away from the heat of the sand.
(ii) They excrete small amounts of urine to preserve water inside their bodies.
(iii) Their dung is dry and this helps to preserve water inside their body.
(iv) Also, they do not sweat – again to preserve water.
(v) Since camels do not lose too much water from their bodies, they can survive for many days without water.
2. How do fishes survive in aquatic habitats?
Answer:
The fish survives in aquatic conditions because of the following adaptations:
(i) The bodies of all fishes are streamlined in shape to help them move easily in water.
(ii) Fishes have slippery scales on their bodies which protect the fish and also help in swimming.
(iii) Fishes have flat fins and tails that help them to change directions and keep balance.
(iv) Gills help them to breathe in oxygen dissolved in water.
3. What adaptations help the deer to survive in grasslands and escape from predators like lions?
Answer:
The deer has the following adaptations:
(i) The deer has strong teeth for chewing hard plant stems.
(ii) It has long ears to make them aware of predators like the lion, which helps them escape.
(iii) It has eyes on the side of the head to look in all directions for approaching predators.
(iv) The speed of the deer helps it escape from predators who are stalking and chasing them.
4. What are some examples of response to stimuli?
Answer:
Here are some examples of responses to certain stimuli:
(i) When we see our favourite food, we feel happy.
(ii) Our eyes naturally shut when we move from a dark place into bright sunlight.
(iii) When you move towards a bird, it flies away.
(iv) Wild animals run away when bright light is flashed towards them.
(v) Cockroaches try to hide if suddenly exposed to light.
(vi) When someone touches leaves of a Mimosa plant, they close.
(vii) Flowers of certain plants bloom only at night.
(viii) In some plants flowers close after sunset.
(ix) Plants bend in the direction of sunlight when they grow.
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) Dicot plants have ________ venation and a _________ root system.
(b) Monocot plants have ________ venation and a ________ root system.
(c) Chickpea has ________ cotyledons.
(d) The Indian botanist ________ played a key role in the ‘Save Silent Valley’ movement.
(e) Silent Valley is located in the ________ district of Kerala.
(f) ________ was called the Birdman of India.
Answers:
(a) Dicot plants have reticulate venation and a tap root system.
(b) Monocot plants have parallel venation and a fibrous root system.
(c) Chickpea has two cotyledons.
(d) The Indian botanist Janaki Ammal played a key role in the ‘Save Silent Valley’ movement.
(e) Silent Valley is located in the Palakkad district of Kerala.
(f) Salim Ali was called the Birdman of India.
Match and Pair:
| Column A | Column B |
| Roots of gram plants | Fibrous root |
| Food maker of the plant | Tender stem |
| Tomato tree | Short legs |
| Camel in hot desert | Leaf |
| Roots of maize plants | Tap root |
| Camel in Ladakh | Long Legs |
Answer:
The correct table is shown below:
| Column A | Column B |
| Roots of gram plants | Tap root |
| Food maker of the plant | Leaf |
| Tomato tree | Tender stem |
| Camel in hot desert | Long Legs |
| Roots of maize plants | Fibrous root |
| Camel in Ladakh | Short legs |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
We have thoroughly answered all ‘Let us enhance our learning’ questions and even included a comprehensive set of extra questions in this material. The idea is to thoroughly explain the concepts to you and give you a taste of what exam questions many look like. You will learn to think logically and critically, which is the new requirement of the CBSE board.
The free PDFs of the solutions are available for download anytime you please! We will keep posting lots more useful study materials and resources, so keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list to be among the first to access them.
The following topics are covered:
2.1 Diversity in Plants and Animals Around Us
– 2.2.1 How to group plants?
– 2.2.2 How to group animals?
2.3 Plants and Animals in Different Surroundings
Of course! You can download the PDF versions of educationroundtheworld.com’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World anytime you please! We have included the entire material in the PDF version for your benefit! Please look towards the top of the page to find the download button!
Learn to classify plants based on the number of cotyledons in seeds, leaf venation, root types and other characteristics. Learn about the different adaptations of plants and animals in their different habitats and how to distinguish between them. Our extra question-set contain excellent examples of what exam questions under the new syllabus may look like, so study them well.
If you need us to simply teach you from scratch, our expert teachers will be there for you! Contact us anytime with your requirements and let us help you out!
If you need additional help, our personable teacher-mentors will be there for you. In addition to exam prep, they will guide you regarding your academic and future professional careers, so you can make the right choices early on. If that sounds good to you, feel free to reach out to us anytime and with your requirements. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Book an appointment now!


