Greetings, students, and welcome to this fascinating lesson about our planet Earth!
Our team of dedicated teachers, educated both in India and overseas, has worked hard to present these solutions in an engaging and informative manner. They have also prepared a comprehensive set of extra questions of different formats which will help you learn in a playful manner.
Find Solutions for NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 2 – “Inside Our Earth” here.
1. Answer the following questions.
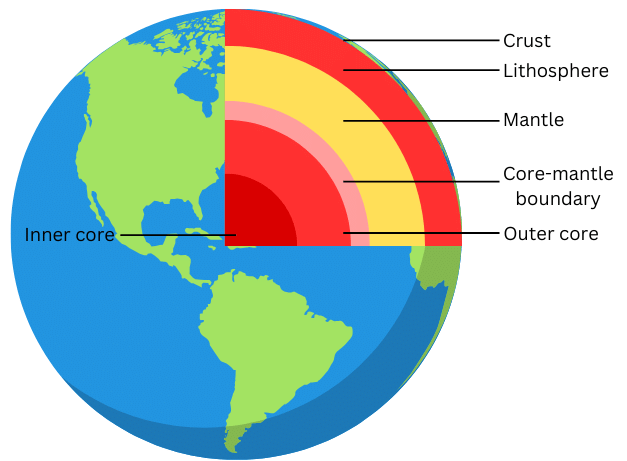
(i) What are the three layers of the earth?
Answer:
The three layers of the earth are:
Crust
Mantle
Core
(ii) What is a rock?
Answer:
A rock is a natural mass of solid mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust. The earth’s crust is made up of rocks of different colours, sizes and textures.
(iii) Name three types of rocks.
Answer:
The three major types of rocks are:
Igneous Rocks
Sedimentary Rocks
Metamorphic Rocks
(iv) How are extrusive and intrusive rocks formed?
Answer:
Extrusive rocks:
Extrusive rocks are formed when fiery red molten lava erupts onto the earth’s surface and solidifies as it cools rapidly. Rapid cooling results in a fine-grained texture. Such rocks formed on the earth’s crust are called extrusive igneous rocks. Basalt, which is found in the Deccan plateau, is an extrusive igneous rock.
Intrusive rocks
Intrusive rocks are formed when the molten magma cools and solidifies beneath the Earth’s surface. As the magma cools slowly over time, large mineral crystals have the opportunity to grow, giving intrusive rocks a coarse-grained texture, for example granite.
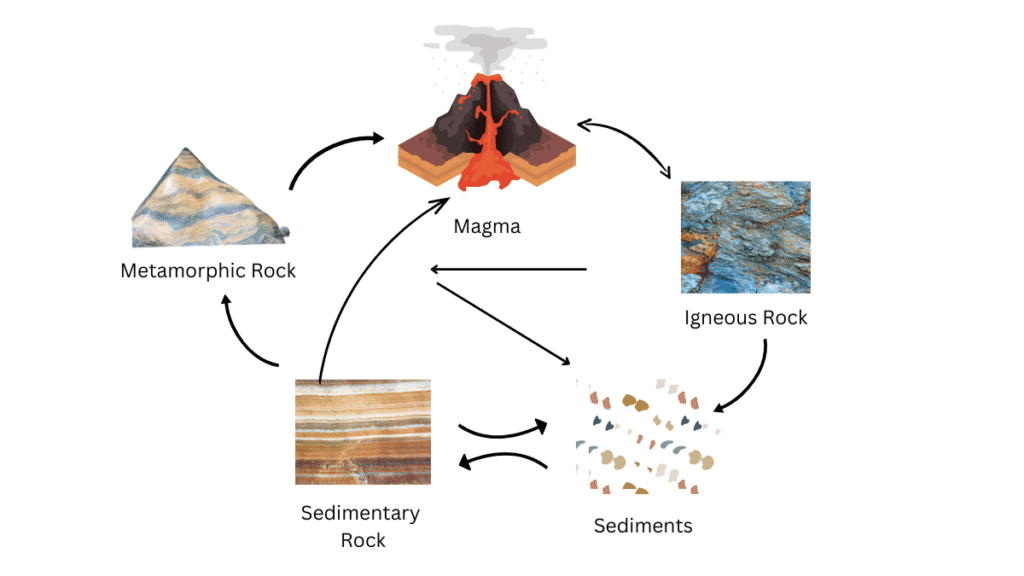
(v) What do you mean by a rock cycle?
Answer:
The rock cycle is a continuous process of transformation of one type of rock to another type under certain conditions in a cyclical manner.
It begins with igneous rocks being formed after cooling of molten magma. These rocks weather into small fragments which are transported and deposited to form sedimentary rocks. Under intense heat and pressure, igneous and sedimentary rocks transform into metamorphic rocks. Afterward, these metamorphic rocks still under intense pressure melt into magma, completing the cycle. The magma again solidifies on cooling and so begins the cycle again.
(vi) What are the uses of rocks?
Answer:
Rocks are used in construction, manufacturing, and technology. Hard rocks like granite and limestone are used as building materials for roads and buildings. Rocks and stones are also used in many games, such as hopscotch and pitthoo. Additionally, rocks contain minerals used in industries, medicine, and fertilizers.
(vii) What are metamorphic rocks?
Answer:
Metamorphic rocks are formed when igneous and sedimentary rocks experience intense heat and pressure. They change their form, for example clay changes into slate and limestone changes into marble.
2. Tick the correct answer
(i) The rock, which is made up of molten magma, is
(a) Igneous
(b) Sedimentary
(c) Metamorphic
Answer: (a) igneous rock
(ii) The innermost layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Core
(c) Mantle
Answer: (b) Core
(iii) Gold, petroleum and coal are examples of
(a) Rocks
(b) Minerals
(c) Fossils
Answer: (b) Minerals
(iv) Rocks which contain fossils are
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(b) Metamorphic rocks
(c) Igneous rocks
Answer: (a) Sedimentary rocks
(v) The thinnest layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Mantle
(c) Core
Answer: (a) Crust
3. Match the following.
| (i) Core | (a) Earth’s surface |
| (ii) Minerals | (b) Used for roads and buildings |
| (iii) Rocks | (c) Made of silicon and alumina |
| (iv) Clay | (d) Has definite chemical composition |
| (v) Sial | (e) Innermost layer |
| (f) Changes into slate | |
| (g) Process of transformation of the rock |
Answer:
| (i) Core | (e) Innermost layer |
| (ii) Minerals | (d) Has definite chemical composition |
| (iii) Rocks | (b) Used for roads and buildings |
| (iv) Clay | (f) Changes into slate |
| (v) Sial | (c) Made of silicon and alumina |
| (a) Earth’s surface | |
| (g) Process of transformation of the rock |
4. Give reasons.
(i) We cannot go to the centre of the earth.
Answer:
We cannot go to the centre of the earth because we would have to dig more than 6000 km under the ocean bed which is not possible with the existing technology. Moreover, human beings would not be able to survive without oxygen or withstand the intense heat and pressure at the centre of the earth which makes even rocks melt.
(ii) Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments.
Answer:
Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments through a series of processes. Rocks are broken down into small fragments through friction as they roll down and hit against each other. These smaller particles called sediments are transported by wind and water and deposited elsewhere. The sediments settle and accumulate in layers. Over time, as more sediments are deposited on top, the weight of the overlying sediments compresses the lower layers hardening them into sedimentary rocks.

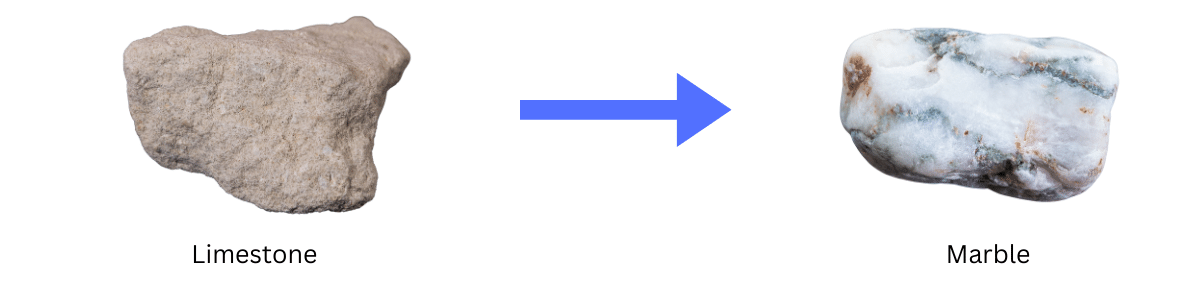
(iii) Limestone is changed into marble.
Answer:
We have seen that sedimentary rocks like limestone change into metamorphic rocks when subjected to intense heat and pressure. The mineral composition of limestone is altered due to heat and pressure resulting in the formation of marble which is a metamorphic rock.
5. For Fun (Page 11)
(i) What are the minerals most commonly used in the following objects?
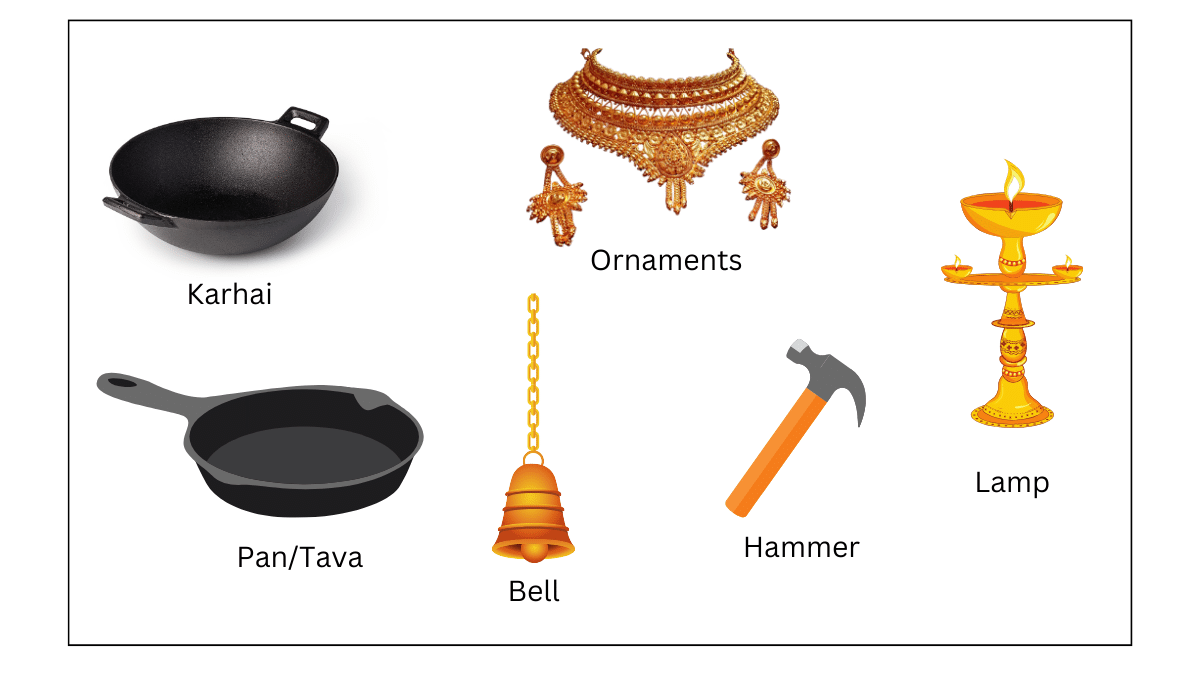
Answer:
| Objects | Minerals most commonly used in them |
| Karhai | Iron, Copper, brass |
| tawa | Iron, copper, brass |
| Hammer | Iron |
| Bell | Copper, silver, brass |
| Lamp | Copper, gold, silver, brass |
| ornaments | Gold, silver |
(ii) Identify some more objects made up of different minerals.
Answer:
Some other objects made up of different minerals are”
Wires – copper, aluminium
Doors – Iron, aluminium
Windows – Iron, aluminium
Buckets – copper, aluminium, iron
Knives – Iron, steel
Solutions for In-text questions of NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 2 “Inside Our Earth”
Let’s do it (Page no 9)
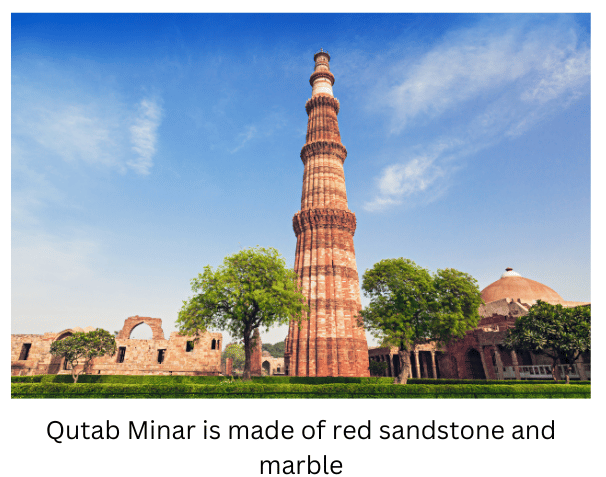
1.Collect pictures of some monuments and find out which are the rocks used to build them.
Answer:



Page 10
2. What are the minerals found in your state? Collect some samples to show in your class.
Answer:
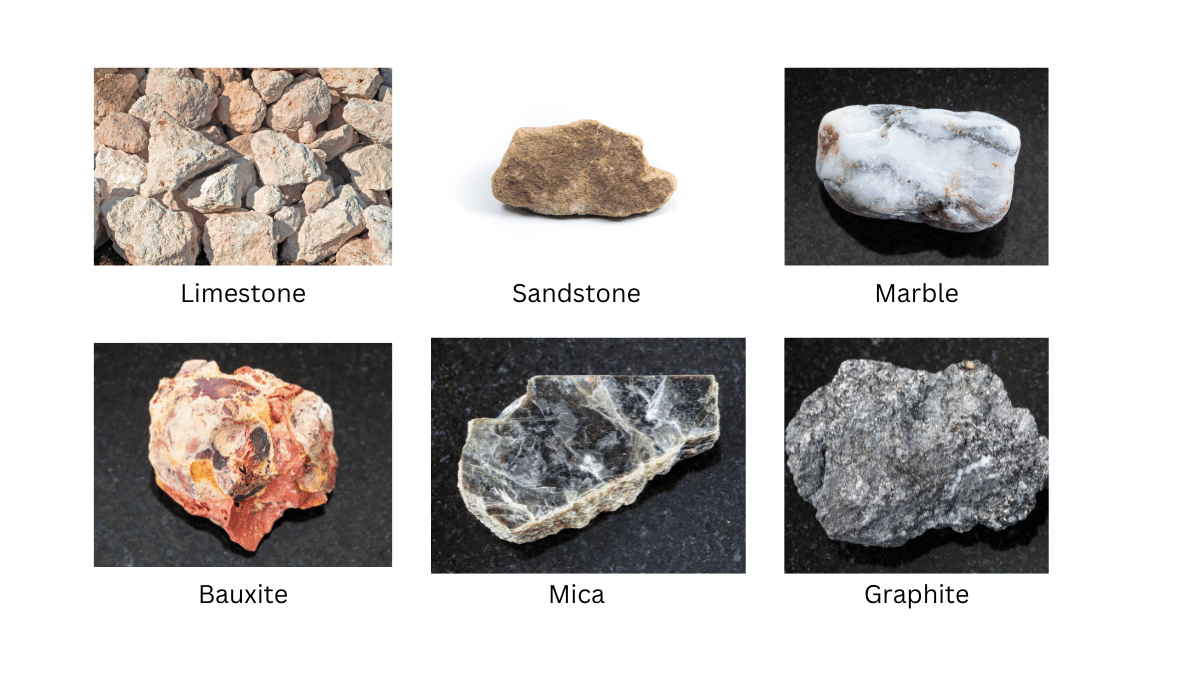
Delhi has abundant reserves of limestone, marble and sandstone which are used in construction and architectural purpose. Also found are bauxite, uranium, manganese, mica and graphite.
Extra Questions for NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 2 – “Inside Our Earth”
A. Multiple Choice type Questions (MCQ)
1. What are the main mineral constituents of the continental mass?
A) Silica
B) Alumina
C) Iron
D) Both A and B
2. What is the thinnest layer of the Earth?
A) Crust
B) Mantle
C) Outer core
D) Lithosphere
3. What is the radius of the Earth’s core?
A) 2900 km
B) 3500 km
C) 6371 km
D) 3700 km
4. The core of the earth is mainly made up of ______ and ________.
A) Silica and magnesium
B) Iron and manganese
C) iron and silica
D) Iron and nickel
5. Which type of rocks are formed by the cooling and solidification of molten magma?
A) Metamorphic
B) Sedimentary
C) igneous
D) magma
6. Which rocks may contain fossils of plants, animals and other micro-organisms?
A) Primary rocks
B) metamorphic rocks
C) Sedimentary rocks
D) Igneous rocks
7. What type of rock is formed when igneous or sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure?
A) Igneous rock
B) Sedimentary rock
C) Metamorphic rock
D) Extrusive rock
8. The deepest mine in the world is in _______.
A) India
B) South Africa
C) New Zealand
D) None of the above
9. The Deccan plateau is made up of_______.
A) marble
B) sandstone
C) limestone
D) basalt
10. ______ is made from grains of sand.
A) silicon
B) sandstone
C) limestone
D) granite
Answer:
1. D) Both A and B
2. A) Crust
3. B) 3500 km
4. D) Iron and nickel
5. C) igneous
6. C) Sedimentary rocks
7. C) Metamorphic rock
8. B) South Africa
9. D) basalt
10. B) sandstone
B. Fill in the blanks with suitable words from the box to complete the following sentences:
| crust | powders | silica | compressed | roads |
| magnesium | rock | buildings | granite | hardened |
1. The oceanic crust mainly consists of _______and _________.
2. Grinding stones used to prepare pastes and ____ of spices and grain are made of ________.
3. The hard rocks are used to make _______ , houses and __________.
4. Any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s ________ is called a _____.
5. These loose sediments are _______ and ___________ to form layers of rocks.
Answer:
1. The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium.
2. Grinding stones used to prepare pastes and powders of spices and grains are made of granite.
3. The hard rocks are used to make roads , houses and buildings.
4. Any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust is called a rock.
5. These loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks.
C. Match the words in column A with those in column B
| A | B |
| ignis | Radius of the earth |
| 6371 km | Mineral constituents of the continental mass |
| sial | Very high temperature and pressure |
| siam | fire |
| Cental core | Mineral Constituents of the oceanic crust |
Answer:
| A | B |
| ignis | fire |
| 6371 km | Radius of the earth |
| sial | Mineral constituents of the continental mass |
| siam | Mineral constituents of the oceanic crust |
| Cental core | Very high temperature and pressure |
D. State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE:
1. The Earth’s crust is thickest on the ocean floors.
2. The mantle extends up to a depth of 2900 km below the crust.
3. Metamorphic rocks can change into sedimentary rocks under great heat and pressure.
4. Igneous rocks are also called primary rocks.
5. Lava is actually fiery red molten magma coming out of the interior of the earth on its surface.
Answer:
1. False – The earth’s crust is thinnest on the ocean floor, it is thickest on continental masses.
2. True
3. False – Metamorphic rocks can melt into molten magama under great heat and pressure. When cooled down this molten magma can solidify into igneous rocks.
4. True
5. True
E. Very Short Answer type Questions:
1. Is the thickness of the earth’s crust uniform?
Answer:
No, the earth’s crust is not uniformly thick. It extends about 35 km on the continental mass and only 5km on the ocean floors.
2. What is the earth’s crust made of?
Answer:
The earth’s crust is made of various types of rocks.
3. What is the radius of the earth’s core?
Answer:
The earth’s core has a radius of around 3500 km.
4. What are the main constituents of the core?
Answer:
The main constituents of the core are nickel and iron. It is usually known as ‘nife’.
5. What is the Deccan plateau made of?
Answer:
The Deccan plateau is made of basalt which is an extrusive igneous rock.
5. How are igneous rocks formed?
Answer:
Molten lava cools down and solidifies to form igneous rocks.
6. What kind of a rock is sandstone?
Answer:
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock made up of sand grains which have been compressed together and hardened over a long period of time.
7. Which is the thinnest of all the layers of the earth?
Answer:
The top most layer of the earth , known as the crust, is the thinnest of all layers.
8. Give an example of igneous rock.
Answer:
Basalt is an example of igneous rock.
9. Name a few sedimentary rocks.
Answer:
A few sedimentary rocks are limestone, sandstone and shale.
10. Name a few metamorphic rocks.
Answer:
Marble, slate and gneiss are metamorphic rocks.
F. Short Answer Type Questions:
1. How do the main mineral constituents of the continental mass and oceanic crust differ?
Answer:
The main mineral constituents of the continental mass are silica and alumina, while the oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium.
2. How does the structure of extrusive igneous rocks, differ from that of intrusive igneous rocks?
Answer:
Extrusive igneous rocks cool rapidly on the Earth’s surface which prevents large crystals from forming so they are fine-grained in structure, whereas the intrusive igneous rocks cool down slowly beneath the earth’s surface resulting in a coarse-grained texture.
3. What are fossils? Why do sedimentary rocks contain fossils?
Answer:
Fossils are the remains of plants and animals trapped in the layers of rocks. Sedimentary rocks may contain fossils because they can preserve the remains of plants, animals, and microorganisms that once lived on them.
4. What happens when metamorphic rocks are subjected to high heat and pressure?
Answer:
When metamorphic rocks are subjected to high heat and pressure deep within the earth, they melt down to form molten magma. This molten lava may cool down again and solidify into igneous rocks.
5. What are minerals? What role do minerals play in human life?
Answer:
Minerals are naturally occurring substances that have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition. They are used by human beings in various ways. Some, like coal, natural gas and petroleum are used as fuels.
They may be used in industries like iron, aluminium, gold and uranium. etc, in medicine and in fertilisers.
6. Why is the outer crust of the earth important to us?
Answer:
The outer crust is important to us because the solidified outer crust of the earth is the base which sustains human life and civilization. It also consists of the valuable soil and gives us most of our minerals.
G. Long Answer Type Questions
1.Write and describe the different types and features of the rocks.
Answer:
Rocks are categorized into three main types: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
(i) Igneous Rocks: These rocks form from the cooling and solidification of molten magma. Igneous rocks are further classified into two types:
- Extrusive Igneous Rocks: When molten lava erupts onto the Earth’s surface and cools rapidly, it forms extrusive igneous rocks. For example, basalt is an extrusive igneous rock.
- Intrusive Igneous Rocks: Sometimes, molten magma cools and solidifies deep within the Earth’s crust, forming intrusive igneous rocks. Since these rocks cool slowly, they have larger grains. Granite is an example of an intrusive igneous rock.
2. Sedimentary Rocks: Loose sediments or small fragments of rocks, sand and organic material are transported by wind and water and deposited in layers. These loose fragments are compressed, and hardened over time to form sedimentary rocks. For example, sandstone is formed from grains of sand that have been transported and deposited by wind or water.
3. Metamorphic Rocks: Existing rocks, whether igneous or sedimentary, can undergo changes due to high heat and pressure. This process transforms them into metamorphic rocks. For example, clay can change into slate, and limestone can change into marble.
2. Describe the interior of the earth.
Answer:
Our planet is composed of several layers arranged concentrically, each distinct from the others. These layers are – the crust, mantle, and core.
The crust, the outermost layer, is thinnest and varies in thickness, about 35 km under continents and 5 km under oceans. The continental crust is rich in silica and alumina, known as sial (si-silica and al-alumina), while the oceanic crust is primarily silica and magnesium, called sima (si-silica and ma-magnesium).
Beneath the crust lies the mantle, extending approximately 2900 km deep.
The core, the innermost layer, has a radius of around 3500 km and is composed mainly of nickel and iron, referred to as nife (ni-nickel and fe-ferrous, i.e., iron). The central core has extremely high temperature and pressure.
3. What are minerals and how do human beings benefit from them.
Answer:
Minerals are naturally occurring substances with specific chemical compositions and physical properties. They are essential for a variety of human activities and industries:
Fuels: Minerals like coal, natural gas, and petroleum are indispensable sources of energy for cooking, heating, generation of electricity, and transportation.
Metals: Minerals such as iron, aluminium, gold, and uranium are used in manufacturing, construction, and technology
Industrial Use: Minerals are used in industries for various purposes, such as iron in steel production, clay in ceramics, and limestone in cement manufacturing
Medicine: Some minerals have medicinal properties and are used in pharmaceuticals and health supplements.
Fertilizers: Minerals like phosphate and potash are essential components of fertilizers used in agriculture.
Construction: Minerals like sand, gravel, and limestone are used in construction for making concrete and building materials.
Gemstones: Precious minerals like diamonds, rubies, and emeralds are used in jewellery and ornamental items.
Technology: Minerals like silicon are used in electronics and technology. Minerals play a crucial role in almost all aspects of human life, from providing energy and materials for industry to supporting agriculture and technology.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 2 – “Inside Our Earth”
Our team of competent subject experts educated both in India and overseas have crafted these accurate solutions taking into account every detail and presenting them in the most easy-to-understand way possible. Every single aspect of the lesson has been explained in a clear and lucid manner. We recommend that you go through them in detail because they will help to clear your concepts.
Feel free to download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime! There’s plenty more helpful study material and other resources on the way – so keep visiting our website and join our email list to get free access to them!
The topics discussed in this chapter are as follows:
Interior of the Earth
Crust
Mantle
Core
Rock and Minerals
a. Sedimentary Rocks
b. Metamorphic Rocks
c. Igneous Rocks
What is the uppermost layer of the earth called?
Name the constituents of the oceanic crust.
What is the earth’s crust made of?
What are minerals? How are they useful for mankind?
Name the main mineral constituent of the continental mass.
What are the main constituents of the core?
How are igneous rocks formed?
What is the radius of the earth’s core?
What are fossils?
How does the structure of extrusive igneous rocks, differ from that of intrusive igneous rocks?
What happens when metamorphic rocks are subjected to high heat and pressure?
What are the uses of rock?
What do you mean by a rock cycle?
Yes indeed! You can download the free PDF versions of these excellent solutions anytime (please look towards the top of the page)!
Yes, certainly. Our team of competent subject teachers have carefully anticipated all the queries you may have about the lesson and crafted these excellent solutions which draw your attention to every detail in the and also explain the essence of the chapter.
We suggest that at first you read the lesson closely and then read the solutions taking in all the details.
Our seasoned subject experts have painstakingly provided many extra questions which are similar to exam questions and are designed to give you sufficient practice.
Go through the solutions before the exam and practice writing out some answers within a specified time period. This is an important step which should not be skipped because practice not only makes perfect, but also boosts your self-confidence. You will be well-equipped to take on any challenge that your examiner may pose! Good luck!
In addition to exam preparation, we also mentor students regarding their future academic and professional careers. This results in all-round development of the students, boosts their confidence and makes them aware of the opportunities that lie ahead.
If you like what we offer, reach out to us anytime and let us assign you a friendly ‘teacher-mentor’. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Book an appointment now!


