Hello, students, and welcome to this captivating lesson about our amazing planet Earth! Our team of passionate teachers, who have been educated both in India and overseas, has put great effort into creating these solutions for you. We aim to make your learning experience both engaging and informative. Additionally, we’ve prepared a diverse set of extra questions in various formats to help you learn in a fun and interactive way.
Find Solutions for NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 3 – “Our Changing Earth” here.
Our Changing Earth
1. Answer the following questions.
(i) Why do the plates move?
Answer:
The plates move due to the circular movement of molten lava inside the earth.
(ii) What are exogenic and endogenic forces?
Answer:
The earth’s movements are divided on the basis of the forces which cause them:
- Exogenic forces are those forces that act on the surface of the earth and cause changes on its surface, for example winds, rivers, glaciers.
- Endogenic forces originate in the interior of the earth and sometimes produce sudden movements like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions which cause destruction on the surface of the earth.
(iii) What is erosion?
Answer:
Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice. The eroded material is carried away by wind, water or ice and deposited elsewhere. This natural process of erosion and deposition creates different land-forms on the surface of the earth.
(iv) How are flood plains formed?
Answer:
Flood plains are formed in the following way:
- During the rainy season rivers overflow their banks
- The surrounding areas are then flooded
- The flood waters deposit a layer of fine soil and other material called sediments along its banks.
- This leads to the formation of flat and fertile floodplains.
(v) What are sand dunes?
Answer:
Sand dunes are low hill-like structures formed by the deposition of sand in the desert. When the wind blows in the desert, it lifts and transports sand from one place to another. When it stops blowing the sand gets deposited into dunes.
(vi) How are beaches formed?
Answer:
Beaches are formed when sea waves deposit sediments along the sea-shore.
(vii) What are ox-bow lakes?
Answer:
Ox- bow lakes are formed when the river enters the plains and starts to meander forming large bends.
The outer bank of the bend is eroded away by the flowing river, while sediment is deposited on the inner bank. Over time the meander loop becomes more pronounced. Eventually the river breaks through the narrow neck of the meander cutting off the loop. The cut-off lake is called an oxbow lake.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which is not an erosional feature of sea waves?
(a) Cliff
(b) Beach
(c) Sea cave
Answer: (b) Beach
(ii) The depositional feature of a glacier is:
(a) Flood plain
(b) Beach
(c) Moraine
Answer: (c) Moraine
(iii) Which is caused by the sudden movements of the earth?
(a) Volcano
(b) Folding
(c) Flood plain
Answer: (a) Volcano
(iv) Mushroom rocks are found in:
(a) Deserts
(b) River valleys
(c) Glaciers
Answer: (a) Deserts
(v) Ox bow lakes are found in:
(a) Glaciers
(b) River valleys
(c) Deserts
Answer: (b) River valleys
3. Match the following:
| (i) Glacier | (a) Sea shore |
| (ii) Meanders | (b) Mushroom rock |
| (iii) Beach | c) River of ice |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (d) Rivers |
| (v) Waterfall | (e) Vibrations of earth |
| (vi) Earthquake | (f) Sea cliff |
| (g) Hard bedrock | |
| (h) Deserts |
Answer:
| (i) Glacier | c) River of ice |
| (ii) Meanders | (d) Rivers |
| (iii) Beach | (a) Sea shore |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (h) Deserts |
| (v) Waterfall | (g) Hard bedrock |
| (vi) Earthquake | (e) Vibrations of earth |
| (b) Mushroom rock | |
| (f) Sea cliff |
4. Give reasons.
(i) Some rocks have the shape of a mushroom.
Answer:
Some rocks have the shape of a mushroom because, in deserts, the wind erodes the lower section of the rock more than the upper part, causing the rocks to have narrower bases and wider tops. Hence, they are shaped like mushrooms.
(ii) Flood plains are very fertile.
Answer:
Flood plains are fertile because when rivers overflow their banks during floods, they deposit layers of fine soil and other materials called sediments along their banks. This process leads to the formation of flat, fertile flood plains.
(iii) Sea caves are turned into stacks.
Answer:
Sea caves are natural cavities formed along coastlines due to the action of waves. Over time, continuous erosion enlarges these cavities till only the roofs of the caves remain, thus forming sea arches. Eventually the roofs of the caves collapse leaving only the walls of the caves standing like tall, vertical columns of rock known as stacks.
(iv) Buildings collapse due to earthquakes.
Answer:
Buildings collapse due to the sudden movements of the earth during earthquakes. Endogenic forces, acting inside the earth, sometimes produce sudden movements, such as earthquakes, that cause massive destruction over the surface of the earth. The intense shaking and ground movements associated with earthquakes can lead to the collapse of buildings and other structures which are not earthquake-proof.
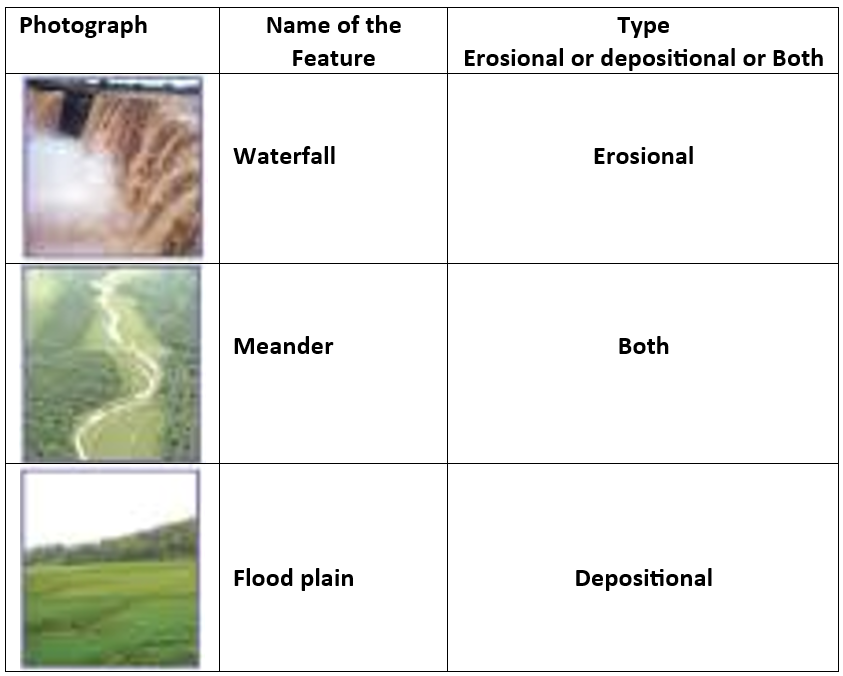
5. Activity
Observe the photographs given below. These are various features made by a river. Identify them and also tell whether they are erosional or depositional or landforms formed by both.
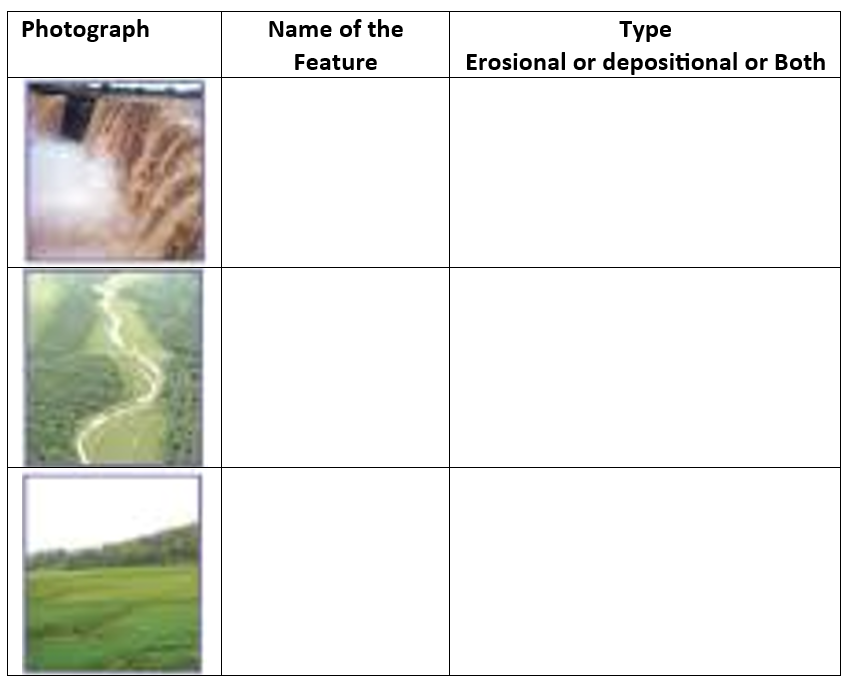
Answer:
6. For Fun
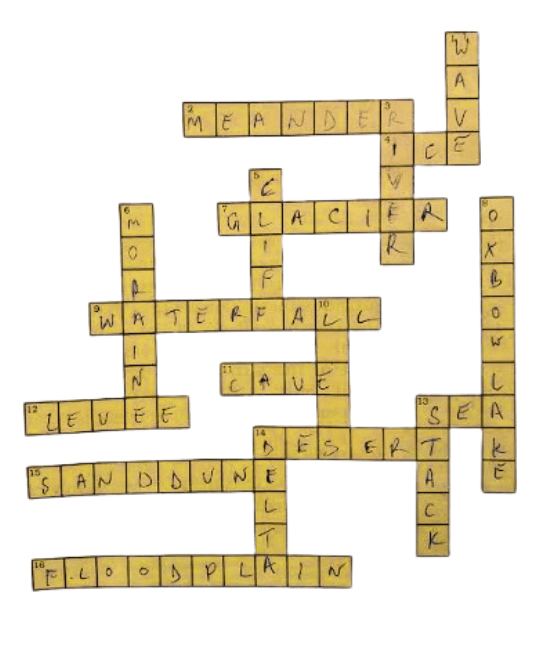
Solve the crossword puzzle with the help of given clues.
| Down | Across |
| 2. Loop like the bend of a river | 1. Rise and fall of water caused by friction of wind on water surface |
| 4. Solid form of water | 3. Flow of water in a channel |
| 7. Moving mass of ice | 5. Steep perpendicular face of a rock along a sea coast |
| 9. Sudden descent of water in the bed of a river | 6. Debris of boulder and coarse material carried by glacier |
| 11. Natural cavity on weak rocks formed by action of waves | 8. Crescent shaped lake formed by a meandering river |
| 12. Embankment on a river that keeps it in its channel | 10. Fine sand deposited by the action of the wind |
| 13. Large body of sea water | 13. Isolated mass of rising steep rock near a coastline |
| 14. Dry area where sand dunes are found | 14. Alluvial tracts of land formed by the river deposits at the mouth of a river |
| 15. Small hill of sand caused by the action of the wind | |
| 16. Flat plain formed by river deposits during time of flood |
Solution:

Solutions for In-text questions of NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 3 “Our Changing Earth”.
Page 13.
Do you know
There are three types of earthquake waves:
1. P waves or longitudinal waves
2. S waves or transverse waves
3. L waves or surface waves
Try to find out the properties of these waves from an encyclopedia.
Answer:
Properties of Earthquake Waves:
1. P Waves (Primary Waves):
They are longitudinal waves.
These are the fastest seismic waves.
They are compressional waves that travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
P waves cause the ground to move in the direction of the wave propagation, similar to sound waves.
2. S Waves (Secondary Waves):
They are transverse waves.
S waves are slower than P waves and arrive at the seismograph station after P waves.
They are transverse waves that move through solids but not through liquids or gases.
S waves cause the ground to move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, shaking the ground side-to-side.
3. L Waves (Surface Waves):
They are surface waves.
L waves are the slowest seismic waves and are the most destructive.
They travel along the Earth’s surface and produce rolling motions that cause the ground to move up and down or side-to-side.
L waves are responsible for most of the damage caused by earthquakes.
Page 14
Activity
1. Read the ‘Earthquake – A case study’ given in the form of headlines that appeared in the newspapers after the quake. Arrange the events in the right sequence of their happening.
Answer:
The events have been arranged in chronological order based on how they are likely to have occurred:
1. Earthquake Hits Bhuj: A massive earthquake measuring 6.9 on Richter scale hit Bhuj Town on 26th January 2001.
2. Destruction of Bhuj: Phone lines, water pipelines, and power stations transmission lines were knocked out.
3. School Worst Affected: At least 971 students and 31 teachers are feared to have lost their lives following the collapse of school buildings.
4. Fire in the City: Hundreds of fires started as charcoal cookers overturned.
5. The CM’s appeal to the Centre: Gujarat appeals for financial help. The Chief minister of Gujarat has launched an appeal for the centre to deal with the disaster.
6. Bhuj Relief Effort Blighted: Three days after the quake, concern rose about food, blankets, and medical supplies not reaching everyone.
7. Emergency Declared in Quake Zone: The President declares a state of emergency.
2. Imagine if a quake suddenly shook in the middle of the school day, where would you go for safety?
Answer:
If an earthquake were to occur suddenly during the school day, it would be important to remain calm and seek safety in a place that offers protection from falling objects and possible collapse of the building. Some safe places which we could choose are:
- Under a sturdy desk or table
- Against an inside wall or corner away from windows
- In a doorway if it is a sturdy, load-bearing doorway.
- If we run outside, we would have to seek an open area away from buildings, trees, electric poles and power lines.
- It is important to stay away from glass windows which may shatter and heavy furniture which might topple over and crush us.
Page 16
Find out the names of a few rivers of the world that form a delta.
Answer:
Some rivers of the world which form deltas are as follows:
The Indus, the Ganges- Brahmaputra, The Danube, The Nile, The Mekong, The Mississippi.
Extra Questions for NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 3 – “Our Changing Earth”
A. Multiple Choice type Questions (MCQ)
1. The molten magma inside the earth moves _________
A) from side to side
B) like waves
C) In a circular manner
D) None of the above
2. The lithospheric plates move a few_________each year.
A) inches
B) miles
C) feet
D) None of the above
3. Which forces act in the interior of the earth?
A) gravitational
B) erosional
C) endogenic
D) All of the above
4. Why do lithospheric plates move?
A) Due to the movement of molten magma
B) Due to the force of gravity
C) Due to the rotation of the Earth
D) Due to the influence of the Moon’s gravity
5. What are the forces that work on the surface of the Earth called?
A) Exogenic forces
B) Endogenic forces
C) Diastrophic forces
D) Erosional forces
6. Which seismic wave travels fastest?
A) P waves
B) S waves
C) L waves
D) Surface wave
7. Which type of seismic wave causes the most damage to buildings?
A) P waves
B) S waves
C) L waves
D) Surface waves
8. Earthquakes are measured with the help of_________.
A) Compass
B) Seismograph
C) Thermometer
D) barometer
9. The place in the earth’s crust where the earthquake originates is called the ________.
A) source
B) origin
C) focus
D) root
10. Weathering means ____________.
A) forecasting the weather
B) breaking up of rocks on the earth’s surface
C) enjoying the weather
D) None of the above
11. What is the name of the sediment deposited by glaciers?
A) Loess
B) Moraine
C) Alluvium
D) Levee
12. What is the primary cause of the formation of sand dunes?
A) River erosion
B) Glacier movement
C) Wind erosion
D) Volcanic activity
Answer:
1. C) In a circular manner
2. D) None of the above – Correct answer is “millimeters”
3. C) endogenic
4. A) Due to the movement of molten magma
5. A) Exogenic forces
6. A) P waves
7. C) L waves
8. B) Seismograph
9. C) focus
10. B) breaking up of rocks on the earth’s surface
11. B) Moraine
12. C) Wind erosion
B. Fill in the blanks with suitable words from the box to complete the following sentences:
| magnitude | vibrates | Angel | surface | deserts |
| earthquakes | mushroom | epicenter | Venezuela | Richter |
1. When the lithospheric plates move, the surface of the earth ________. These vibrations are called ________.
2. The place on the _________above the focus is called the __________.
3. The ________ of an earthquake is measured on a _________- scale.
4. The highest waterfall in the world is the ________ Falls of _______ in South America.
5. In ____ you can see rocks in the shape of a _______.
Answer:
1. When the lithospheric plates move, the surface of the earth vibrates. These vibrations are called earthquakes.
2. The place on the surface above the focus is called the epicenter.
3. The magnitude of an earthquake is measued on a Richter scale.
4. The highest waterfall in the world is the Angel Falls of Venezuela in South America
5. In deserts, you can see rocks in the shape of a mushroom.
C. Match the words in column A with those in column B
| A | B |
| Large deposits of Loess | work of sea waves |
| Victoria falls | deposition by glaciers |
| stacks | Richter scale |
| moraine | China |
| earthquake | border of Zambia and Zimbabwe, in Africa |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Large deposits of Loess | China |
| Victoria falls | border of Zambia and Zimbabwe, in Africa |
| stacks | work of sea waves |
| moraine | deposition by glaciers |
| earthquake | Richter scale |
D. State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE:
1. Endogenic forces work on the surface of the Earth, causing changes like the formation of mountains
2. Oxbow lakes are formed by the erosion of wind.
3. Buildings collapse during earthquakes due to volcanic eruptions.
4. Sand dunes are formed by the erosion of glaciers.
5. Sea caves are turned into sea arches due to the erosion of sea waves.
Answer:
1. False – Endogenic forces work inside the Earth
2. False – Oxbow lakes are formed by river meandering
3. False – Buildings collapse due to the sudden movements of the Earth
4. False – Sand dunes are formed by the erosion of wind
5. True
E. Very Short Answer type Questions:
1. How does molten magma move inside the earth?
Answer:
Molten magma inside the earth moves in a circular manner.
2. What is a volcano?
Answer:
A volcano is a vent or an opening in the earth’s crust through which molten lava erupts suddenly.
3. What is the difference between ‘focus’ and ‘epicentre’ of an earthquake?
Answer:
The place in the earth’s crust where the movement originates during an earthquake is called ‘focus’, while the place on the earth’s surface directly above is called ‘epicenter’.
4. How are river meanders formed?
Answer:
River meanders are formed by the twisting and turning of a river as it flows across a flat floodplain.
5. What causes the ends of a meander loop to come closer and closer?
Answer:
Continuous erosion and deposition along the sides of the meander cause the ends of the loop to come closer.
6. What landform is created when a meander loop cuts off from the river?
Answer:
An oxbow lake is formed when a meander loop cuts off from the main river.
7. What are levees along a river bank?
Answer:
Levees are raised banks along a river that are formed by the deposition of sediment during flooding.
8. How do distributaries form in a river?
Answer:
As a river approaches the sea, it slows down and begins to break up into a number of streams called distributaries.
9. How are deltas formed at the mouth of a river?
Answer:
The deposition of sediments from all the distributaries forms a delta at the mouth of a river.
10. What is the primary cause of erosion along coastal areas?
Answer:
The primary cause of erosion along coastal areas is the action of sea waves.
11. How do glaciers erode the landscape?
Answer:
Glaciers erode the landscape by bulldozing soil and stones to expose the solid rock below.
12. What type of sediment is deposited by glaciers?
Answer:
Glacial sediment includes rocks big and small, sand, and silt that are carried and deposited by the glacier.
13. How do sand dunes change over time?
Answer:
Sand dunes change shape and size over time as wind continues to erode (blow away) and deposit sand.
14. What are some common features created by rivers?
Answer:
Some common features created by rivers include waterfalls, meanders, floodplains, and deltas.
15. Where is the Niagara Falls located?
Answer:
The Niagara Falls is located on the border between Canada and the USA in North America.
16. What do the processes of erosion and deposition create?
Answer:
The processes of erosion and deposition are responsible for creating different landforms on the surface of the earth.
F. Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is the difference between P waves and S waves?
Answer:
P waves are longitudinal waves that travel faster and can pass through solids, liquids, and gases, while S waves are transverse waves that travel slower and can only pass through solids.
2. What do you know about the lithospheric plates? How do the lithospheric plates move?
Answer:
The earth’s crust is broken up into a number of plates called lithospheric plates. These plates move around very slowly across the Earth’s surface at a rate of a few millimetres per year.
The movement of lithospheric plates is caused by circular movement of the molten magma in the Earth’s interior. The movement of these plates brings about changes on the surface of the earth.
3. What is an earthquake? What are some common earthquake prediction methods?
Answer:
An earthquake is a sudden and violent shaking of the ground, often caused by sudden movements of the Earth’s lithospheric plates.
When the lithospheric plates move, the surface of the earth vibrates. The vibrations can travel all around the earth. These vibrations are called earthquakes.
Some common earthquake prediction methods include studying animal behaviour, fish in the ponds get agitated, snakes come to the surface. Further, changes in the level of groundwater or well water have been observed before some earthquakes.
4. Write a brief guideline about earthquake preparedness
Answer:
Earthquakes, being natural disasters, are beyond our control. However, we can significantly reduce their impact through preparedness.
In the event of an earthquake, it is crucial to move to a safe location. Taking cover under a sturdy kitchen counter, table, or desk, preferably against an interior wall, can offer protection. It is important to avoid areas near fireplaces, chimneys, and windows that could shatter, including mirrors and picture frames.
Additionally, raising awareness among friends and family members about earthquake safety measures is essential for overall preparedness.
5. What are glaciers? What do you know about the work they do?
Answer:
Glaciers are ‘rivers of ice’. Glaciers also erode the landscape as they move by scooping up rocks, soil, and other debris, which can range in size from tiny particles to large boulders.
This material is carried along by the glacier and can scrape and shape the underlying rock, sometimes carving out deep hollows.
As the ice melts these hollows get filled up with water and become beautiful glacial lakes in the mountains.
The material carried by the glacier such as rocks big and small, sand and silt gets deposited. These deposits form glacial moraines.
G. Long Answer Type Questions
1. Discuss the work of a river.
Answer:
The work of a river is a dynamic process that involves erosion, transportation, and deposition of sediment, shaping the landscape over a period of time.
Erosion occurs as running water wears down rocks and soil. The flowing water in a river gradually wears down rocks and soil and forms distinctive features.
When a river encounters steep terrain or hard rocks, it cascades down, creating a waterfall.
As the river enters a flat plain, it meanders, forming large bends. Erosion and deposition along the meander’s sides cause the ends of the meander loop to come closer and closer. Eventually, the meander loop cuts off from the river, forming an oxbow lake.
Periodically, the river floods its banks, depositing layers of fertile sediment along its edges and in the surrounding areas, creating a rich floodplain. The raised edges of the floodplain are called levees.
As the river nears the sea, its speed decreases, and it divides into several smaller streams called distributaries. These distributaries gradually slow down and deposit their sediment load. Each distributary forms its own mouth, and the collection of sediment from all the mouths creates a triangular landmass known as a delta.
2. Describe the work of wind in deserts.
Answer:
Wind plays a significant role in both erosion and deposition in desert environments.
One common feature shaped by wind erosion is the mushroom rock, where the lower part of the rock erodes more quickly than the upper part, resulting in a narrower base and a wider top.
Wind also transports sand, lifting it from one place and depositing it elsewhere when it stops blowing. This process creates sand dunes, which are low hill-like structures formed by the accumulation of sand.
In areas where the sand grains are very fine and light, the wind can carry them over long distances. When this fine sand is deposited over large areas, it forms deposits known as loess. Large deposits of loess are found in China
3. What do you know about the work of sea waves?
Answer:
Sea waves shape coastal landscapes through erosion and deposition.
Waves continuously batter rocks, leading to the development of cracks that gradually widen into hollow caves, known as sea caves.
Over time, these caves can erode further until only the cave’s roof remains, forming sea arches. Eventually, erosion may break through the roof, leaving behind tall walls known as stacks.
Along the coast, steep rocky cliffs rise vertically from the sea, known as sea cliffs.
Additionally, sea waves deposit sediments along the shoreline, forming beaches.
This process of erosion and deposition by sea waves creates diverse coastal landforms that result in the dynamic nature of coastal environments.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 3 – “Our Changing Earth”
Our dedicated team of expert educators, with diverse backgrounds in education from both India and abroad, has meticulously crafted these solutions to ensure they are accurate and comprehensive. We understand the importance of clarity and simplicity in learning, which is why every aspect of the lesson has been explained meticulously in an easy-to-understand manner.
We encourage you to delve into these solutions in detail, as they will undoubtedly help clarify your concepts and deepen your understanding of the subject.
Additionally, we offer free downloadable PDFs of the solutions for your convenience.
But our support doesn’t end there! We are continuously developing more study materials and resources to aid your learning journey. Stay updated by visiting our website regularly and joining our email list to access these valuable resources for free. Your success is our priority, and we are here to support you every step of the way!
The topics discussed in this chapter are as follows:
1. The Changing Environment on Earth and Its Effects
2. Case Study on Earthquake
3. Major Landforms
a. Work of River
b. Work of Sea Waves
c. Work of Ice
d. Work of Wind
Define focus’ and ‘epicentre’.
What is a seismograph?
Where is Victoria Falls located?
How are glacial moraines formed?
Name the scale on which the magnitude of the earthquake is measured.
Name the two processes which wear away the landscape.
What is an earthquake? What are some common earthquake prediction methods?
Give an account of earthquake preparedness.
Explain the work of a river.
Give an account of the work of wind.
How do ox-bow lakes form?
Write short note on the work of sea waves.
Discuss the work of a river.
Yes indeed! You can download the free PDF versions of these excellent solutions anytime (please look towards the top of the page)!
Absolutely! Our team of expert subject teachers has meticulously crafted these solutions to address every possible question you may encounter in your study of the lesson. These solutions not only highlight key details but also delve into the essence of the chapter, ensuring a comprehensive understanding.
We recommend starting by closely studying the lesson before diving into our solutions. Our solutions provide detailed explanations and insights, enriching your learning experience. Additionally, our experts have included numerous extra questions, akin to those you might encounter in exams, to provide ample practice.
As you prepare for your exams, we advise going through these solutions thoroughly and practicing writing out answers within a specific time frame. This practice not only enhances your understanding but also boosts your confidence. With our solutions, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle any challenge your exam may present!
Don’t hesitate to make the most of our resources and embark on your journey towards academic excellence. Best of luck!
Apart from assisting with exam preparation, we also provide personalized mentorship to students, guiding them towards a future of academic and professional success. This holistic approach to education nurtures students’ overall development, instilling confidence and opening their eyes to the vast opportunities that await them.
If our offerings resonate with you, feel free to connect with us anytime and let us pair you with a supportive ‘teacher-mentor’. Our expert mentors provide individualized online coaching tailored to your schedule and requirements, empowering you to pursue your dreams with confidence and determination.
Your dreams are within reach, and we are here to help you every step of the way. Embrace the possibilities and embark on a journey of growth and achievement! Book your appointment(s) now!


