Hello folks! Find below solutions to the end – text questions and a variety of extra questions of many formats for practice. We advise that you work out the problems yourselves alongside studying them. This will boost your understanding and retention.
Find NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Studies (Geography) Chapter 4 ‘Air’ here.
1. Answer the following questions.
(i) What is atmosphere?
Answer:
The earth is surrounded by a huge blanket of air called the atmosphere. It provides us the air we breathe in and protects us from the harmful effects of the sun. Nitrogen and oxygen are two gases which make up the bulk of the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon, and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.
(ii) Which two gases make the bulk of the atmosphere?
Answer:
The two gases that make the bulk of the atmosphere are:
- Oxygen (21%)
- Nitrogen (78%)
(iii) Which gas creates a greenhouse effect in the atmosphere?
Answer:
The gas which creates greenhouse effect in the atmosphere is carbon dioxide.
(iv) What is weather?
Answer:
Weather is the hour-to-hour or the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere. Weather can change dramatically from day-to-day. It may be classified as hot, dry, cold or wet.
(v) Name three types of rainfall.
Answer:
The three types of rainfall are as follows:
- Convectional rainfall
- Orographic rainfall
- Cyclonic rainfall
(vi) What is air pressure?
Answer:
Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. The air pressure decreases as altitude or height increases and is the highest at the sea level.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which of the following gases protects us from harmful sun rays?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Ozone
Answer: (c) Ozone
(ii) The most important layer of the atmosphere is
(a) Troposphere
(b) Thermosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Answer: (a) Troposphere
(iii) Which of the following layers of the atmosphere is free from clouds?
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Answer: (b) Stratosphere
(iv) As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Remains the same
Answer: b) Decreases
(v) When precipitation comes down to the earth in the liquid form, it is called
Answer: (b) Rain
3. Match the following.
| (i) Trade Winds | (a) Incoming solar energy |
| (ii) Loo | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (c) The horizontal movement of air |
| (iv) Wind | (d) A layer of ozone gas |
| (e) Permanent wind | |
| (f) Local wind |
Answer:
| (i) Trade Winds | (e) Permanent wind |
| (ii) Loo | (f) Local wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iv) Wind | (c) The horizontal movement of air |
4. Give reasons.
(i) Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day?
Answer:
Wet clothes take longer to dry on a humid day because the air already contains a lot of water vapour. It cannot absorb much more moisture from the wet clothes, so the rate of evaporation decreases and the process of drying takes longer.
(ii) Amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards poles?
Answer:
The amount of insolation decreases from the equator to the poles because the vertical rays of the sun fall on the equator covering less space, while slanting sun rays fall on the poles covering more space. So, the earth absorbs more solar energy at the equator than it does at the poles causing differences in insolation.
5. For Fun
(i) Solve this crossword puzzle with the help of given clues:
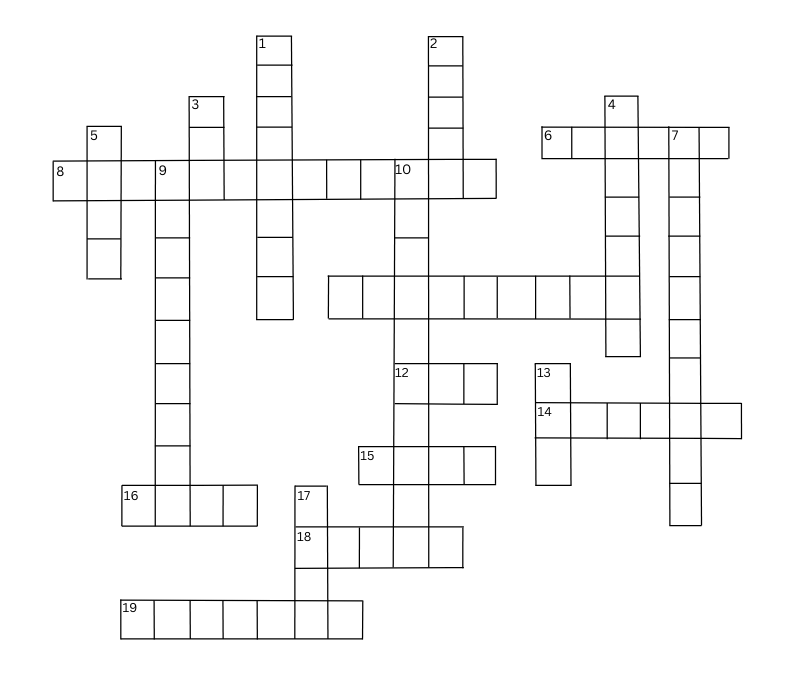
Across:
6. An Indian tree having extraordinary quality of providing oxygen round the clock. – Peepal
8. Gas present in atmosphere occupying only 0.03% by volume – Carbon dioxide
11. Outermost layer of atmosphere- exosphere
12. Mixture of many gases –air
14. Life giving gas – oxygen
15. Air in motion – wind
16. An indian tree valued highly for medicinal properties – Neem
18. Gas protecting us from harmful sun rays – Ozone
19. Low pressure area – Cyclone
Down
1. Amount of water vapour in air – Humidity
2. Condensation of water vapours around dust particles in atmosphere – Cloud
3. Example of local wind blowing in summer in northern India – Loo
4. Short term changes in atmosphere – Weather
5. Precipitation in liquid form – Rain
7. Blanket of air around the earth – Atmosphere
9. Instrument to measure pressure – Barometer
10. Incoming solar radiation – Insolation
13. Reduces visibility in winters – Fog
17. It is time when sun is overhead – Noon
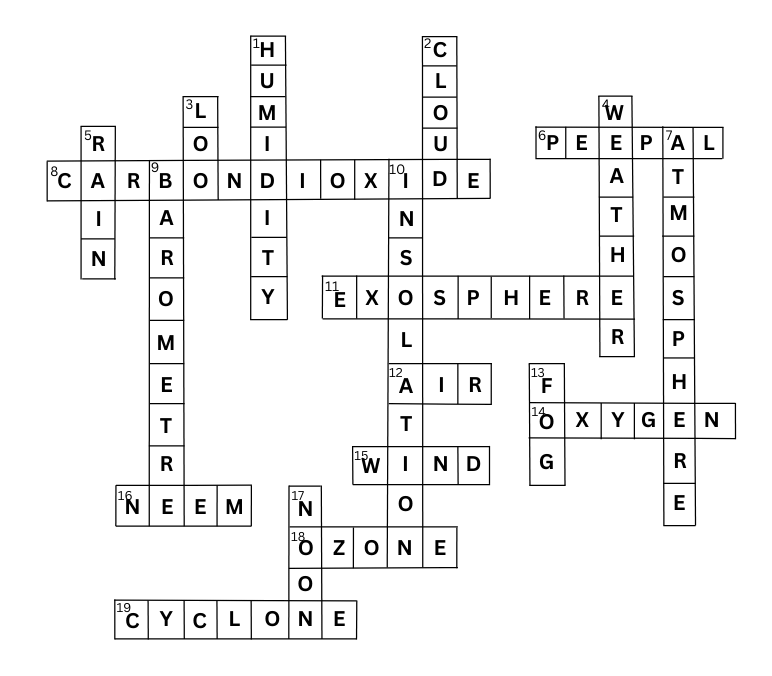
(ii) Make a weather calendar for one week. Use pictures on symbols to show different types of weather. You can use more than one symbol in a day, if the weather changes. For example the sun comes out when rain stops. An example is given below:
Answer:
Extra Questions NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 4 ‘Air”
A. Multiple Choice type Questions (MCQ)
1. What is the function of the atmosphere?
(i) it provides us with the air we breathe
(ii) it protects us from the harmful effects of the sun’s rays
(iii) it makes the earth inhabitable
(iv) all of the above
2. Which gas is most plentiful?
(i) argon
(ii) nitrogen
(iii) carbon dioxide
(iv) None of the above
3. Carbon dioxide constitutes ____% of the atmosphere.
(i) )0.93%
(ii) 21%
(iii) 0.39 %
(iv) 0.3%
4. Why does cold air sink?
(i) because it freezes
(ii) because it is denser and heavy
(ii) because it is light
(iv) None of the above
5. Which of the following human activities does not harm the environment?
(i) burning leaves
(ii) planting saplings
(iii) using plastic
(iv) running industries
6. Which layer of the atmosphere contains a layer of ozone?
(i) exosphere
(ii) Mesosphere
(iii) troposhere
(iv) None of the above
7. In which layer of the atmosphere would you find the ionosphere?
(i) exosphere
(ii) mesosphere
(iii) thermosphere
(iv)None of the above
8. The thermosphere extends between ______________.
(i) 90 – 370 km
(ii) 100 – 350 km
(iii) 50 – 300 km
(iv) 80 – 400 km
9. The instrument which measures pressure is_______.
(i) Barometer
(ii) Thermometer
(iii) Wind vane
(iv) None of these
10. Which of the following are local winds?
(i) westerlies
(ii) loo
(iii) land and sea breeze
(iv) Both (ii) and (iii) above
Answer:
1. (iv) all of the above
2. (ii) nitrogen
3. (iv) 0.3%
4. (ii) because it is denser and heavy
5. (ii) planting saplings
6. (iv) None of the above
7. (iii) thermosphere
8. (iv) 80 – 400 km
9. (i) Barometer
10. (iv) Both (ii) and (iii) above
B. Fill in the blanks with suitable words to complete the following sentences:
| air | altitude | trade | precipitation | highest | wind | humidity |
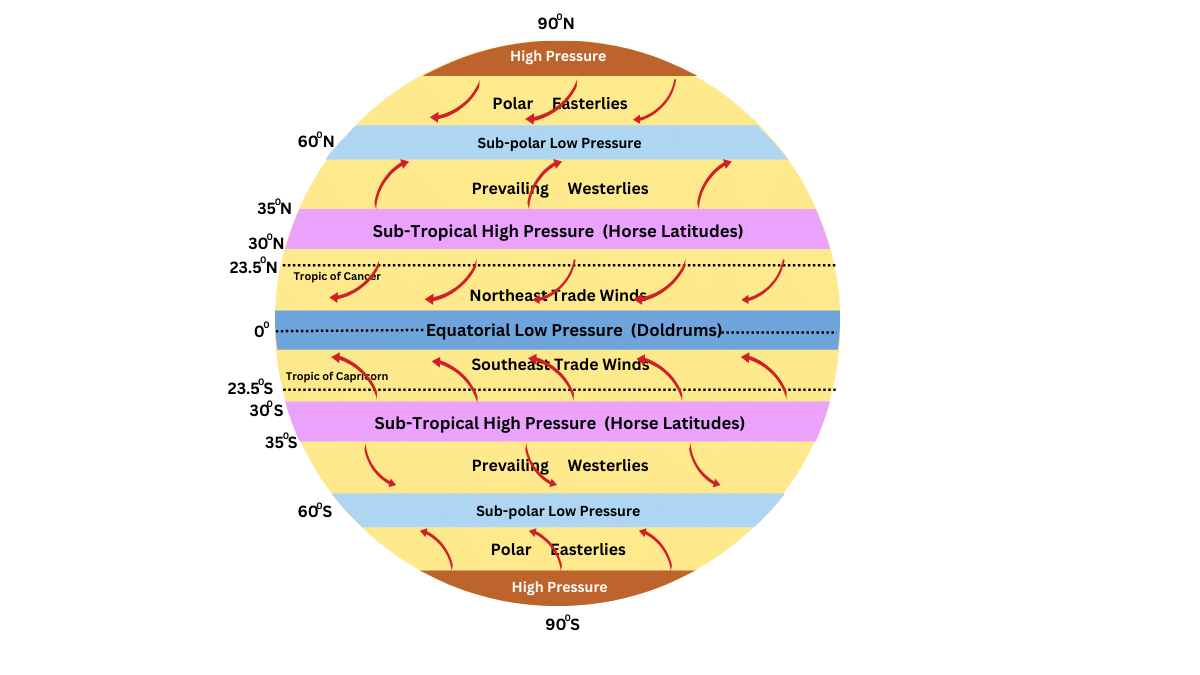
1. The _________ winds are permanent winds which blow constantly throughout the year.
2. The air pressure is the __________ at sea level and decreases with __________.
3.The movement of _______from high pressure to low pressure areas is called _____.
4. Moisture in the air at any time is known as _____________.
5.____________that comes down to earth in liquid form is known as rain.
Answer:
1. The trade winds are permanent winds which blow constantly throughout the year.
2. The air pressure is the highest at sea level and decreases with altitude..
3.The movement of air from high pressure to low pressure areas is called wind.
4. Moisture in the air at any time is known as humidity.
5. Precipitation that comes down to earth in liquid form is known as rain.
C. Match the words in column A with those in column B
| A | B |
| Troposphere | Meteorites burn up in this layer while entering space |
| Stratosphere | Ionosphere is a part of this layer |
| Mesosphere | The upper most layer of the atmosphere |
| Thermosphere | The air we breathe exists here |
| Exosphere | Contains a layer of ozone gas |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Troposphere | The air we breathe exists here |
| Stratosphere | Contains a layer of ozone gas |
| Mesosphere | Meteorites burn up in this layer on entering from space |
| Thermosphere | Ionosphere is a part of this layer |
| exosphere | The upper most layer of the atmosphere |
D. State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE:
1. An important factor that influences the distribution of temperature is insolation.
2. As we go up the layers of atmosphere, the pressure increases rapidly.
3. The average weather condition of a place for a longer period of time represents the climate of the place.
4. Green plants produce carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
5. Apart from the gases, dust particles are also present in the air.
Answer:
1. True
2. False – As we go up the layers of atmosphere, the pressure decreases rapidly.
3. True
4. False – Green Plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and release oxygen during photosynthesis.
5. True
E. Very Short Answer type Questions:
1. Why is carbon dioxide called a greenhouse gas?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is called a greenhouse gas because it creates a greenhouse effect by trapping the heat radiated from the earth.
2. Why are greenhouse gases essential?
Answer:
Without the greenhouse gases, the earth would have been too cold to live in.
3. What happens if the level of carbon dioxide increases due to factory smoke or car fumes?
Answer:
The temperature of the earth rises resulting in global warming.
4. Which is the most plentiful gas in the atmosphere?
Answer:
Nitrogen is the most plentiful gas in the atmosphere.
5. What happens when air is heated?
Answer:
Air expands, becomes lighter and rises when heated.
6. What is temperature?
Answer:
The degree of hotness or coldness of the air is known as temperature.
7. What is insolation?
Answer:
Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.
8. What is the standard unit for measuring temperature?
Answer:
The standard unit for measuring temperature is degree Celsius.
9. What are the freezing point and boiling point of water on the Celsius scale?
Answer:
The freezing point of water is 00C and the boiling point of water is 1000C on the Celsius scale.
10. How do green plants use carbon dioxide?
Answer:
Green plants use carbon dioxide during photosynthesis to make their food and release oxygen.
11. In which layer of the atmosphere do all weather phenomena occur?
Answer:
The troposphere is the layer where all weather phenomena like rainfall, fog, hailstorm occur.
12. Why is layer of ozone gas in the stratosphere important for us?
Answer:
The ozone layer protects us from the harmful effect of the sun rays.
13. What is air pressure?
Answer:
Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface.
14. What is the relationship between air pressure and altitude?
Answer:
The air pressure decreases as the altitude increases.
15. Why is there no air pressure on the moon?
Answer:
There is no air pressure on the moon because there is no air on the moon.
16. Why are cold regions high pressure areas?
Answer:
Cold air, which is dense and heavy, sinks creating high pressure.
17. How does air move?
Answer:
Air moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
18. What is wind?
Answer:
The movement of air from high pressure areas to low pressure areas is called wind.
19. How is a wind named?
Answer:
A wind is named after the direction from which it blows.
20. What is called humidity?
Answer:
Moisture in the air at any time is known as humidity.
F. Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is the atmosphere composed of?
Answer:
The atmosphere is composed mainly of two gases—nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Other gases like carbon dioxide (0.3%), argon(0.93%), helium, ozone, and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities. Apart from these gases, tiny dust particles are also present in the air.
2. What is global warming? What are the effects of global warming?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide released in the atmosphere creates a greenhouse effect by trapping the heat radiated from the earth. However, when the level of carbon dioxide in the air increases due to factory smoke or car fumes, the heat retained increases the temperature of the earth. This is called global warming.
The rise in temperature causes the snow in the coldest parts of the earth to melt. As a result, the sea level rises causing floods in the coastal areas. There may be drastic changes in the climate of a place leading to the extinction of some plant and animal species in the long run.
3. How does the ozone layer protect us?
Answer:
The ozone layer is a high concentration of ozone found in the stratosphere about 15 to 30 kilometers above the earth’s surface. It protects us and other living organisms from the harmful Ultra Violet rays of the sun.
4. How do bacteria help plants use nitrogen?
Answer:
Plants need nitrogen for their survival. But, plants cannot absorb nitrogen directly from the air. Bacteria, that live in the soil and roots of some plants, take nitrogen from the air and change its form so that plants can use it.
5. Discuss how nature balances our life? What is the result if this balance is disturbed?
Answer:
Human beings and animals take in oxygen from the air as they breathe in, and release carbon dioxide as they breathe out. Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and release oxygen. The amount of carbon dioxide released by humans or animals seems to be equal to the amount used by the plants creating a perfect balance.
But this balance is disturbed by the burning of fuels such as coal and oil, which add billions of tons of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere each year. As a result, the increased volume of carbon dioxide is affecting the earth’s weather and climate.
6. Where is the ionosphere found? What is its function?
Answer:
The ionosphere is a part of the thermosphere. It extends from 80 to 400 km above the earth. This layer helps in radio transmission. The radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by the ionosphere.
7. Why is temperature in cities much higher than that of villages?
Answer:
In cities the temperature is much higher than that in villages. The concrete and metals in buildings and the asphalt of roads get heated up during the day. This heat is released during the night.
Another reason is that the crowded high-rise buildings of the cities trap the warm air and thus raise the temperature of the cities. There are also a lot of vehicles on city roads which emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases to raise the temperature in cities.
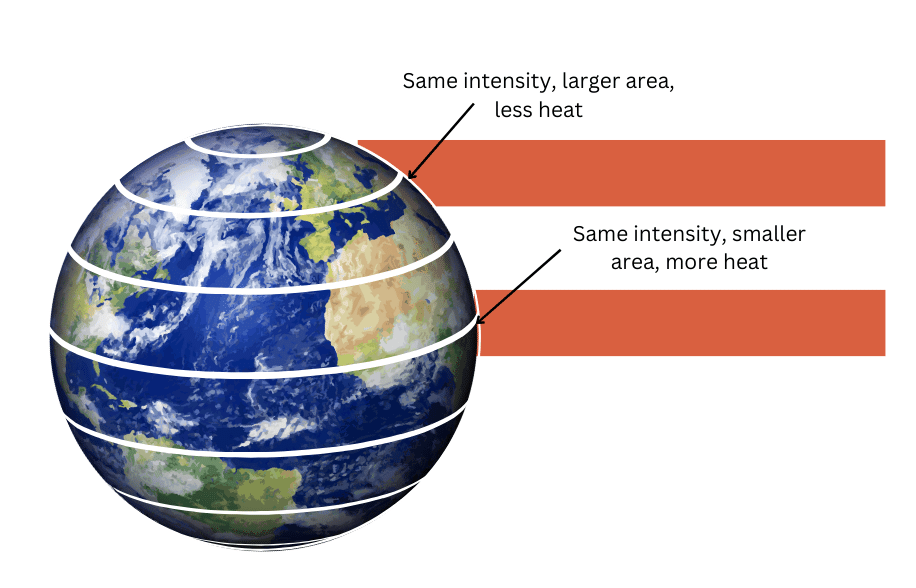
8. What is insolation? How does it affect the temperature of a place?
Answer:
Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by earth.
An important factor that influences the distribution of temperature is insolation. The amount of insolation decreases from the equator to the poles. This happens because the vertical rays of the sun which fall on the equator, cover less space and heat up a smaller area intensely. On the other hand, the slanting sun rays, which fall on the poles, cover more space so the heat is spread over a larger area making the polar region cooler. The earth absorbs more solar energy at the equator than it does at the poles causing differences in temperature.
10. Why do astronauts wear special protective suits when they go to the moon?
Answer:
Since there is no air on the moon, there is no air pressure exerted either. But our bodies exert a pressure from inside to counter the pressure of air which presses us with great force from all directions on earth. Astronauts have to wear special protective space suits filled with air when they go to the moon. If they did not wear these space suits, the counter pressure exerted by the body of the astronauts would make the blood vessels burst and the astronauts would bleed.
11. What happens when air is heated?
Answer:
When air is heated it expands, becomes lighter and rises. Cold air is denser and heavy, so it tends to sink down. When hot air rises, cold air from the surrounding area rushes in to fill the empty space created. This is how air circulation takes place.
12. What is wind? What are the different kinds of wind?
Answer:
The movement of air from high pressure to low pressure areas is called wind. A wind is named after the direction from which is blows, for example, the wind blowing from the west is called a westerly.
Winds can be divided into three types as follows:
- Permanent winds
These winds blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction. The trade winds, the westerlies and the easterlies are the permanent winds. - Seasonal winds
These winds change their direction in different seasons. For example, the monsoons in India. - Local winds
These blow only during a particular period of the day or year in a small area. For example, land and sea breeze, or the hot and dry local wind of northern India called ‘Loo’.
13. What is humidity? What happens when the air gets warmer?
Answer:
When water evaporates from seas, rivers and different water bodies, water vapour is formed and the air becomes moist. Moisture in the air is known as humidity. When the air is full of water vapour we call it a humid day.
As the air gets warmer, its capacity to hold water increases, so it becomes more and more humid. On a humid day, clothes take longer to dry and sweat from our body does not evaporate easily.
14. What is precipitation?
Answer:
When water vapour rises it becomes cooler and condenses to form droplets of water. Clouds are masses of such droplets of water. When these droplets become too heavy to float in air, they come down as precipitation. Precipitation which comes down in liquid form is called rain. Other forms of precipitation are snow, hail or sleet.
15. What are the different kinds of rainfall?
Answer:
The different kinds of rainfall are as follows:
1. Convectional rainfall
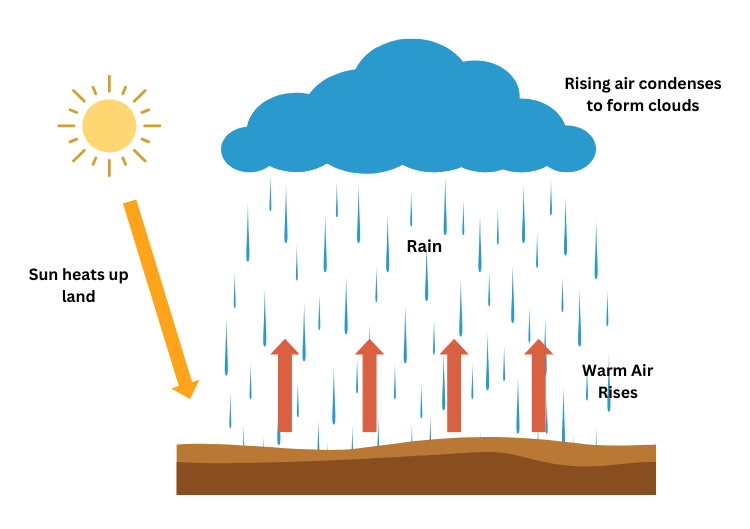
2. Relief or orographic rainfall
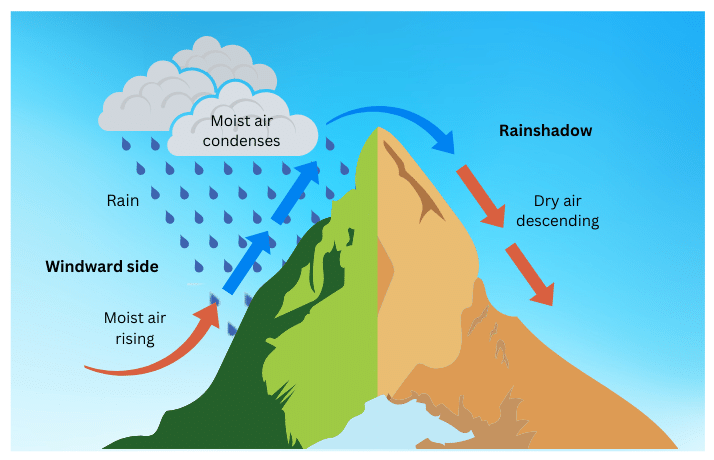
3. Cyclonic Rainfall
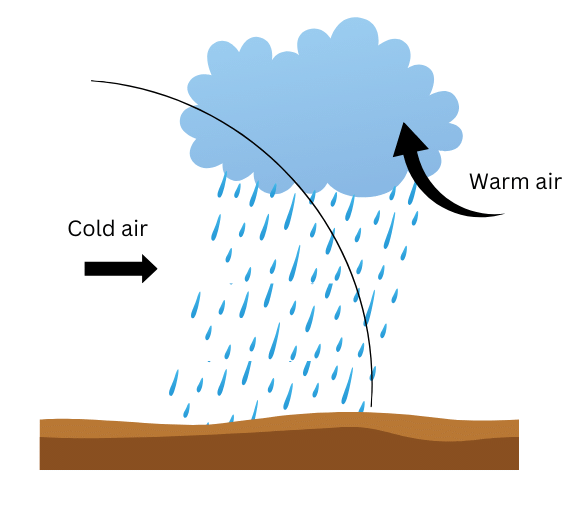
16. Why is rainfall necessary for life on earth? What happens when there is excess rain?
Answer:
Rainfall is very important for the survival of plants and animals. It brings fresh water to the earth’s surface. If rainfall is less, there is water scarcity and sometimes droughts occur. If there is excess rain, floods take place which can be devastating.
G. Long Answer Type Questions
1. Discuss the different layers of the atmosphere
Answer:
Our atmosphere is divided into five different layers starting from the earth’s surface which are as follows:
- Troposphere: This is the most important layer of the atmosphere with an average height of 13 km from the earth. It is in this layer that we find the air that we breathe. Almost all the weather phenomena such as rainfall, fog, and hailstorm occur in this layer.
- Stratosphere: This layer extends up to a height of 50 km. It is free from clouds and associated weather phenomenon. It presents the most ideal conditions for flying aeroplanes. It contains a layer of ozone gas which protects us from the harmful effects of the sunrays.
- Mesosphere: This layer extends up to a height of 80 km. Meteorites bum up in this layer on entering from the space.
- Thermosphere: In this layer, the temperature rises very rapidly with increasing height. The ionosphere is a part of this layer. It extends between 80—400 km. This layer helps in radio transmission. Radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by this layer.
- Exosphere: It is the uppermost layer where there is very thin air. Light gases such as helium and hydrogen float into space from here.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Class 7 Geography Our Environment Chapter 4 ‘Air”
These solutions and extra material have been designed by an expert team of Indian and foreign-educated subject teachers. They have designed them logically and scientifically to ensure maximum learning and retention. All the techniques you need to know are explained with attractive figures wherever necessary. You will find similar concepts and problems in your exams, so practise them on your own as well.
The free PDFs of the solutions are available for download anytime! If you like our material and want plenty more from us, keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list. We will send all the latest study material and other resources that you need straight to your inbox!
The main topics covered in Chapter 4 of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography are:
Composition of the Atmosphere
Structure of the Atmosphere:
Troposphere
Mesosphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Exosphere
Weather and Climate
Temperature
Air pressure
Wind
Moisture
How does carbon dioxide create greenhouse effect?
How do green plants use carbon dioxide?
How is the ozone layer important for us?
What is humidity?
How is the flooding of low-lying areas caused?
What is the composition of the atmosphere?
How do bacteria help plants use nitrogen?
How does nature balance our life? What is the result if this balance is disturbed?
Write a short note on air pressure.
How is rainfall important for us? What happens when there is excess rain?
Describe the different layers of the atmosphere.
What is wind? Mention the different type of wind.
Yes of course! You can download the PDF version of educationroundtheworld.com’s NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter “Air’ anytime you please! The solutions including the self-designed extra questions are included in the PDF version! Please look towards the top of the page to find the download button!
Absolutely! Our team of highly skilled subject teachers has thoughtfully anticipated all the questions you might have about the lesson. They have created outstanding solutions that highlight every detail and explain the essence of the chapter.
We recommend that you first read the lesson thoroughly and then review the solutions, absorbing all the details. Our experienced experts have also provided numerous extra questions that resemble exam questions, designed to give you ample practice.
Make sure to go through the solutions before the exam and practice writing some answers within a specified time limit. This step is crucial, as practice not only leads to perfection but also enhances your self-confidence. You’ll be well-prepared to tackle any challenge your examiner might present! Best of luck!
Alongside rigorous training, our teachers also provide excellent counselling regarding your future academic and professional careers. We have found that this approach gives students confidence and prepares them well for their future.
We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Feel free to reach out to us with your requirements anytime and let us help you out! Book an online appointment now!


