Welcome students! Let us help you master Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes. We understand that clear step-by-step figures and concise explanations are needed to learn the concepts in this chapter. And we have done our best to give you exactly that. Feel free to go through our answers in detail – we are confident they will benefit you. After that go through the extra problem set we have included for additional practice.
Solutions to Exercise 13.1 (Page No 202) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes –
1. Identify the nets which can be used to make cubes (cut out copies of the nets and try it):
(i) The net is shown below:
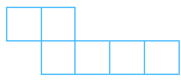
Answer: The net can be folded as follows:
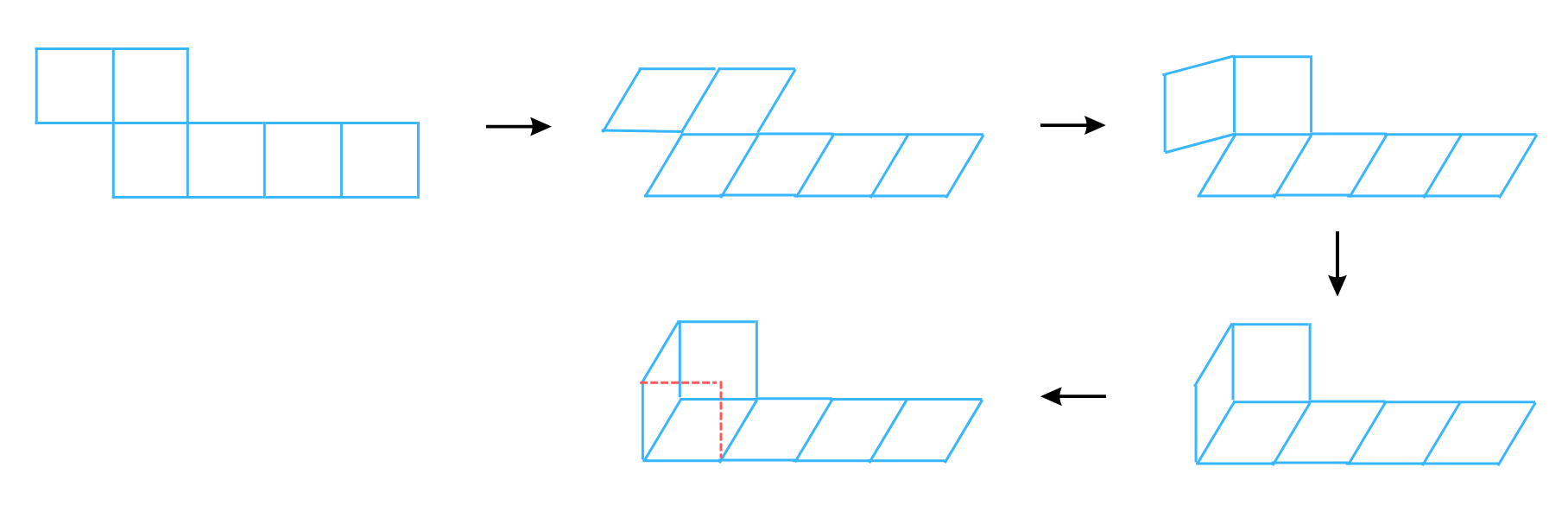
It is easy to see that after folding the face marked in red dotted lines remains empty. Therefore, the net cannot form a complete cube.
(ii) The net is shown below:
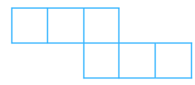
Answer:
The net can be folded as follows:
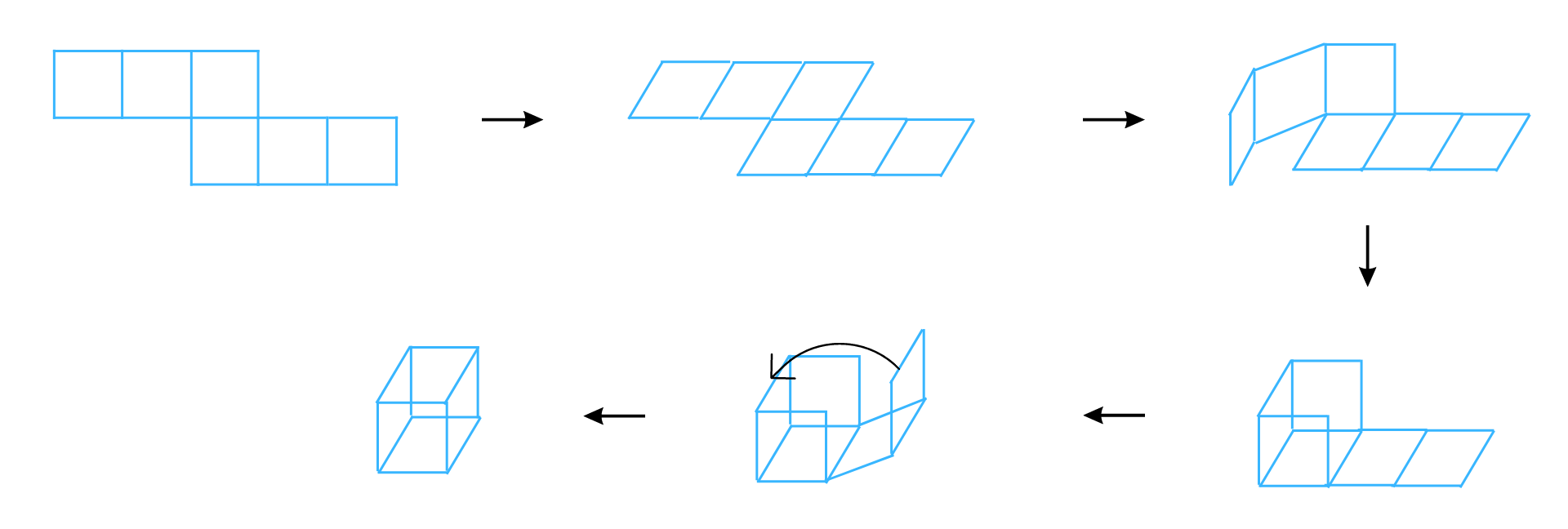
It is easy to see that after folding that the net forms a complete cube.
(iii) The net is shown below:
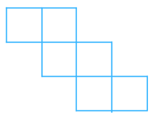
Answer: The net can be folded as follows:
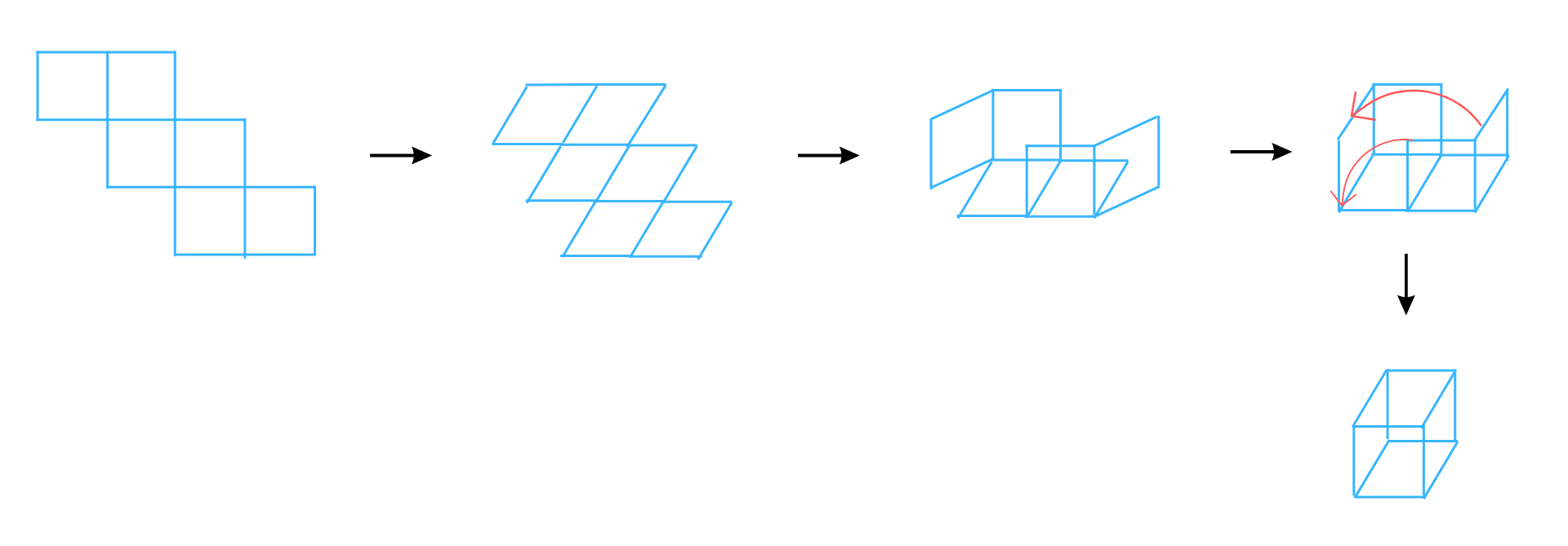
It is easy to see that after folding that the net forms a complete cube.
(iv) The net is shown below:
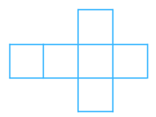
Answer: The net can be folded as follows:
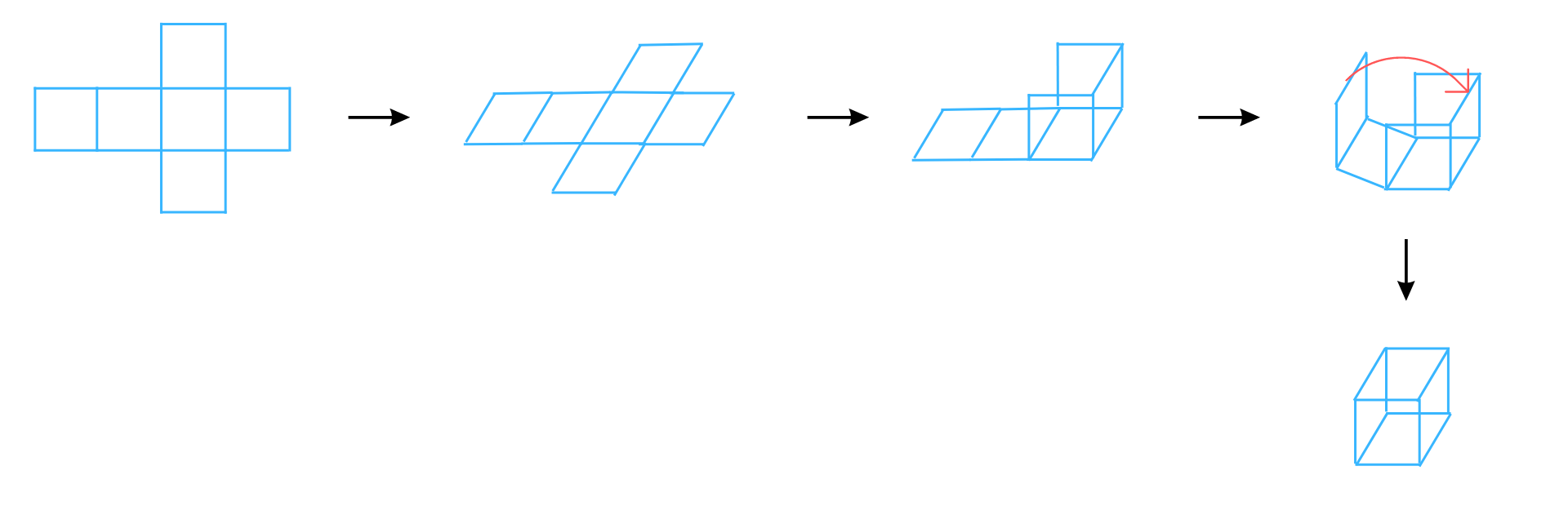
It is easy to see that after folding that the net forms a complete cube.
(v) The net is shown below:
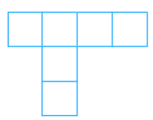
Answer:
The net can be folded as follows:
It is easy to see that after folding the face marked in red dotted lines remains empty. Therefore, the net cannot form a complete cube.
(vi) The net is shown below:
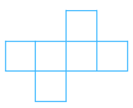
Answer: The net can be folded as follows:
It is easy to see that after folding that the net forms a complete cube.
Therefore, the nets (ii), (iii), (iv) and (vi) form cubes.
2. Dice are cubes with dots on each face. Opposite faces of a die always have a total of seven dots on them.
Here are two nets to make dice (cubes); the numbers inserted in each square indicate the number of dots in that box.

Insert suitable numbers in the blanks, remembering that the number on the opposite faces should total to 7.
Answers:
(i) The first net is shown below:

Answer: The net can be folded to form a cube (die) as follows:
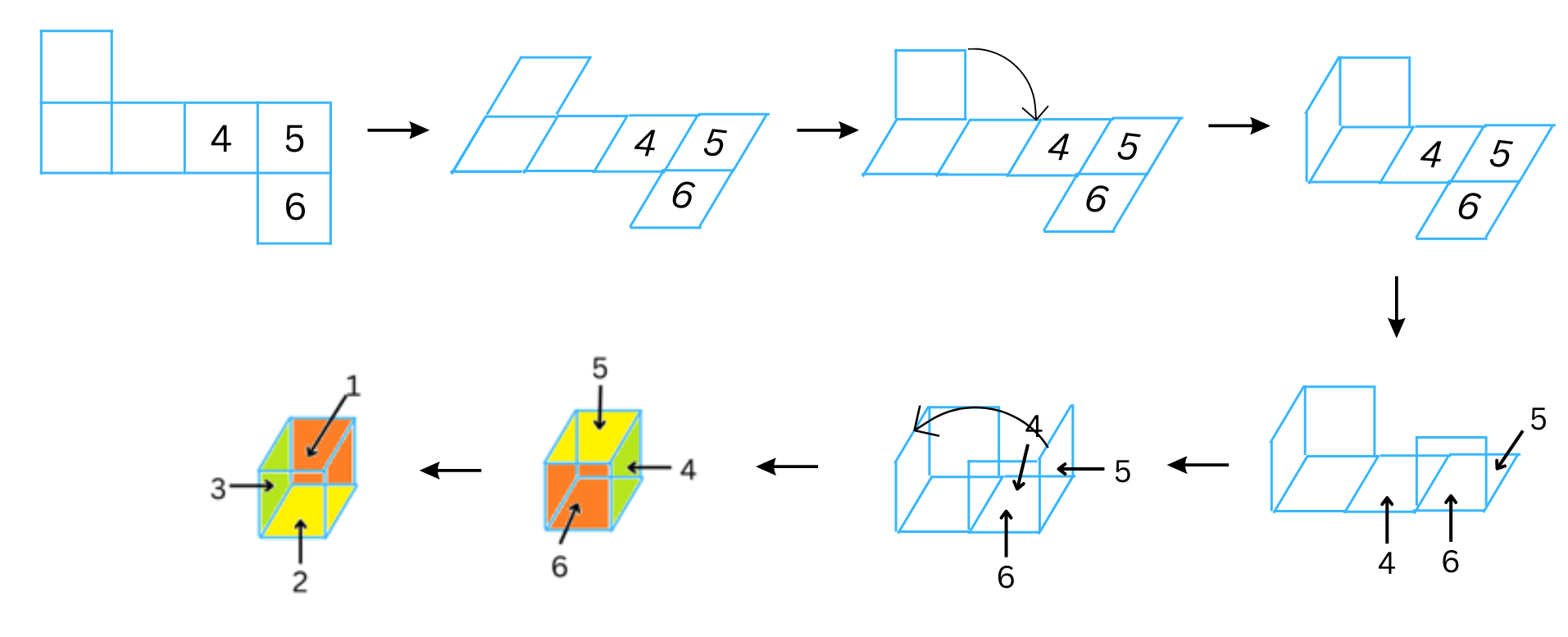
For the cube to form a real die, the sum of the numbers on the opposite faces should equal to 7. Therefore, the numbers 1, 2, 3 are assigned to the appropriate squares in the cube for this to happen. We note: 1 + 6 = 7, 3 + 4 = 7, 2 + 5 = 7. We have shaded the opposite faces of the die with the same colour.
Now, to confirm where the numbers 1, 2, 3 should be on the net, we open the cube (die) again to reform the original net.
Please find the completed net with the right numbers in the right places above.
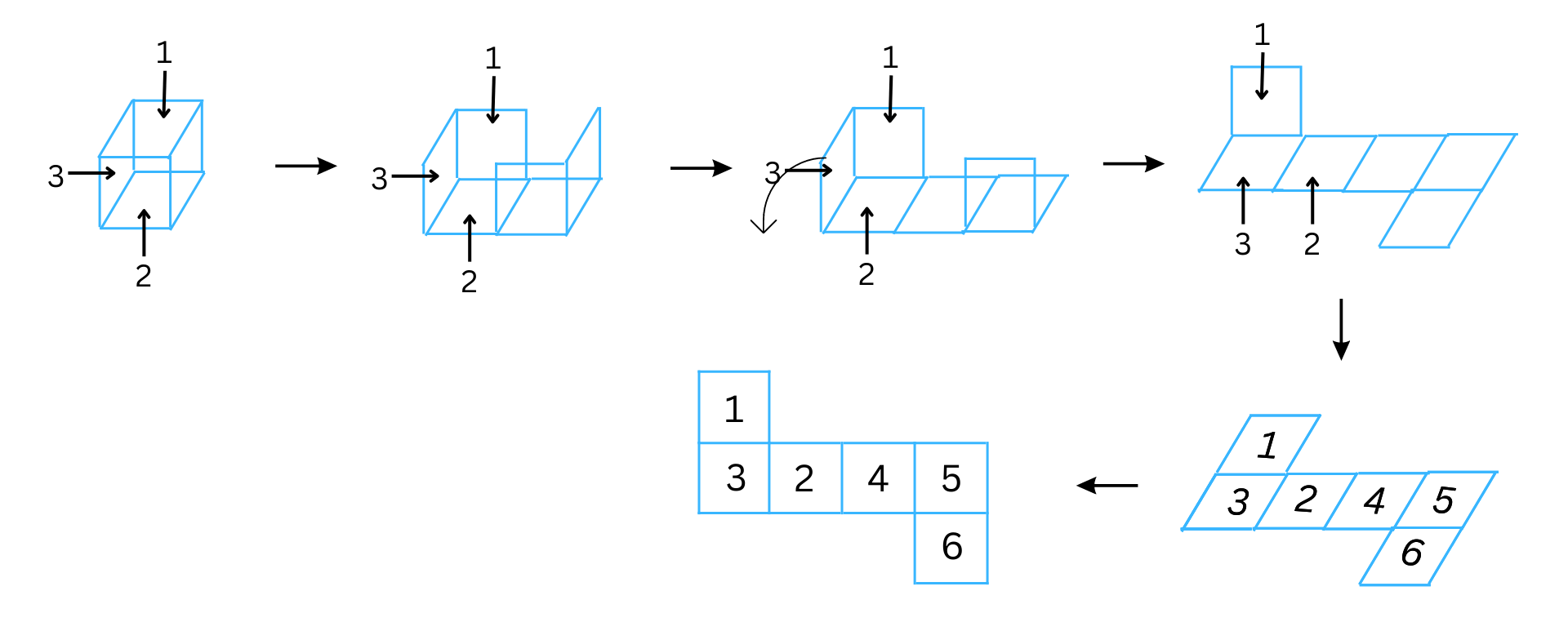
(ii) The second net is shown below:
The net can be folded to form a cube (die) as follows:
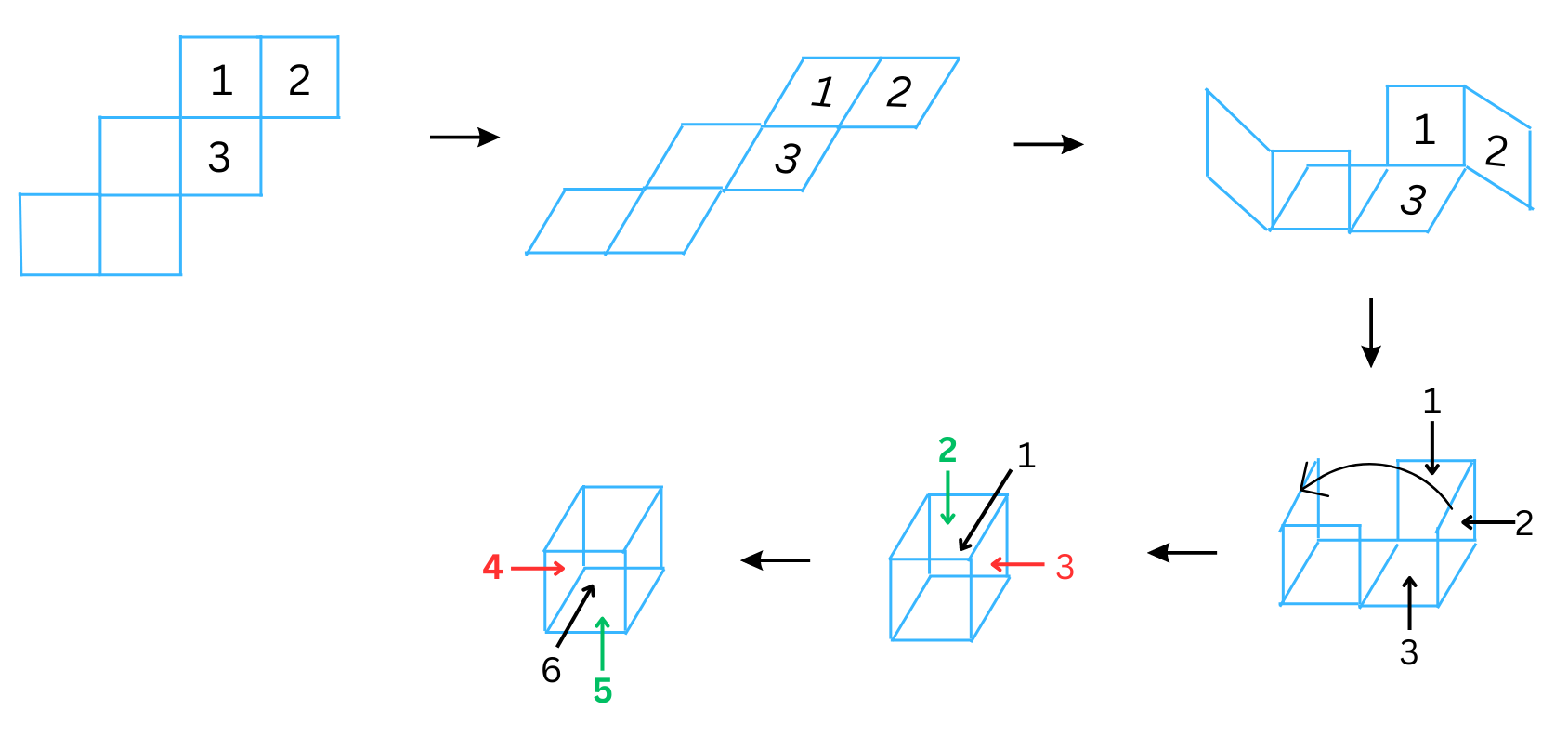
For the cube to form a real die, the sum of the numbers on the opposite faces should equal to 7. Therefore, the numbers 4, 5, 6 are assigned to the appropriate squares in the cube for this to happen. We note 6 + 1 = 7, 4 + 3 = 7, 5 + 2 = 7. We have shaded the numbers and arrows corresponding to the opposite faces of the die with the same colour.
Now, to confirm where the numbers 4, 5, 6 should be on the net, we open the cube (die) again to reform the original net.
Please find the completed net with the right numbers in the right places above.
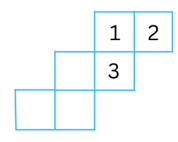
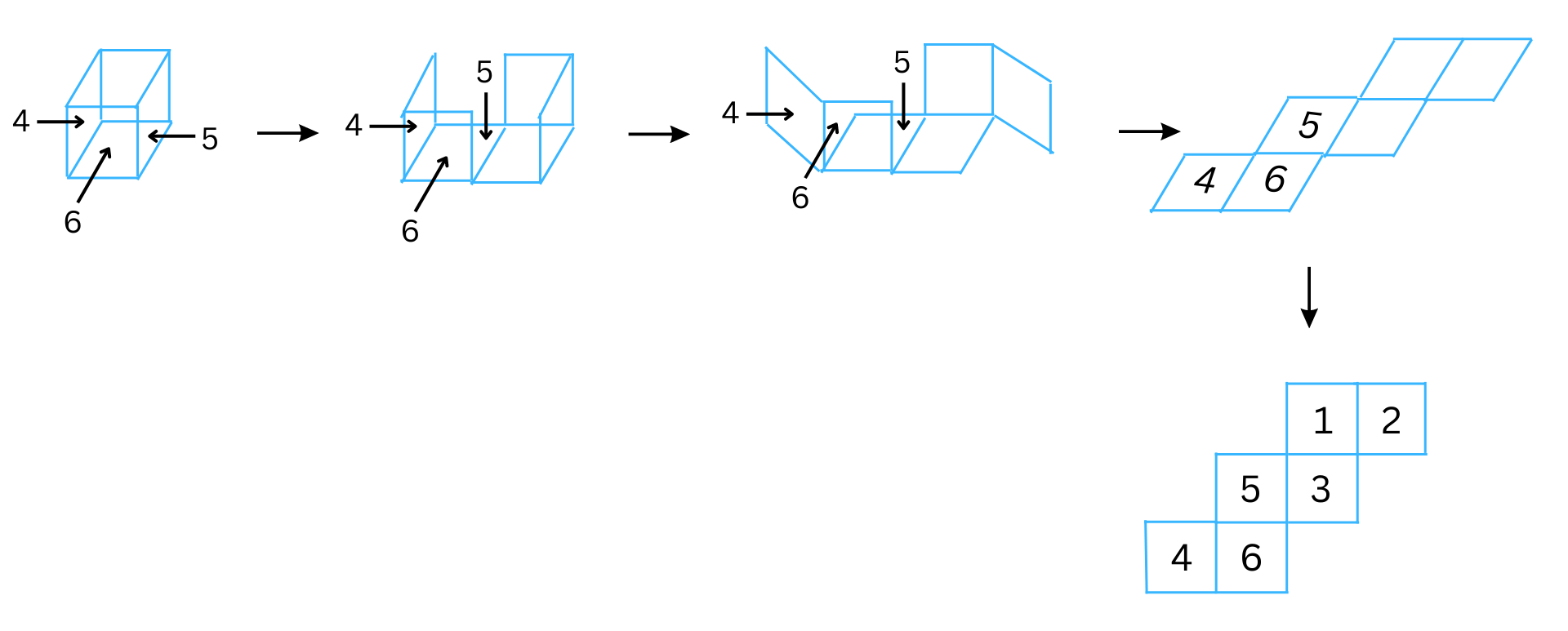
3. Can this be a net for a die?
Explain your answer.
Answer: The net can be folded to form a cube (die) as follows:
For the cube to form a real die, the sum of the numbers on the opposite faces should equal to 7. We have shaded the numbers and arrows corresponding to the opposite faces of the die with the same colour. We note that the sum of the numbers on the opposite faces are as follows: 1 + 4 = 5, 5 + 2 = 7, 6 + 3 = 9. We can see that the numbers on the opposite faces don’t add up to 7 in two cases. Therefore, a die cannot be formed with the given net.
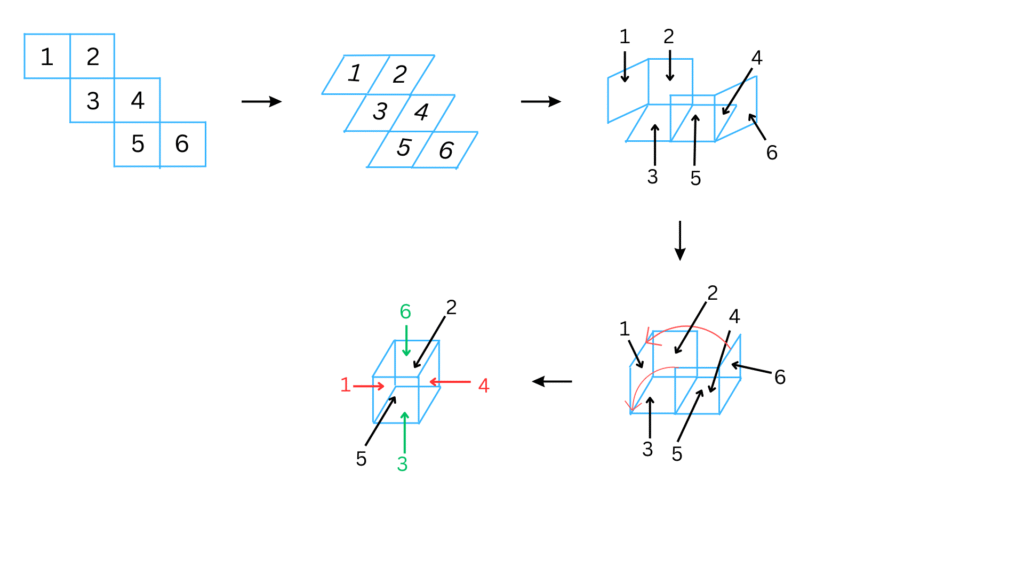
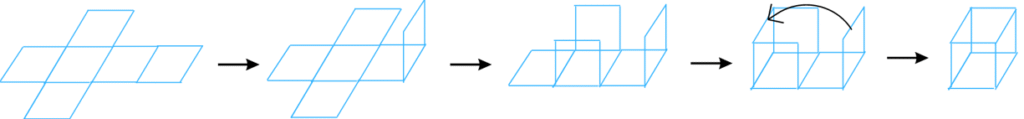
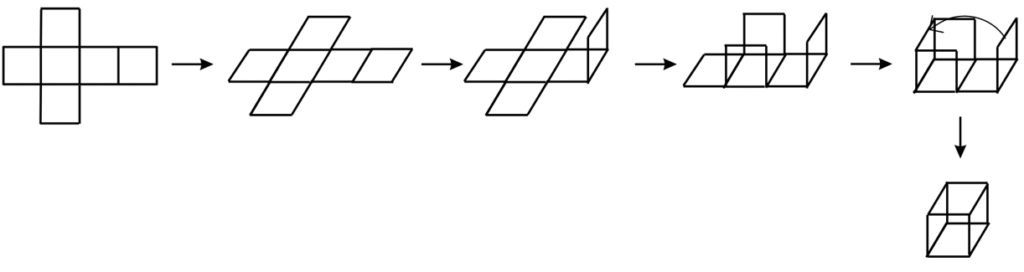
4. Here is an incomplete net for making a cube. Complete it in at least two different ways. Remember that a cube has six faces. How many are there in the net here?
(Give two separate diagrams. If you like, you may use a squared sheet for easy manipulation.)

Answer: A cube has six faces. The net give in the question has 3 faces.
The first net is shown below:

The above net can be folded in the following ways to form a cube:
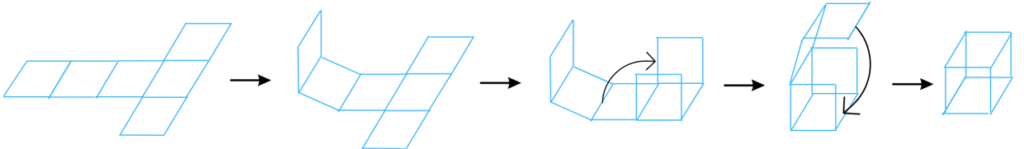
The second net is shown below:

The above net can be folded in the following ways to form a cube:
5. Match the nets with appropriate solids:
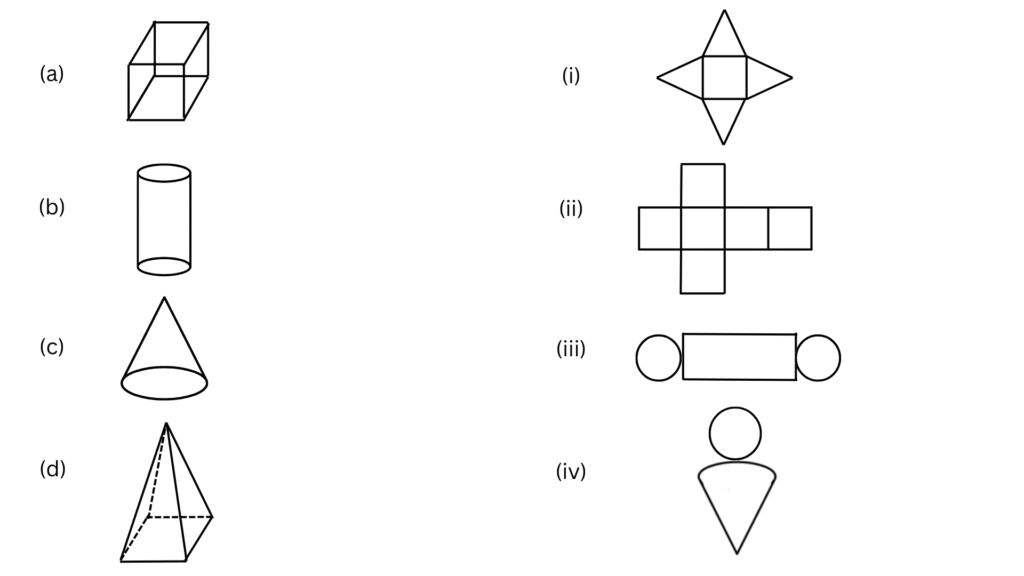
Answer:
(a) can be matched with (ii). The net can be folded as shown below:
(b) can be matched with (iii). The net can be folded as shown below:
(c) can be matched with (iv). The net can be folded as shown below:
(d) can be matched with (i). The net can be folded as shown below:
Solutions to Exercise 13.2 (Page No 206) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes –
1. Use isometric dot paper and make an isometric sketch for each one of the given shapes:
(i) The oblique sketch is shown below:
The corresponding isometric sketch is shown below:
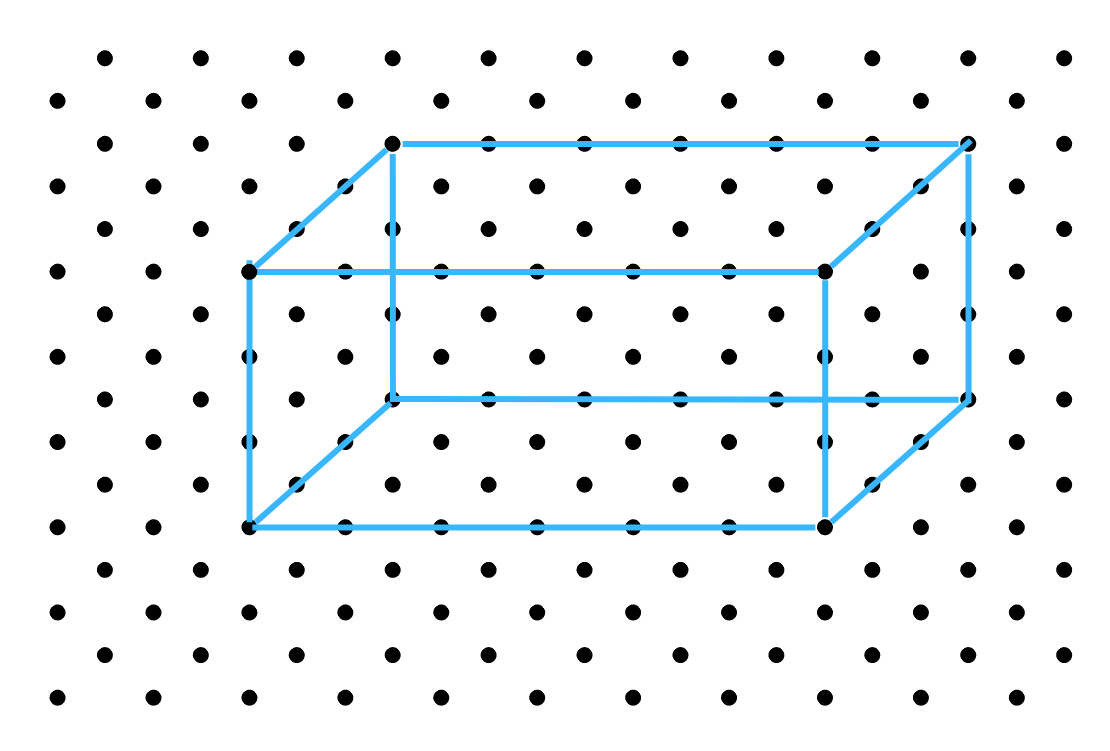
(ii) The oblique sketch is shown below:
The corresponding isometric sketch is shown below:

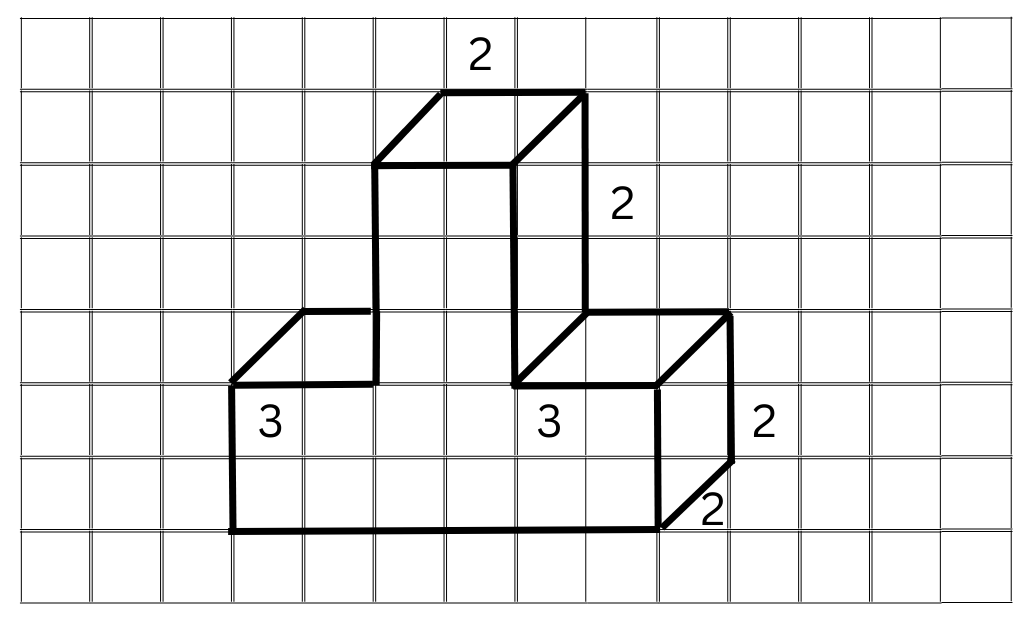
(iii) The oblique sketch is shown below:
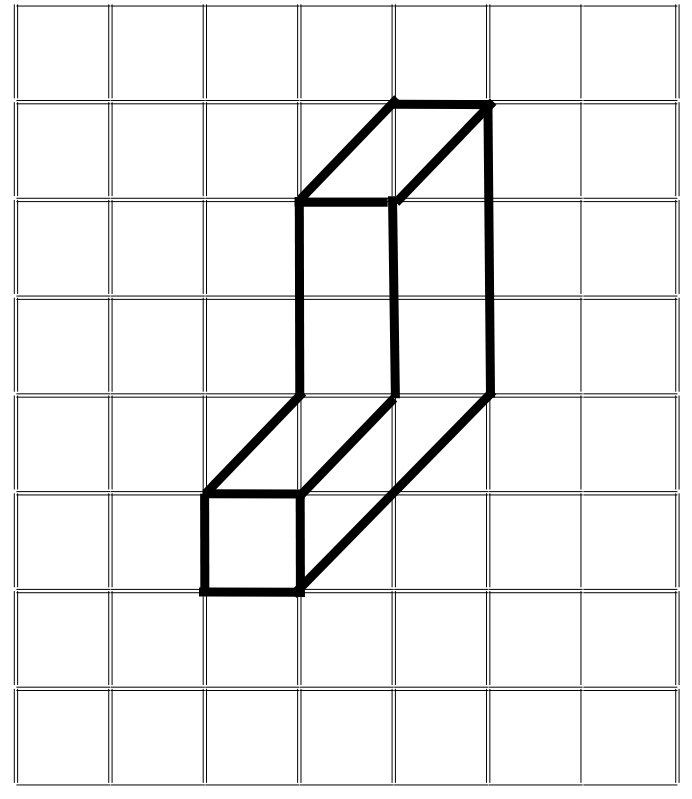
The corresponding isometric sketch is shown below:
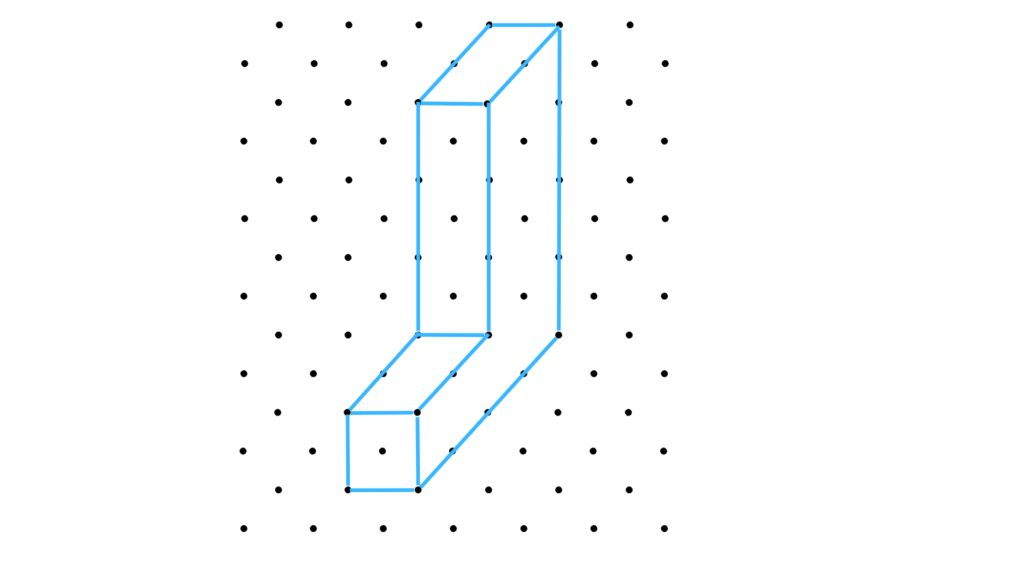
(iv) The oblique sketch is shown below:
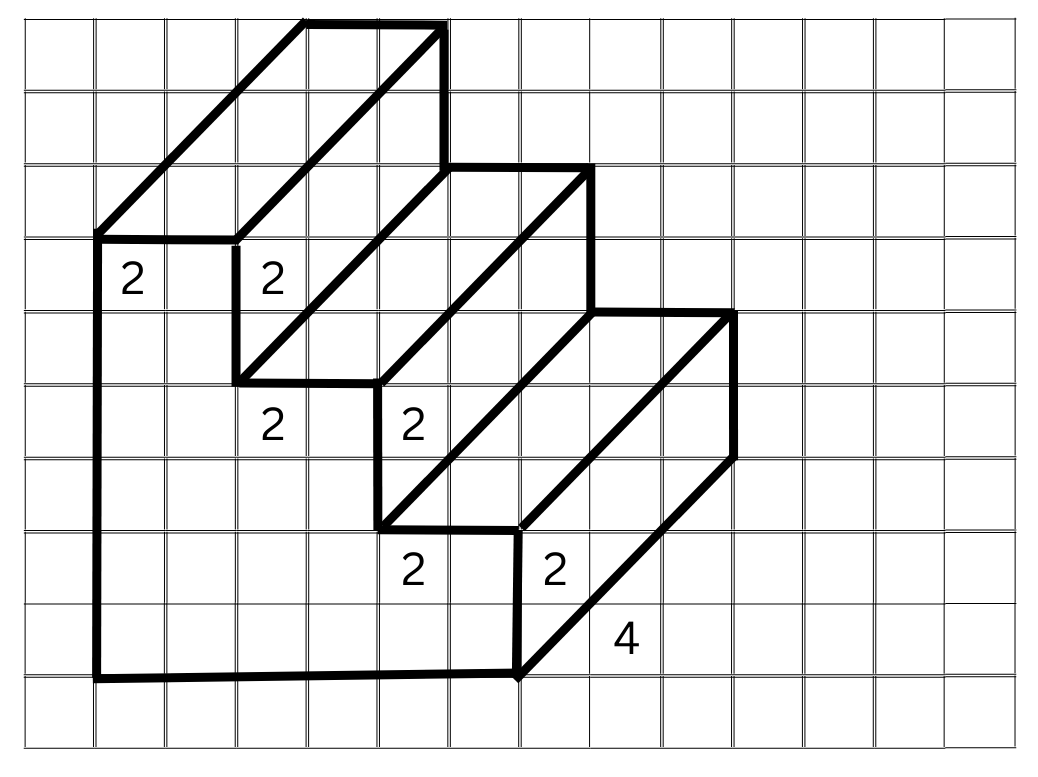
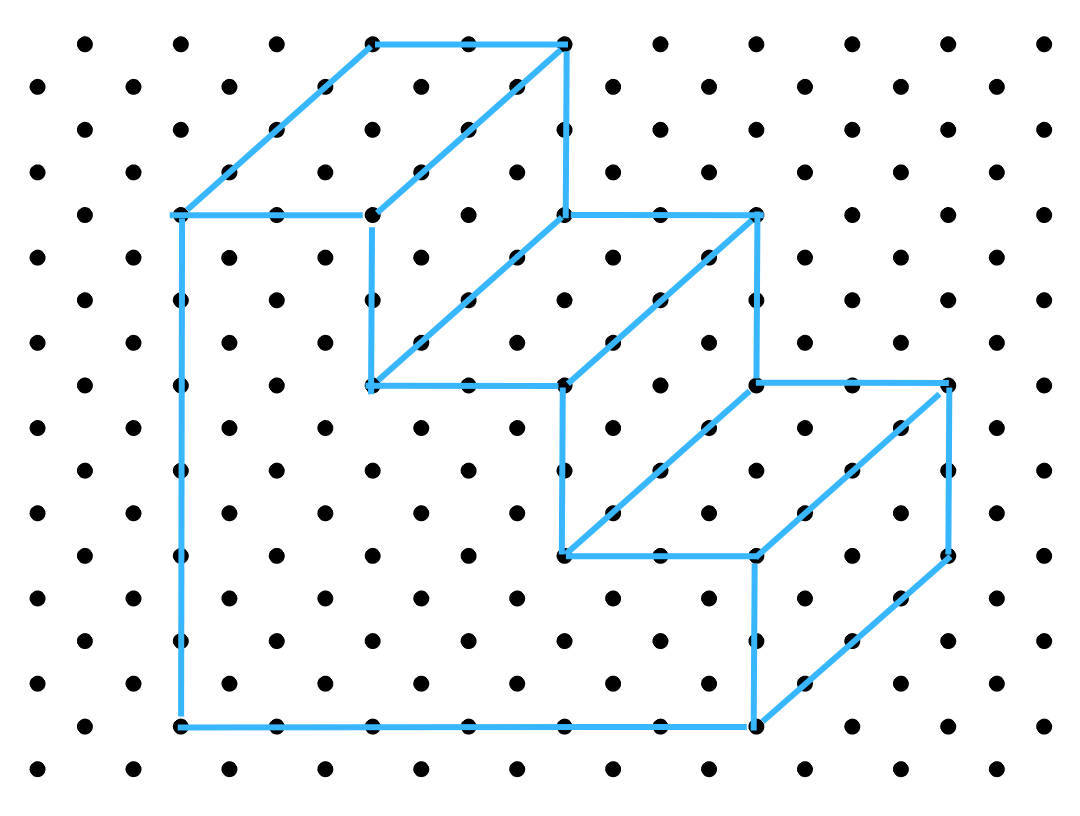
The corresponding isometric sketch is shown below:
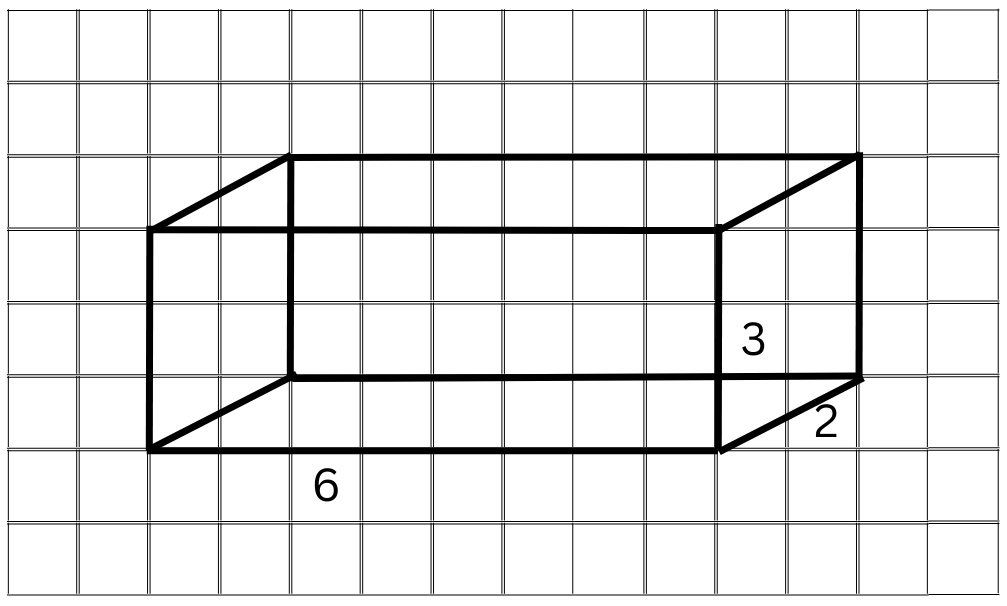
2. The dimensions of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm. Draw three different isometric sketches of this cuboid.
Answer: We use the dimensions of the cuboid: 5 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm and an isometric dot sheet to draw the three different isometric sketches of the cuboid:
The first sketch is as follows:
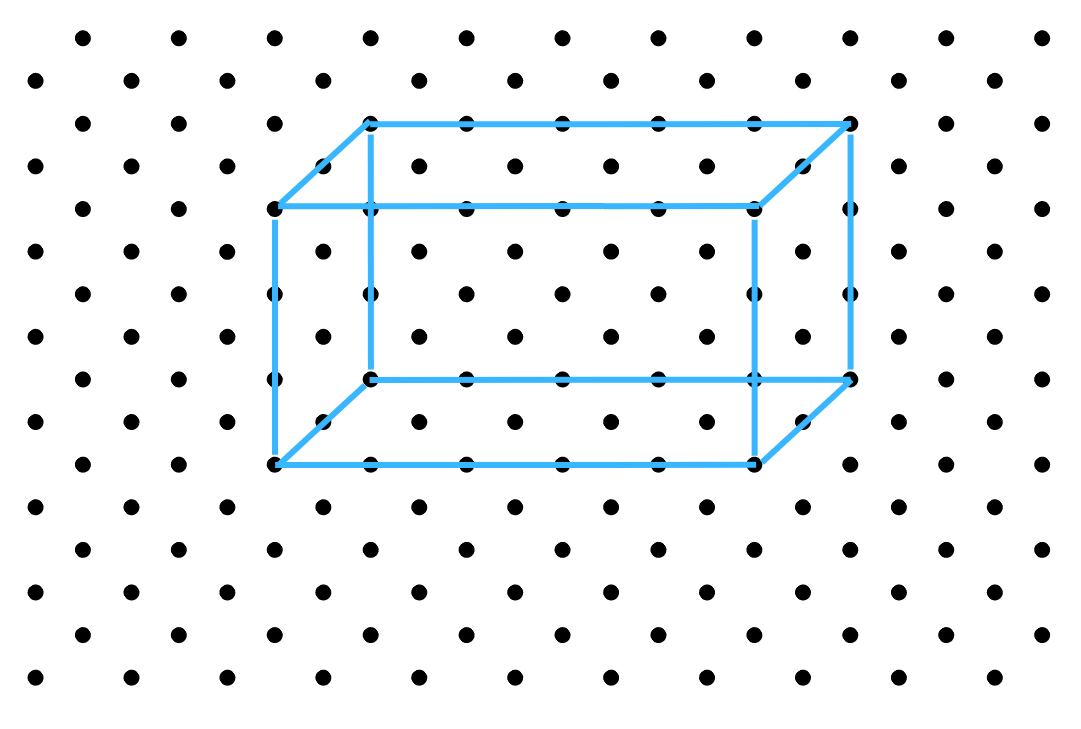
The second sketch is as follows:
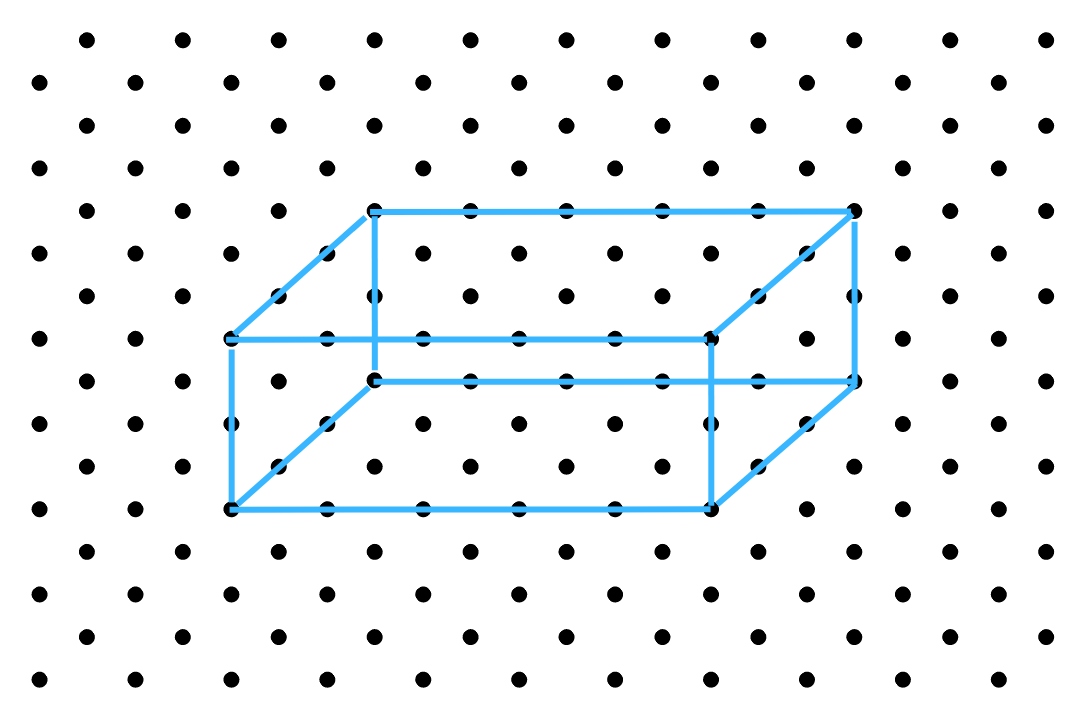
The third sketch is as follows:
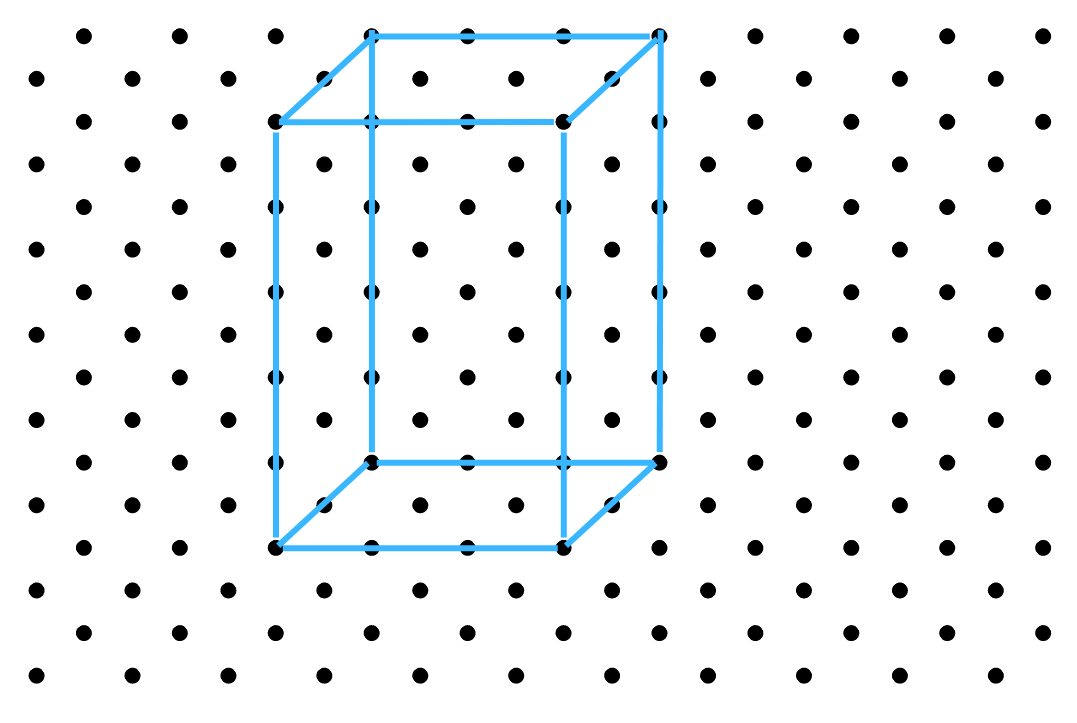
3. Three cubes each with 2 cm edge are placed side by side to form a cuboid. Sketch an oblique or isometric sketch of this cuboid.
Answer: The oblique sketch of the cuboid formed by three cubes each with 2 cm edge are placed side by side is shown below:
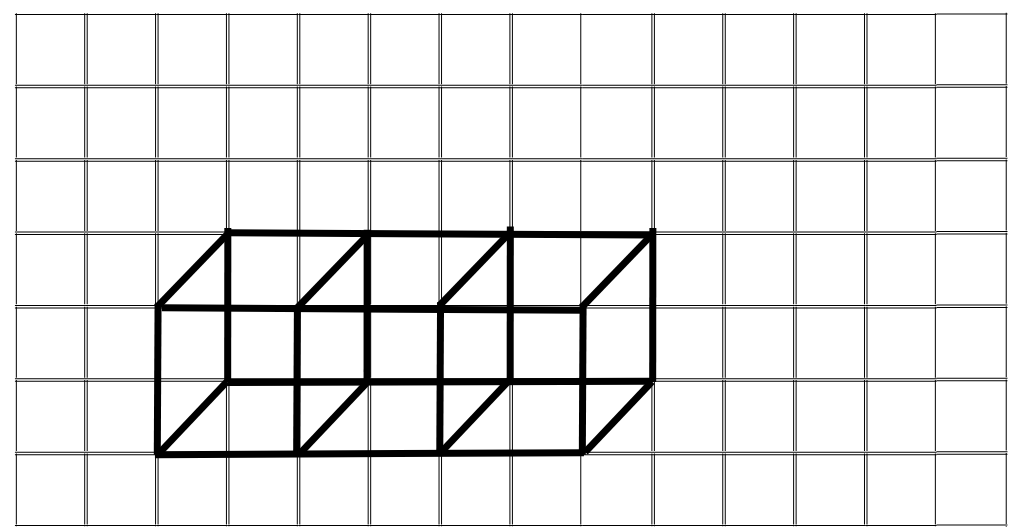
The isometric sketch of the cuboid formed by three cubes each with 2 cm edge placed side by side is shown below:
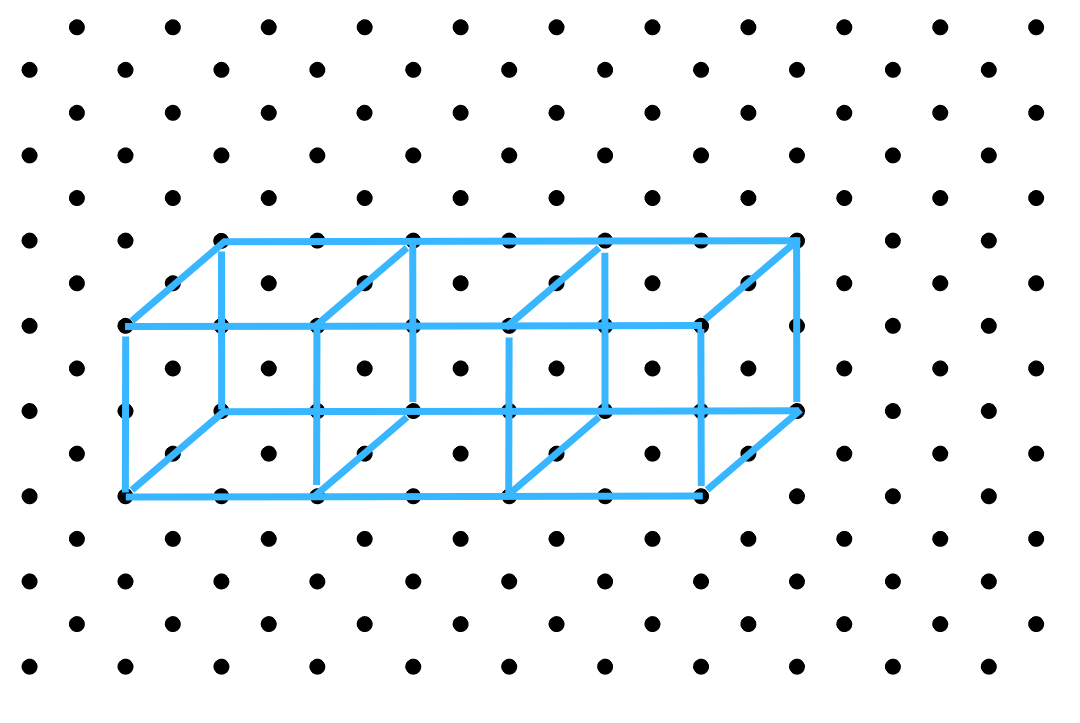
4. Make an oblique sketch for each one of the given isometric shapes:
(i) The first isometric shape is shown below:
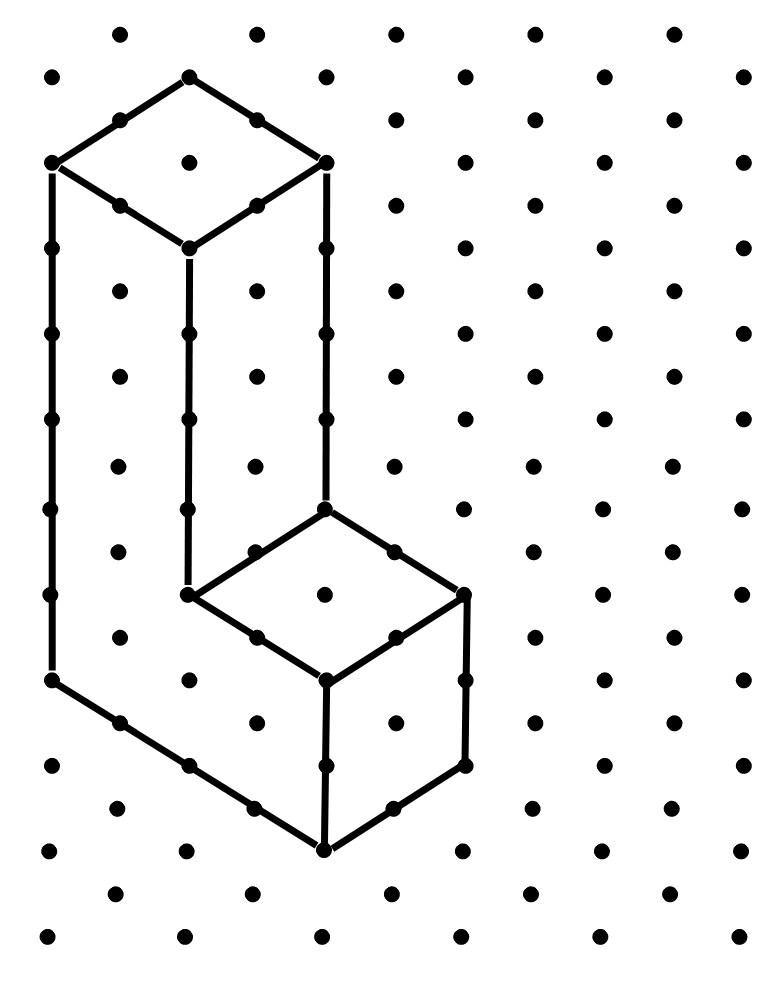
Answer: The corresponding oblique sketch is shown below:
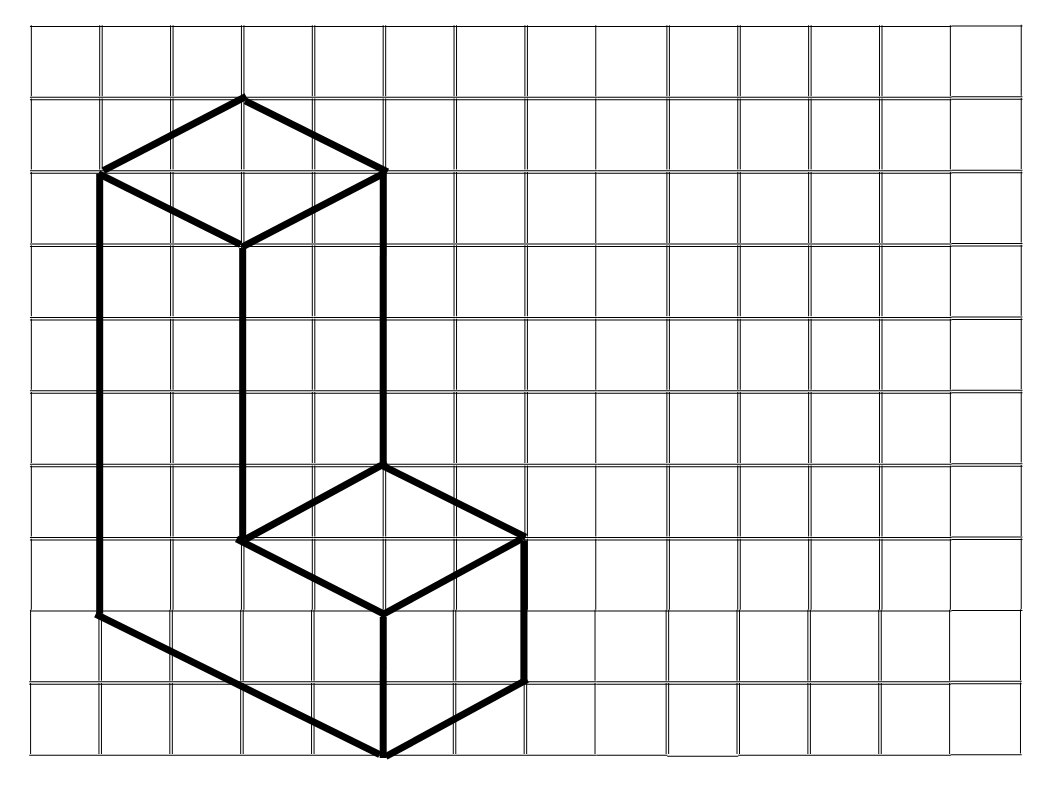
(ii) The second isometric shape is shown below:
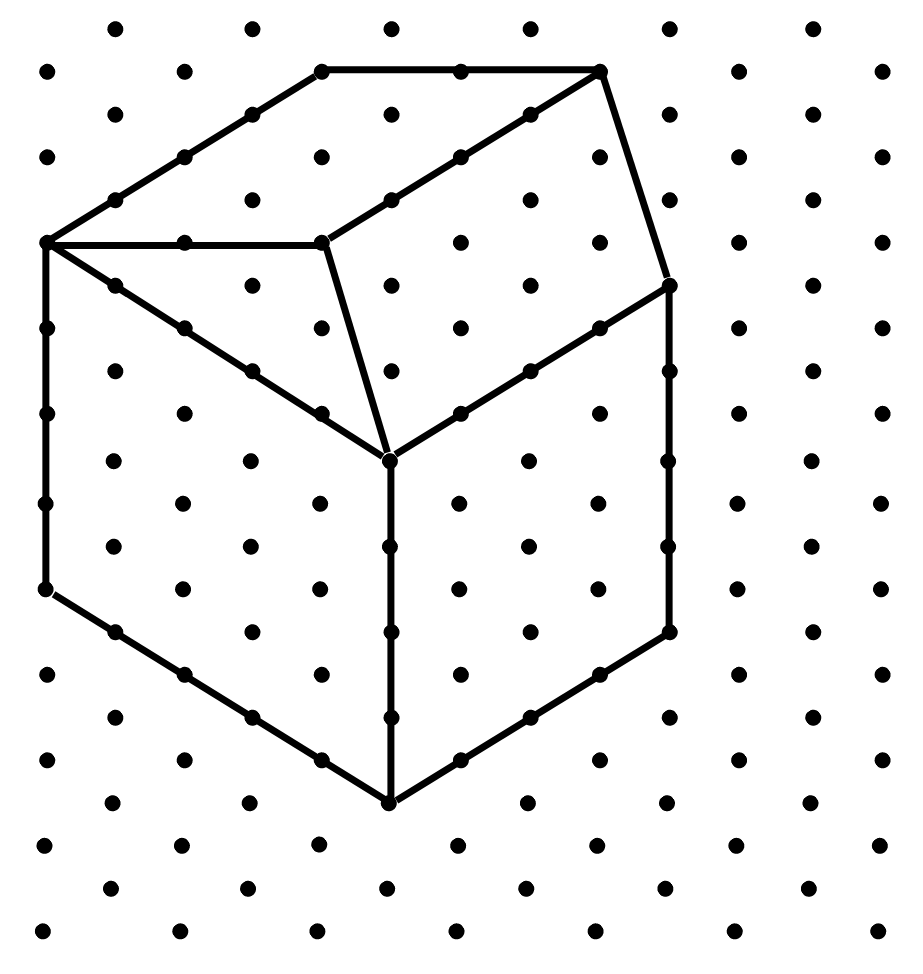
Answer: The corresponding oblique sketch is shown below:
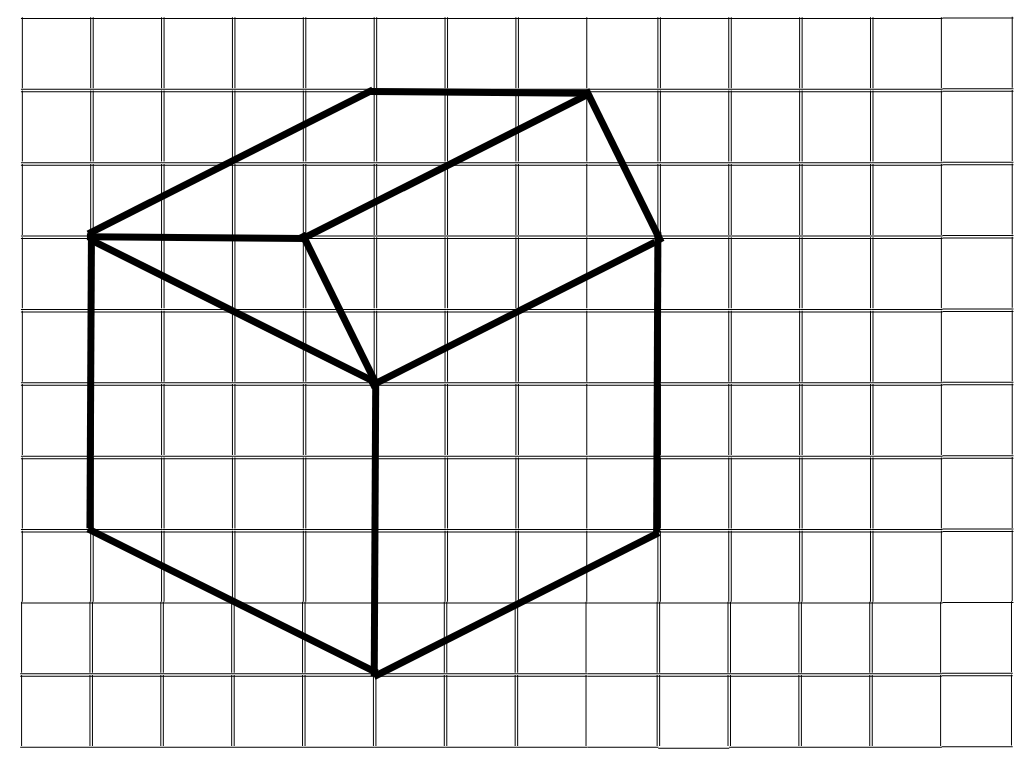
5. Give (i) an oblique sketch and (ii) an isometric sketch for each of the following:
(a) A cuboid of dimensions 5 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm. (Is your sketch unique?)
(b) A cube with an edge 4 cm long.
An isometric sheet is attached at the end of the book. You could try to make on it some cubes or cuboids of dimensions specified by your friend.
Answers:
(a) The oblique sketch of the cuboid of dimensions 5 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm is shown below:
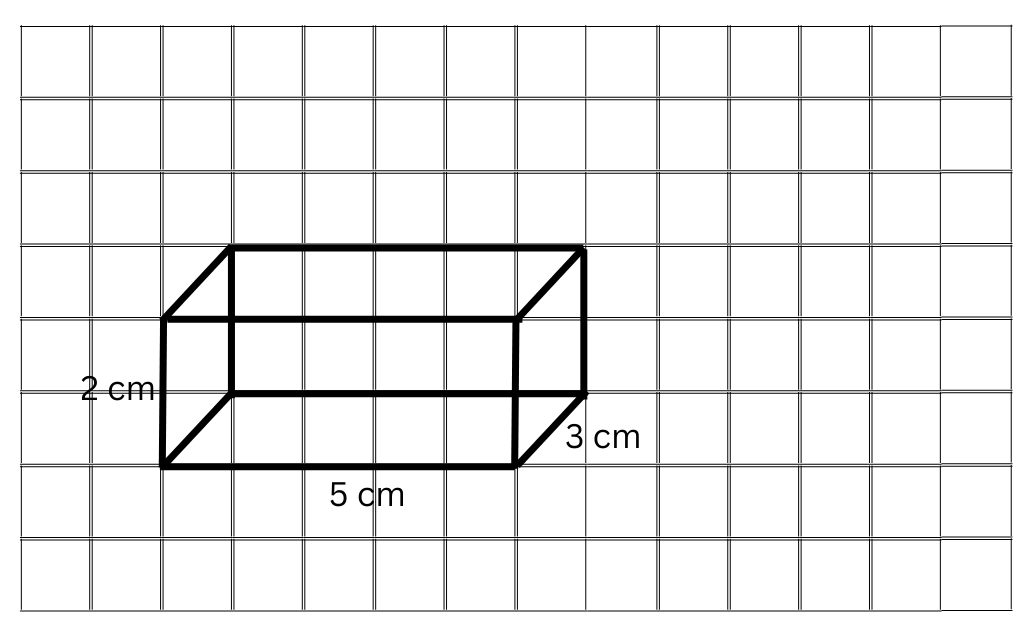
The isometric sketch of the cuboid of dimensions 5 cm, 3 cm and 2 cm is shown below:
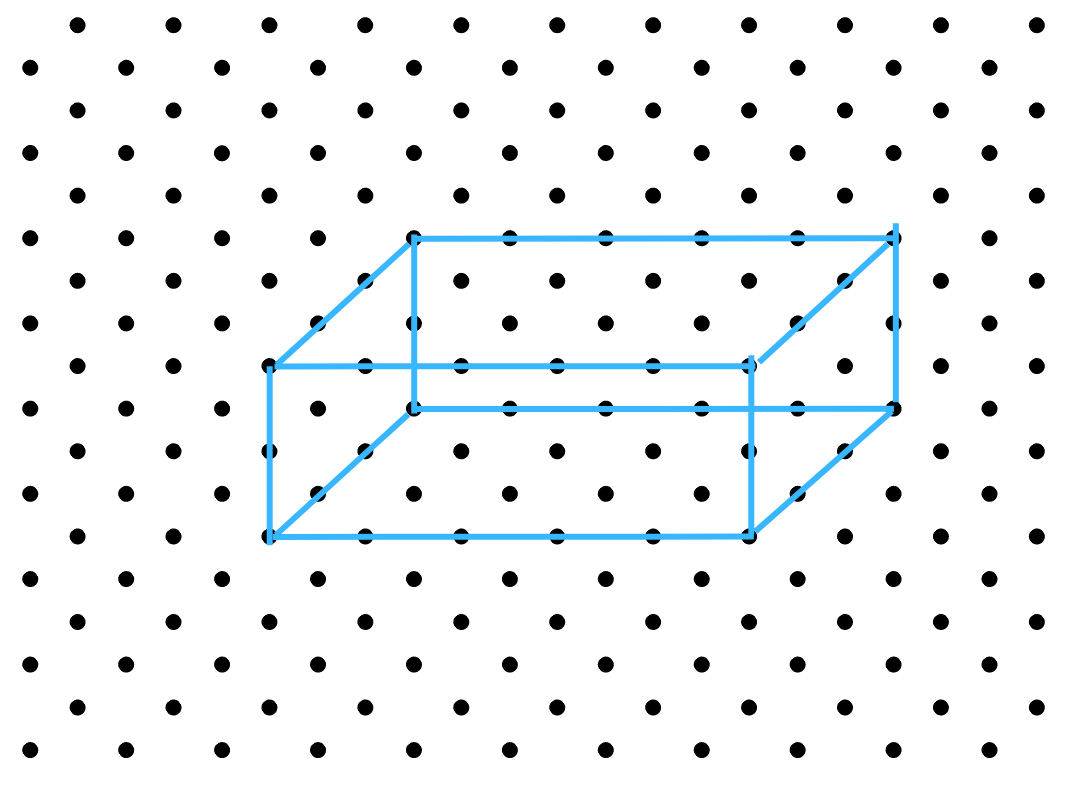
Both the oblique and isometric sketches of the cuboid are not unique because the length, breadth and height can have different values, among the given values. They need not be exactly like we have drawn above.
(b) The oblique sketch of the cube with an edge 4 cm long is shown below:
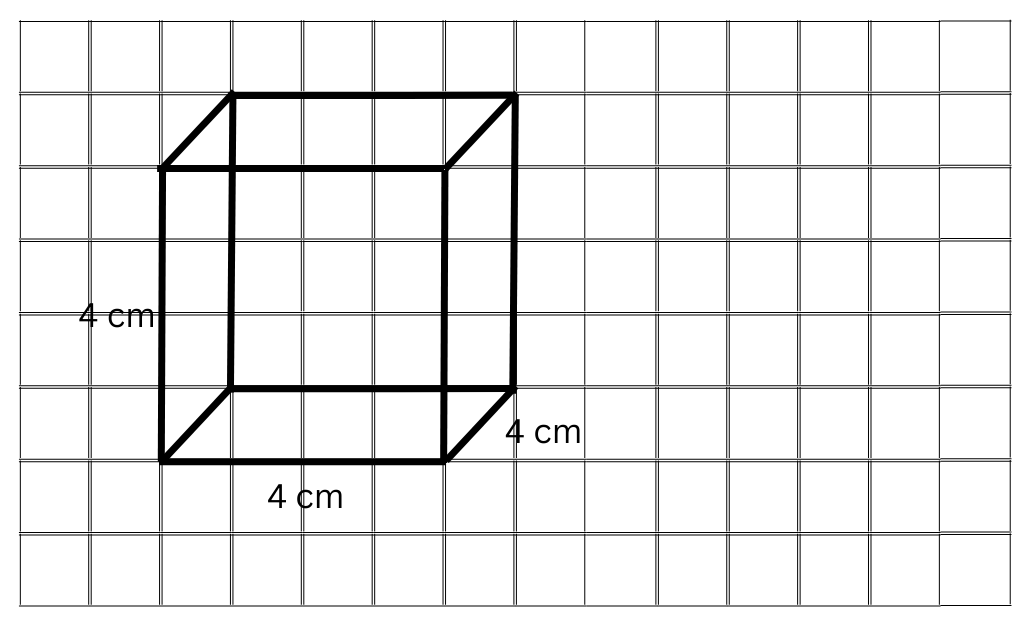
The isometric sketch of the cube with an edge 4 cm long is shown below:
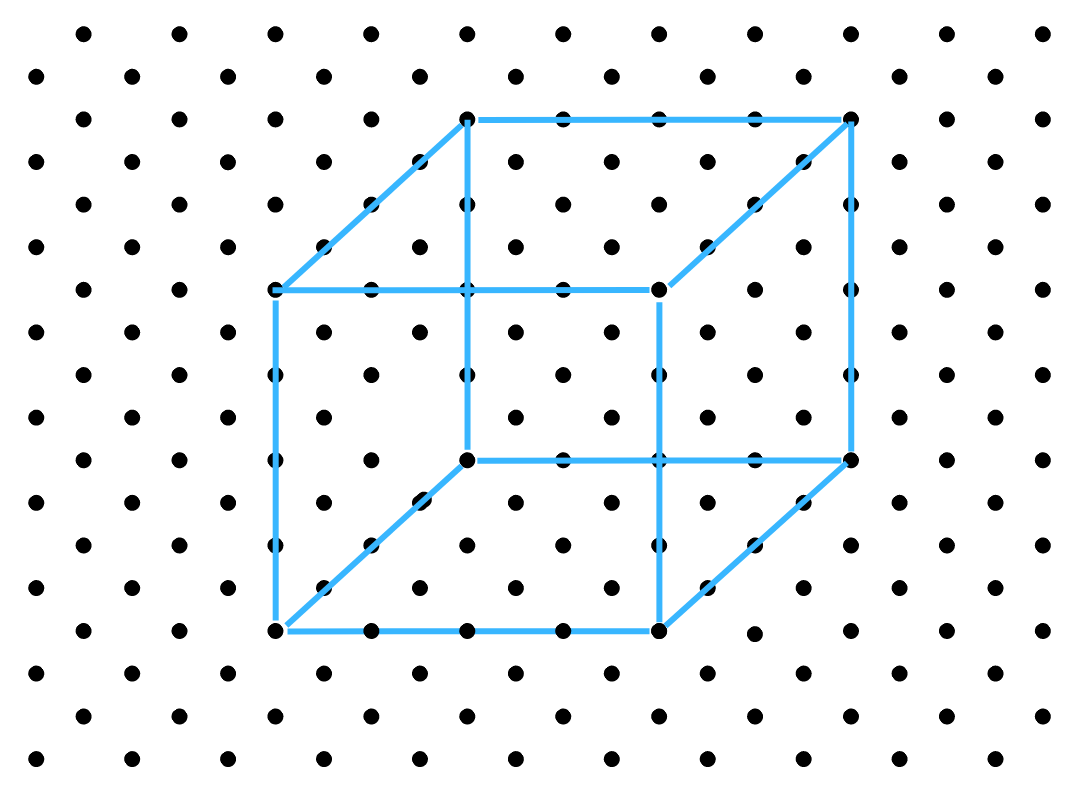
Solutions to Exercise 13.3 (Page No 209) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes –
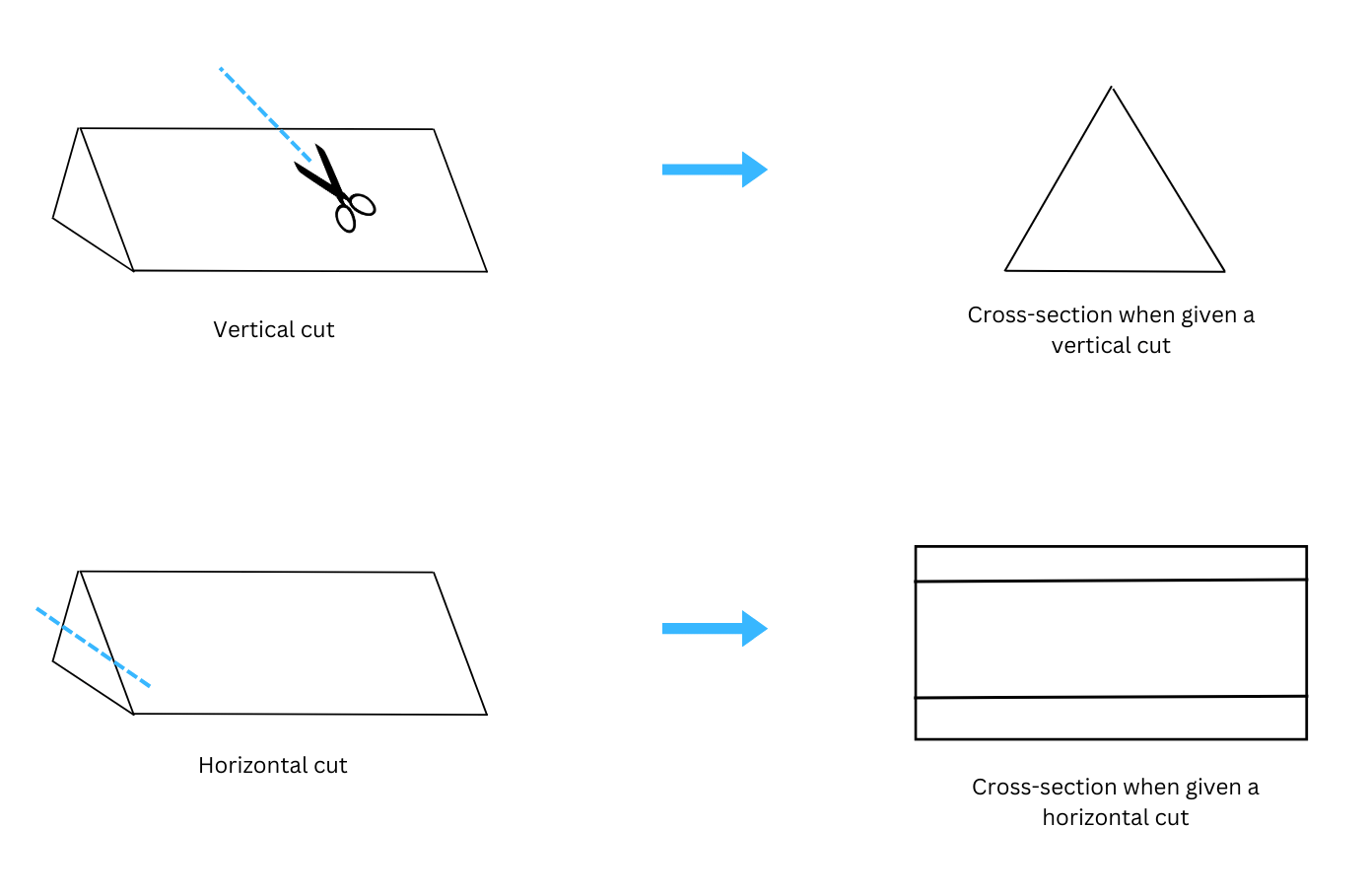
1. What cross-sections do you get when you give a
(i) vertical cut (ii) horizontal cut
to the following solids?
(a) A brick
Answer:
(i) When a brick is given a vertical cut we get a rectangular cross-section as shown:
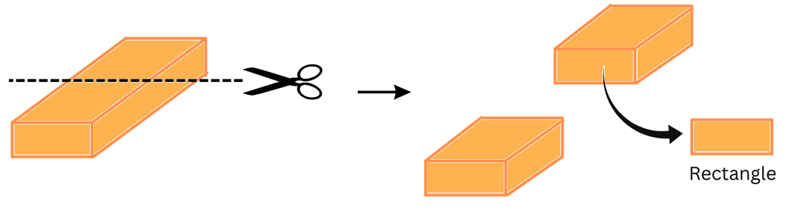
(ii) When a brick is given a horizontal cut we also get a rectangular cross-section as shown:
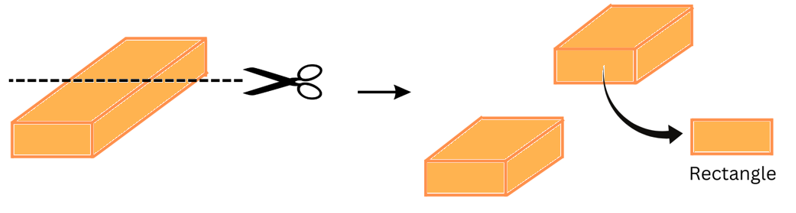
(b) A round apple
Answer:
(i) When a round apple is given a vertical cut we get a circular cross-section as shown:
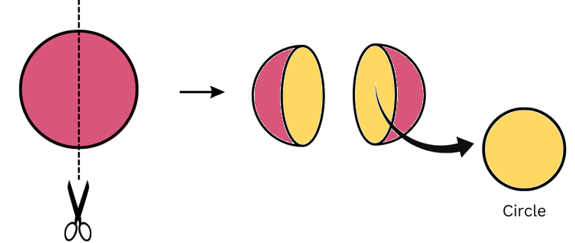
(ii) When a round apple is given a horizontal cut we get a circular cross-section as shown:
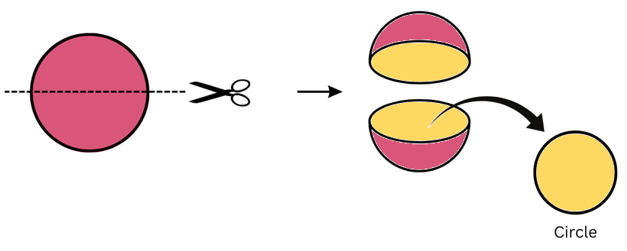
(c) A die
Answer:
(i) When a die (cube shaped) is given a vertical cut we get a square cross-section as shown:
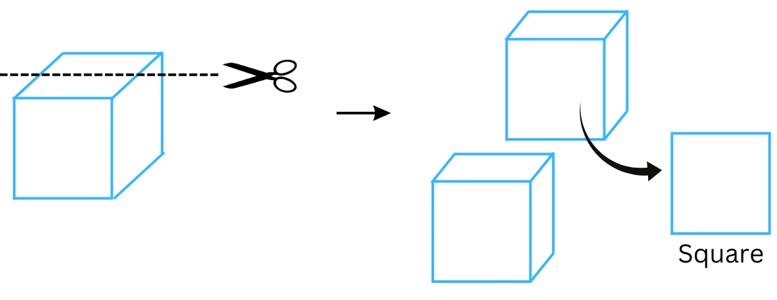
(ii) When a die (cube shaped) is given horizontal cut we also get a square cross-section as shown:
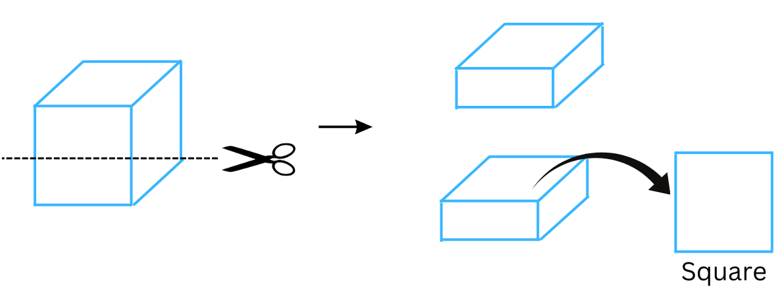
(d) A circular pipe
Answer:
(i) When a circular pipe is given a vertical cut we get a circular cross-section as shown:
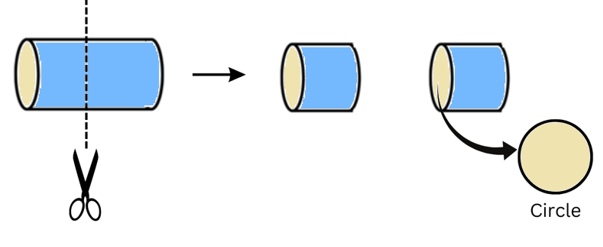
(ii) When a circular pipe is given a horizontal cut we get a rectangular cross-section as shown:
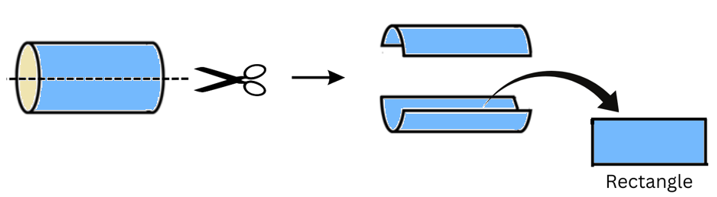
(e) An ice cream cone
Answer:
(i) When an ice cream cone is given a vertical cut we get a triangular cross-section as shown:
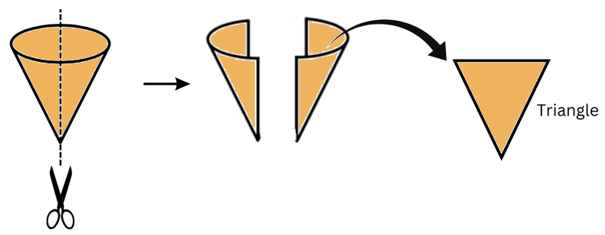
(ii) When an ice cream cone is given a horizontal cut we get two cross-sections, one for the upper half and one for the lower half:
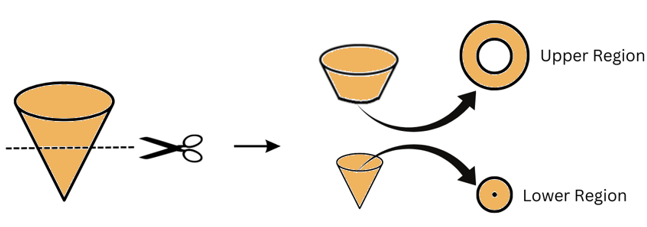
Solutions to Exercise 13.4 (Page No 289) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes –
1. A bulb is kept burning just right above the following solids. Name the shape of the shadows obtained in each case. Attempt to give a rough sketch of the shadow. (You may try to experiment first and then answer these questions).
(i) A ball
Answer: The shape of the shadow obtained in case of a ball is a circle and is shown below:
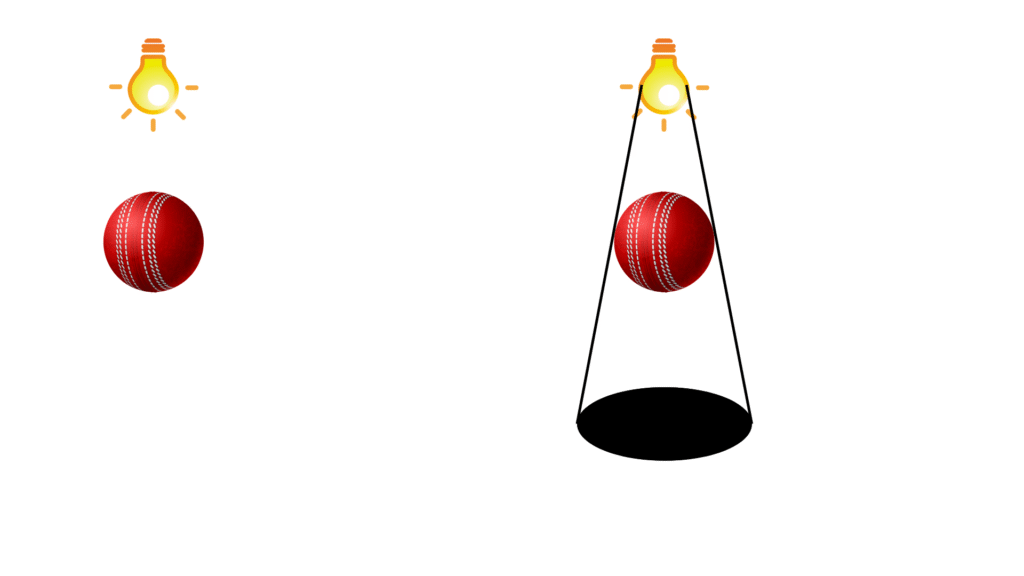
(ii) A cylindrical pipe
Answer: The shape of the shadow obtained in case of the cylindrical pipe is a rectangle and is shown below:
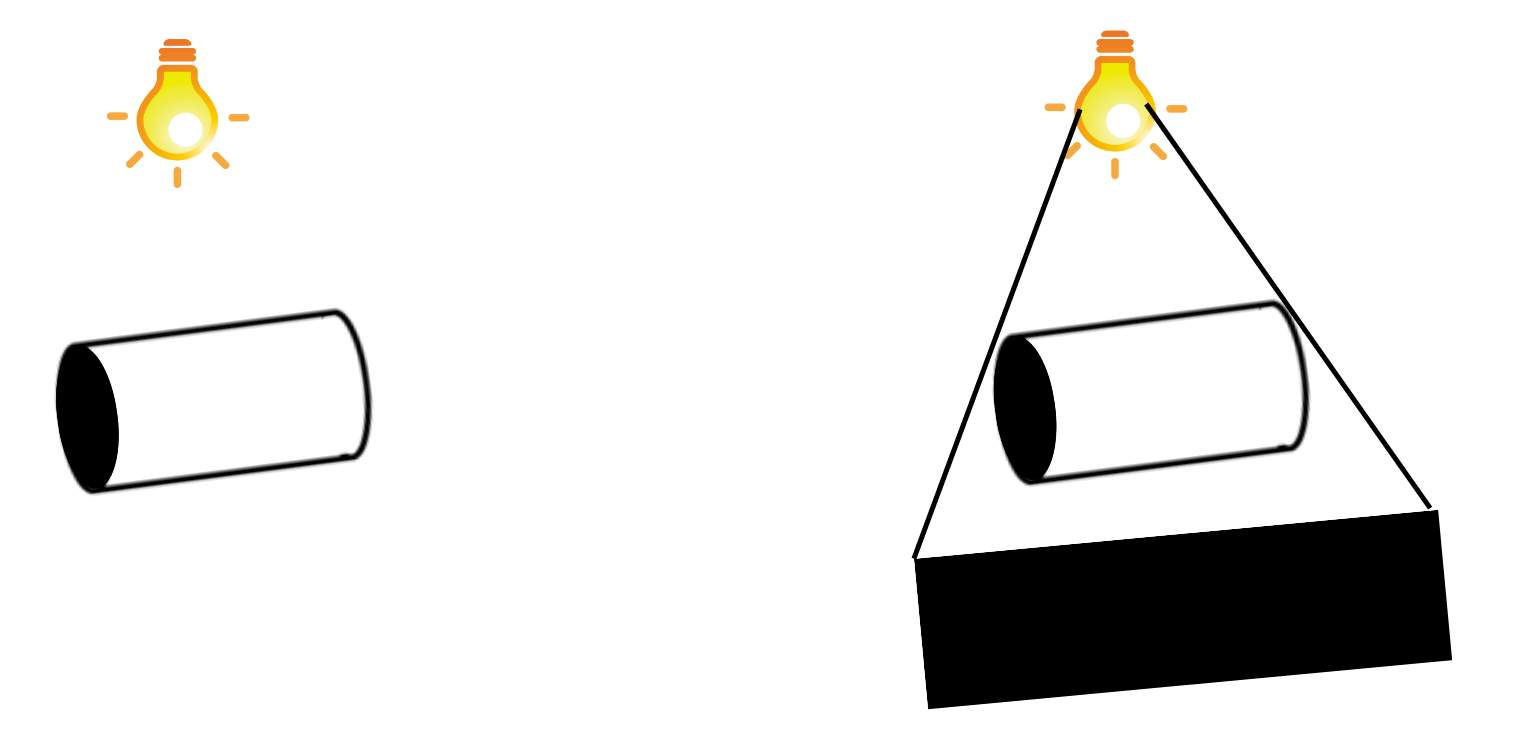
(iii) A book
Answer: The shape of the shadow obtained in case of the book is a rectangle and is shown below:
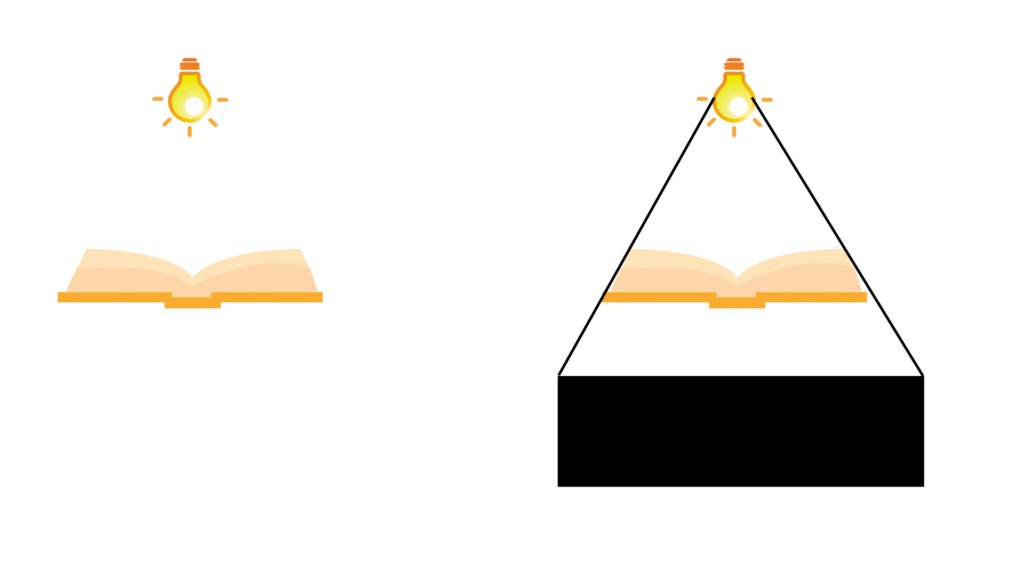
2. Here are the shadows of some 3-D objects, when seen under the lamp of an overhead projector. Identify the solid(s) that match each shadow. (There may be multiple answers for these!)
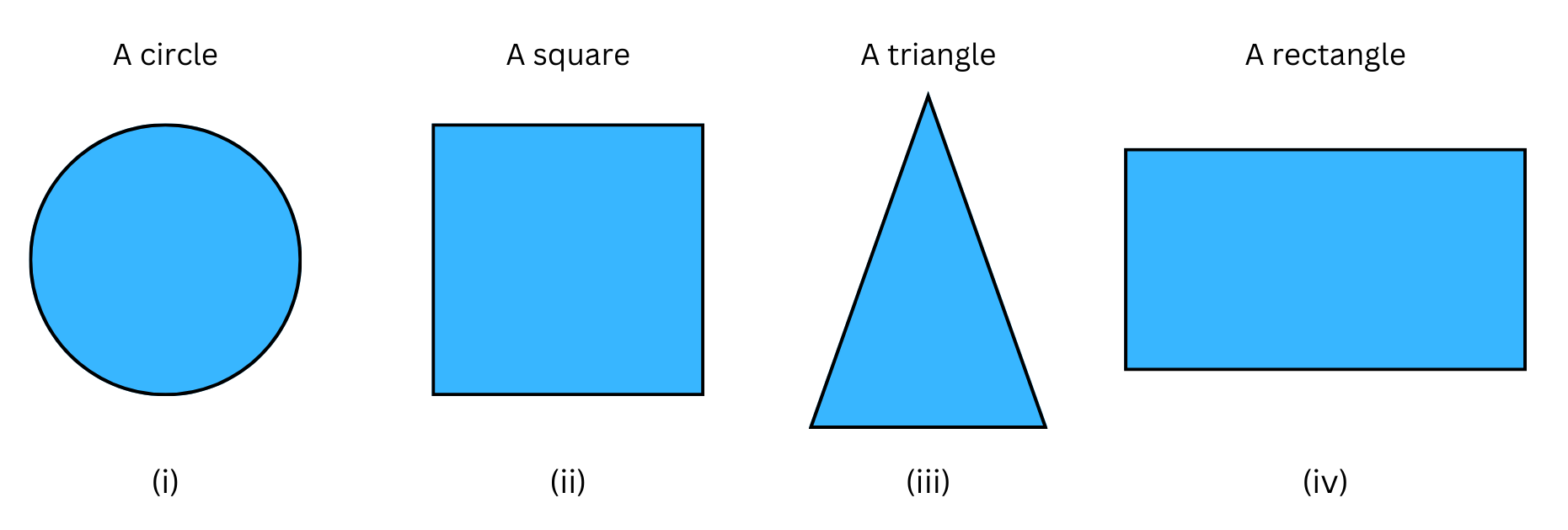
Answer:
The shadows will represent the cross-sections of the 3-D objects.
(i) Therefore, the shadow of a circle will be formed for a 3-D object with circular cross-section. So, it can be a cricket ball, a coin, a wheel.
(ii) The shadow of a square will be formed for a 3-D object with square cross-section. So, it can be a die, a picture frame.
(iii) The shadow of a triangle will be formed for a 3-D object with triangular cross-section. So, it can be a pyramid, an ice-cream cone etc.
(iv) The shadow of a rectangle will be formed for a 3-D object with rectangular cross-section. So, it can be a brick, a TV etc.
3. Examine if the following are true statements:
(i) The cube can cast a shadow in the shape of a rectangle.
Answer: The shadow will represent the cross-section of the object. The cross-section of a cube is a square. So, the shadow cast by a cube can only be a square and not a rectangle. Therefore, the statement is False.
(ii) The cube can cast a shadow in the shape of a hexagon.
Answer: The shadow will represent the cross-section of the object. The cross-section of a cube is a square. So, the shadow cast by a cube can only be a square and not a hexagon. Therefore, the statement is False.
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes:
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Name a solid with two surfaces.
Answer:
Right circular cone.
2. Name a solid without any edge.
Answer:
A sphere is solid without any edge.
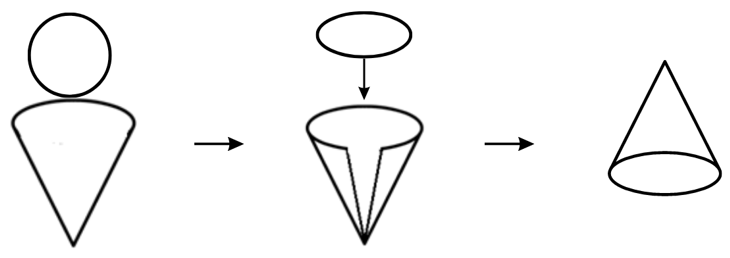
3. If you rotate a right-angled triangle about its base what shape will you get?
Answer:
You will get a right circular cone.
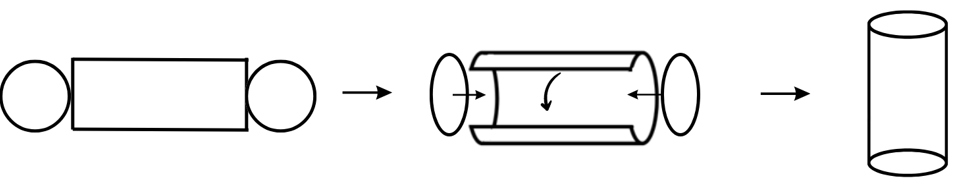
4. If you roll a rectangular piece of paper along its length what shape will you get?
Answer:
You will get a cylinder.
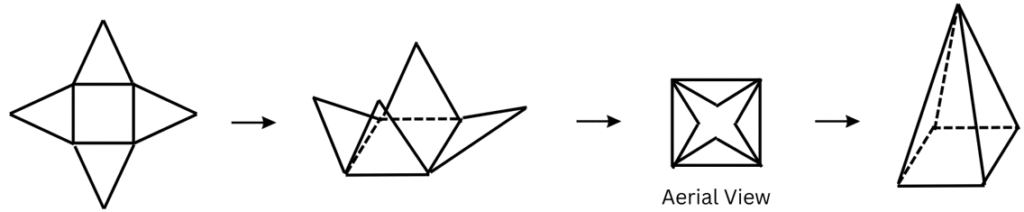
5. How many triangles are there in a pyramid with square base?
Answer:
There are 4 triangles.
6. If You change the direction of light on an object, what is the effect on the shadow?
Answer:
The shape and position of the shadow formed will change.
7. Name two solids with same number of faces?
Answer:
A cube and a cuboid have the same number of faces.
8. If you shine light directly on the circular face of a cone, what kind of shadow do you get?
Answer:
The shadow will be a circle.
9.If you shine light directly on the face of a tetrahedron, what kind of shadow do you get?
Answer:
The shadow will be a triangle.
10. How many faces does a square pyramid have?
Answer:
A square pyramid has 5 faces.
Short and Long Answer Type Questions:
1. Make an oblique sketch for the isometric shape given below:
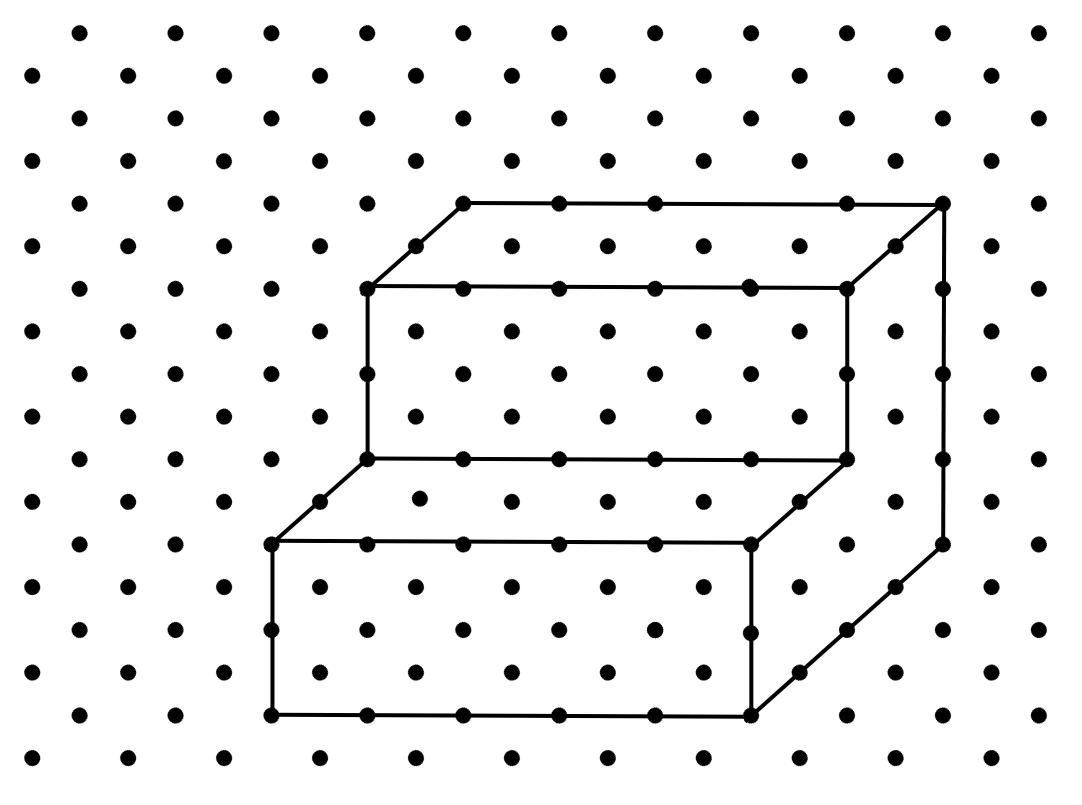
Answer: The corresponding oblique sketch is shown below:
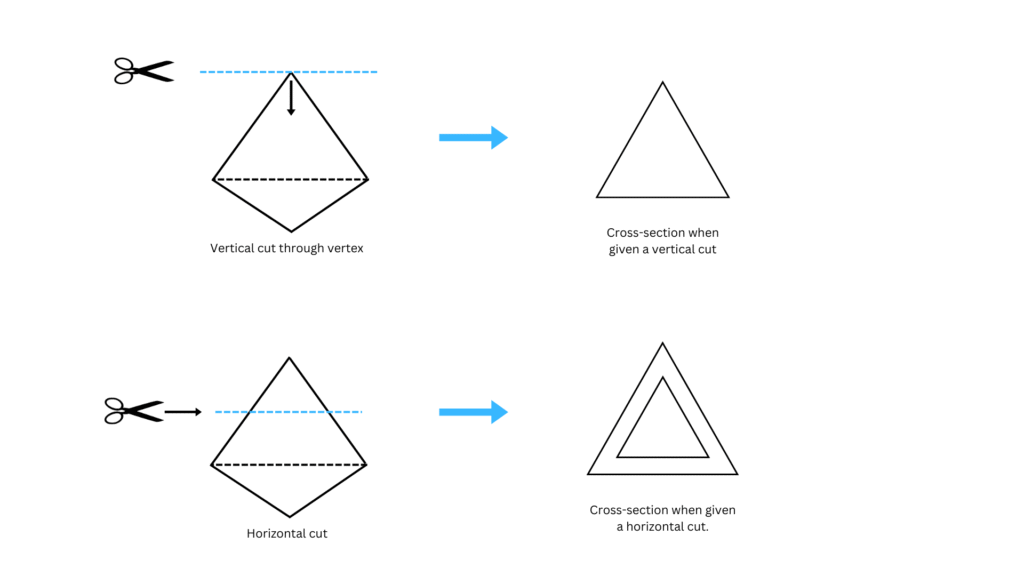
2. What cross-sections do you get when you slice a tetrahedron
(i) Horizontally (ii) Vertically through the vertex
Answer:
The cross-sections you get when you slice tetrahedron horizontally and vertically are shown below:
3. Here you find four nets. There are two correct nets among them to make a tetrahedron. See if you can work out which nets will make tetrahedron.
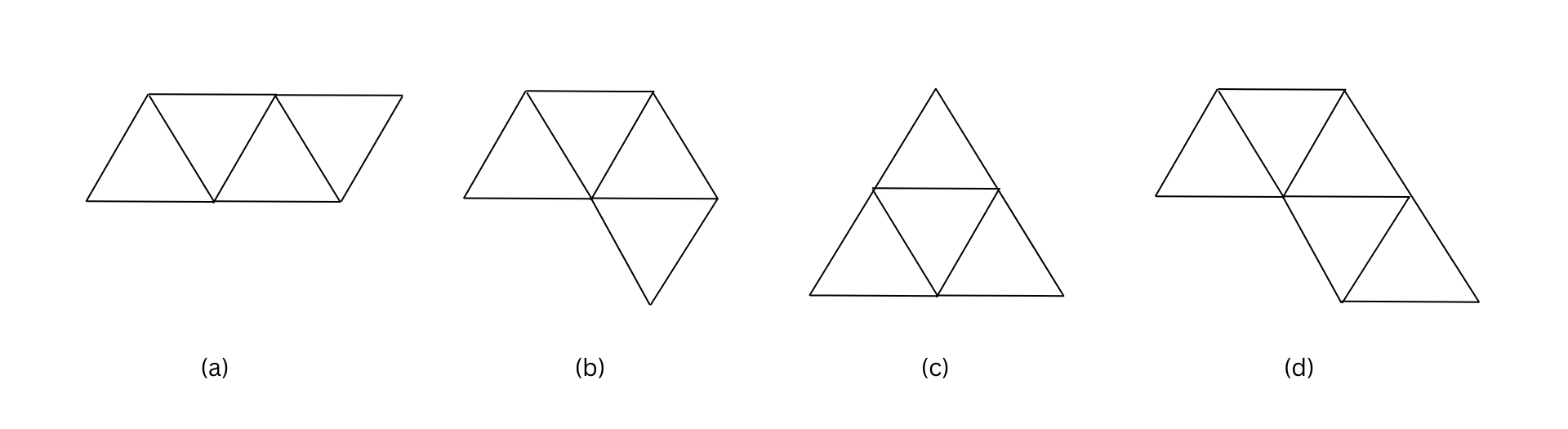
Answer:
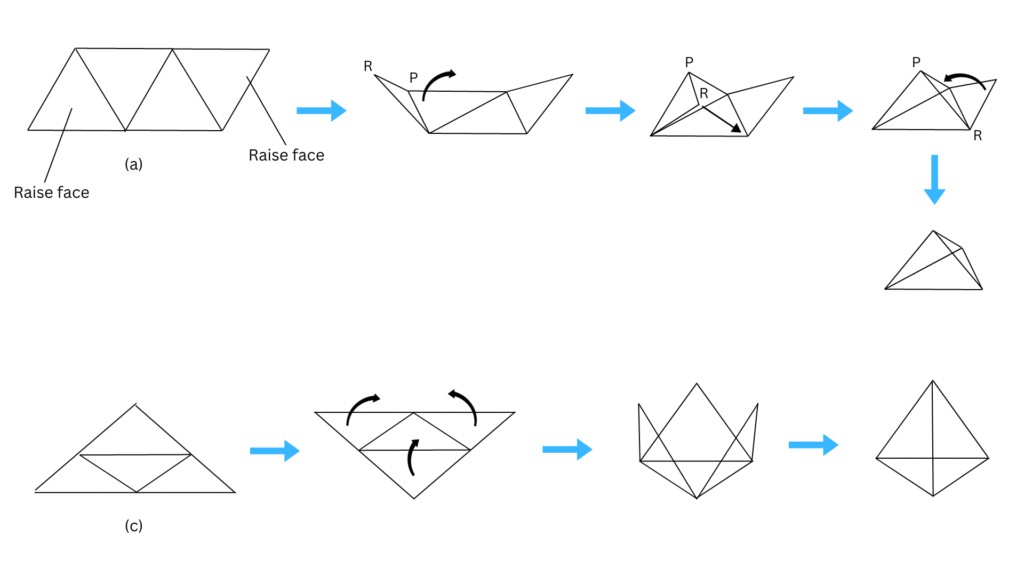
The two correct nets among them to make a tetrahedron are (a) and (c) as shown below:
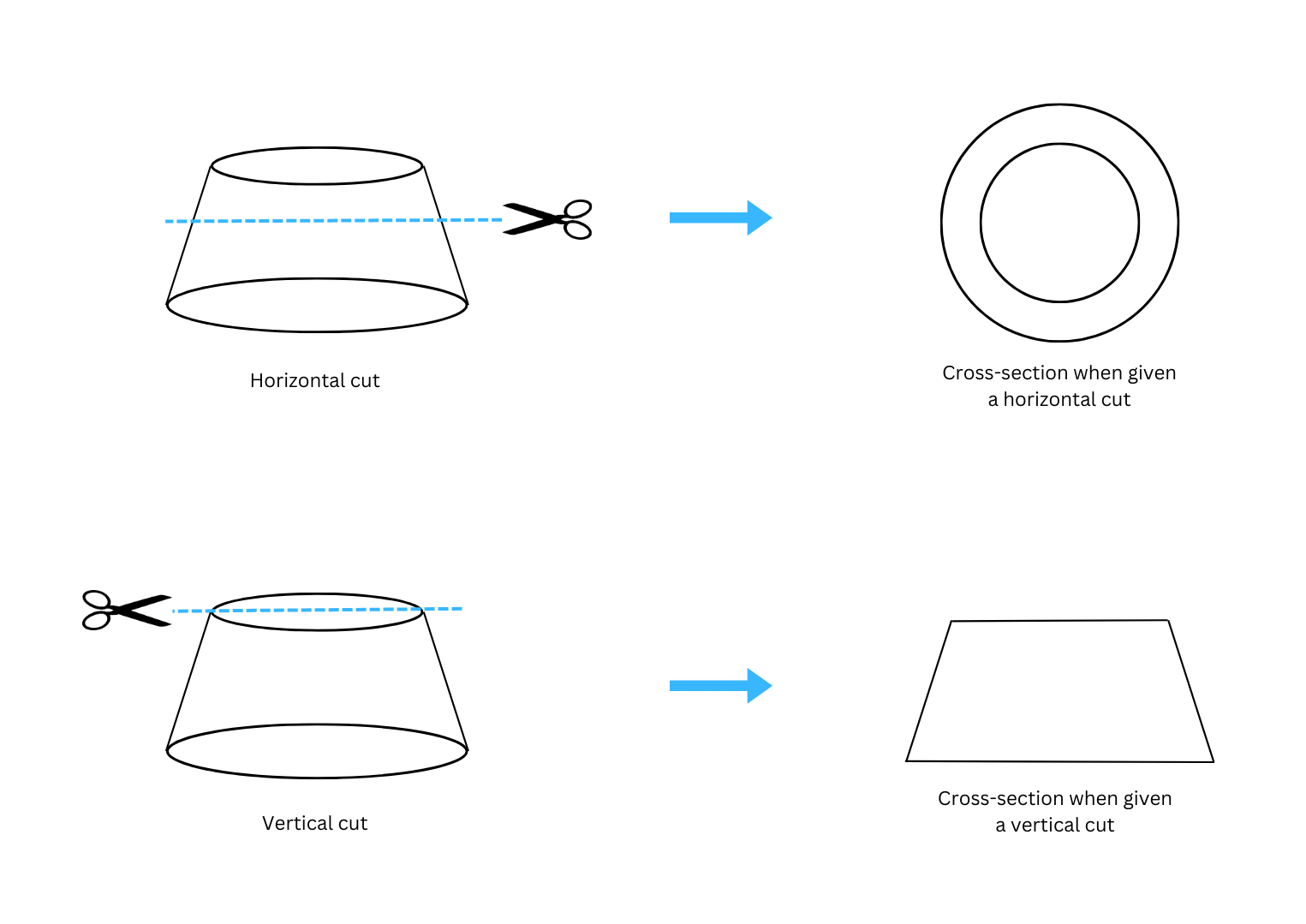
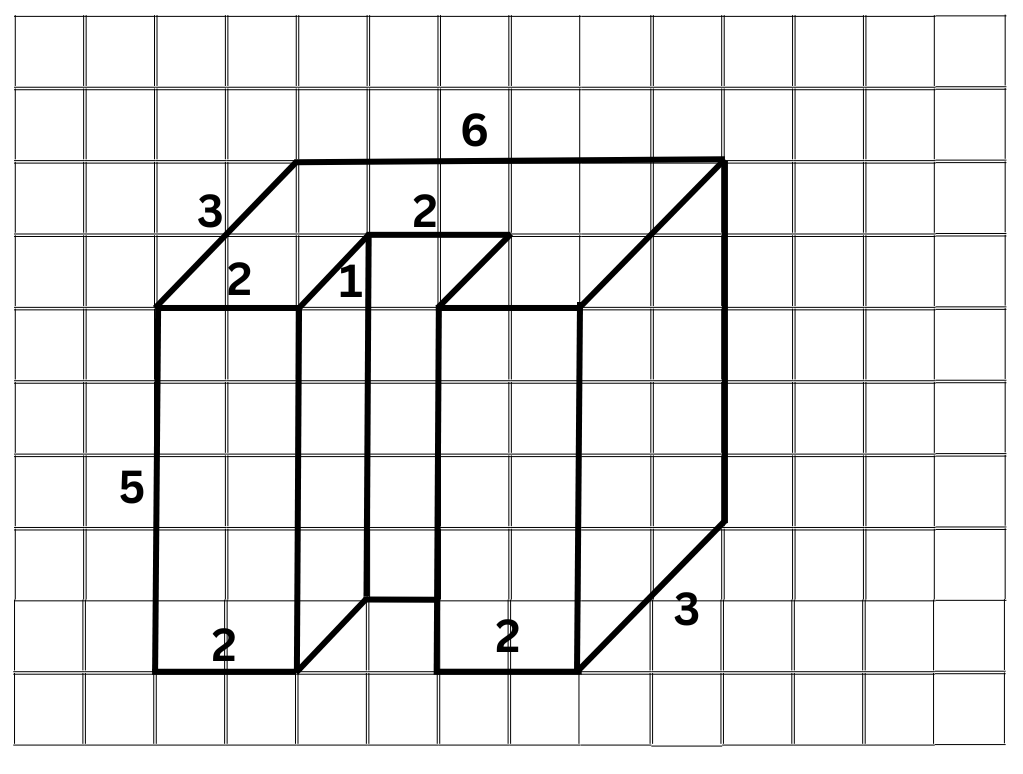
4. Find the horizontal cross-section and vertical cross-section of the shape below:
Answer:
The horizontal and vertical cross-sections of the shape are shown below:
5. Find the horizontal cross-section and vertical cross-section of the shape below:
Answer: The horizontal and vertical cross-sections of the shape are shown below:
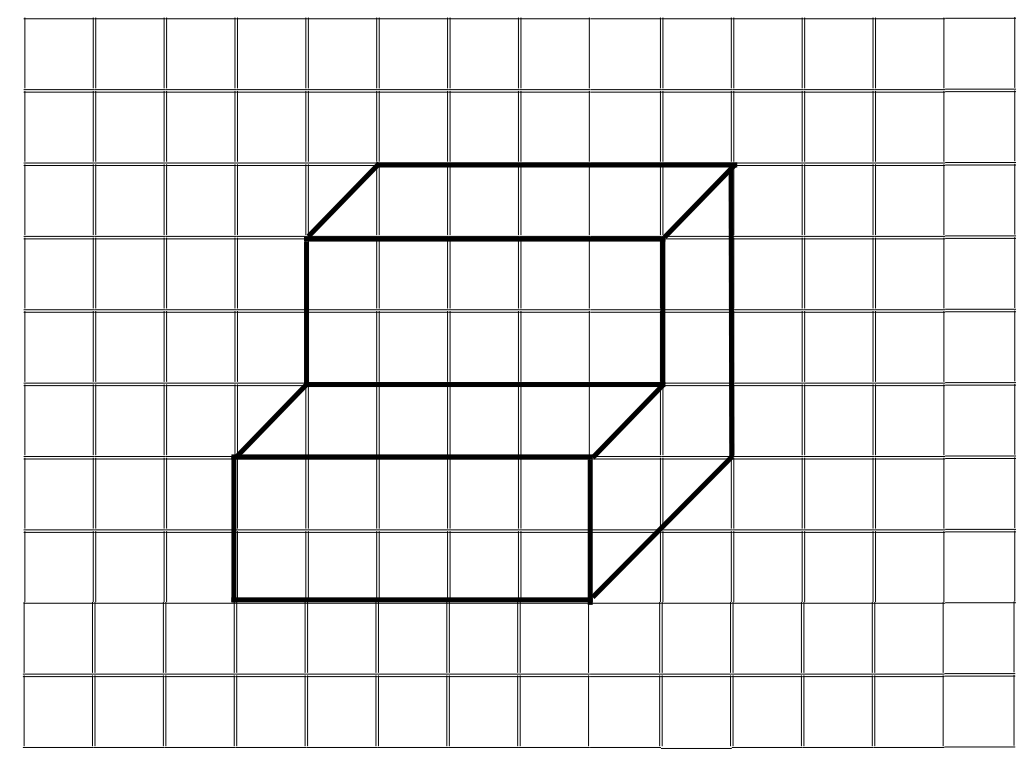
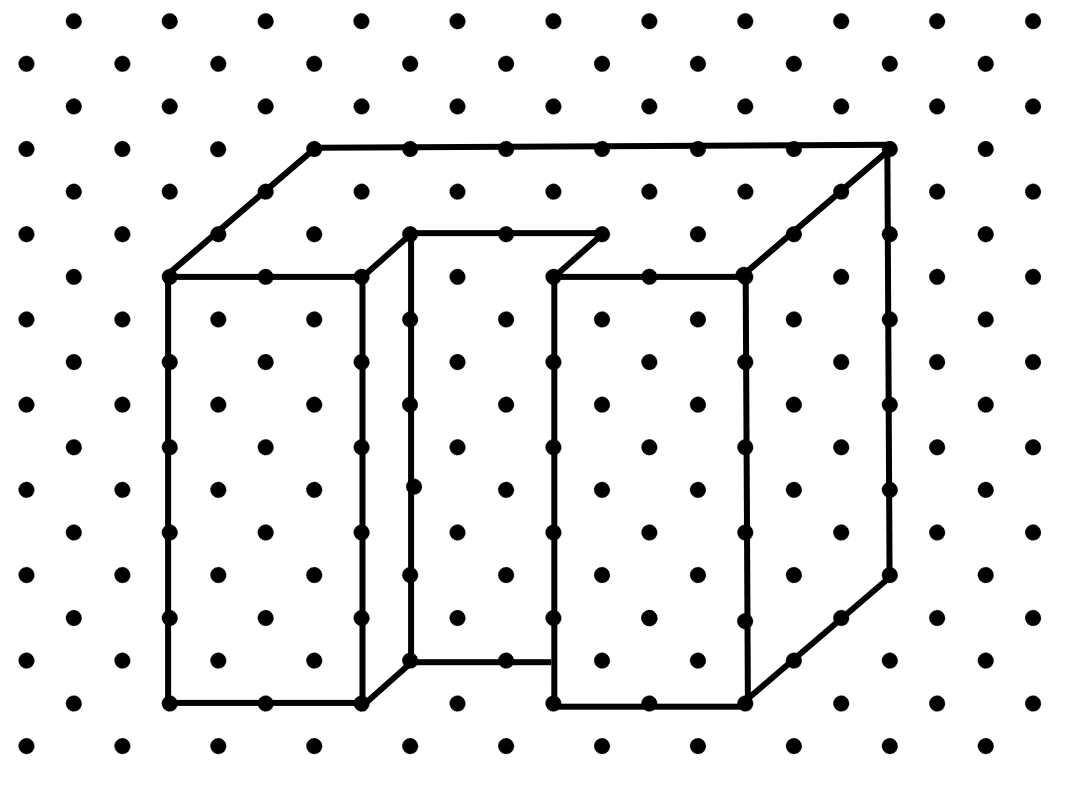
6. Draw an isometric sketch for the below shape:
Answer: The isometric sketch is shown below:
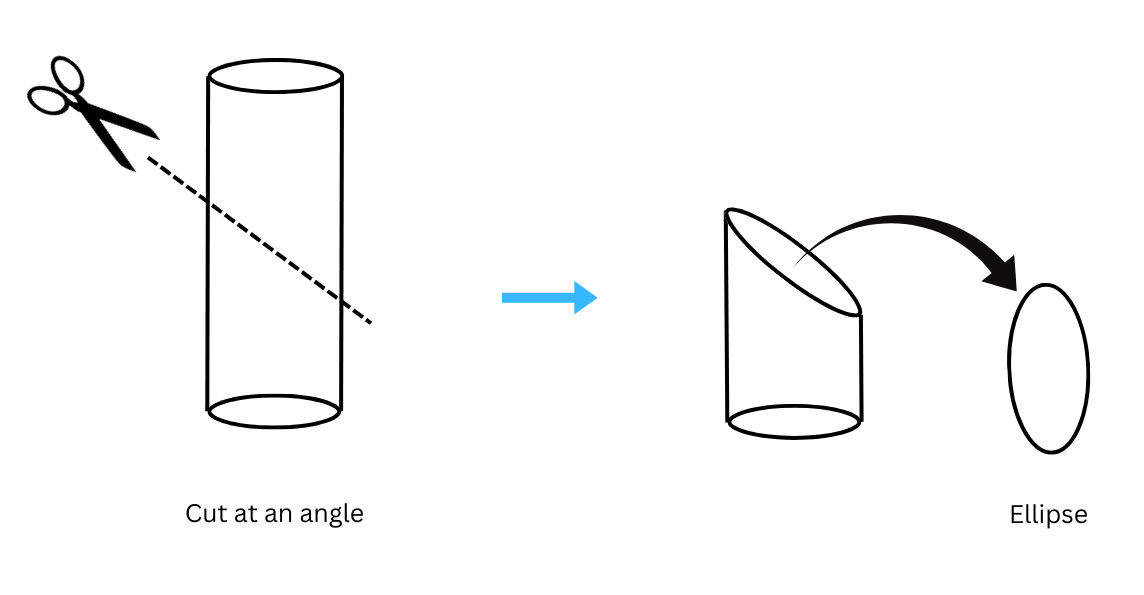
7. Picture a cylinder. If you cut it at an angle (not parallel to the base), what would the cross-section look like?
Answer: If the cylinder is cut at an angle which is not parallel to the base, the cross-section would look like an ellipse. This is shown below:
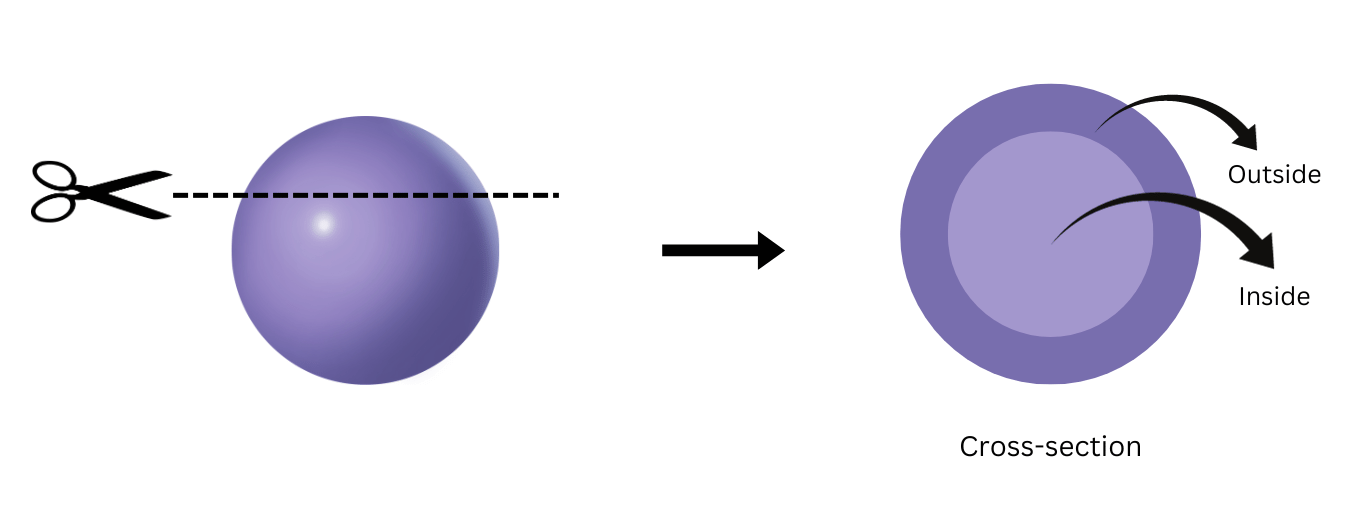
8. Visualize a sphere. If you cut it parallel to the base but not through the centre, what shape would the cross-section be?
Answer: If you cut the sphere parallel to the base but not through the centre, the cross-section would be as shown below:
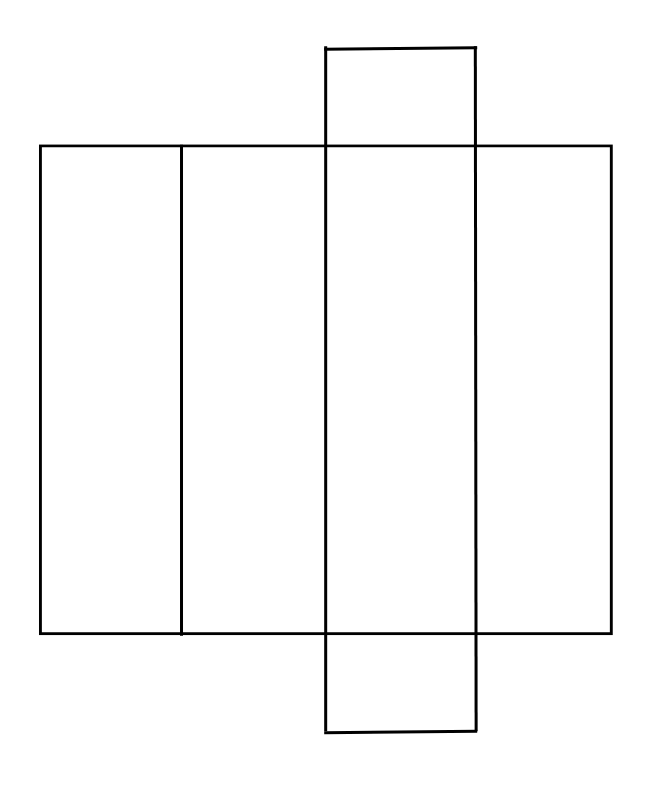
9. Draw the net of a cuboid.
Answer:
The net of a cuboid is shown below:
10. Answer the following:
(a) Draw the top view of the below shape:
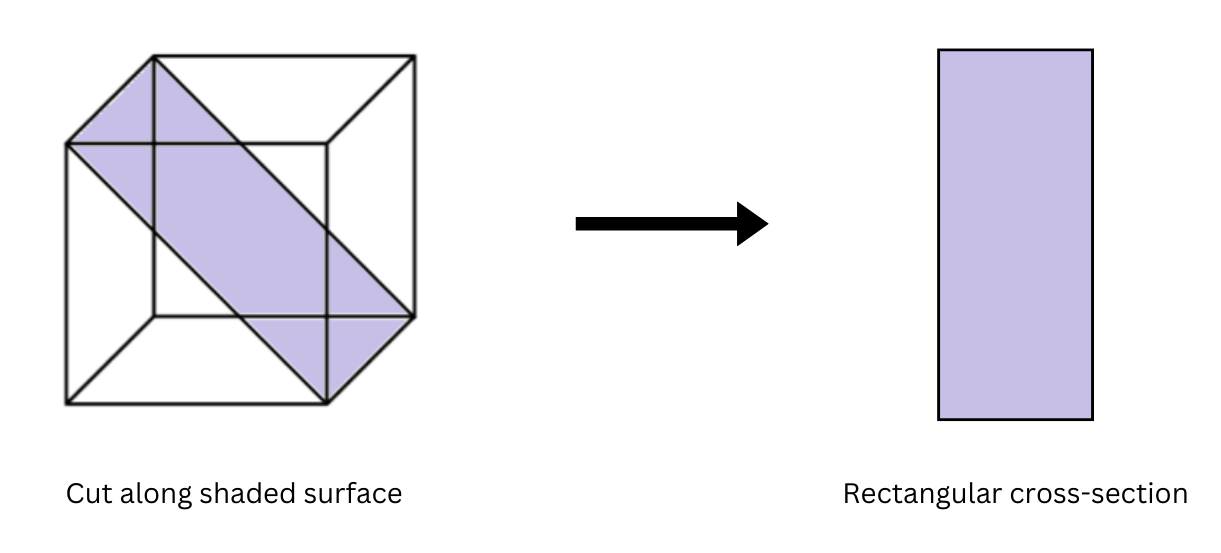
(b) Cut a cube in such a way that you get a rectangular cross-section.
Answers:
(a) The top-view of the given figure is shown below:
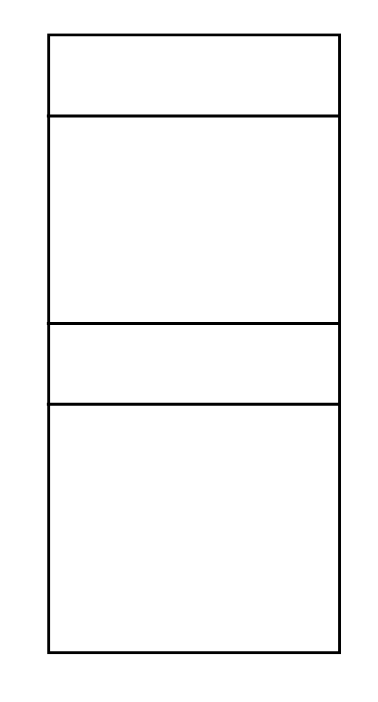
(b) If you cut the cube along the shaded region as shown below, you get a rectangular cross-section:
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) Measurements agree with those of the solid in _________ sketches.
(b) If a 3-D object is kept in front of a light, the shadow formed will be _________ dimensional.
(c) If a cuboid of sides 4 cm, 2 cm, 2 cm is cut to form two cubes, the length of side of each cube is _________.
(d) A sphere is sliced through the middle to form two _________.
(e) A _________ can be formed using concentric circles starting from a circle of finite size all the way up to a point circle.
Answers:
(a) Measurements agree with those of the solid in isometric sketches.
(b) If a 3-D object is kept in front of a light, the shadow formed will be 2 dimensional.
(c) If a cuboid of sides 4 cm, 2 cm, 2 cm is cut to form two cubes, the length of side of each cube is 2 cm.
(d) A sphere is sliced through the middle to form two hemispheres.
(e) A cone can be formed using concentric circles starting from a circle of finite size all the way up to a point circle.
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Maths Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes:
Our expert team of Indian and foreign educated engineers have designed these solutions with pinpoint precision, to help you understand this topic as a beginner. We have included excellent figures that will help you visualise each situation clearly and step-by-step. We’ve done our best to present the solutions in a way that will give you the maximum benefit. The extra problems have been carefully designed to help you learn the concepts even better and give you additional practice.
You can download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime you please! And of course, we will keep providing you with plenty of top-quality study material and resources so make sure you keep visiting our website and join our email list to get free access to them and stay updated!
The main topics covered are:
13.1 – Introduction: Plane Figures and Solid Shapes
13.2 – Faces, Edges and Vertices
13.3 – Nets for Building 3-D shapes
13.4 – Drawing Solids on a Flat Surface
13.5 – Viewing Different Sections of a Solid
Here are the number of problems by each chapter:
Exercise 13.1 – 5 questions
Exercise 13.2 – 5 questions
Exercise 13.3 – 1 question
Exercise 13.4 – 3 questions
You will need to be able to visualise shapes and nets in different orientations. For this we recommend that you study our solutions and practise drawing the figures on your own in different orientations and then visualise them closely and try to draw them out on your own as well. This method will train your eye to be able to visualise and draw the right conclusions about any shape.
The concepts in this chapter can be asked in many different ways. So go beyond the NCERT textbook and practise different kinds of questions from reference books and past exam papers. This way you will gain valuable experience on how to handle different kinds of problems.
As always, our expert teacher-mentors will be there for you anytime you need them. Feel free to reach to us anytime with your requirements and we will be happy to help you out.
Anytime you need additional coaching, we will be there for you. Our expert teacher-mentors thoroughly enjoy teaching and mentoring young students like you and are fully committed to helping you succeed. Just contact us with your requirements anytime and let us help you out! We provide on-demand one-to-one coaching, based on your convenience and your needs – have it completely your way! Book live classes now!
Good luck for Class 8!


