Welcome students! We have provided excellent solutions to all Chapter 5 exercise questions, extended learning – activities and projects, in-text questions and in-text activities. These are scientifically designed to help clear your concepts and answer all your questions. The self-designed extra question set will give you additional practice. We encourage you to study this material in detail and then practise answering the questions on your own. This will give you confidence to answer similar questions in your exams.
Solutions to Exercise (Page No 54) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes:
1. Classify the changes involved in the following processes as physical or chemical changes:
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Dissolving sugar in water
(c) Burning of coal
(d) Melting of wax
(e) Beating aluminium to make aluminium foil
(f) Digestion of food
Answers:
(a) Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical change. This is because in photosynthesis new substances like starch and oxygen are produced which have different properties. It is an irreversible change.
(b) Dissolving sugar in water
Dissolving sugar in water is a physical change because only the state of the substance changes and no new substances are formed. When we dissolve sugar in water to form a solution, we can get solid sugar back by evaporating the water. It is a reversible change.
(c) Burning of coal
Burning of coal is a chemical change. Burning of coal produces mainly carbon dioxide, which is a new substance with new properties and the change is irreversible.
(d) Melting of wax
Melting of wax is a physical change. Melted wax becomes solid wax again on cooling. Therefore, only the state of the substance has changed and no new substances are formed, making it a physical change.
(e) Beating aluminium to make aluminium foil
Beating aluminium to make aluminium foilis a physical change because no new substance is formed and the properties remain the same. Therefore, it is a physical change.
(f) Digestion of food
Digestion of food is a chemical change.The stomach acids react with the food to break it down into simpler substances with new properties and the change cannot be reversed. Therefore, it is a chemical change.
2. State whether the following statements are true or false. In case a statement is false, write the corrected statement in your notebook.
(a) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change. (True/False)
(b) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change. (True/False)
(c) Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily. (True/False)
(d) Iron and rust are the same substances. (True/False)
(e) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change. (True/False)
Answers:
(a) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change. (True/False)
False. Cutting a log into pieces only changes the size and shape and no new substances are formed. Therefore, it is a physical change.
(b) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change. (True/False)
False. Formation of manure from leaves is a chemical change. When leaves decompose they form manure which is a new substance with new properties and the change cannot be reversed. Therefore, it is a chemical change.
(c) Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily. (True/False)
True. Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily because galvanisation using zinc forms a protective coating on iron. This prevents the iron from coming into contact with oxygen and moisture and thus prevents rusting.
(d) Iron and rust are the same substances. (True/False)
False. Iron and rust are different substances.Iron reacts with oxygen and moisture to form rust, which is a new substance.
(e) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change. (True/False)
True. Condensation of steam is a physical change. Steam condenses to form water which is just a change of state and no new substances are formed. So, it is a physical change.
3. Fill in the blanks in the following statements:
(a) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of _________.
(b) The chemical name of baking soda is _________.
(c) Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are _________ and _________.
(d) Changes in which only _________ properties of a substance change are called physical changes.
(e) Changes in which new substances are formed are called _________ changes.
Answers:
(a) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
(b) The chemical name of baking soda is sodium bicarbonate.
(c) Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are painting and galvanisation.
(d) Changes in which only physical properties of a substance change are called physical changes.
(e) Changes in which new substances are formed are called chemical changes.
4. When baking soda is mixed with lemon juice, bubbles are formed with the evolution of a gas. What type of change is it? Explain.
Answer:
When baking soda is mixed with lemon juice, bubbles are formed because carbon dioxide gas is evolved. Since carbon dioxide and other new substances are formed which have new properties, it is a chemical change.
5. When a candle burns, both physical and chemical changes take place. Identify these changes. Give another example of a familiar process in which both chemical and physical changes take place.
Answer:
When a candle burns, the physical change is the melting of the wax since it only involves a change of state. The chemical change is the burning of the wax to produce new substances like carbon dioxide.
Another example where which both chemical and physical changes take place is the burning of wood.
Physical change – Physical change is the moisture in the wood getting vapourised since it only involves a change of state.
Chemical change – Chemical change is the burning of the wood which produces carbon dioxide along with substances. Thus, new substances are formed and the reaction is not reversible.
6. How would you show that the setting of curd is a chemical change?
Answer:
It can be shown that setting of curd is a chemical change because curd tastes and smells different and is of a different colour than milk.When curd is formed it cannot be converted back into milk. Thus, a new substance is formed and the change is irreversible, making it a chemical change.
7. Explain why burning wood and cutting it into small pieces are considered two different types of changes.
Answer:
When wood is burnt it produces new substances like ash, carbon dioxide etc and the change is not reversible. Hence, it is a chemical change.
When you cut a log into pieces it only changes the physical properties like size and shape and no new substance is formed. Therefore, it is a physical change.
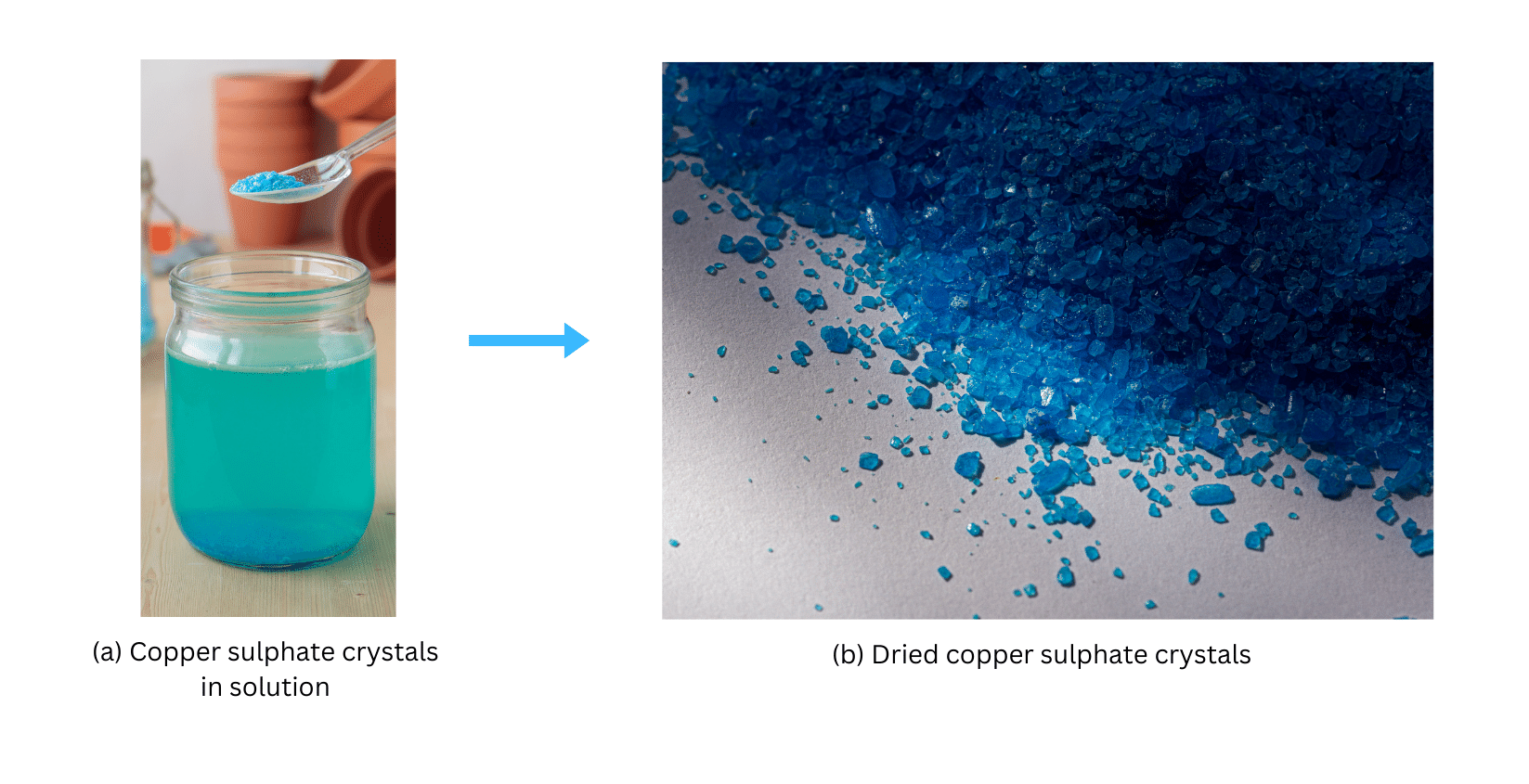
8. Describe how crystals of copper sulphate are prepared.
Answer:
Crystals of copper sulphate are prepared by boiling a solution of water and dilute sulphuric acid, while adding copper sulphate powder. When no more powder can be dissolved, the solution is filtered and cooled. The copper sulphate crystals will start forming.
The preparation of copper sulphate crystals is described in detail below:
Aim: To prepare copper sulphate crystals.
Materials Required: Beaker,water, dilute sulphuric acid, copper sulphate powder.
Procedure:
(i) Fill the beaker with a cupful of water and carefully add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid.
(ii) Heat the water until it boils.
(iii) Add copper sulphate powder slowly while continuously stirring the mixture to help the powder dissolve. Continue until no more powder can be dissolved.
(iv) Filter the solution and allow it to cool without any disturbance.
(v) Wait until blue copper sulphate crystals appear at the bottom of the beaker.
Observation:
After some time blue crystals of copper sulphate will begin to appear in the solution. The blue copper sulphate crystals, both in the solution and after separation using filter paper, are shown below:
9. Explain how painting an iron gate prevents it from rusting.
Answer:
Painting an irongate prevents it from rusting by forming a protective layer on top. Iron rusts on exposure to oxygen and water (or water vapour). If the iron gate is painted, it forms a protective layer on top which prevents exposure of iron to oxygen and water. This prevents it from rusting.
10. Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Answer:
Rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts because of excess moisture in coastal areas. Rusting occurs when iron comes into contact with oxygen and moisture. The air in coastal areas is much higher in moisture content than deserts, which makes it easier for rust to form on iron objects.
11. The gas we use in the kitchen is called liquified petroleum gas (LPG). In the cylinder it exists as a liquid. When it comes out from the cylinder, it becomes a gas (Change – A) then it burns (Change – B). The following statements pertain to these changes. Choose the correct one.
(i) Process – A is a chemical change.
(ii) Process – B is a chemical change.
(iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes.
(iv) None of these processes is a chemical change.
Answer: (ii) Process – B is a chemical change.
Process – A is just a change of state from liquid to gas. Therefore, it is a physical change.
In Process – B the LPG burns to form new substances like carbon dioxide and water and is an irreversible change. Therefore, it is a chemical change.
12. Anaerobic bacteria digest animal waste and produce biogas (Change – A). The biogas is then burnt as fuel (Change – B). The following statements pertain to these changes. Choose the correct one.
(i) Process – A is a chemical change.
(ii) Process – B is a chemical change
(iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes.
(iv) None of these processes is a chemical change.
Answer: (iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes.
In Process – A, anaerobic bacteria decompose animal waste and form a new substance biogas. Therefore, Process – A is a chemical change. In Process – B, biogas burns to produce new substances like carbon dioxide. Therefore, Process – B is also a chemical change.
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 56) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes:
1. Describe two changes that are harmful. Explain why you consider them harmful. How can you prevent them?
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects Question 1
2. Take three glass bottles with wide mouths. Label them A, B and C. Fill about half of bottle A with ordinary tap water. Fill bottle B with water which has been boiled for several minutes, to the same level as in A. In bottle C, take the same boiled water and of the amount as in other bottles. In each bottle put a few similar iron nails so that they are completely under water. Add a teaspoonful of cooking oil to the water in bottle C so it forms a film on its surface. Put the bottles away for a few days. Take out nails from each bottle and observe them. Explain your observations.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects Question 2
3. Prepare crystals of alum.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects Question 3
4. Collect information about the types of fuels used for cooking in your area. Discuss with your teachers/parents/others which fuels are less polluting and why.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects Question 4
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes:
1. (Page 52) We learnt in Chapter 1 that plants produce their food by a process called photosynthesis. Can we call photosynthesis a chemical change?
Answer:
We learnt in Chapter 1 that plants produce their food by a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a chemical change because new substances like carbohydrates and oxygen form from carbon dioxide and water. The new substances have different properties and the reaction is irreversible. Therefore, it is a chemical change.
2. (Page 52) Paheli said that even digestion is a chemical change.
Answer:
Paheli is right in saying that digestion of food is a chemical change.The stomach acids react with the food to break it down into simpler substances, so that digestion can occur easily. These substances have new properties and the change cannot be reversed. Therefore, it is a chemical change.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes:
1. Complete Activity 5.1 (Page 47). Cut a piece of paper in four square pieces. Cut each square piece further into four square pieces. Lay these pieces on the floor or a table so that the pieces acquire the shape of the original piece of paper (Fig. 5.1). Obviously, you cannot join the pieces back to make the original piece, but is there a change in the property of the paper?
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 5.2 (Page 47). Collect the chalk dust lying on the floor near the chalkboard in your classroom. Or, crush a small piece of chalk into dust. Add a little water to the dust to make a paste. Roll it into the shape of a piece of chalk. Let it dry. Did you recover chalk from the dust?
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 5.3 (Page 47). Take some ice in a glass or plastic tumbler. Melt a small portion of ice by placing the tumbler in the sun. You have now a mixture of ice and water. Now place the tumbler in a freezing mixture (ice plus common salt). Does the water become solid ice once again?
Answer:
4. Complete Activity 5.4 (Page 48). Boil some water in a container. Do you see the steam rising from the surface of water? Hold an inverted pan by its handle over the steam at some distance from the boiling water. Observe the inner surface of the pan. Do you see any droplet of water there?
Answer:
5. Complete Activity 5.5 (Page 48). Hold a used hack-saw blade with a pair of tongs. Keep the tip of the free end of the blade on the gas stove. Wait for a few minutes. Does the colour of the tip of the blade change? Remove the blade from the flame. Observe the tip once again after some time. Does it get back its original colour?
Answer:
6. Complete Activity 5.6 (Page 49). Get a small piece of a thin strip or ribbon of magnesium. Clean its tip with sandpaper. Bring the tip near a candle flame. It burns with a brilliant white light (Fig. 5.3). When it is completely burnt it leaves behind a powdery ash. Does the ash look like the magnesium ribbon? Collect the ash and mix it with a small amount of water. Stir the mixture (aqueous solution) well. Test the mixture with blue and red litmus papers. Does the mixture turn red litmus blue? Does the mixture turn blue litmus red? On the basis of this test, how do you classify the aqueous solution — acidic or basic?
Answer:
7. Complete Activity 5.7 (Page 50). (To be demonstrated by the teacher) Dissolve about a teaspoonful of copper sulphate (blue vitriol or neela thotha) in about half a cup of water in a glass tumbler or a beaker. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the solution. You should get a blue coloured solution. Save a small sample of the solution in a test tube or a small glass bottle. Drop a nail or a used shaving blade into the remaining solution. Wait for half an hour or so. Observe the colour of the solution. Compare it with the colour of the sample solution saved separately (Fig. 5.4). Do you see any change in the colour of the solution? Take out the nail or the blade. Has it changed in any way?
Answer:
8. Complete Activity 5.8 (Page 50). Take about a teaspoonful of vinegar in a test tube. Add a pinch of baking soda to it. You would hear a hissing sound and see bubbles of a gas coming out. Pass this gas through freshly prepared lime water as shown in Fig. 5.5. What happens to the lime water?
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes:
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Your mother may ask you to dissolve sugar in water to make a drink. What kind of a change is this?
Answer:
In this change solid sugar is dissolved in water and a liquid solution is formed. So only the state of the substance changes making it a physical change.
2. When food goes bad, what kind of a change is it?
Answer:
It is a chemical change because when food rots chemical reactions happen and new substances are formed.
3. You learnt that chemical changes are not reversible. Can you think of a physical change which is also not reversible?
Answer:
When we cut or tear a piece of paper into smaller pieces, we cannot join them back to recover the original bigger piece. So, it is a physical change (no new substance is formed) which cannot be reversed.
4. Milk turns sour. What kind of a change is this?
Answer:
During souring of milk bacteria coverts lactose in milk to lactic acid, which is a new substance. So, it is a chemical change.
5. Have you ever stretched a rubber band. What kind of change does it represent?
Answer:
When a rubber band is stretched, only the size and shape changes and no new substance is formed. So, it is a physical change.
6. A certain change produces energy. Could it be a physical change?
Answer:
The change yields energy which is a new substance with different properties. Therefore, it is a chemical change.
7. Can rust form in vacuum?
Answer:
Rust needs oxygen to form. There is no oxygen in vacuum and so rust will not form.
8. A jug of water is emptied into three glasses. What kind of a change is this?
Answer:
When the water in the jug is emptied into three glasses, the only change is in the amount of water. No new substance is formed with new properties. Therefore, it is a physical change.
9. What is the process of coating iron with copper called?
Answer:
The process of depositing copper on iron is called electroplating.
10. How can you easily tell whether a piece of cut apple, potato or brinjal has undergone a change?
Answer:
The colour of cut fruit or vegetable will turn brownish. The enzymes present in the fruit will react with the oxygen in air producing a chemical change.
11. If the odour of a substance changes, what change does it indicate?
Answer:
Change of odour indicates that new substances have been formed with different properties. This is a chemical change.
12. Name a monument in India that has not rusted in 1600 years.
Answer:
The iron pillar in front of the Qutub Minar in Delhi has not rusted in 1600 years.
Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Collect the chalk dust lying on the floor near the chalkboard in your classroom. Or, crush a small piece of chalk into dust. Add a little water to the dust to make a paste. Roll it into the shape of a
piece of chalk. Let it dry. Did you recover chalk from the dust? What kind of change is it?
Answer:
Yes, you can recover chalk from the dust. When chalk was crushed into dust and made into chalk again:
(i) The size and shape changed.
(ii) There was no new substance formed with new properties.
Therefore, it is a physical change.
2. Take some ice in a glass or a plastic tumbler. Melt a small portion of ice by placing the tumbler in the sun. You have now a mixture of ice and water. Now place the tumbler in a freezing mixture (ice plus common salt). Does the water become solid once again?
Answer:
Yes, the water will become solid ice once again. In this change:
(i) Only the state of the substance (water) changed.
(ii) There were no new substances formed with new properties.
Therefore, it is a physical change.
3. Boil some water in a container. Do you see steam rising from the surface of water? Hold an inverted pan by its handle over the steam at some distance from the boiling water. Observe the inner surface of the pan. Do you see any droplet of water there? What kind of a change is this?
Answer:
Yes, you will see droplets of water on the inner surface of the pan. In this activity:
(i) Water changed into steam and back into water.
(ii) Only the state of the substance changed.
(iii) There were no new substances formed with new properties.
Therefore, it is a physical change.
4. Hold a used hack-saw blade with a pair of tongs. Keep the tip of the free end of the blade on the gas stove. Wait for a few minutes. Does the colour of the tip of the blade change? Remove the blade from the flame. Observe the tip once again after some time. Does it get back its original colour?
Answer:
When the free end of the blade is kept in contact with the gas stove for a few minutes the colour of the blade tip changes to red. When the blade was removed from the flame it changed back to its original colour after some time. In this change:
(i) Only the colour of the substance changed.
(ii) There were no new substances formed with new properties.
Therefore, it is a physical change.
5. Suppose a glass jar in your kitchen falls by accident and breaks. What kind of change is it?
Answer:
When a glass jar falls and shatters into many tiny pieces:
(i) Only the size and shape changes.
(ii) No new substance is formed with new properties.
Therefore, it is a physical change even though it is not reversible (we cannot put the pieces back together to form the jar again).
6. You have learnt about the water cycle in Class 6. What kind of a change is this?
Answer:
In the water cycle, water from water bodies turn into water vapour by evaporation. This forms clouds in the sky which condense and fall on the earth as rain. The rain becomes groundwater and also returns to the water bodies like rivers and oceans. Thus, you can see that only the state of the water changes and there is no new substance formed. Therefore, it is a physical change.
7. You have seen in Chapter 4 that water gets heated by the process of convection. Is this a chemical change?
Answer:
No, it is a physical change. When water gets heated it becomes lighter and rises up and cold water comes in from the sides to take its place. This convection process only involves a change in temperature and the substance remains the same with the same properties. Therefore, it is a physical change.
8. Suppose sea water is heated and crystals of salt are obtained. What kind of a change is this?
Answer:
When sea water is heated the salt present in it separates out and forms solid crystals. The only change is in the state of the matter (i.e. salt) and no new substances are formed with new properties. Thus, it is a physical change.
9. What is the danger of using pure iron water pipes in your house? How can you prevent it?
Answer:
Iron water pipes will eventually rust due to exposure to oxygen and water and might break. Also, iron on rusting produces iron oxides. The water inside the pipes will contain these iron oxide impurities and can cause health hazards if we drink it. You can prevent it by depositing a layer of zinc on it by the process of galvanization. This forms a protective outer layer on the pipes and prevents rusting by reducing exposure to oxygen and water.
10. Why is the danger of rusting much higher than normal in ships?
Answer:
A large portion of the ship’s hull, the propellors etc stay submerged under water. Even above the surface, water droplets cling to the ship’s outer body and wet the surface. Also, sea water is salty and accelerates the process of rusting. All these factors contribute to excessive rusting in ships.
11. Lots of substances made of iron have to be partially or completely replaced every year due to rusting. Can you imagine the monetary loss to the world?
Answer:
The global monetary loss due to corrosion is estimated to be 2 – 3 trillion dollars every year! In India alone lakhs of crores of rupees every year are lost due to corrosion.
Long Answer Type Questions:
1. Name the main differences between physical change and chemical change?
Answer:
The main differences between physical change and chemical change are:
| Physical Change | Chemical Change |
| (i) Only the shape, size, colour and state of the substance changes. The substance remains the same. | (i) New substances are formed. |
| (ii) The properties of the substance remain the same. | (ii) The new substances formed have different properties. |
| (iii) Lots of physical changes can be reversed. | (iii) All chemical changes are irreversible. |
| (iv) Examples: Boiling of water, heating of iron etc. | (iv) Examples: Rusting, chemical reactions, photosynthesis. |
2. Give an example of a chemical reaction for each of the following situations: (NCERT Exemplar)
(a) A change in colour is observed.
(b) A gas is evolved.
(c) Sound is produced.
Answers:
(a) When grey iron is exposed to moisture and air, orange-brown coloured rust is formed:
Iron + Oxygen (O2) + Water (H2O) → Iron Oxide (Rust)
(b) The acid-base neutralisation reaction between acidic vinegar (Acetic Acid) and basic baking soda (Sodium Hydrogencarbonate) leads to the evolution of carbon dioxide gas:
Vinegar (acid) + Baking Soda (base) → Sodium Acetate (salt) + Carbon Dioxide + Water
(c) When a firecracker explodes the reactants form new substances with completely different properties like gases, heat, light and sound.
3. Describe a chemical change that occurs with the formation of light.
Answer:
A chemical change that emits light is the burning of magnesium ribbon in air:
Aim: To prove that burning of magnesium ribbon in air emits light.
Materials Required: Magnesium ribbon, sandpaper, Bunsen burner, tweezers.
Procedure:
(i) Get a thin strip of magnesium ribbon.
(ii) Clean the tip of the ribbon by rubbing with sandpaper.
(iii) Light a Bunsen burner and hold the magnesium ribbon directly on the flame with a pair of tweezers. Observe what happens. (Caution: do not stare too long directly at the flame, it can harm your eyes)
Observation: The magnesium ribbon burns with a brilliant white flame. It forms a powdery ash which is white in colour, unlike the magnesium ribbon.
Conclusion: A chemical change takes place because magnesium reacts with the oxygen in air to form magnesium oxide and light, which are new substances with new properties. The chemical reaction is shown below:
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → Magnesium oxide (MgO) + Light
4. You have learnt that iron can be coated with paint or grease to prevent it from corroding due to rusting. Can iron be coated with another metal to prevent corrosion? Describe with an experiment.
Answer:
Iron can be coated by copper (metal) using the following process:
Aim: To coat iron using copper metal.
Materials Required: Beaker, any other container, copper sulphate (blue vitriol), water, dilute sulphuric acid, iron blade.
Procedure:
(i) Pour some water into a glass beaker and dissolve a teaspoon of copper sulphate (blue vitriol) in it.
(ii) Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the solution.
(iii) Save some of the solution. Pour the rest into a container with a wide enough mouth and drop an iron blade into it.
(iv) Wait for half an hour and observe what happens.
Observation: The copper sulphate solution which was saved was blue in colour. The remaining solution to which the iron blade was added will turn green in colour. Also, the iron blade itself will have turned brown in colour.
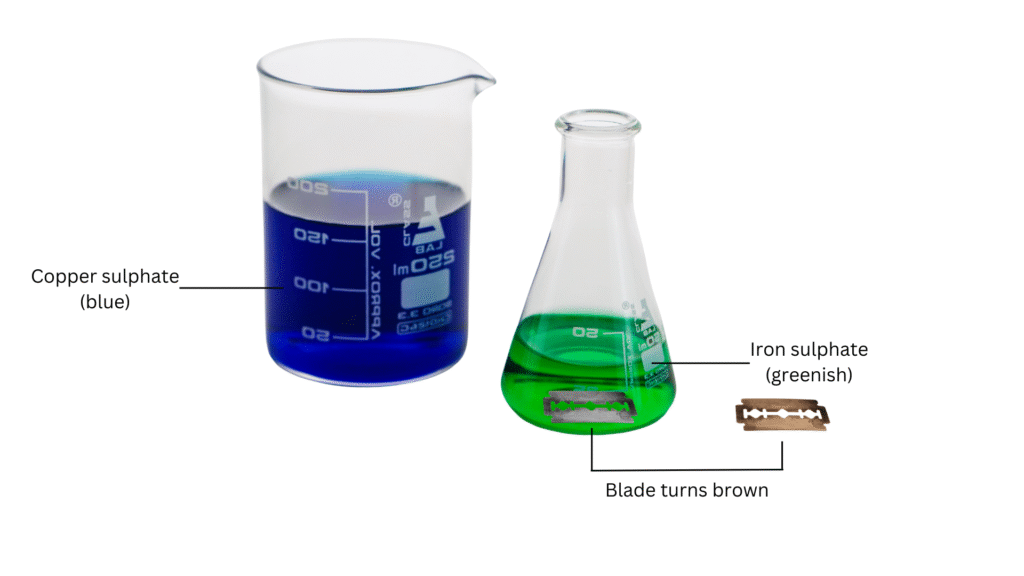

Conclusion:
A chemical reaction happened here. The copper sulphate solution reacted with the iron in the blade to form a new substance iron sulphate and this turned the solution green in colour. In turn, the copper in copper sulphate got deposited on the iron blade making it brown. The reaction is shown below:
Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Iron (Fe) → Iron Sulphate (FeSO4) + Copper (Cu)
This technique of depositing copper on iron is one example of a technique called electroplating. The protective layer of copper protects the iron from corrosion.
5. What are the different ways to prevent iron from rusting?
Answer:
The different ways to prevent iron from rusting are as follows:
(i) You can regularly apply a coat of grease or paint on iron to prevent exposure to oxygen and moisture.
(ii) You can deposit other metals like copper, zinc, chromium on iron to form a protective coating. The process of depositing copper on iron is called electroplating, while that of depositing zinc is called galvanisation.
(iii) You can also mix iron with carbon and metals like chromium, nickel and manganese to form stainless steel. Stainless steel contains a protective outer layer and does not rust.
Complete the table:
1. Classify the following as physical and chemical changes:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Burning of plant matter | |
| (ii) Crystallisation | |
| (iii) Generation of electricity | |
| (iv) Folding of paper | |
| (v) Mixing water and oil |
Answer:
The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Burning of plant matter | Chemical change |
| (ii) Crystallisation | Physical change |
| (iii) Generation of electricity | Chemical change |
| (iv) Folding of paper | Physical change |
| (v) Mixing water and oil | Physical change |
Fill in the blanks:
heat, rust, coating, physical, permanent
(a) A chemical change is a _________ change.
(b) Changes caused by _________ can be both physical and chemical.
(c) One way to reduce rusting in ships is apply _________ on the outer deck.
(d) Suppose you throw a ball with all your strength. This is a _________ change.
(e) Heavy rains during rainy season can cause _________.
Answers:
(a) A chemical change is a permanent change.
(b) Changes caused by heat can be both physical and chemical.
(c) One way to reduce rusting in ships is apply coating on the outer deck.
(d) Suppose you throw a ball with all your strength. This is a physical change.
(e) Heavy rains during rainy season can cause rust.
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes:
An expert team of Indian and foreign educated teachers, engineers and scientists have prepared these solutions, taking into account every detail and every concept. All the extended learning projects and in-text activities have been answered for your benefit. We believe that the best way to learn the concepts is to test yourself with different kinds of questions. The extra questions we have included will help clarify your concepts and help you solve similar questions in exams.
The free PDFs of the solutions are available for download anytime! It is our duty to keep providing you with top-quality study material which will help clear your concepts and help you prepare. So, keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list to access them early and for free!
The following topics are covered:
5.1 – Physical Changes
5.2 – Chemical Change
5.3 – Rusting of Iron
5.4 – Crystallisation
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 1 Classification Type Question (Question 1)
(ii) 1 True/False Type Question (Question 2)
(iii) 1 Fill in the Blanks Type Question (Question 3)
(iv) 6 Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10)
(v) 1 Long Answer Type Questions (Question 8)
(vi) 2 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) (Questions 11, 12)
Yes of course! You can download the free PDF versions of educationroundtheworld.com’s NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes anytime for free! All the different types of additional questions are also included in the PDF version! Please look towards the top of the page!
You will need to learn the differences between physical and chemical changes and how to identify the various types of physical and chemical changes.
Start by reading the chapter. Then test your knowledge by trying to answer all the different questions in the solutions material, including the extra questions we have designed ourselves. We have designed the questions in a scientific way to help clear your concepts and prepare you to answer similar questions in the exam.
In terms of coaching and mentoring we offer the complete package. Our expert teacher-mentors excel in coaching and mentoring young students like you and will go the extra mile. Contact us anytime and we’ll be happy to help you!
We offer top-quality education and academic and career mentoring as a complete package. It is our job to make you aware of your hidden talents and the opportunities that lie ahead, so you can make the most of them. If that is what you are looking for, feel free to reach out to us. Our expert teacher-mentors would love to get to know you. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Contact us with your requirements and we’ll be happy to help you out! Book an appointment now!


