Hello students and welcome to Chapter 6! Find excellent solutions to all exercise questions and extended learning activities right here. We have also taken care to answer all the in-text questions and in-text activities for your benefit. We have even designed extra questions of various formats for practice and attractive figures have also been included wherever necessary. The topic has been covered comprehensively and studying these materials in detail will prepare you well for your exams.
Solutions to Exercise (Page No 67) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms:
1. Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Answer: An athlete breathes faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race because:
(i) During the race a lot of oxygen is needed by the body to produce energy to carry out the physical activity. So, the oxygen level in the body gets depleted and faster and deeper breaths are needed after the race to replenish the oxygen level.
(ii) During the race the athlete’s muscle cells also respire anaerobically to meet the extra demand for energy. During this process lactic acid is accumulated which causes cramps. Taking deep breaths increases the supply of oxygen to the muscle cells, which breaks down the lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water. This helps to get relief from cramps.
(iii) Faster and deeper breaths also help to expel the excess carbon dioxide accumulated in the body during the race.
2. List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer: The similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration are as follows:
(i) Both break down glucose to release energy which is used by our body to function.
(ii) Both take place in the cells of organisms.
(iii) Both produce by-products by breaking down glucose.
The differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration as follows:
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| (i) Occurs in the presence of oxygen. | (i) Occurs in the absence of oxygen. |
| (ii) Releases a greater amount of energy. So, it is more effective. | (ii) Releases a lesser amount of energy. So, it is less effective. |
| (iii) The by-products are carbon dioxide and water. | (iii) The by-products are carbon dioxide and alcohol. |
| (iv) It lasts for a long time. | (iv) It is a short-term process. |
| (v) It is more common. | (v) It is less common. |
| (vi) Aerobic respiration occurs in plants, animals but not bacteria, yeast etc. | (vi) Anaerobic respiration occurs in plants, animals and also in bacteria, yeast. |
3. Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
Answer:
When we inhale a lot of dust-laden air, some of these dust particles may get past the nasal hairs and irritate the lining of the cavity. This triggers a reflexive sneeze which expels the potentially harmful foreign particles from our nose and enables dust-free clean air to enter our body.
4. Take three test-tubes. Fill ¾th of each with water. Label them A, B and C. Keep a snail in test-tube A, a water plant in test-tube B and in C, keep snail and plant both. Which test-tube would have the highest concentration of CO2?
Answer:
In test tube A, the snail will breathe in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. This will keep increasing the level of CO2 in test tube A.
In test tube B, the water plant will take in CO2 and gives out oxygen. So, the level of CO2 in test tube B will keep on decreasing.
In test tube C, both the snail and the plant are present. The snail will release CO2 during respiration. However much of this CO2 released by the snail will be absorbed by the plant during respiration and oxygen will be released. So, the level of CO2 in test tube C will be less than test tube A.
As a result, the test tube A will have the highest concentration of CO2.
5. Tick the correct answer:
(a) In cockroaches, air enters the body through
(i) lungs (ii) gills
(iii) spiracles (iv) skin
(b) During heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation of
(i) carbon dioxide (ii) lactic acid
(iii) alcohol (iv) water
(c) Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest is
(i) 9–12 (ii) 15–18
(iii) 21–24 (iv) 30–33
(d) During exhalation, the ribs
(i) move outwards (ii) move downwards
(iii) move upwards (iv) do not move at all
Answers:
(a) (iii) spiracles
(b) (ii) lactic acid
(c) (ii) 15–18
(d) (ii) move downwards
6. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Yeast | (i) Earthworm |
| (b) Diaphragm | (ii) Gills |
| (c) Skin | (iii) Alcohol |
| (d) Leaves | (iv) Chest cavity |
| (e) Fish | (v) Stomata |
| (f) Frog | (vi) Lungs and skin |
| (vii) Tracheae |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Yeast | (iii) Alcohol |
| (b) Diaphragm | (iv) Chest cavity |
| (c) Skin | (i) Earthworm |
| (d) Leaves | (v) Stomata |
| (e) Fish | (ii) Gills |
| (f) Frog | (vi) Lungs and skin |
7. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(i) During heavy exercise, the breathing rate of a person slows down. (T/F)
(ii) Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day and respiration only at night. (T/F)
(iii) Frogs breathe through their skins as well as their lungs. (T/F)
(iv) Fishes have lungs for respiration. (T/F)
(v) The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation. (T/F)
Answers:
(i) During heavy exercise, the breathing rate of a person slows down. (T/F)
False.During heavy exercise, the breathing rate of a person increases to take in more oxygen that is needed to meet the extra demand for energy.
(ii) Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day and respiration only at night. (T/F)
False. Most plants do carry out photosynthesis only during the day, but respiration happens both during the day and night.
(iii) Frogs breathe through their skins as well as their lungs. (T/F)
True. Frogs breathe through their skins while underwater and through their lungs while on land.
(iv) Fishes have lungs for respiration. (T/F)
False. Fishes do not have lungs for respiration, they have gills for respiration. Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration happen through blood vessels on the gills.
(v) The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation. (T/F)
True. The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation.During inhalation the ribs move up and outwards and diaphragm moves down, thereby increasing space in the chest cavity.
8. Given below is a square of letters in which are hidden different words related to respiration in organisms. These words may be present in any direction — upwards, downwards, or along the diagonals. Find the words for your respiratory system. Clues about those words are given below the square.
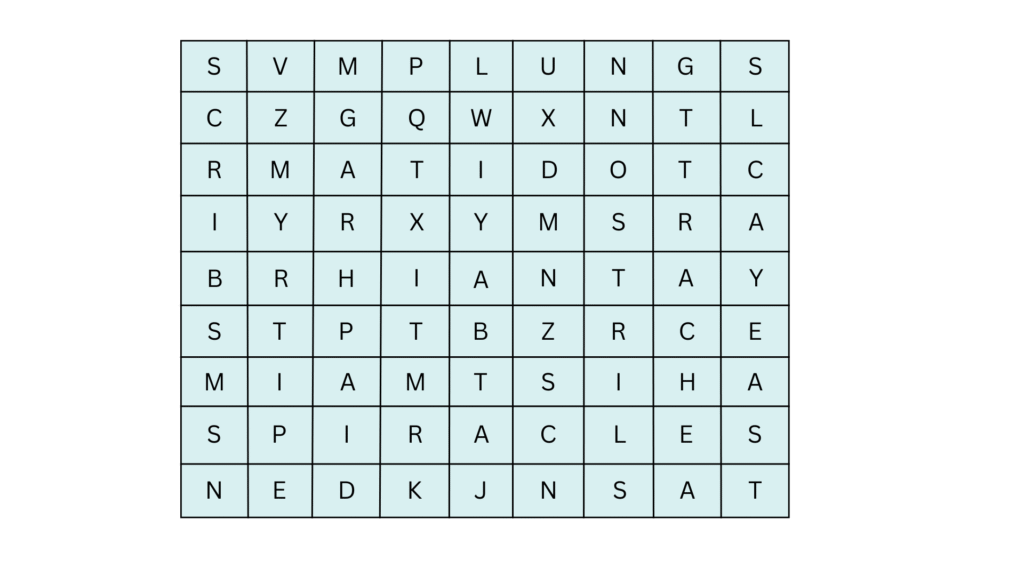
(i) The air tubes of insects
(ii) Skeletal structures surrounding chest cavity
(iii) Muscular floor of chest cavity
(iv) Tiny pores on the surface of a leaf
(v) Small openings on the sides of the body of an insect
(vi) The respiratory organs of human beings
(vii) The openings through which we inhale
(viii) An anaerobic organism
(ix) An organism with tracheal system
Answers:
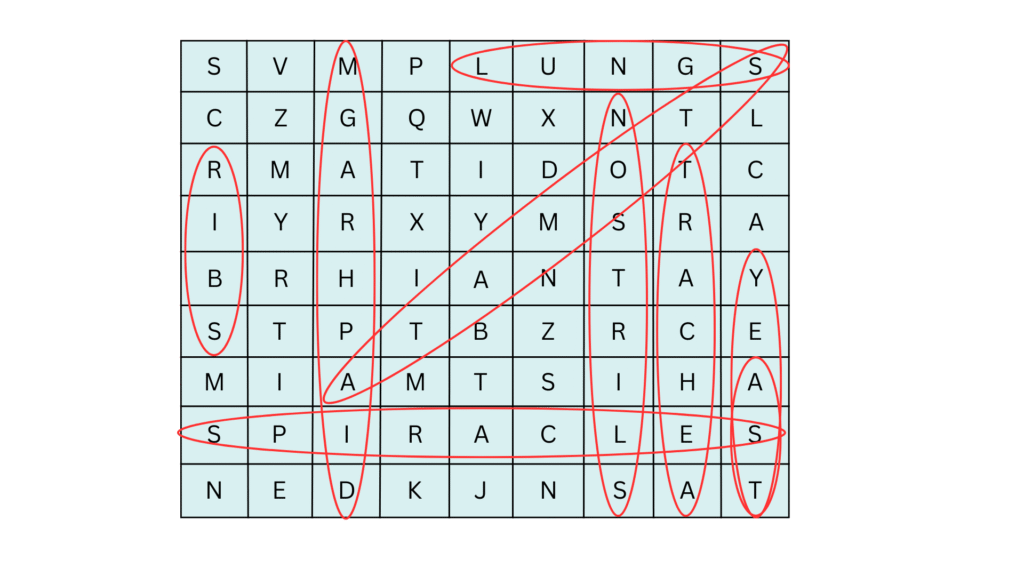
Find the required words marked above in red ovals and also listed below:
(i) Trachea
(ii) Ribs
(iii) Diaphragm
(iv) Stomata
(v) Spiracles
(vi) Lungs
(vii) Nostrils
(viii) Yeast
(ix) Ant
9. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because:
(a) At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air.
(b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
(c) The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground.
(d) The pressure of air is higher than that on the ground.
Answers: (b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
There is less amount of air particles and hence, oxygen, present in the air at high altitudes. So, to compensate for the lack of oxygen mountaineers need to carry oxygen cylinders and oxygen masks.
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 69) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms:
1. Observe fish in an aquarium. You will find flap like structures on both sides of their heads. These are flaps which cover the gills. These flaps open and close alternately. On the basis of these observations, explain the process of respiration in the fish.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Question 1
2. Visit a local doctor. Learn about the harmful effects of smoking. You can also collect material on this topic from other sources. You can seek help of your teacher or parents. Find out the percentage of people of your area who smoke. If you have a smoker in your family, confront him with the material that you have collected.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Question 2
3. Visit a doctor. Find out about artificial respiration. Ask the doctor:
(a) When does a person need artificial respiration?
(b) Does the person need to be kept on artificial respiration temporarily or permanently?
(c) From where can the person get supply of oxygen for artificial respiration?
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Question 3
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms:
1. (Page 57) One day Boojho was eagerly waiting to meet his grandparents who were coming to the town after a year. He was in a real hurry as he wanted to receive them at the bus-stop. He ran fast and reached the bus-stop in a few minutes. He was breathing rapidly. His grandmother asked him why he was breathing so fast. Boojho told her that he came running all the way. But the question got stuck in his mind. He wondered by running makes a person breathe faster?
Answer:
Oxygen taken in during respiration is used to produce energy. When Boojho was running fast, he needed more energy and so the demand for oxygen was much more than normal. Therefore, the oxygen level in his body got depleted and he had to breathe faster and deeper to restore the normal oxygen level in his body.
2. (Page 57) Even when we are eating, sleeping or reading we require energy. But, where does this energy come from? Can you say why your parents insist that you should eat regularly?
Answer:
Even when we are eating, sleeping or reading we require energy.The energy needed to function comes from food. For that reason you need to eat regularly, otherwise you will feel tired and not be able to carry out your daily activities properly.
3. (Page 58) Have you every wondered why you get muscle cramps after heavy exercise?
Answer:
During heavy exercise temporary anaerobic respiration also takes place alongside aerobic respiration to help meet the excess demand for oxygen. During this anaerobic respiration process lactic acid forms from partial breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen:
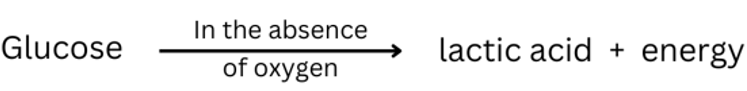
This lactic acid accumulates in the muscles and causes muscle cramps which can be painful.
4. (Page 58) We get relief from cramps after a hot water bath or a massage. Can you guess why it is so?
Answer:
A hot water bath or a massage improves the blood circulation and hence, transport of oxygen in the body. So, a greater amount of oxygen reaches the muscle cells quickly and complete breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water occurs. The accumulated lactic acid is thus removed and you get relief from cramps and the associated pain.
5. (Page 59) Boojho noticed that when he released his breath after holding it for some time, he had to breathe heavily. Can you tell him why it was so?
Answer:
Boojho noticed that when he released his breath after holding it for some time, he had to breathe heavily.This is because the oxygen in his lungs got used up by the body and the carbon dioxide level increased. Hence, Boojho had to breathe deeply to restore the depleted oxygen level in his body.
6. (Page 60) Why do we feel hungry after a physical activity?
Answer:
During a physical activity our body needs extra energy than normal. So, a person breathes faster to take in more oxygen which speeds up the breakdown of food in the cells and releases extra energy. Hence the food in our body gets used up fast and we feel hungry after an intense physical activity.
7. (Page 60) When you feel drowsy, does your breathing rate slow down? Does your body receive sufficient oxygen?
Answer:
Yes, our breathing rate slows down when we feel drowsy. During drowsiness we are less physically active and so less energy is required by the body to carry out the necessary biological processes. So even though the breathing rate slows down, the supply of oxygen is still enough for the body to function normally.
8. (Page 60) Paheli wants to know why we yawn when we are sleepy or drowsy?
Answer:
We yawn when we are sleepy or drowsy to take in extra oxygen. When we are sleepy our breathing rate slows down and the oxygen level in our body decreases and carbon dioxide level increases. Yawning helps to restore the balance by taking in extra oxygen and eliminating carbon dioxide from the body.
9. (Page 61) Take a deep breath. Keep your palm on the abdomen, feel the movement of the abdomen. What do you find?
Answer:
You will find that your abdomen expands as you inhale and contracts as you exhale. When you inhale the diaphragm which is positioned below the lungs and the heart moves downwards and results in expansion of the abdomen. Conversely, when you exhale the diaphragm moves upwards and results in contraction of the abdomen.
10. (Page 63) You are aware that air we inhale or exhale is a mixture of gases. What do we exhale? Do we exhale only carbon dioxide or a mixture of gases along with it?
Answer:
The air we exhale contains a mixtures of gases namely: carbon dioxide, oxygen, water vapour, nitrogen and small amounts of certain other gases.
11. (Page 63) You must have observed that if you exhale on a mirror, a film of moisture appears on its surface. From where do these droplets come from?
Answer:
The air you exhale contains water vapour which condenses on the colder surface of the mirror to form liquid. Many tiny liquid droplets collect on the surface of a mirror and gives it the foggy appearance.
12. (Page 63) Boojho wants to know how much air a person can hold in the lungs?
Answer:
The maximum air a person can hold in the lungs is 4.5 – 6 litres of air on average. These are average values and the lung capacity varies from person to person according to the person’s age, gender and physical condition.
13. (Page 64) Boojho wants to know if cockroaches, snails, fish, earthworms, ants and mosquitoes also have lungs?
Answer:
Only land snails have lungs. Cockroaches, aquatic snails, fish, earthworms, ants and mosquitoes do not have lungs.
| Organisms | Mode of Respiration |
| Cockroaches | Using spiracles and tracheal tubes |
| Snails | Using lungs and gills (depends on the type of snail) |
| Fish | Gills |
| Earthworms | Using skin |
| Ants | Using spiracles and tracheal tubes |
| Mosquitoes | Using spiracles and tracheal tubes |
14. (Page 65) Boojho has seen in television programmes that whales and dolphins often come up to the water surface. They even release a fountain of water sometimes while moving upwards. Why do they do so?
Answer:
Whales and dolphins often come up to the water surface and even release a fountain of water sometimes while moving upwards.This is because they breathe through their blowholes or nostrils. When whales and dolphins surface and exhale, water vapour in contact with the cold air of the atmosphere condenses and appears like a fountain.
5. (Page 65) Can we breathe and survive in water? There any organisms which live in water. How do they breathe under water?
Answer:
We humans cannot breathe and survive in water because our lungs are not designed to breathe underwater.
Organisms such as fish are equipped with gills which are rich in blood vessels. These blood vessels effectively absorb the oxygen from water into the bloodstream. This enables many aquatic organisms like fish to breathe under water.
16. (Page 65) Paheli wants to know whether roots, which are underground also take in oxygen? If so, how?
Answer:
Yes, roots which are underground also taken in oxygen. Root cells also need oxygen using which it generates energy to carry out essential biological processes. So, root hairs take in oxygen from air that is trapped in the spaces between the soil particles.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms:
1. Complete Activity 6.1 (Page 58). Close your nostrils and mouth tightly and look at a watch. What did you feel after some time? How long were you able to keep both of them closed? Note down the time for which you could hold your breath. (Caution: Do this activity under the supervision of your teacher)
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 6.2 (Page 59). Generally we are not aware that we are breathing. However, if you try you can count your rate of breathing. Breathe in and out normally. Find out how many times you breathe in and breathe out in a minute? Did you inhale the same number of times as you exhaled? Now count your breathing rate (number of breaths/minute) after brisk walk and after running. Record your breathing rate as soon as you finish and also after complete rest. Tabulate your findings and compare your breathing rates under different conditions with those of your classmates.
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 6.3 (Page 60). Figure 6.3 shows the various activities carried out by a person during a normal day. Can you say in which activity, the rate of breathing will be the slowest and in which it will be the fastest? Assign numbers to the pictures in the order of increasing rate of breathing according to your experience.
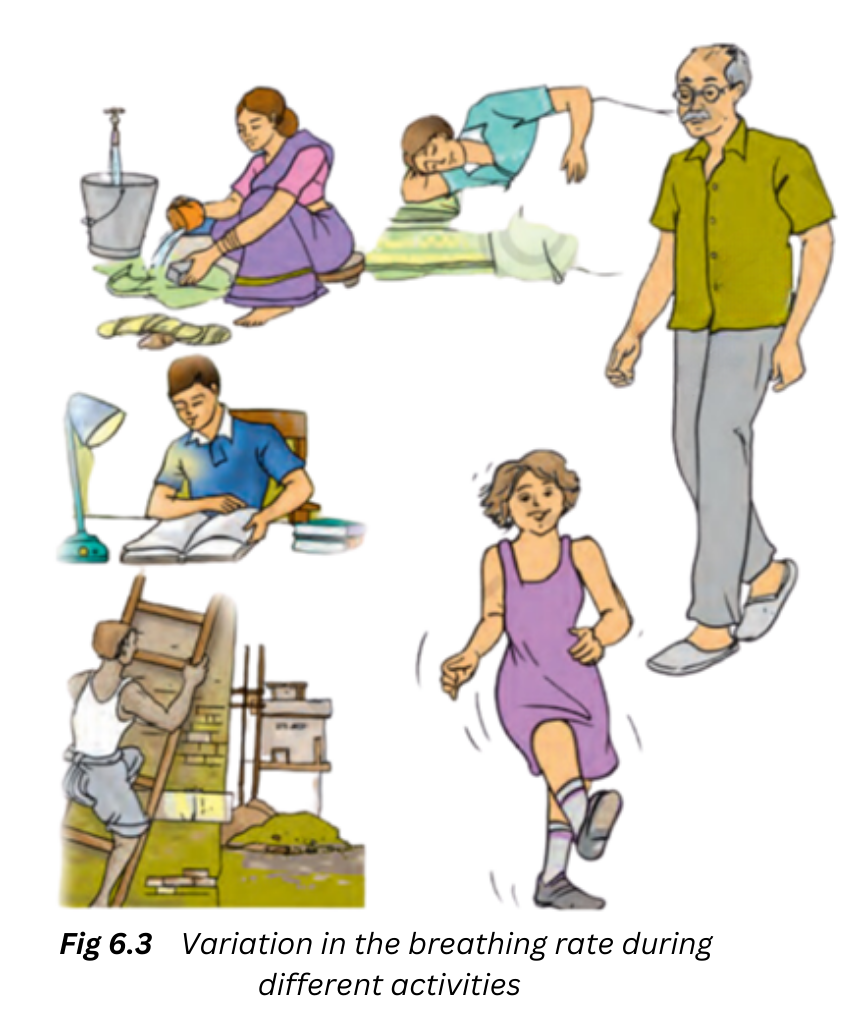

Answer:
4. Complete Activity 6.4 (Page 62). Take a deep breath. Measure the size of the chest with a measuring tape (Fig. 6.6) and record your observations in Table 6.2. Measure the size of the chest again when expanded and indicate which classmate shows the maximum expansion of the chest.
Answer:
5. Complete Activity 6.5 (Page 62). Take a wide plastic bottle. Remove the bottom. Get a Y-shaped glass or plastic tube. Make a hole in the lid so that the tube may pass through it. To the forked end of the tube fix two deflated balloons. Introduce the tube into the bottle. Now cap the bottle. Seal it to make it airtight. To the open base of the bottle tie a thin rubber or plastic sheet using a rubber band. To understand the expansion of the lungs, pull the rubber sheet from the base downwards and watch the balloons. Next, push the rubber/plastic sheet up and observe the balloons. Did you see any changes in the balloons?
What do the balloons in this model represent? What does the rubber sheet represent?Now, you should be able to explain the mechanism of breathing.
Answer:
6. Complete Activity 6.6 (Page 63). Take a slender, clean test tube or a glass/plastic bottle. Make a hole in its lid and fix it on the bottle. Pour some freshly prepared lime water in the test-tube. Insert a plastic straw through the hole in the lid in such a way that it dips in lime water. Now blow gently through the straw a few times. Is there a change in the appearance of lime water? Can you explain this change on the basis of what you learnt in Chapter 6?
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms:
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. You know that carbon dioxide is expelled from our body during breathing. What happens if excess carbon dioxide is present in our blood?
Answer:
If you have excess carbon dioxide in your blood it might lead to breathing trouble, weakness and even loss of consciousness.
2. Why do people suffocate if they are caught in a fire?
Answer:
During a fire toxic gases like carbon monoxide will be released. Any person in the immediate vicinity will inhale these toxic gases and suffocate due to oxygen deprivation.
3. Where is the diaphragm located?
Answer:
The diaphragm is a muscular sheet which is located below the lungs and the heart.
4. What is the diaphragm made of?
Answer:
The diaphragm is made of muscle.
5. Name an animal that breathes through more than one organ.
Answer:
Frogs can breathe through both their lungs and skin.
6. There is a similarity between how plants and insects breathe. What do you think it is?
Answer:
Plants breathe through tiny pores called stomata in the leaves and insects breathe through tiny pores called spiracles on their body.
7. The air we inhale contains more oxygen than the air we exhale. Why is this so?
Answer:
Some of the oxygen we inhale is absorbed by the lungs and is used up by the body, so the air we exhale contains less oxygen.
8. Butterflies breathe through lungs. Is the statement true or false?
Answer:
False. Butterflies are insects and breathe through spiracles and tracheae.
9. We all breathe oxygen. But can you think of a situation where oxygen might actually be harmful for you?
Answer:
Yes, pure or 100% oxygen can actually be quite harmful for your body.
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Breathing is a process that (NCERT Exemplar)
(i) provides O2 to the body.
(ii) breaks down food to release energy.
(iii) helps the body to get rid of CO2.
(iv) produces water in the cells.
Answer: Correct answer:(i) and (iii)
Breathing is a part of the respiration process that involves taking in O2 and giving out carbon dioxide. So, steps (i) and (iii) are correct.
2. What happens if you water your plants too much?
(i) The plants thrive and grow even bigger.
(ii) The plants cannot breathe and die.
(iii) The plants remain stunted.
(iv) The plants are able to carry out photosynthesis more effectively.
Answer: Correct answer: (ii) The plants cannot breathe and die.
The root cells of plants breathe in air trapped in the spaces between soil particles. If you water the plants too much the water fills the spaces inside the soil where air used to exist. Thus, the plant will not be able to breathe properly and eventually die.
Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Are breathing and respiration the same? Explain.
Answer:
No breathing is only a part of the respiration process:
- The respiration process starts with us breathing in air which contains oxygen.
- This air is transported to all parts of our body and ultimately reaches each cell.
- In the cell oxygen is used to break down food and release energy.
Thus, we can see that the respiration process is elaborate and only starts with breathing.
2. Explain why humans cannot produce alcohol like yeast?
Answer:
Yeast respires anaerobically and uses oxygen to break down sugarslike glucose intoalcohol and carbon dioxide. Humans on the other hand respire aerobically in the presence of oxygen and this process does not involve the production of alcohol. Thus, yeast and not humans can be used to produce alcohol like wine and beer.
3. On a very cold morning, Boojho and Paheli were talking with each other as they walked down to their school. They observed that the air coming out of their mouth looked like smoke. They were amused and wondered how it happened. Help them find the answer. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
The air they exhale contains water vapour and is warmer than the cold air outside. Therefore, it condenses on contact with the cold air outside to form mist, which looks like white smoke.
4. Why is it dangerous to hold your breath for too long?
Answer:
If you hold your breath for long enough your body will be deprived of oxygen and the carbon dioxide level in your body will increase. This imbalance can damage all your organs such as the brain, heart etc.
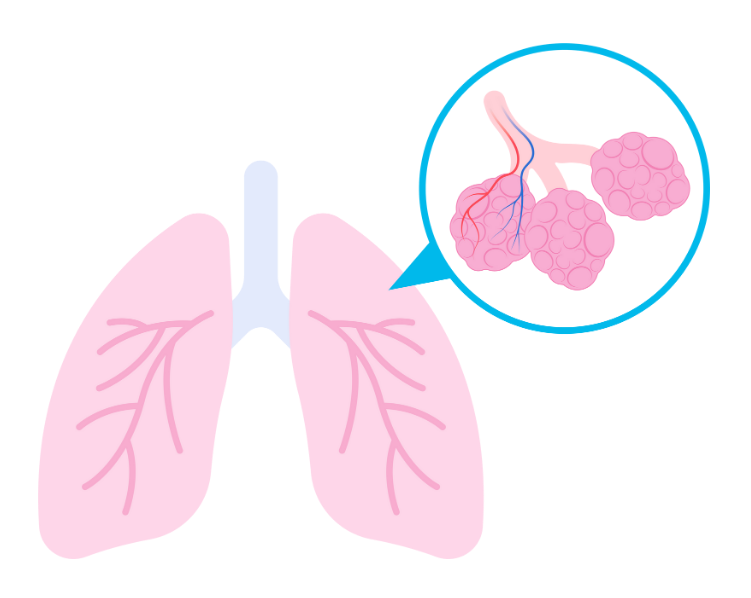
5. Name and label the vital organs involved in the respiratory process.
Answer:
The vital organs involved in the respiration process are the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. Find the organs labelled in the figure below:
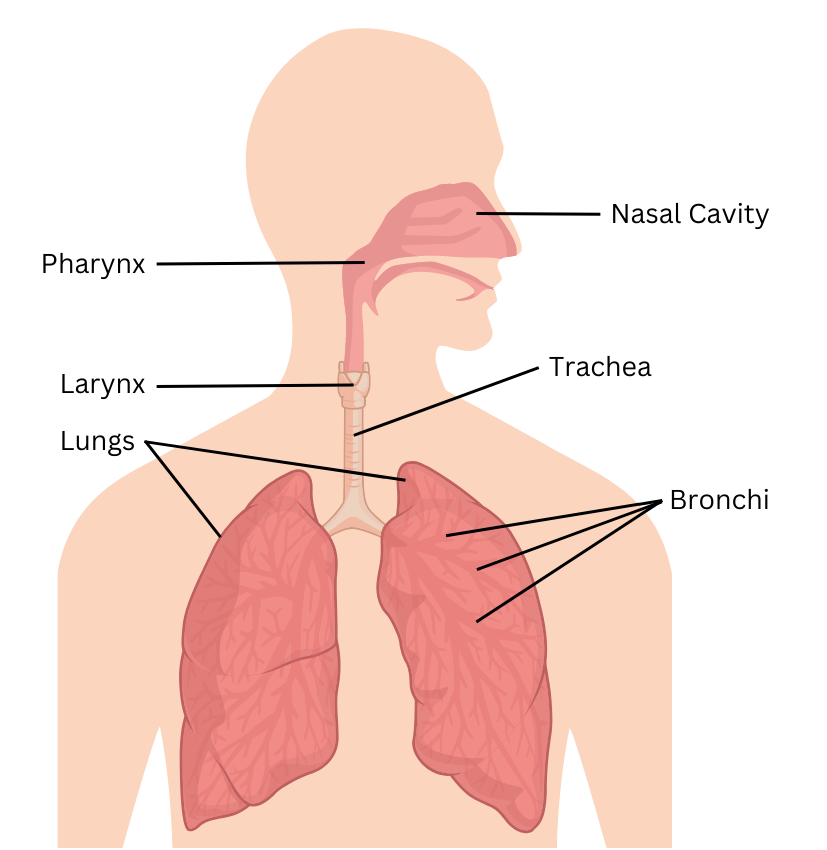
6. We all know that during respiration oxygen in inhaled and carbon dioxide is expelled from out body. Where does this process actually happen?
Answer:
The process of exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide taken place within tiny air sacs called alveoli in the lungs. The oxygen we take in enters the alveoli inside the lungs and is then absorbed into the bloodstream. Conversely, the waste carbon dioxide enters the alveoli from the bloodstream and is then expelled during exhalation.
7. What are the advantages of large sized lungs?
Answer:
The benefits of large sized lungs are as follows:
(i) More Oxygen Intake: If your lungs have higher capacity then more oxygen can be inhaled with each breath. This oxygen can then be used to break down food to release more energy for intense physical activities.
(ii) Carbon Dioxide Removal: Large lungs can be more effective at removing carbon dioxide and other waste gases from the body during exhalation.
8. Why does an earthworm have moist skin?
Answer:
An earthworm should have moist skin to enable easy exchange of gases during breathing. If the skin of an earthworm dries out, it will have trouble breathing and suffocate.
9. How does pranayama keep you healthy?
Answer:
Doing pranayama (breathing exercises) on a daily basis increases the capacity of the lungs. This increases the amount of oxygen supplied to the cells which results in faster breakdown of food and more energy is released. This helps us to stay more energetic and reduces fatigue.
Long Answer Type Questions:
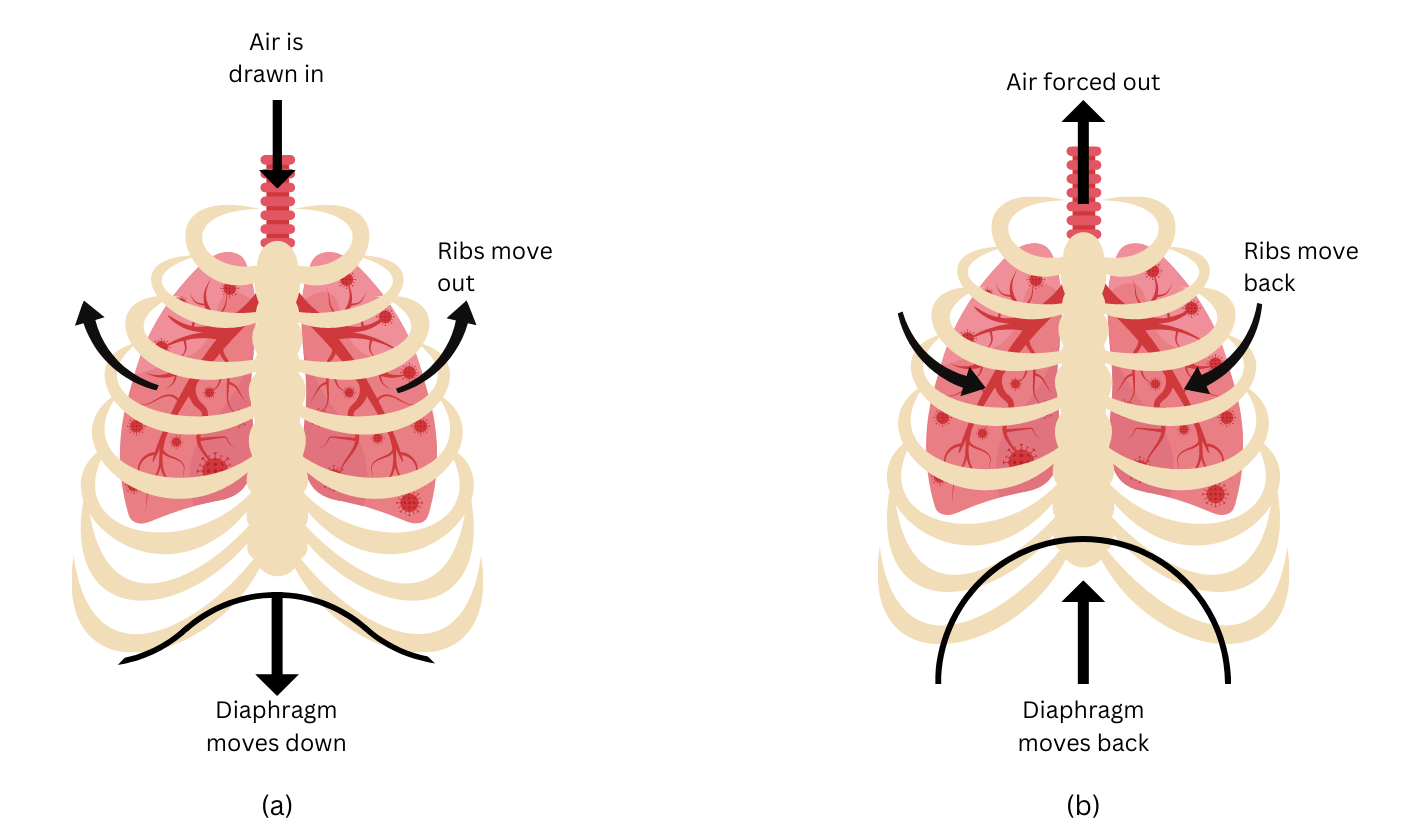
1. Describe the mechanism of breathing in humans with diagram.
Answer: The mechanism of breathing can be described as follows:
Step 1 Inhalation: When you inhale the ribs move up and outwards and the diaphragm moves down, thereby increasing the space in the chest cavity and allowing the lungs to expand. When the lungs expand air is drawn in through the airways into the lungs. The process is shown in Figure (a).
Step 2 Exhalation: When you exhale the ribs move down and inwards and the diaphragm moves upwards. This decreases the volume of the chest cavity and as a result the pressure inside the lungs increases, thereby pushing out the air from the lungs. This is shown in Figure (b).
2. Give the differences in the modes of respiration for humans and cockroaches.
Answer: The differences in the modes of respiration for humans and cockroaches are as follows:
| Humans | Cockroaches |
| (i) Humans inhale air through the nose. | (i) Cockroaches take in air through spiracles. |
| (ii) The air we inhale passes through the pharynx, larynx and then the trachea (windpipe) to reach the lungs. | (ii) In cockroaches air passes through a network of air tubes called tracheae. |
| (iii) The exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide etc happens inside the lungs. | (iii) The exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide etc happens inside the tracheal tubes. |
| (iv) Humans exhale through the nose. | (iv) Cockroaches exhale through the spiracles. |
Complete the Table:
1. Look at the table below and indicate which of the following organisms breathe through their lungs. If they do not, then indicate how they breathe.
| Organism | Mode of Respiration |
| Elephant | |
| Lion | |
| Cow | |
| Frog | |
| Lizard | |
| Cockroach | |
| Snail | |
| Snake | |
| Birds | |
| Goat | |
| Grasshopper | |
| Earthworm | |
| Whale | |
| Dolphin | |
| Crocodile | |
| Ant | |
| Fish | |
| Tadpole |
Answer: The completed table is shown below:
| Organism | Mode of Respiration |
| Elephant | Lungs |
| Lion | Lungs |
| Cow | Lungs |
| Frog | Lungs |
| Lizard | Lungs |
| Cockroach | Using spiracles and tracheal tubes |
| Snail | Using lungs and gills (depends on the type of snail) |
| Snake | Lungs |
| Birds | Lungs |
| Goat | Lungs |
| Grasshopper | Using spiracles and tracheal tubes |
| Earthworm | Using skin |
| Whale | Lungs |
| Dolphin | Lungs |
| Crocodile | Lungs |
| Ant | Using spiracles and tracheal tubes |
| Fish | Gills |
| Tadpole | Gills |
Fill in the Blanks:
aerobic, carbon dioxide, oxygen, ribs, anaerobic, yeast, diaphragm
(a) _________ can survive in the absence of air.
(b) In muscle cells of humans _________ respiration is temporary and _________ respiration is permanent.
(c) Breathing is possible due to movement of the _________ and _________.
(d) Humans cannot survive on Mars due to lack of _________.
(e) Excess _________ build up in the lungs can be fatal.
Answers:
(a) Yeast can survive in the absence of air.
(b) In muscle cells of humans anaerobic respiration is temporary and aerobic respiration is permanent.
(c) Breathing is possible due to movement of the ribs and diaphragm.
(d) Humans cannot survive on Mars due to lack of oxygen.
(e) Excess carbon dioxide build up in the lungs can be fatal.
Match and Pair:
1. Match the items of Column I with suitable items in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Athletes | (i) Cellular respiration |
| (b) Tracheae | (ii) Exchange of gases |
| (c) Breakdown of glucose | (iii) Large lung size |
| (d) Alveoli | (iv) Can cause cancer |
| (e) Smoking | (v) Insects |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Athletes | (iii) Large lung size |
| (b) Tracheae | (v) Insects |
| (c) Breakdown of glucose | (i) Cellular respiration |
| (d) Alveoli | (ii) Exchange of gases |
| (e) Smoking | (iv) Can cause cancer |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms:
Our expert team of Indian and foreign-educated engineers, scientists and education experts have formulated these solutions and extra questions keeping in mind the needs of the student and the examination question pattern. All the concepts have been covered in a clear and engaging manner and will definitely kindle your interest in the subject. We suggest that you carefully study the figures that we have included alongside the solutions for a better learning experience.
You can download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime! If you like our study material and want lots more from us on a regular basis, keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list to get immediate access to all our latest material!
The following topics are covered:
6.1 – Why Do We Respire
6.2 – Breathing
6.3 – How Do We Breathe?
6.4 – What Do We Breathe Out?
6.5 – Breathing In Other Animals
6.6 – Breathing Under Water
6.7 – Do Plants Also Respire
3. How many problems are there in the exercises for NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms?
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 3 Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 1, 3, 4)
(ii) 1 Long Answer Type Question (Questions 2)
(iii) 2 Multiple Choice Type Questions (Questions 5, 9)
(iv) 1 Match and Pair Type Question (Question 6)
(v) 1 True/False Type Question (Question 7)
(vi) 1 Word Puzzle Type Question (Question 8)
Yes and for free! You can download the PDF versions of NCERT Solutions for educationroundtheworld.com’s Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms anytime for free! All the different types of extra questions in the PDF version! Please look towards the top of the page!
It is vital that you understand the mechanisms of respiration in humans and other organisms and are able to differentiate between them. We recommend that you start by reading the chapter and understanding the concepts instead of just memorising them. Then you can study our solutions to the exercise problems, extended learning activities, in-text questions, activities and also the extra questions of different formats we have included ourselves. The concepts are explained very clearly along with attractive figures wherever necessary for further clarity. We advise you to study the explanations and figures together for maximum benefit.
Need additional coaching and practice? We have the right teachers and right programs for all your preparation needs! Contact us anytime and let us help you out!
At educationroundworld.com, we believe in a teacher-mentor approach. In addition to top-quality coaching, our teacher-mentors will expertly guide you regarding your future academic and professional careers. This helps in building awareness and realising where your true talents lie. This is a complementary free service we offer out of care for our students. Sounds good? Feel free to contact us anytime and we’ll be happy to help you out. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Book an appointment and let us help you out! (Insert hyperlink)


