Welcome students! We have prepared these materials taking care to explain all the concepts and answer all the questions you might have on this topic. Alongside the solutions to all exercise questions and extended learning activities, we have also answered all the in-text questions and explained all the activities for your benefit. We have also included a plethora of extra questions which we deem important for your exams, so we suggest you study them well!
Solutions to Exercise (Page No 80) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transportation in Animals and Plants:
1. Match structures given in Column I with functions given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (I) Stomata | (a) Absorption of water |
| (ii) Xylem | (b) Transpiration |
| (iii) Root hairs | (c) Transport of food |
| (iv) Phloem | (d) Transport of water |
| (e) Synthesis of carbohydrates |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (I) Stomata | (b) Transpiration |
| (ii) Xylem | (d) Transport of water |
| (iii) Root hairs | (a) Absorption of water |
| (iv) Phloem | (d) Transport of food |
2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) The blood from the heart is transported to all parts of the body by the _____________.
(ii) Haemoglobin is present in _____________ cells.
(iii) Arteries and veins are joined by a network of _____________.
(iv) The rhythmic expansion and contraction of the heart is called _____________.
(v) The main excretory product in human beings is _____________.
(vi) Sweat contains water and _____________.
(vii) Kidneys eliminate the waste materials in the liquid form called _____________.
(viii) Water reaches great heights in the trees because of suction pull caused by _____________.
Answers:
(i) The blood from the heart is transported to all parts of the body by the arteries.
(ii) Haemoglobin is present in red blood cells.
(iii) Arteries and veins are joined by a network of capillaries.
(iv) The rhythmic expansion and contraction of the heart is called heartbeat.
(v) The main excretory product in human beings is urea.
(vi) Sweat contains water and salts.
(vii) Kidneys eliminate the waste materials in the liquid form called urine.
(viii) Water reaches great heights in the trees because of suction pull caused by transpiration.
3. Choose the correct option:
(a) In plants, water is transported through
(i) xylem (ii) phloem
(iii) stomata (iv) root hair
(b) Water absorption through roots can be increased by keeping the plants
(i) in the shade
(ii) in dim light
(iii) under the fan
(iv) covered with a polythene bag
Answers:
(a) Correct option: (i) xylem.
Xylem forms a continuous network of channels throughout the plant and thus transports water throughout the entire plant.
(b) Correct option: (iii) under the fan.
The evaporation of water from the surface of the leaves by the process of transpiration will be accelerated if the plant is placed below the fan. This increased rate of evaporation creates a greater suction pull which increases the absorption of water through roots.
4. Why is transport of materials necessary in a plant or in an animal? Explain.
Answer:
Transport of materials is necessary in animals and plants because both require a steady supply of nutrients and oxygen and also need a mechanism for removal of waste materials.
(i) We all need food in order to survive. Hence, it is essential that the digested food in the small intestine be transported to various of the body.
(ii) The food is broken down in the cells by oxygen that we inhale and energy is released in this process which enables us to function. So, transportation of oxygen to the cells is vital for our survival.
(iii) The waste carbon dioxide produced during respiration also must be transported back to the lungs from the body for removal.
(iv) Other forms of waste present in the blood must also be transported and properly removed from the body.
Transport of materials is necessary in a plant because:
(i) In plants water and nutrients absorbed by the roots have to be transported to the leaves for food preparation during photosynthesis.
(ii) The food prepared by the leaves has to be transported to all parts of the plant.
5. What will happen if there are no platelets in the blood?
Answer:
In case of an injury platelets quickly gather in the damaged region and help the blood to quickly clot, which seals the wound and prevents further bleeding. If there were no platelets in the blood then blood clots would not form and bleeding would continue indefinitely.
6. What are stomata? Give two functions of stomata.
Answer:
Stomata are tiny pores present on surface of the leaves.
Two functions of stomata are:
- Exchange of gases happen through stomata.
- The evaporation of water by the process of transpiration happens through stomata.
7. Does transpiration serve any useful function in the plants? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, transpiration serves a very useful function in plants.Evaporation of water from the leaves by the process of transpiration creates a suction pull which draws water and nutrients from the roots to all parts of the plant. This is essential for photosynthesis to take place.
Other functions are as follows:
(i) Evaporation of water by the process of transpiration through stomata also helps to cool down the plant tissues. This is especially useful in hot environments.
(ii) Transpiration releases excess water inside the plant. This prevents any damage to the plant tissues due to accumulation of excess water.
(iii) Transpiration also helps in exchange of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
8. What are the components of blood?
Answer:
The largest component of blood is called plasma in which other components such as red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC) and platelets are suspended.
(i) Plasma: Blood is composed of a fluid called plasma in which different types of cells are suspended.
(ii) Red Blood Cells (RBC): These cells contain a red pigment called haemoglobin which takes part in oxygen transport.
(iii) White Blood Cells (WBC): White blood cells help to fight germs and protect our body from diseases and infections.
(iv) Platelets: Platelets help the blood to clot in case of an injury and prevents further bleeding.
9. Why is blood needed by all the parts of a body?
Answer:
Blood is needed by all the parts of a body because:
- Blood transports essential food and oxygen to the cells where energy is released via respiration.
- It transports waste carbon dioxide to the lungs for removal from the body.
- White blood cells (WBC) in blood quickly reach any part of the body and fight infections caused by germs.
- Platelets in blood enable blood clotting in case of an injury and hence prevent further bleeding.
- Blood transmits heat throughout the body and helps in temperature regulation.
10. What makes the blood look red?
Answer:
Blood mostly consists of red blood cells (RBC) which contain a red pigment called haemoglobin. Haemoglobin gives the blood its red appearance.
11. Describe the function of the heart.
Answer:
The heart acts as an intermediary pump and circulates blood between the lungs and the rest of the body. It supplies the body with oxygen-rich blood and nutrients and helps in removal of carbon dioxide-rich blood and other wastes from the body.
The circulation of blood is described as follows:
(i) When you inhale the oxygen enters the lungs and is absorbed by the blood which is then carried from the lungs to the heart via the pulmonary vein.
(ii) The heart then pumps the oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body via arteries and eventually reaches the capillaries where oxygen is released to the cells and carbon dioxide is picked up.
(iii) The now carbon dioxide-rich blood is carried from all parts of the body to the heart via veins.
(iv) Next the pulmonary artery carries the carbon dioxide-rich blood from the heart to the lungs, where the waste substances like carbon dioxide are removed and the blood picks up fresh oxygen.
The entire process is repeated continuously. The entire blood circulation process is shown in the schematic below:
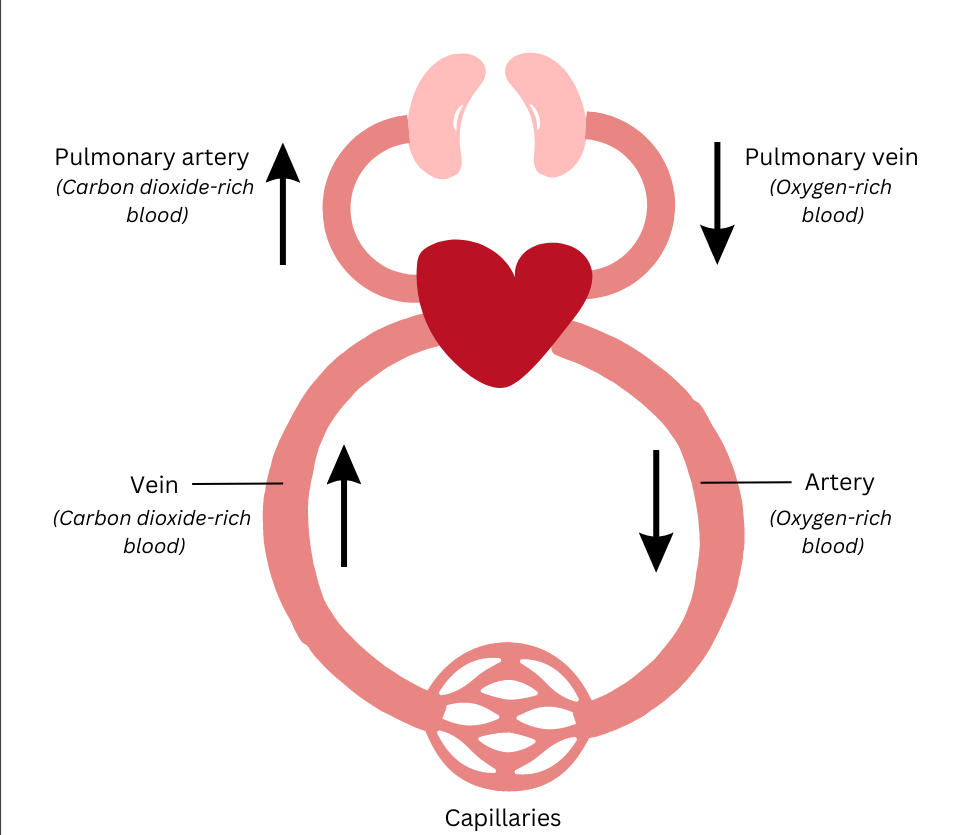
Since both oxygen-rich blood and carbon dioxide-rich blood pass through the heart, the partition between the chambers of the heart works to prevent the two types of blood from mixing.
12. Why is it necessary to excrete waste products?
Answer:
It is necessary to excrete waste products because toxicwaste products like carbon dioxide, urea and uric acid can be harmful to the body. Also, excess water eliminated from the body through urine helps to maintain the correct water balance in the body.
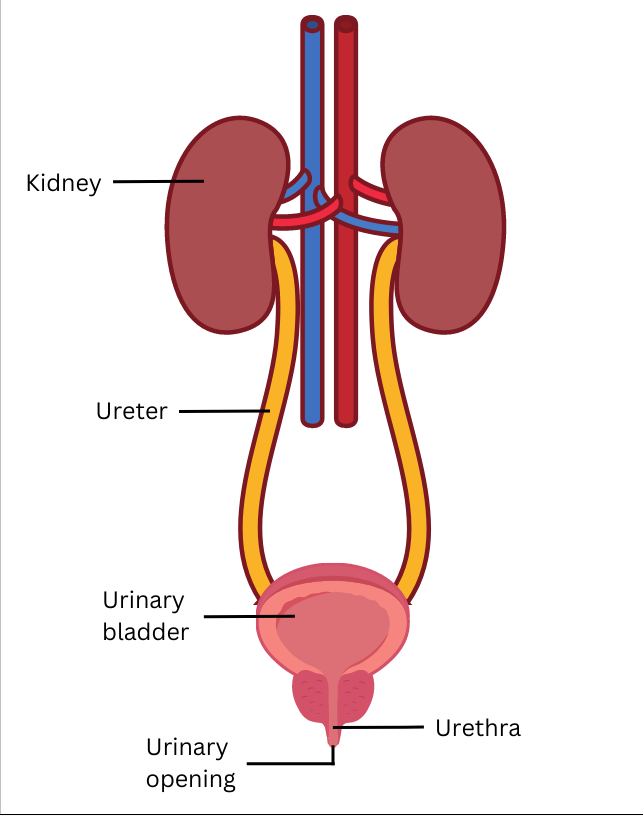
13. Draw a diagram of the human excretory system and label the various parts.
Answer:
The kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra together form the human excretory system as shown below:
14. Name one way in which waste materials are excreted in plants?
Answer:
Waste materials like excess water vapour and other waste materials like salts etc are excreted in plants via transpiration through stomata.
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 81) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transportation in Animals and Plants:
1. Find out about blood groups and their importance.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Question 1
2. When a person suffers from chest pain, the doctor immediately takes an ECG. Visit a doctor and get information about ECG. You may even look up an encyclopaedia or the internet.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Question 2
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transportation in Animals and Plants:
1. (Page 70) You have learnt earlier that all organisms need food, water and oxygen for survival. They need to transport all these to various parts of the body. Further, animals need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. Have you wondered how all this is achieved?
Answer:
The heart and the blood vessels (veins and arteries) together form the circulatory system and are responsible for the transport of substances in the body. The heart continuously pumps the blood containing dissolved oxygen, nutrients, waste products etc through the blood vessels to appropriate parts of the body.
2. (Page 70) What happens when you get a cut on your body?
Answer:
When you get a cut on your body blood vessels in that area get ruptured and the blood from inside spills out, leading to bleeding. Then cells called platelets present in the blood gather at that area and initiate the process of blood clotting, which prevents further bleeding.
3. (Page 70) What is blood?
Answer:
Blood is the fluid substance which flows through the blood vessels, namely arteries and veins. It is involved in the transport of various substances to all parts of the body. It transports digested food such as glucose which is absorbed from the small intestine to the rest of the body. It also transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells. Lastly, it transports waste materials dissolved in it for removal from the body.
4. (Page 70) How does the blood carry various substances?
Answer:
Blood is composed of a liquid substance called plasma in which different types of cells, namely red blood cells (RBC) white blood cells (WBC) and platelets, are suspended.
The role of plasma is to transport water, salts, nutrients, waste products and some other substances to all parts of the body. Red blood cells (RBC) contain a pigment called haemoglobin which transports oxygen to all cells of the body. White blood cells (WBC) rush through the bloodstream to the site of an infection and protect our body from germs and infections. Platelets travel through the bloodstream to the area of a cut and help in forming blood clots.
5. (Page 70) Why is the colour of blood red?
Answer:
Blood mostly consists of red blood cells (RBC) which contain a red pigment called haemoglobin. Hence haemoglobin is abundantly present in blood and gives blood the red colour.
6. (Page 72) Boojho says: I am confused! I have learnt that an artery always carries oxygen-rich blood.
Answer:
All arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart. Although the pulmonary artery carries carbon dioxide-rich blood, it still carries the carbon dioxide-rich blood away from the heart and not towards it. Therefore, it is an artery.
7. (Page 73) What will happen of the blood rich in oxygen and the blood rich in carbon dioxide mix with each other?
Answer:
If oxygen-rich blood and carbon dioxide-rich blood are allowed to mix, then the amount of oxygen in the initially oxygen-rich blood would decrease and the carbon dioxide content would increase. Thus, our body would receive less oxygen and excess waste carbon dioxide would accumulate in the body which can have very harmful effects.
8. (Page 73) Paheli wonders which side of the heart will have oxygen-rich blood and which side will have carbon dioxide-rich blood.
Answer:
The left side of the heart contains oxygen-rich blood. Oxygen-rich blood flows through the left atrium and the left ventricle. The right side of the heart contains carbon dioxide rich-blood. Carbon dioxide rich-blood flows through the right atrium and the right ventricle.
9. (Page 75) Boojho wonders if sponges and hydra also have blood?
Answer:
Sponges and hydra do not have blood which circulates in their bodies. They live underwater and their requirements of food and oxygen are satisfied by the water that enters their body. Waste removal also happens through water.
10. (Page 75) The waste which is present in the blood has to be removed by the body. How can this be done?
Answer:
The first type of waste removal process starts in the kidneys. When blood enters the kidneys, the useful substances present in the blood and the waste substances are separated. The useful substances are absorbed back into the bloodstream. The remaining waste products and excess water enter the urinary bladder and are excreted out as urine.
The second type of waste removal process happens in the form of sweat via which excess water and some dissolved waste products are excreted in the form of sweat.
11. (Page 76) Boojho has seen that sometimes in summer, white patches are formed on our clothes, especially in areas like underarms. These marks are left by salts present in the sweat. Does sweat serve any other function?
Answer:
We sweat during excessive hot weather or when we exert ourselves. Due to evaporation of sweat from our body, the body heat gets reduced and our body cools down. Thus, sweat also helps in regulating body temperature.
12. (Page 76) Paheli wants to know whether other animals also urinate?
Answer:
Yes, other animals also urinate. The exact mechanism of urination in the animal depends on the availability of water. For example, aquatic animals like fish excrete waste ammonia into the water through their gills. However, land animals like birds, lizards etc excrete a semi-solid white compound called uric acid.
13. (Page 77) Have you ever wondered how water and nutrients absorbed by the root are transported to the leaves?
Answer:
Water and nutrients absorbed by the root are transported to the leaves through a continuous network of vascular tissue present throughout the plant known as xylem.
14. (Page 77) How is the food prepared by the leaves carried to the parts which cannot make food?
Answer:
The food prepared by the leavesis carried to all parts of the plant through a continuous network of vascular tissue called phloem.
15. (Page 77) Boojho thinks that plants may have pipes to transport water to the entire plant like we have in our homes for the supply of water.
Answer:
Boojho is right because plants do have pipe-like vessels made of special vascular tissue called xylem to transport water to the entire plant. Xylem forms a continuous network of channels for efficient distribution of water and nutrients absorbed by the roots throughout the plant.
16. (Page 78) Paheli says her mother puts ladyfinger and other vegetables in water if they are somewhat dry. She wants to know how water enters into them.
Answer:
The upward movement of absorbed water in the ladyfinger and other vegetableswill happen through special vascular tissue called xylem which form a continuous network of channels throughout the plant.
17. (Page 78) Boojho wants to know why plants absorb a large quantity of water from the soil, then give it off by transpiration!
Answer:
Plants absorb excess water than needed from the soil which they then release by transpiration because:
- Transpiration creates a suction force upwards which helps absorption of water and nutrients.
- The evaporation of water by transpiration helps to cool the plant down.
- It also plays a role in gas exchange.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transportation in Animals and Plants:
1. Complete Activity 7.1 (Page 71). Place the middle and index finger of your right hand on the inner side of your left wrist. Can you feel some throbbing movements? Why do you think there is throbbing? Count the number of pulse beats in one minute. How many pulse beats could you count? The number of beats per minute is called the pulse rate. Find other places in your body where you can feel the pulse. Record your own pulse beats per minute and those of your classmates. Insert the values you obtained in Table 7.1 and copied them.
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 7.2 (Page 74). Take a small funnel of 6-7 cm in diameter. Fix a rubber tube (50 cm long) tightly on the stem of the funnel. Stretch a rubber sheet (or a balloon) on the mouth of the funnel and fix it tightly with a rubber band. Put the open end of the tube on one of your ears. Place the mouth of the funnel on your chest near the heart. Now try to listen carefully. Do you hear a regular thumping sound? The sound is that of heart beats. How many times did your heart beat in a minute? Count again after running for 4-5 minutes. Compare your observations.
Record your own pulse rate and heartbeat and that of your friends while resting and after running and record in Table 7.2. Do you find any relationship between your heartbeat and pulse rate?
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 7.3 (Page 78). We would require a glass tumbler, water, red ink, a tender herb (e.g., Balsam), and a blade for this activity. Pour water to fill one-third of the tumbler. Add a few drops of red ink to the water. Cut the base of the stem of the herb and place it in the glass as shown in the figure. Observe it the next day. Does any part of the herb appear red. If yes, how do you think the colour reached there? You can cut the stem across and look for the red colour inside the stem.
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transportation in Animals and Plants:
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Which component of blood is responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body?
Answer:
Haemoglobin pigment present in red blood cells (RBC) in blood is responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
2. Name one organ without which blood circulation in the body would not happen?
Answer:
Heart is the organ which acts as a pump and is responsible for blood circulation throughout the body.
3. Which part of the heart contains oxygen-rich blood?
Answer:
Oxygen-rich blood circulates in the left atrium and the left ventricle on the left side of the heart.
4. Which part of the heart contain carbon dioxide-rich blood?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide-rich blood circulates in the right atrium and the right ventricle on the right side of the heart.
5. Name one artery that pumps oxygen-rich blood from the heart to different parts of the body.
Answer:
Aorta is one artery that pumps oxygen-rich blood from the heart to different parts of the body.
6. What is the heart mostly made up of?
Answer:
The heart is mostly made up of cardiac muscle.
7. Where does the absorption of nutrients and gas exchange between blood and tissues take place?
Answer:
The absorption of nutrients and gas exchange between blood and tissues takes place in the tiny, thin-walled blood vessels called capillaries.
8. Name the smallest blood vessels in the body.
Answer:
The smallest blood vessels in the body are called capillaries.
9. What is the main substance that is removed through urine?
Answer:
Excess water is the main substance that is expelled through urine, comprising 95% of the urine.
10. Name two substances which are common to both sweat and urine except water?
Answer:
Urea and uric acid are two substances which are common to both sweat and urine apart from water.
11. We know that xylem transports water and minerals upwards. What is another function does it serve?
Answer:
Xylem provides strength to the plant and helps to maintain the shape and structure of the plant.
12. Blood is essential for survival. If a person loses a large amount of blood what should be done to save the person’s life?
Answer:
If a person loses a large amount of blood or if the body is unable to produce sufficient blood, then the only way to replenish the blood supply is through blood transfusion donated by volunteers.
Short Answer Type Questions:
1. We know that veins carry blood towards the heart. How is blood prevented from flowing backwards?
Answer:
Veins are equipped with valves along the length. When blood flows towards the heart (correct direction) the valves stay open and allow the blood to smoothly pass through. However, if the blood is somehow forced to flow in the opposite direction, the valves close and the flow of blood in the reverse direction is prevented.
2. What is the function of pulmonary circulation?
Answer:
Pulmonary circulation refers to the part of the circulatory system that circulates blood between the heart and the lungs and via which vital exchange of gases takes place. It allows oxygen-rich blood to enter the heart from the lungs (pulmonary vein) which is then pumped to the rest of the body. It also facilitates removal of waste carbon dioxide by carrying carbon dioxide-rich blood from the heart to the lungs (pulmonary artery).
3. Name two veins which carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from different parts of the body to the heart.
Answer:
The superior vena cava carries carbon dioxide-rich blood from the upper body to the right atrium and inferior vena cava carries carbon dioxide-rich blood from the lower body also to the right atrium.
4. You know the heart pumps blood. But how does the pumping action of the heart happen?
Answer:
Electrical signals are generated in the heart and spread through the heart muscles, causing them to contract. This contraction pushes the blood into the arteries. Following contraction, the heart muscles relax again and this allows the chambers of the heart to fill with blood and the cycle repeats. This rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart pumps the blood out from inside.
5. What prevents oxygen-rich blood and carbon dioxide-rich blood from mixing inside the heart?
Answer:
The left and right halves of the heart are separated by a septum which prevents the oxygen-rich blood and carbon dioxide-rich blood from mixing. The left and right atria of the heart are separated by the interatrial septum and the left and ventricles of the heart are separated by the interventricular septum.
6. Veins are dark red in colour. So why do the veins in your hand appear blue?
Answer:
When light enters the skin, it interacts with the blood and the surrounding tissues in certain ways. Some colours of light such as red are absorbed and the colour blue is not absorbed and is reflected back to our eyes. This makes the veins appear blue in colour.
7. What causes high blood pressure?
Answer:
In certain stressful situations or during intense physical exertion, the heart starts beating faster than normal and pumps more blood into the body. This results in high blood pressure.
9. How are waste products produced in the body?
Answer:
Biological processes such as respiration which take place in the cells of organisms produce waste products such as carbon dioxide, urea, salts, water etc and these are removed from the body by means of excretion.
10. Where are the kidneys located?
Answer:
The kidneys are located in the abdomen below the rib cage on either side of the spine.
11. What will happen if your kidneys are damaged?
Answer:
In case of kidney damage, waste materials and fluids will accumulate in your body, causing swelling in your body, weakness, nausea and heart disease.
12. What treatment options are available in case of kidney damage?
Answer:
In case of kidney damage,you can undergo a procedure called dialysis. Dialysis artificially filters and removes unwanted waste substances and excess fluid which have accumulated in the body. In extreme cases of kidney failure you might have to undergo a kidney transplant.
13. Give the main differences between xylem and phloem.
Answer:
The main differences between xylem and phloem are as follows:
| Xylem | Phloem |
| (i) Xylem transports water and dissolved nutrients from the roots to the other parts of the plant. | (i) Phloem transports food prepared by leaves to all parts of the plant. |
| (ii) Xylem transports water and nutrients in one direction, mainly upwards. | (ii) Phloem transports sugars and other nutrients in both the upward and downward directions. |
| (iii) The movement of water and nutrients through xylem is directly affected by transpiration. | (iii) The movement of food through phloem is not directly affected by transpiration. |
Long Answer Type Questions:
1. Give the main differences between arteries and veins.
Answer:
The main differences between arteries and veins are as follows:
| Arteries | Veins |
| (i) Arteries have thick walls and more smooth muscle. | (i) Veins have thin walls and less smooth muscle. |
| (ii) Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body. | (ii) Veins carry carbon dioxide-rich from all parts of the body to the heart. |
| (iii) Pulmonary circulation happens through the pulmonary artery. | (iii) Pulmonary circulation happens through the pulmonary vein. |
| (iv) The pulmonary artery carries carbon dioxide-rich blood from the heart to the lungs for removal from the body. | (iv) The pulmonary vein carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart which is then pumped to the rest of the body. |
| (v) The heart pumps blood through the arteries, so you can feel a pulse in the arteries. | (v) The heart does not pump blood through the veins and the blood flow is steady, so you cannot feel a pulse. |
| (vi) The blood pressure in arteries is high due to pumping action of the heart. | (vi) The blood pressure in veins is low due to steady blood flow. |
| (vii) Colour of arteries is bright red. | (vii) Colour of veins is actually a darker red but appears blue due to reflection of light. |
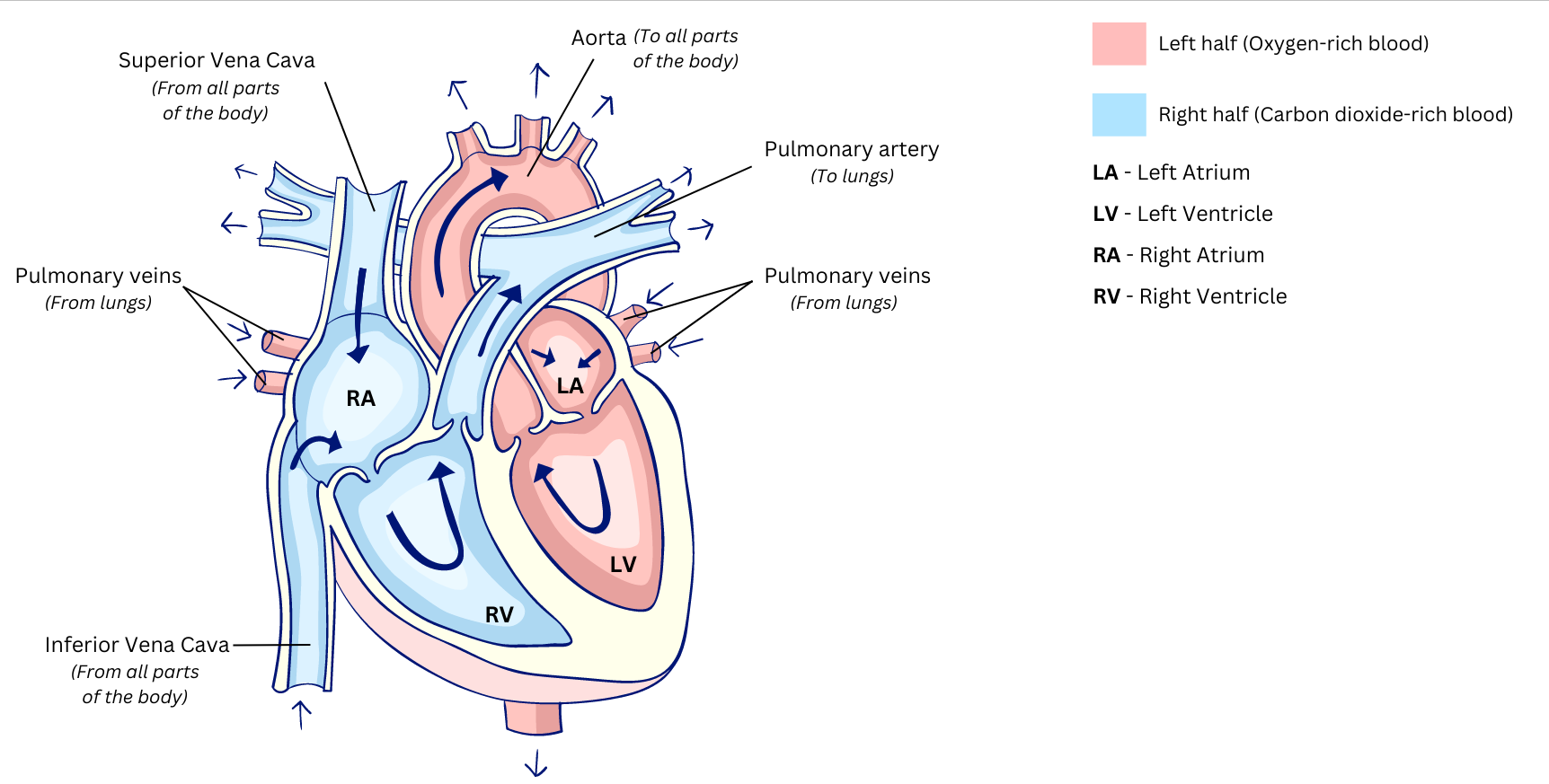
2. Describe the process of circulation in the heart with a diagram.
Answer: The process of circulation in the heart can be described as follows:
Occurs in left half of heart:
(i) Oxygen-rich (or oxygenated) blood enters the left atrium of the heart from the lungs through the pulmonary veins.
(ii) From the left atrium the oxygenated blood flows into the left ventricle located right below.
(iii) The muscles of the walls of the left ventricle contract and pump the blood into the aorta, which is the largest artery in the body.
(iv) The aorta distributes the oxygenated blood to all parts of the body.
(v) The oxygenated blood eventually reaches the capillary network where oxygen and nutrients are supplied to the cells and carbon dioxide is picked up.
Occurs in right half of heart:
(vi) The now carbon dioxide-rich (or deoxygenated) blood is carried from all parts of the body to the right atrium of the heart via the two veins – the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava.
(vii) From the right atrium the deoxygenated blood flows into the right ventricle located right below.
(viii) The muscles of the walls of the right ventricle contract and pump the blood into the pulmonary artery.
(ix) The pulmonary artery splits into two branches and carries the deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where waste carbon dioxide is removed and the blood picks up fresh oxygen.
The entire process is repeated continuously and is clearly shown in the figure below (the arrows indicate the direction of blood flow):
3. Give the main differences between red blood cells and white blood cells.
Answer:
The main differences between red blood cells (RBC) and white blood cells (WBC) as follows:
| Red Blood Cells (RBC) | White Blood Cells (WBC) |
| (i) Smaller in size. | (i) Larger in size. |
| (ii) Contain a red pigment called haemoglobin. | (ii) Do not contain pigment. |
| (iii) Red in colour due to presence of haemoglobin. | (iii) Colourless as they do not contain any pigment. |
| (iv) Primary purpose is to transport oxygen to from lungs to all parts of the body (using haemoglobin). | (iv) Primary purpose is to fight germs which may enter our body and protect our body from diseases. |
| (v) Much higher in number. | (v) Much lower in number. |
4. Give the main differences between pulmonary artery and pulmonary veins.
Answer:
The main differences between pulmonary veins and pulmonary artery are as follows:
| Pulmonary Artery | Pulmonary Veins |
| (i) Pulmonary artery carries carbon dioxide-rich blood from the heart to the lungs. | (i) Pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart. |
| (ii) The pulmonary artery starts from the right ventricle of the heart. | (ii) The pulmonary veins drain into the left atrium of the heart. |
| (iii) It has thicker walls. | (iii) They have thin walls. |
| (iv) The main pulmonary artery divides into two branches, left and right. | (iv) There are four pulmonary veins. |
| (v) Contains a valve. | (v) Do not contain valves. |
5. Describe the working of a stethoscope with a diagram.
Answer:
Refer to the diagram below:
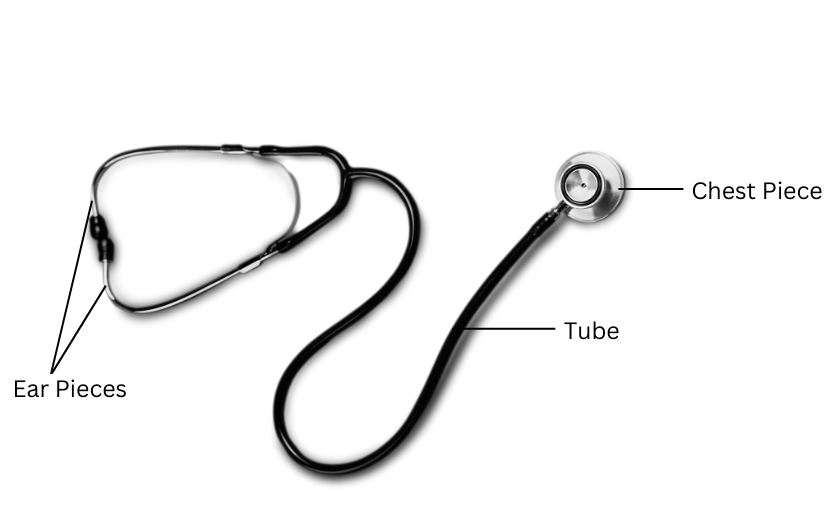
The working of the parts of a stethoscope is as described as follows:
Chest Piece: The chest piece is meant to be placed on the patient’s chest to listen for sounds such as the heartbeat. It consists of the diaphragm and bell which are very sensitive to picking up all kinds of sounds and amplifies them.
Tube: The sounds picked up by the chest piece are transmitted through the tubes to the ear pieces.
Ear Pieces: The medical expert places the ear pieces in their ears which enables them to listen to the sounds in the patient’s body and detect any abnormalities.
Fill in the Blanks:
ammonia, oxygenated, heart, absorption, aorta, deoxygenated
(a) _________ blood is low in oxygen content and _________ blood is high in oxygen content.
(b) _________ is the largest artery in the body.
(c) _________ is located in the chest cavity with its lower tip slightly tilted towards the left.
(d) _________ waste is produced in the bodies of aquatic animals like fishes.
(e) Root hairs increase the _________ of water and nutrients from the soil.
Answers:
(a) Oxygenated blood is low in oxygen content and deoxygenated blood is high in oxygen content.
(b) Aorta is the largest artery in the body.
(c) The heart is located in the chest cavity with its lower tip slightly tilted towards the left.
(d) Ammonia waste is produced in the bodies of aquatic animals like fishes.
(e) Root hairs increase the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil.
Match and Pair:
1. Match the items of Column I with suitable items in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Aorta | (i) Amplification |
| (b) Stethoscope | (ii) Filtering mechanism |
| (c) Blood circulation | (iii) No valve |
| (d) Kidneys | (iv) 70-80 times per minute |
| (e) Transpiration | (v) William Harvey |
| (f) Normal heartbeat for an adult | (vi) Negative pressure |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Aorta | (iii) No valve |
| (b) Stethoscope | (i) Amplification |
| (c) Blood circulation | (v) William Harvey |
| (d) Kidneys | (ii) Filtering mechanism |
| (e) Transpiration | (vi) Negative pressure |
| (f) Normal heartbeat for an adult | (iv) 70-80 times per minute |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transportation in Animals and Plants:
These study materials have been formulated by an expert team of Indian and foreign-educated engineers, taking care to explain the important concepts step-by-step to enable quick learning and retention. Alongside the exercise solutions and extended learning activities, all the in-text questions and activities have been explained with attractive diagrams wherever necessary. A plethora of extra questions of all formats have been included to give you a boost in your preparation efforts.
The free PDFs of the solutions are available for download anytime! Like our study material? Keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list to be among first to receive all the latest study materials, news and other resources – all for free!
The following topics are covered:
7.1 – Circulatory System
Blood
Blood Vessels
Heart
Heartbeat
7.2 – Excretion in Animals
7.3 – Transport of Substances in Plants
Transport of Water and Minerals
Transpiration
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 1 Match and Pair Type Question (Question 1)
(ii) 1 Fill in the Blanks Type Question (Question 2)
(iii) 1 Multiple Choice Type Questions (Question 3)
(iv) 2 Long Answer Type Questions (Questions 4, 11)
(v) 8 Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13)
Yes of course! You can download the PDF versions of educationroundtheworld.com’s NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transportation in Animals and Plants anytime for free! We have also included all the different types of extra questions in the PDF version! Please look towards the top of the page!
Thoroughly understanding the mechanisms of the circulatory system and the excretory system in humans is of utmost importance. The second most important part of the chapter is the transport of substances in plants. The key here is to logically understand the processes occurring inside the human body and the plant. Refer to the figures we have included while studying the processes step-by-step. This will help your understanding and retention.
Need additional help? Our expert teachers will provide systematic training from the ground-up and help you succeed in any exam! Just contact us with your requirements and let us help you out!
The right kind of coaching and mentoring can help you reach new heights. Alongside fulfilling all your preparation needs, our expert teacher-mentors will also counsel you regarding your future academic and professional career. This approach can make all the difference and put you ahead of your competition. If that is what you are looking for, feel free to contact us anytime with your requirements.
We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Book an appointment now and let us help you out!


