Hello students and welcome to Class 8! The first chapter is called Crop Production and Management and we have prepared top-quality solutions to all exercise questions, extended learning activities, in-text questions, activities and self-designed extra questions for you to study. The concepts are explained with attractive diagrams wherever necessary. The entire chapter has been covered comprehensively in this material and will give you a boost in your preparation efforts.
Solutions to Exercises (Page No 13) of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management –
1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Answers:
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of the water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and super phosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
Answer:
The correct table is shown below:
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (e) Paddy and maize |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (b) Urea and super phosphate |
| (iv) Organic manure | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant waste |
3. Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer:
Two examples of kharif crops which grow in the rainy season are paddy and maize. Two examples of rabi crops which grow in the winter season are wheat and gram.
4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil (b) Sowing
(c) Weeding (d) Threshing
Answers:
(a) Preparation of soil:
Preparation of the soilis the first step beforegrowing a crop. In this step, the soil is turned and loosened by the process of tilling or ploughing. This allows the roots of plants to penetrate deep into the soil. It also brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants use them.
(b) Sowing
Sowing the act of scattering seeds in the soil after tilling is complete. Before sowing, healthy seeds are selected. Sowing is done using traditional tools which are shaped like a funnel. Nowadays the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. Steps are taken to prevent overcrowding.
(c) Weeding
Weeding is the process of removing undesirable plants called weeds which grow among crops. Weeds are removed by the process of tilling before sowing of crops and manually uprooting or cutting them. Weeds are also killed using certain chemicals called weedicides. Weeding is necessary because weeds compete with crops for water, nutrients, space, light.
(d) Threshing
Threshing is the process of separating the grain seeds from the chaff, after the crop has been harvested. Threshing is done using a machine called ‘combine’, which is both a harvester as well as a thresher.’
5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer:
Fertilisers are man-made in factories whereas manure occurs naturally by the decomposition of cattle dung and plant residues in the field. Fertiliser does not add humus to the soil whereas manure adds a lot of humus to the soil. Fertilisers are rich in plant nutrients whereas manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients.
6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer:
Irrigation is the supply of water to crops at regular intervals. Two methods of irrigation which conserve water are the sprinkler system and the drip system.
(a) Sprinkler System: The sprinkler system is more useful on uneven land where sufficient water is not available. Perpendicular pipes with rotating nozzles on top are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. A pump works to push the water through the main pipe under pressure and the water escapes through the rotating nozzles. The water thus ejected out gets sprinkled on the crop.
(b) Drip System: In this system the water falls drop by drop directly near the roots, giving it the name ‘drip system’. This technique ensures that water is not wasted.
7. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer:
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, the plants would rot due to excess rain from June to September. Also, in the kharif season, the temperature would be too hot for wheat plants to grow properly.
8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer:
Soil gets affected negatively by the continuous plantation of crops in a field because of nutrient depletion. Continuous plantation of crops makes the soil poor in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium etc. Thus crops do not get the necessary nutrients to grow well.
9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer:
Weeds are undesirable and uncultivated plants that grow naturally with the crop and compete with crops for water, nutrients, space, light. We can control them by removing them in a process called weeding. Wedding is done using tilling, manual removal using khurpi and certain chemicals called weedicides.
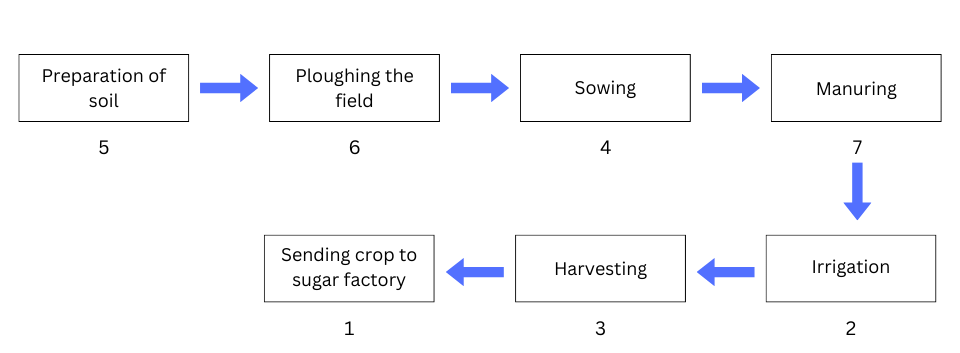
10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
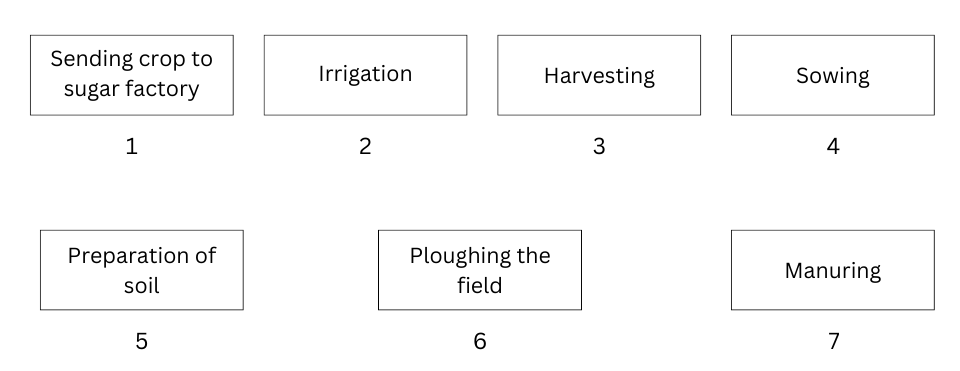
Answer:
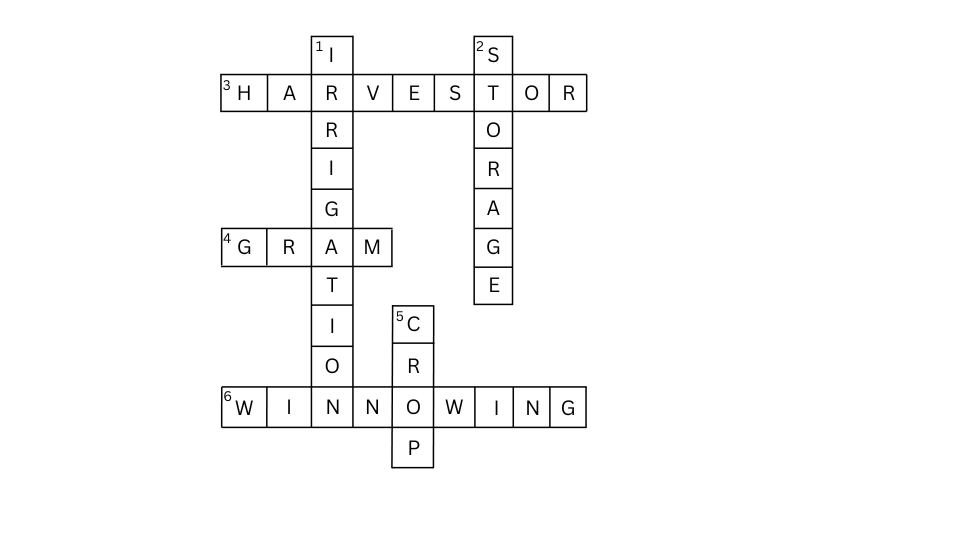
11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of the clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind are grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop, which is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from the chaff.
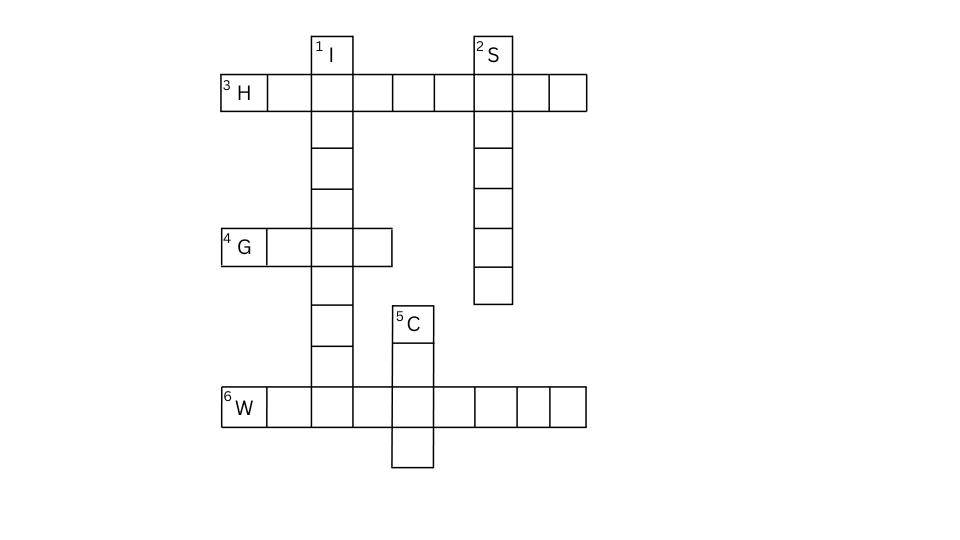
Answer:
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 15) of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management –
1. Sow some seeds in the soil and arrange to water them by drip irrigation. Observe daily.
(i) Do you think it can save water?
(ii) Note the changes in the seed.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 1
2. Collect different types of seeds and put them in small bags. Label them.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 2
3. Collect pictures of some other agricultural machines and paste them in a file. Write their names and uses.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 3
4. Project Work
Visit a farm, nursery or a garden nearby. Gather information about
(i) importance of seed selection.
(ii) method of irrigation
(iii) effect of extreme cold and extreme hot weather on the plants.
(iv) effect of continuous rain on the plants. (v) fertilisers/manure used.
Answers:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 4
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management –
1. (Page 1) I want to know where and how we use these tools.
Answer:
These tools are used in crop production in the farms such as in soil preparation, sowing, weed removal and harvesting.
2. (Page 1) Since we all need food, how can we provide food to a large number of people in our country?
Answer:
We can provide food to a large number of people in our country by producing food on a large scale. In order to do this regular crop production, organised management and distribution is necessary.
3. (Page 2) Why paddy can not be grown in the winter season?
Answer:
Paddy cannot be grown in the winter season because paddy requires a lot of water. There is very less water in the winter season, so it has to be grown only in the rainy season.
4. (Page 2) Why does the loosening of soil allow the roots to breathe easily?
Answer:
Loosening of soil allows air pockets to enter into the soil. This leads to increased oxygen inside the soil, which allows the roots to breathe easily.
5. (Page 4) One day I saw my mother put some gram seeds in a vessel and pour some water on them. After a few minutes some seeds started to float on top. I wonder why some seeds float on water!
Answer:
Some seeds float in water because they are damaged. Damaged seeds lose the nutrients inside and become hollow and light. Therefore, they float in water while intact seeds tend to sink.
6. (Page 5) There is a nursery near my school. I found that little plants were kept in small bags. Why are they kept like this?
Answer:
The little plants are kept in small bags in the nursery to shield them from harsh environmental conditions and provide controlled growth conditions. Once they reach maturity, they will be transferred to field conditions for further development.
7. (Page 5) I saw a healthy crop growing in a farm. In the neighbouring farm, the plants were weak. Why do some plants grow better than others?
Answer:
Some plants grow better then others because of adequate usage of fertiliser and manure. The crops in the first farm were adequately fertilised and hence were healthy.In the neighbouring farm, the plants were weak because they were not adequately fertilised.
8. (Page 10) Have these other plants been planted purposely?
Answer:
No, these other plants have not been planted purposely. In a crop field many undesirable pants grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds and need to be removed.
9. (Page 10) Do weedicides have any effect on the person handling the weedicide sprayer?
Answer:
Yes, weedicides may have adverse effects on the health of the person handling the weedicide sprayer. Weedicides may be toxic to the person and the person’s nose and mouth should be covered with cloth during spraying.
10. (Page 11) I saw my mother putting some dried neem leaves in an iron drum containing wheat. I wonder why?
Answer:
Your mother may be using dried neem leaves in the iron drum containing wheat to repel insects. Neem leaves have natural anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties, making them a popular choice for protecting stored grains like wheat.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management –
1. Complete Activity 1.1 (Page 4). Take a beaker and fill half of it with water. Put a handful of wheat seeds and stir well. Wait for some time.
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 1.2 (Page 6). Take moong or gram seeds and germinate them. Select three equal sized seedlings. Take three empty glasses or similar vessels. Mark them A, B and C. To glass A add little amount of soil mixed with a little cow dung manure. In glass B put the same amount of soil mixed with a little urea. Take the same amount of soil in glass C without adding anything [Fig. 1.3(a)]. Now pour the same amount of water in each glass and plant the seedlings in them. Keep them in a safe place and water them daily. After 7 to 10 days observe their growth.
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 1.3 (Page 12). Make the following Table in your note book and complete it.
| S. No. | Food | Sources |
| 1. | Milk | Cow, Buffalo, She-goat, She-camel… |
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
| 4. |
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management –
(A) Very Short Answer Type:
1. Name one use of khurpi.
Answer:
Khurpi is used to remove weeds.
2. Name one use of the sickle.
Answer:
Sickle is used for harvesting.
3. Name the process by which crops synthesize their own food.
Answer:
Crops synthesize their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
4. Name two major types of crops grown in India.
Answer:
Kharif and rabi crops.
5. Name two crops which are grown in the summer.
Answer:
Pulses and vegetables.
6. Why should tractors be used for cultivation?
Answer:
Machines such as tractor save labour and time.
7. Name one method od artificially adding nutrients to soil.
Answer:
Fertilisers.
8. Name two sources of water for irrigation.
Answer:
Lakes and rivers.
9. When is the best time for removal of weeds?
Answer:
The best time for removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
10. Where are grains stored on the large scale?
Answer:
Grains are stored in silos and granaries.
(B) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ):
1. Which of the following is not a crop?
(a) Cereals
(b) Vegetables
(c) Fruits
(d) Chaff
Answer: (d) Chaff
Explanation: Chaff is the husk surrounding a seed which is thrown away.
2. Which of the following is used to remove weeds?
(a) Plough
(b) Hoe
(c) Sickle
(d) Seed drill
Answer: (a) Plough, (b) Hoe, (d) Seed drill
3. Name a natural fertiliser.
(a) Urea
(b) Manure
(c) NPK
(d) All fertilisers are artificial
Answer: (b) Manure
4. Name the processes by which grain seeds are separated from the chaff.
(a) Threshing
(b) Harvesting
(c) Cutting
(d) Winnowing
Answer: (a) Threshing, (d) Winnowing
5. Which of the following is not true regarding storage of grains?
(a) Farmers store grains in jute bags.
(b) Large scale storge of grains is done in granaries.
(c) Chemical treatment is not needed if grains are stored in godowns.
(d) Dried need leaves are used for storing food grains at home.
Answer: (c) Chemical treatment is not needed if grains are stored in godowns. Chemical treatment is needed to protect graisn from pests and microorganisms in godowns.
(C) Short Answer Type:
1. A wide variety of crops can be grown in our country. Explain.
Answer:
India is a vast country and climatic conditions like temperature, humidity and rainfall vary from on region to region. Due to these diverse climatic conditions, a wide variety of crops can be grown in different parts of the country.
2. Why should the field be levelled before sowing?
Answer:
The field needs to be levelled before sowing to ensure uniformity in crop growth. Also, it helps in irrigation by ensuring uniform distribution of water.
3. What are the benefits of using a seed drill?
Answer:
The benefits of using a seed drill are that it ensures that seeds are sown uniformly at equal distance and depth. It also ensures that seeds get covered by soil after sowing, which protects seeds from being eaten by birds. Thirdly, sowing using a seed drill also saves time and labour.
4. Why should the field be left fallow from time to time?
Answer:
The field should be left uncultivated or fallow from time to time because continuous cultivation causes nutrient depletion in the soil. Allowing a field to lie fallow enables the soil to replenish its nutrient levels naturally. Fallow periods also prevent the growth of harmful weeds and pests.
5. How can you prepare manure?
Answer:
You can accumulate plant and animals wastes in pits at open places and allow them to decompose by microorganisms. The decomposed matter is used as organic manure.
6. Earlier, farmers in northern India used to grow legumes as fodder in one season and wheat in the next season. Explain.
Answer:
Leguminous plants form a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria called Rhizobium. These bacteria take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a form that plants can use, enriching the soil with nitrogen. This nitrogen is then used by the next batch of crops grown in the next season.
7. Why should crops not be stored immediately after being harvested?
Answer:
Crops should be dried after harvesting and then stored. The reason is that crops contain moisture and may get spoilt or attacked by organisms like pests, bacteria, fungi etc. Therefore, they are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them.
8. How are healthy seeds separated from unhealthy seeds?
Answer:
The seeds are immersed in water, following which the lighter damaged seeds float up and the healthy seeds settle down at the bottom.
(D) Long Answer Type:
1. Why should the soil be loosened or turned before sowing?
Answer:
Soil should be loosened or turned before sowing because:
(i) Loosening the soil allows air pockets to enter deep into the soil. Thus the roots of plants are able to breathe even when they deep inside the soil.
(ii) Loosened soil also helps in growth of earthworms and microbes, which further till the soil and add humus to it.
(iii) Thirdly, turning of the soil brings the nutrient-rich soil back to the top to be used by plants.
For these reasons loosening and turning of the soil is essential for the cultivation of crops.
2. What are the advantages of organic manure over fertilisers?
Answer:
The advantages of organic manure over fertilisers are as follows:
(i) They can be used excessively without making the soil less fertile.
(ii) They are not hazardous and do not cause chemical pollution.
(iii) They improve soil texture.
(iv) They improve the soil’s water retaining capacity.
(v) Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil.
(vi) It makes the soil porous which facilitates exchange of gases.
(vii) It increases the number of friendly microbes.
(viii) Manure does not need to be produced in factories.
3. Why is irrigation essential for healthy growth of crops?
Answer:
Irrigation is essential for healthy growth of crops for the following reasons:
- Water is needed for proper growth and development of plants.
(ii) Along with water, minerals and fertilisers are also absorbed.
(iii) Germination of seeds cannot take place under dry conditions.
(iv) Water acts as a medium to transport nutrients to all parts of the plant. (v) Water also protects the crop from both frost and hot air currents.
(E) Fill in the Blanks:
Vitamin D, sprinkler, animal husbandry, vermicomposting
(a) You can prepare manure by the process of ___________.
(b) Cod liver oil is rich in _________.
(c) ___________ system is best for preventing wastage of water.
(d) Rearing of animals on a large scale is called __________.
(e) The __________method of irrigation operates using a pulley-system
Answers:
(a) You can prepare manure by the process of vermicomposting.
(b) Cod liver oil is rich in Vitamin D.
(c) Sprinkler system is best for preventing wastage of water.
(d) Rearing of animals on a large scale is called animal husbandry.
(e) The moat method of irrigation operates using a pulley-system.
(F) Match and Pair:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Potash | (a) Traditional irrigation |
| (ii) Chain pump | (b) Harvesting |
| (iii) 2,4-D | (c) Fertiliser |
| (iv) Nabanya | (d) June-September |
| (v) Paddy | (e) Weedicide |
Answer:
The completed table is shown below:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Potash | (c) Fertiliser |
| (ii) Chain pump | (a) Traditional irrigation |
| (iii) 2,4-D | (e) Weedicide |
| (iv) Nabanya | (b) Harvesting |
| (v) Paddy | (d) June-September |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management –
We offer the complete solutions package for Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management. We have solved all exercise questions, extended learning activities, in-text questions, in-text activities and even extra questions to give you a complete learning experience. We have also included attractive diagrams wherever possible which will further boost your preparation efforts.
The free PDFs of the solutions are available for download anytime! We will be uploading plenty more top-quality study material for you, so keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list to be among the first to access them.
The following topics are covered:
1.1 – Agricultural Practices
1.2 – Basic Practices of Crop Production
1.3 – Preparation of Soil
1.4 – Sowing
1.5 – Adding Manure and Fertilisers
1.6 – Irrigation
1.7 – Protection from Weeds
1.8 – Harvesting
1.9 – Storage
1.10 – Food from Animals
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 1 Fill in the Blanks Question (Question 1)
(ii) 1 Match and Pair Question (Question 2)
(iii) 5 Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 3, 5, 7, 8, 9)
(iv) 2 Long Answer Type Questions (Questions 4, 6)
(v) 1 Flowchart Question (Question 10)
(vi) 1 Crossword Puzzle Question (Question 11)
Yes indeed! You can download the PDF versions of educationroundtheworld.com’s NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management anytime you please! We have included the entire material in the PDF version. Please look towards the top of the page to find the download button!
Understand and memorise the details of the crop production process, from start to finish. We have included typical questions from the entire chapter in this material, which are good starting point for exam preparation. So, go through them and understand the related concepts.
If you need additional help, we are here for you! Our experts love teaching young students like you and will be happy to help you out. Get in touch now!
In addition to thorough coaching and exam preparation, we also counsel students regarding their academic and future professional careers. If you are facing any difficulties feel free to tell us and we’ll happy to help you out. We have found this approach to be very helpful for mental well-being of students. We offer this as a free optional service, so feel free to take advantage of it!
If you like what we offer, please feel free to reach out to us anytime. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Book an appointment now!


