Hello students and welcome to Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe! Find top-quality solutions to all exercise questions, extended learning activities, in-text questions, activities and self-designed extra questions for you to study. This solutions package has been scientifically prepared to give you the best study experience and covers the chapter in detail. Attractive diagrams have also been included which will further help your learning.
Solutions to Exercises (Page No 29) of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe –
1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a ____________.
(b) Blue-green algae fix __________ directly from the air and enhance the fertility of the soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of __________.
(d) Cholera is caused by __________.
Answer:
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a microscope.
(b) Blue-green algae fix nitrogen directly from the air and enhance the fertility of the soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of Yeast.
(d) Cholera is caused by bacteria.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(a) Yeast is used in the production of
(i) sugar (ii) alcohol (iii) hydrochloric acid (iv) oxygen
Answer: (ii) alcohol
Explanation: Yeast converts sugar into alcohol by the process of fermentation.
(b) The following is an antibiotic
(i) Sodium bicarbonate (ii) Streptomycin (iii) Alcohol (iv) Yeast
Answer: (ii) Streptomycin
(c) Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is
(i) female Anopheles mosquito (ii) cockroach (iii) housefly (iv) butterfly
Answer: (i) female Anopheles mosquito
(d) The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
(i) ant (ii) housefly (iii) dragonfly (iv) spider
Answer: (ii) housefly
(e) The bread or idli dough rises because of
(i) heat (ii) grinding (iii) growth of yeast cells (iv) kneading
Answer: (iii) growth of yeast cells
(f) The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
(i) nitrogen fixation (ii) moulding (iii) fermentation (iv) infection
Answer: (iii) fermentation
3. Match the organisms in Column A with their action in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Bacteria | (a) Fixing nitrogen |
| (ii) Rhizobium | (b) Setting of curd |
| (iii) Lactobacillus | (c) Baking of bread |
| (iv) Yeast | (d) Causing malaria |
| (v) A protozoan | (e) Causing cholera |
| (vi) A virus | (f) Causing AIDS |
| (g) Producing antibodies |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Bacteria | (e) Causing cholera |
| (ii) Rhizobium | (a) Fixing nitrogen |
| (iii) Lactobacillus | (b) Setting of curd |
| (iv) Yeast | (c) Baking of bread |
| (v) A protozoan | (d) Causing malaria |
| (vi) A virus | (f) Causing AIDS |
4. Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Answer:
No, microorganisms are so small in size that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. They can be seen with the help of a microscope or magnifying glass.
5. What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Answer:
The four major groups of microorganisms are bacteria, fungi, protozoa and algae.
6. Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Answer:
Microorganisms such as Rhizobium and blue green algae fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
7. Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Answer:
10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives are as follows:
1. The bacterium Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd. It multiplies in milk and converts it into curd.
2. Bacteria are also involved in the making of cheese, pickles and other food items.
3. Bacteria and yeast are also helpful for fermentation of rice idlis and dosa batter.
4. Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of gas fill dough and increases its volume. Hence, yeast is used in the baking industry for making breads, pastries and cakes.
5. Yeast converts sugar into alcohol by the process of fermentation.
6. Bacteria and fungi are used to produce antibiotics.
7. Dead or weakened microbes help a vaccine work.
8. Microorganisms such as Rhizobium and blue green algae fix atmospheric nitrogen to nitrogen compounds in the soil.
9. Certain bacteria convert nitrogenous compounds into nitrogen gas and help keep the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere constant.
10. Microorganisms decompose organic waste, turn it into manure and clean the environment in the process.
8. Write a short paragraph on the harmful effects of microorganisms.
Answer:
Harmful microorganisms called pathogens cause diseases in humans, animals and plants. Pathogens enter the human body through air, water, food or by direct contact with an infected person and cause cholera, chicken pox, tuberculosis. In animals microorganisms cause diseases like anthrax, foot and mouth disease. Common plant diseases caused by microorganisms are citrus canker, rust of wheat.
9. What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Answer:
Antibiotics are medicines produced by microorganisms that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. Precautions that must be taken while taking antibiotics are: antibiotics should only be taken under supervision of a qualified doctor. Also, the full course prescribed by the doctor must be completed.
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 30) of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe –
1. Pull out a gram or bean plant from the field. Observe its roots. You will find round structures called root nodules on the roots. Draw a diagram of the root and show the root nodules.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 1
2. Collect the labels from the bottles of jams and jellies. Write down the list of contents printed on the labels.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 2
3. Visit a doctor. Find out why antibiotics should not be overused. Prepare a short report.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 3
4. Project : Requirements – 2 test tubes, marker pen, sugar, yeast powder, 2 balloons and lime water. Take two test tubes and mark them A and B. Clamp these tubes in a stand and fill them with water leaving some space at the top. Put two spoonfuls of sugar in each of the test tubes. Add a spoonful of yeast in test tube B. Inflate the two balloons incompletely. Now tie the balloons on the mouths of each test tube. Keep them in a warm place, away from sunlight. Watch the setup every day for next 3-4 days. Record your observations and think of an explanation. Now take another test tube filled 1/4 with lime water. Remove the balloon from test tube B in such a manner that gas inside the balloon does not escape. Fit the balloon on the test tube and shake well. Observe and explain.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 4
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friends and Foe –
1. (Page 17) Do you know what these structures are and where do these come from?
Answer:
These structures are microorganisms called Rhizopus (bread mould). They are present in the surroundings and reproduce under favourable conditions.
2. (Page 19) I saw that my mother added a little curd to warm milk to set curd for the next day. I wonder why?
Answer:
My mother added a little curd to warm milk to set curd for the next day. This is because the curd which is added contains bacterium Lactobacillus. These act best in warm temperature to convert milk to curd.
3. (Page 19) An important ingredient of rava (sooji ) idlis and bhaturas is curd. Can you guess why?
Answer:
An important ingredient of rava (sooji) idlis and bhaturas is curd because curd contains the bacterium Lactobacillus. Lactobacillus produces carbon dioxide during the process of anaerobic respiration. The carbon dioxide released makes the dough rise and gives it the light and fluffy texture.
4. (Page 21) Why are children/infants given vaccination?
Answer:
Children/infants are given vaccinations to prevent diseases which they might susceptible to at a young age. The right vaccinations given at the right age produces suitable antibodies and protects against diseases like chicken pox, hepatitis, measles and mumps.
5. (Page 21) In your childhood, you must have been given injections to protect yourself against several diseases. Can you prepare a list of these diseases?
Answer:
A list of these diseases are as follows: chickenpox, polio, diphtheria, flu, Hepatitis B, measles, mumps, rubella, tetanus, tuberculosis, influenza.
6. (Page 23) Why does the teacher keep telling us not to let water collect anywhere in the neighbourhood?
Answer:
The teacher keeps telling us not to let water collect anywhere in the neighbourhood because mosquitoes breed in water. If water collects in coolers, tyres, flower pots etc then mosquitoes will get a chance to breed and spread harmful diseases like malaria, dengue fever etc.
7. (Page 25) How do we preserve cooked food at home?
Answer:
We can preserve cooked food at home by boiling or refrigerating them. Boiling kills microorganisms and low temperature inhibits their growth. You can also use preservatives like salt, edible oils, sugar, vinegar etc.
8. (Page 25) Is spoiling of food a chemical reaction?
Answer:
Yes, spoiling of food is a chemical reaction because it has bad taste, odour and new substances with different chemical compositions are formed.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms : Friend and Foe –
1. Complete Activity 2.1 (Page 17). Collect some moist soil from the field in a beaker and add water to it. After the soil particles have settled down, observe a drop of water from the beaker under a microscope. What do you see ?
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 2.2 (Page 17). Take a few drops of water from a pond. Spread on a glass slide and observe through a microscope.
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 2.3 (Page 20). Take ½ kg flour (atta or maida), add some sugar and mix with warm water. Add a small amount of yeast powder and knead to make a soft dough. What do you observe after two hours? Did you find the dough rising?
Answer:
4. Complete Activity 2.4 (Page 20). Take a 500 mL beaker filled upto ¾ with water. Dissolve 2-3 teaspoons of sugar in it. Add half a spoon of yeast powder to the sugar solution. Keep it covered in a warm place for 4-5 hours. Now smell the solution. Can you get a smell?
Answer:
5. Complete Activity 2.5 (Page 22). Take two pots and fill each pot half with soil. Mark them A and B. Put plant waste in pot A and things like polythene bags, empty glass bottles and broken plastic toys in pot B. Put the pots aside. Observe them after 3-4 weeks.
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe –
(A) Very Short Answer Type:
1. Give two examples of protozoa.
Answer:
Amoeba and paramecium.
2. Name a drug obtained from penicillium.
Answer:
Penicillin.
3. Which among the four groups of microorganisms are multicellular?
Answer:
Algae and fungi.
4. Name a microorganism used for commercial production of alcohol.
Answer:
Yeast.
5. Who discovered fermentation?
Answer:
Louis Pasteur.
6. What are diseases causing microorganisms called?
Answer:
Pathogens.
7. What is an organism that needs a host body to survive called?
Answer:
Parasite.
8. Name a disease which affects both humans and animals.
Answer:
Anthrax.
9. Name one common ingredient used to preserve meat and fish.
Answer:
Common salt.
10. Name the gas which is present in largest proportion in the atmosphere.
Answer:
Nitrogen.
(B) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ):
1. Which of the following is a communicable disease?
(a) Chicken pox
(b) Malaria
(c) Food poisoning
(d) Dengue fever
Answer: (a) Chicken pox
2. Chicken pox is caused by:
(a) Bacteria
(b) Virus
(c) Protozoa
(d) Fungi
Answer: (a) Bacteria
3. Cholera and typhoid are examples of:
(a) Water-borne diseases
(b) Air-borne diseases
(c) Diseases caused by virus
(d) Diseases caused by protozoa
Answer: (a) Water-borne diseases
4. In humans nitrogen is found in:
(a) Proteins
(b) Melanin
(c) Nucleic acids
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) Proteins and (c) Nucleic acids
5. Name the microorganism present in curd.
(a) Lactobacillus
(b) Yeast
(c) Algae
(d) Mould
Answer: (a) Lactobacillus
(C) Short Answer Type:
1. How are viruses different from other microorganisms?
Answer:
Unlike other microorganisms, viruses reproduce only inside the cells of the host organisms such as a plant, animal or bacterium. Also, unlike certain bacteria, viruses do not have any beneficial effects and only cause diseases.
2. Does drinking water contain microorganisms?
Answer:
Yes, water from various sources can contain microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and algae.
3. Give two ways in which bacteria increase the fertility of the soil.
Answer:
Bacteria decompose organic waste into manure which increases the fertility of the soil. Bacteria also fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds which can be used by plants.
4. Name three antibiotics obtained from bacteria.
Answer:
Three antibiotics obtained from bacteria are streptomycin, tetracycline, erythromycin.
5. How can hepatitis B disease be prevented?
Answer:
Hepatitis B can be prevented using a vaccine. The vaccine injected into the body contains a harmless part of the hepatitis B virus. This induces the body to produce antibodies to help fight the invader. These antibodies remain in the body and we are protected from the disease.
6. Name the preservatives used in jams.
Answer:
Sodium benzoate, sodium metabisulphite, sugar are preservatives used in jams.
7. What is pasteurisation.
Answer:
Pasteurisation is the process by which milk is heated to 700 C for about 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. This prevents the growth of microbes which spoil milk.
8. Briefly describe how animals get nitrogen required by the body.
Answer:
Bacteria and blue green algae present in the soil fix nitrogen in the atmosphere into nitrogenous compounds. Roots of plants take in this nitrogen which is then used to synthesize plants proteins and other compounds. Animals feed on these plants and get these proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds needed by the body.
9. Why is it not advisable to eat food infested by flies?
Answer:
Flies can be carriers of diseases causing microbes. When flies sit on garbage and animal excreta, pathogens stick to their bodies. When flies sit on open food, these pathogens get transferred to it. When humans eat this food the pathogens make them fall sick.
(D) Long Answer Type:
1. Observe the figure below and answer the questions that follow.
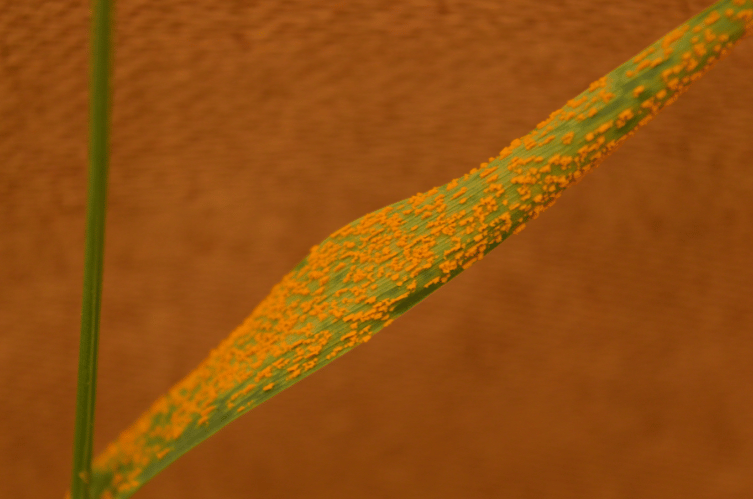
a) Write the name of the disease.
(b) Name the causative agent of this disease?
(c) How does the disease spread from one plant to another?
(d) How can the disease be managed?
Answers:
(a) Rust of wheat.
(b) Fungi
(c) The disease spreads from one plant to another via air and seeds.
(d) The diseases can be managed by judicious use of fungicide.
(E) Fill in the Blanks:
antibodies, bacteria, parasite, algae, sugar
(a) Yeast converts _________ into alcohol.
(b) ________ produced by vaccines protect against certain diseases.
(c) Plasmodium is a type of _________.
(d) __________ can exist in extremely harsh environments.
(e) Spirogyra is a type of __________.
Answer:
(a) Yeast converts sugar into alcohol.
(b) Antibodies produced by vaccines protect against certain diseases.
(c) Plasmodium is a type of parasite.
(d) Bacteria can exist in extremely harsh environments.
(e) Spirogyra is a type of algae.
(F) Match and Pair:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Aspergillus | (a) Small-pox |
| (ii) Edward Jenner | (b) Proteins |
| (iii) Vinegar | (c) Fungi |
| (iv) Nitrogen | (d) Malaria |
| (v) Protozoans | (e) Preservative |
Answer:
The completed table is shown below:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Aspergillus | (c) Fungi |
| (ii) Edward Jenner | (a) Small-pox |
| (iii) Vinegar | (e) Preservative |
| (iv) Nitrogen | (b) Proteins |
| (v) Protozoans | (d) Malaria |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe –
We have thoroughly solved all Chapter 2 exercise questions, extended learning activities, in-text questions, in-text activities and even extra questions. All your questions on the chapter have been answered in this complete solutions package. Attractive diagrams have been included wherever necessary which will further help you visualize and understand the concepts.
You can download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime! There’s lots more top-quality free study material on the way, so make sure you keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list!
The following topics are covered:
2.1 – Microorganisms
2.2 – Where do Microorganisms Live?
2.3 – Microorganisms and Us
2.4 – Harmful Microorganisms
2.5 – Food Preservation
2.6 – Nitrogen Fixation
2.7 – Nitrogen Cycle
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 1 Fill in the Blanks Question (Question 1)
(ii) 1 Tick the Correct Answer Question (Question 2)
(iii) 1 Match and Pair Question (Question 3)
(iii) 5 Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 4, 5, 6, 8, 9)
(iv) 1 Long Answer Type Questions (Question 7)
Of course! Feel free to download the PDF versions of educationroundtheworld.com’s NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foeanytime you please! The entire material is included in the PDF version. Please look towards the top of the page to find the download button!
Study the beneficial and harmful effects of microorganisms in detail. Also, the concepts of nitrogen fixation and the nitrogen cycle are important for your exams. This chapter contains a lot of factual details, so thorough studying is necessary to master the chapter.
If you need additional help, our expert teachers are here for you! Feel free to contact us anytime and let us help you out! Cheers! (Insert hyperlink)
We have expert teacher-mentors on staff who will love to prepare you for your exams and counsel you regarding your future academic and professional careers. Are you facing any difficulties? Let us know, so we can help you! We have found that this approach boosts students’ confidence and exam performance as well. So, if you like what we offer, please feel free to contact us anytime. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Book an appointment now!


