Welcome, students! Dive into the world of tissues with our comprehensive solutions material, covering all your in-text questions, exercises, and activities in one convenient resource. Our solutions are designed to make complex concepts easy to understand, ensuring you grasp fundamental principles with clarity. Plus, we’ve included extra practice questions on Chapter 6 to help you sharpen your skills and prepare for exams.
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Page 60:
1. What is a tissue?
Answer:
A tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function.
2. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Answer:
The utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms is to provide structural support and to cause movement, carry messages, to transport oxygen, food, hormones and waste material and so on.
Page 65:
1. Name types of simple tissues.
Answer:
The types of simple tissues are parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
2. Where is apical meristem found?
Answer:
Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots.
3. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer:
Sclerenchymatous tissue, which is a type of permanent tissue, makes up the husk of the coconut.
4. What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
Phloem is made up of five types of cells: sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma.
Page 69:
1. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer:
Muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body. Muscles contain special proteins called contractile proteins, which contract and relax to cause movement.
2. What does a neuron look like?
Answer:
A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair-like parts arise. Each neuron has a single long part, called the axon, and many short, branched parts called dendrites. An individual nerve cell may be up to a metre long.
3. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
Cardiac muscles are involuntary, cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
4. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
Areolar tissue is a type of connective tissue present in animals. It is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. It fills the space inside the organs, supports internal organs and helps in repair of tissues.
Solutions to Exercises (Page No 70) of NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
1. Define the term “tissue”.
Answer:
A tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function.
2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
Mainly four types of elements together make up the xylem tissue. They are tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
Simple tissues are different from complex tissues in plants in that simple tissues are made of one type of cells, while complex tissues are made of more than one type of cells.
4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer:
Parenchyma has thin cell walls, collenchyma has irregularly thickened cell walls at the corners of the cells and sclerenchyma has cells walls so thick due to lignin that there is no internal space inside the cell.
5. What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer:
Stomata are necessary for exchanging gases with the atmosphere. Transpiration (loss of water in the form of water vapour) also takes place through stomata.
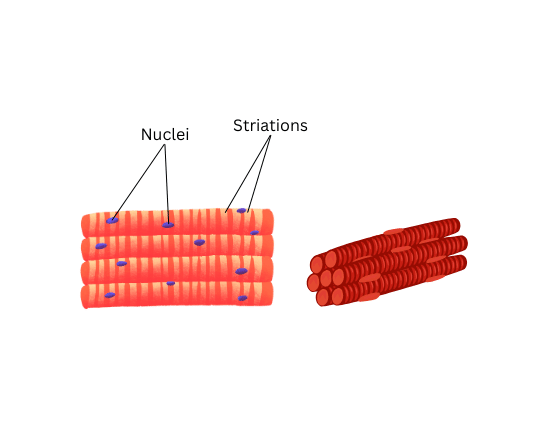
6. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer:
The three types of muscle fibres are striated, unstriated and cardiac muscle.
Striated Muscles:
- They are attached to bones and help in body movement.
- They are voluntary muscles.
- Cells are long and cylindrical in shape.
- Cells are unbranched.
- Cells are multinucleate.
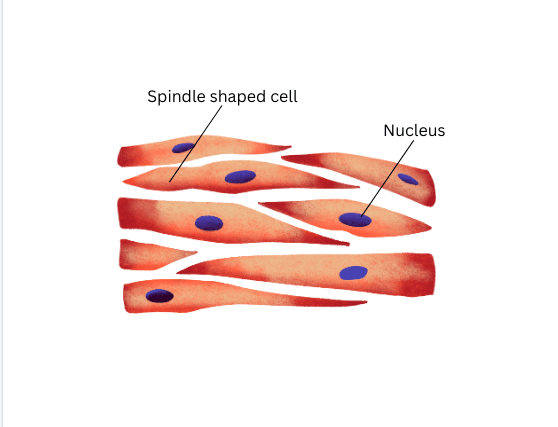
Unstriated Muscles:
- Present in alimentary canal, in the iris of the eye, in ureters and in the bronchi of the lungs.
- They are involuntary muscles.
- Cells are spindle-shaped.
- Cells are unbranched.
- Cells are uninucleate.
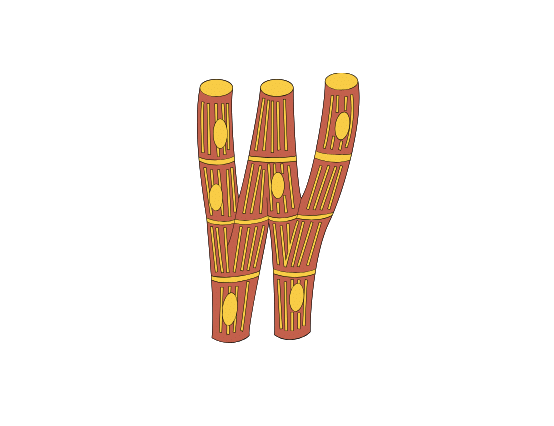
Cardiac Muscles:
- Present in the heart.
- They are involuntary muscles.
- Cells are cylindrical.
- Cells are branched.
- Cells are uninucleate.

7. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer:
The cardiac muscle enables involuntary rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart which enables blood flow throughout the body.
8. Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
Based on Structure:
| Striated | Unstriated | Cardiac |
| Cells are long and cylindrical in shape, unbranched, multinucleate, alternate light and dark bands or striations are present. | Cells are spindle-shaped, unbranched, cells are uninucleate, no bands or striations are present. | Cells are cylindrical, branched, uninucleate. Bands or striations are present. |
Based on site/location
| Striated | Unstriated | Cardiac |
| They are attached to bones and help in body movement. | Present in alimentary canal, in the iris of the eye, in ureters and in the bronchi of the lungs. | Present in the heart. |
9. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron
Answer:
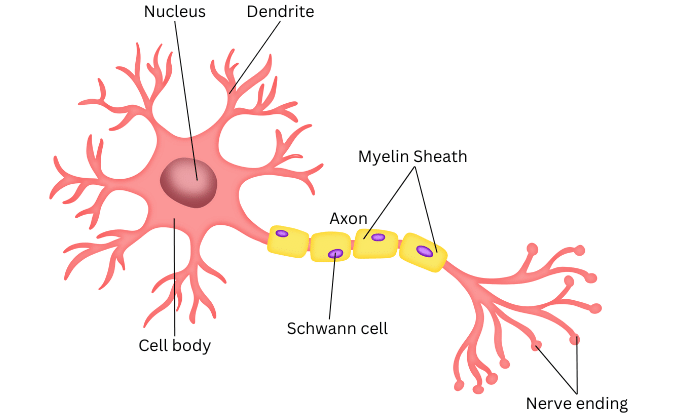
10. Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answers:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth is epithelial tissue.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans is tendon.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants is phloem.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body is adipose tissue.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix is blood.
(f) Tissue present in the brain is nervous tissue.
11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
Skin – Stratified squamous epithelium.
Bark of tree – Cork (Protective tissue with dead cells)
Bone – Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule – Cuboidal epithelial tissue
Vascular bundle – Xylem and phloem (types of complex permanent tissues)
12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer:
The regions in which parenchyma tissue is present arethe pith of stems and roots, leaves, aquatic plants, xylem, phloem, flowers, fruits.
13. What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer:
The role of the outer covering epidermis is to protect the plant from mechanical damage, protect against water loss in dry habitats and also from invasion by parasitic fungi.
14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer:
Cork cells are compactly arranged without intercellular spaces which aids in protection. They also have a substance called suberin in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water.
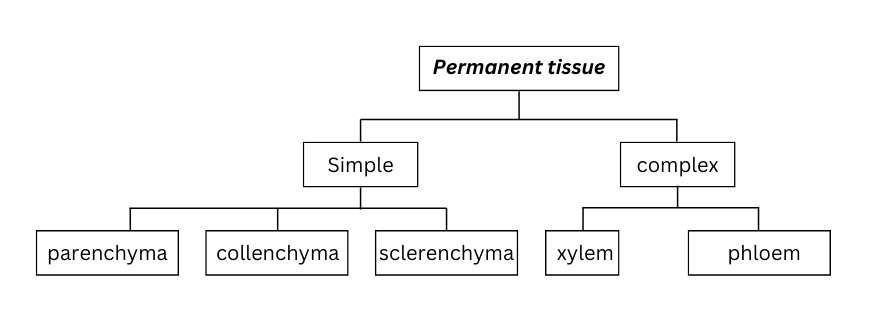
15. Complete the following chart:
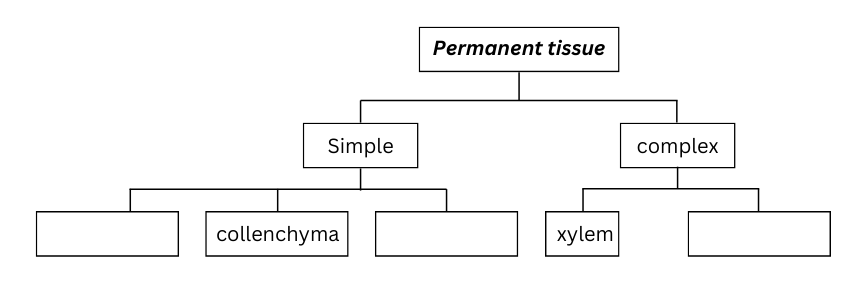
Answer:
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
1. Complete Activity 6.1 (Page 61).
• Take two glass jars and fill them with water.
• Now, take two onion bulbs and place one on each jar, as shown in Fig. 6.1.
• Observe the growth of roots in both the bulbs for a few days.
• Measure the length of roots on day 1, 2 and 3.
• On day 4, cut the root tips of the onion bulb in jar 2 by about 1 cm. After this, observe the growth of roots in both the jars and measure their lengths each day for five more days and record the observations in tables, like the table below:
| Length | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 |
| Jar 1 | |||||
| Jar 2 |
• From the above observations, answer the following questions:
1. Which of the two onions has longer roots? Why?
2. Do the roots continue growing even after we have removed their tips?
3. Why would the tips stop growing in jar 2 after we cut them?
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 6.2 (Page 62).
• Take a plant stem and with the help of your teacher cut into very thin slices or sections.
• Now, stain the slices with safranin. Place one neatly cut section on a slide, and put a drop of glycerine.
• Cover with a cover-slip and observe under a microscope. Observe the various types of cells and their arrangement. Compare it with Fig. 6.3.
• Now, answer the following on the basis of your observation:
1. Are all cells similar in structure?
2. How many types of cells can be seen?
3. Can we think of reasons why there would be so many types of cells? • We can also try to cut sections of plant roots. We can even try cutting sections of root and stem of different plants.
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 6.3 (Page 63).
• Take a freshly plucked leaf of Rhoeo.
• Stretch and break it by applying pressure.
• While breaking it, keep it stretched gently so that some peel or skin projects out from the cut.
• Remove this peel and put it in a petri dish filled with water.
• Add a few drops of safranin.
• Wait for a couple of minutes and then transfer it onto a slide. Gently place a cover slip over it.• Observe under microscope.
Answer:
4. Complete Activity 6.4 (Page 66). Take a drop of blood on a slide and observe different cells present in it under a microscope.
Answer:
5. Complete Activity 6.5 (Page 68). Compare the structures of different types of muscular tissues. Note down their shape, number of nuclei and position of nuclei within the cell in the Table 6.1.
Table 6.1:
| Features | Striated | Smooth | Cardiac |
| Shape | |||
| Number of nuclei | |||
| Position of nuclei |
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Name the tissue which is responsible for growth of the plant.
Answer:
Meristematic tissue.
2. Name two involuntary muscles in the human body.
Answer:
Smooth muscle and cardiac muscle.
3. What tissue is present in the growing tip of the plant stem?
Answer:
Apical meristem.
4. Which is the most common type of simple permanent tissue?
Answer:
Parenchyma.
5. What tissue is present in the hard outer covering of seeds like coconut?
Answer:
Sclerenchymatous tissue.
6. What is the outer surface of plants called?
Answer:
Epidermis.
7. Which cells are responsible for the movement of our chest?
Answer:
Muscle cells.
8. What is the matrix of blood called?
Answer:
Plasma.
9. Where are fats stored in the body?
Answer:
Adipose tissue.
10. Name the tissue which is most responsive to stimuli.
Answer:
Nervous tissue.
11. What are the cells of the nervous tissue called?
Answer:
Nerve cells or neurons.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. Which of the following tissues is located near the nodes of plants?
(A) Apical meristem
(B) Intercalary meristem
(C) Lateral meristem
(D) Permanent tissue
Answer: (B) Intercalary meristem
2. Which tissue helps flowers float on the water surface?
(A) Parenchyma
(B) Collenchyma
(C) Sclerenchyma
(D) Aerenchyma
Answer: (D) Aerenchyma
In aquatic plants, the tissue called aerenchyma is present. Large air cavities are present in aerenchyma to help the plants float.
3. Which of the constituents of phloem are dead?
(A) Sieve cells
(B) Phloem fibres
(C) Sieve tubes
(D) Companion cells
Answer: (B) Phloem fibres
4. Blood is a type of:
(A) Fluid
(B) Tissue
(C) Organ
(D) Matrix
Answer: (B) Tissue
5. Lung alveoli are made up of:
(A) Epithelial tissue
(B) Connective tissue
(C) Muscular tissue
(D) Nervous tissue
Answer: (A) Epithelial tissue
6. Bone is a type of:
(A) Epithelial tissue
(B) Connective tissue
(C) Muscular tissue
(D) Nervous tissue
Answer: (B) Connective tissue
Short Answer Type Questions:
1. How does the pattern of growth differ between plants and animals?
Answer:
Growth in plants is limited to certain regions, with some tissues capable of dividing throughout their life (meristematic tissue). In animals, cell growth is more uniform, and there is no clear demarcation between dividing and non-dividing regions.
2. What fundamental differences contribute to the varied organ system design in animals and plants?
Answer:
The organ system design is different in animals and plants because of their different feeding methods. Also, the organs are differently adapted for a sedentary existence on one hand (plants) and active locomotion on the other (animals).
3. Why do cells of meristematic tissue lack vacuoles?
Answer:
Cells of meristematic tissue lack vacuoles because their main function is to divide and form new cells. They constantly need food in order to divide and hence there is no requirement of storage of food and waste products, which vacuoles are used for.
4. What are the different types of simple permanent tissue in plants?
Answer:
The different types of simple permanent tissue in plants are parenchyma, chlorenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
5. Where are involuntary muscles located in the human body?
Answer:
Involuntary muscles are found in the walls of the stomach, intestines, and other digestive organs. They are also present in present in the walls of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries. They are also found in the iris of the eye, in ureters and in the bronchi of the lungs. Heart muscles are involuntary muscles.
6. Define differentiation in plants.
Answer:
Cells of meristematic tissue lose their ability to divide and take up a specific role to form permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation.
7. Can you identify the main components of xylem and phloem?
Answer:
The main components of xylem are tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. The main components of phloem are sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma.
8. What are the functions are xylem cells?
Answer:
Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Tracheids and vessels are tubular structures, which allows them to transport water and minerals vertically. The parenchyma stores food. Xylem fibres mainly offer support to the plant.
9. Why would cells need oxygen?
Answer:
Cells need oxygen for aerobic respiration, a process that generates energy (ATP) by breaking down glucose molecules in the presence of oxygen. Our body uses this energy in order to function.
10. Why is blood a connective tissue?
Answer:
Blood is categorized as a specialized connective tissue due to its role in connecting all body systems and facilitating the transport of gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic wastes throughout the body.
11. The bone is a strong and nonflexible tissue. What would be the advantage of these properties for bone functions?
Answer:
The advantage of bone tissue being strong and nonflexible is that it provides structural support and protection to vital organs. Bones serve as a framework for the body, supporting muscles and other tissues, and protecting delicate organs such as the brain and heart.
12. Where is cartilage present in the body?
Answer:
Cartilage is present at bone joints, nose, ear, trachea and larynx.
Long Answer Type Questions:
1. What are the functions of different kinds of epithelial tissues in the animal body?
Answer:
The functions of different kinds of epithelial tissues in the animal body are:
(i) Simple Squamous Epithelium: Found in areas where transportation of substances occurs through a selectively permeable surface, such as the lining of blood vessels or lung alveoli. It facilitates diffusion and filtration due to its thin and flat structure.
(ii) Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Found in skin and consists of cells arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear.
(iii) Ciliated Columnar Epithelium: Found in the respiratory tract, where the cilia on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells help in moving mucus forward to clear it.
(iv) Cuboidal Epithelium: Forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands, providing mechanical support.
(v) Glandular Epithelium: Specialized epithelial tissue that forms glands capable of secreting substances. It may form multicellular glands through inward folding of epithelial tissue.
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) The two types of plant tissues are ___________ tissue and ___________ tissue.
(b) The __________ of desert plants is thicker to protect against water loss.
(c) Xylem and phloem are both __________ tissues and form a _________ bundle.
(d) The protective tissues in the animal body are __________ tissues.
(e) The _________ connects two bones to each other and _________ connect muscles to bones.
Answers:
(a) The two types of plant tissues are meristematic tissue and permanent tissue.
(b) The epidermis of desert plants is thicker to protect against water loss.
(c) Xylem and phloem are both conducting tissues and form a vascular bundle.
(d) The protective tissues in the animal body are epithelial tissues.
(e) The ligament connects two bones to each other and tendons connect muscles to bones.
Match and Pair:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Chlorenchyma | (a) Bending of tendrils |
| (ii) Collenchyma | (b) Connective tissue |
| (iii) Stomata | (c) Photosynthesis |
| (iv) Areolar tissue | (d) Voluntary |
| (v) Skeletal muscles | (e) Transpiration |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Chlorenchyma | (c) Photosynthesis |
| (ii) Collenchyma | (a) Bending of tendrils |
| (iii) Stomata | (e) Transpiration |
| (iv) Areolar tissue | (b) Connective tissue |
| (v) Skeletal muscles | (d) Voluntary |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
We have provided comprehensive solutions to all in-text questions, exercises, and activities, meticulously crafted by our team of experts. With captivating figures to enhance your understanding, our material offers a seamless learning experience. Enjoy our additional problem set for extra exam preparation. Also, access free PDF downloads of the solutions anytime, anywhere!
Like what we offer? Stay ahead with our latest materials and exclusive offers by visiting our website regularly and subscribing to our email list. (insert hyperlink)
6.1 Are Plants and Animals Made of Same Types of Tissues?
6.2 Plant Tissues
6.3 Animal Tissues
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 8 Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 1 – 5, 7, 12 – 14)
(ii) 2 Long Answer Type Questions (Question 6, 8)
(iii) 1 Diagram-based Question (Question 9)
(iv) 1 Name the Following Question (Question 10)
(v) 1 Identification-based Question (Question 11)
(vi) 1 Chart-based Question (Here are the number of problems for the chapter
Learn the part on meristematic tissue well, it is important. The part on xylem and phloem is also very important. Learn to distinguish between different types of muscular tissue in animals. You will need to learn the chapter in detail because you will see detailed questions in the exams. The best way to do this is to understand and visualise the concepts first, before you memorise.
If you need expert coaching, we will be there for you anytime. Feel free to contact us anytime with your requirements and let us help you out! (Insert hyperlink)
Embark on a journey of academic and professional success with our exceptional coaching services, complemented by personalized guidance and mentorship. We’re dedicated to empowering you to shape your future, providing expert advice tailored specifically to your needs and schedule. Whether you’re seeking guidance on your studies or career goals, we’re here to support you every step of the way. So reach out us anytime you need help! We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way!


