Hello students! Learning Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals? Our experts have crafted the perfect solutions material for this chapter, to make fractions and decimals easy for you. We are confident our carefully prepared solutions to NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals and extra problem-set will be of good use to you. We only suggest that you study the solutions step-by-step in detail for maximum benefit.
Solutions to Exercise 2.1 (Page No 24) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals –
1. Which of the drawings (a) to (d) show:
(i) 2 × 1/5 (ii) 2 × 1/2 (iii) 3 × 2/3 (iv) 3 × 1/4
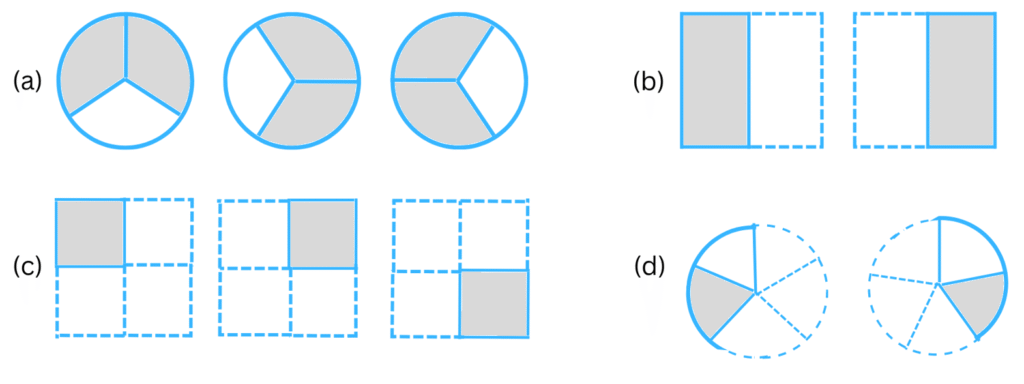
(a) In Figure (a), the shaded portion of each circle = 2/3 (2 parts out of 3 equal parts).
There are 3 circles. Therefore, Figure (a) represents the fraction = 3 × 2/3, that is fraction (iii).
(b) In Figure (b), the shaded portion of each rectangle = 1/2 (1 part out of 2 equal parts).
There are 2 rectangles. Therefore, Figure (b) represents the fraction = 2 × 1/2, that is fraction (ii).
(c) In Figure (c), the shaded portion of each square = 1/4 (1 part out of 4 equal parts).
There are 3 squares. Therefore, Figure (c) represents the fraction = 3 × 1/4, that is fraction (iv).
(d) In Figure (d), the shaded portion of each circle = 1/5 (1 part out of 5 equal parts).
There are 2 circles. Therefore, Figure (d) represents the fraction = 2 × 1/5, that is fraction (i).
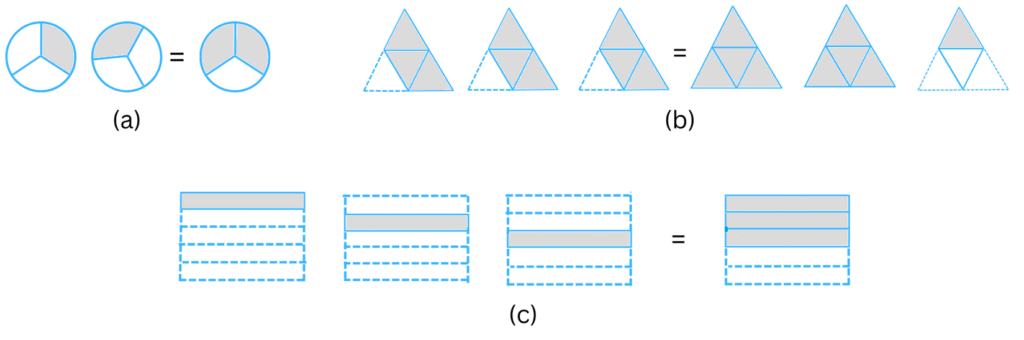
2. Some pictures (a) to (c) are given below. Tell which of them show:
(i) 3 × 1/5 = 3/5 (ii) 2 × 1/3 = 2/3 (iii) 3 × 3/4 = 2 1/4
Answer:
(a) In Figure (a), LHS has 2 circles. The shaded portion of each circle = 1/3 (1 part out of 3 equal parts).
Therefore, the LHS together represents the fraction = 2 × 1/3.
The RHS has 1 circle. The shaded portion = 2/3 (2 parts out of 3 equal parts).
We know, 2 × 1/3 = 2/3
Therefore, Figure (a) represents the expression (ii).
(b) In Figure (b), LHS has 3 triangles. The shaded portion of each triangle = 3/4 (3 parts out of 4 equal parts).
Therefore, the LHS together represents the fraction = 3 × 3/4.
The RHS has 3 triangles. The first two are completely shaded (each form a whole) and in the third triangle 1 part out of 4 equal parts are shaded and therefore, the shaded portion in the third triangle = 1/4.
Therefore, the RHS together represents the fraction = 1 + 1 + 1/4 = 2 1/4.
We know, 3 × 3/4 = 9/4 = 2 1/4 (when converted into mixed fractions).
Therefore, Figure (b) represents the expression (iii).
(c) In Figure (c), LHS has 3 rectangles. The shaded portion of each rectangle = 1/5 (1 part out of 5 equal parts).
Therefore, the LHS together represents the fraction = 3 × 1/5.
The RHS has 1 rectangle. The shaded portion = 3/5 (3 parts out of 5 equal parts).
We know, 3 × 1/5 = 3/5
Therefore, Figure (c) represents the expression (i).
3. Multiply and reduce to lowest form and convert into a mixed fraction:
(i) 7 × 3/5
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 7 × 3/5 = (7 × 3)/5 = 21/5 = 4 1/5 (converted into a mixed fraction).
(ii) 4 × 1/3
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 4 × 1/3 = (4 × 1)/3 = 4/3 = 1 1/3 (converted into a mixed fraction).
(iii) 2 × 6/7
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 2 × 6/7 = (2 × 6)/7 = 12/7 = 1 5/7 (converted into a mixed fraction).
(iv) 5 × 2/9
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 5 × 2/9 = (5 × 2)/9 = 10/9 = 1 1/9 (converted into a mixed fraction).
(v) 2/3 × 4
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 2/3 × 4 = (2 × 4)/3 = 8/3 = 2 2/3 (converted into a mixed fraction).
(vi) 5/2 × 6
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 5/2 × 6 = (5 × 6)/2 = 30/2 = 15.
(vii) 11 × 4/7
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 11 × 4/7 = (11 × 4)/7 = 44/7 = 6 2/7.
(viii) 20 × 4/5
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 20 × 4/5 = (20 × 4)/5 = 16.
(ix) 13 × 1/3
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 13 × 1/3 = (13 × 1)/3 = 13/3 = 4 1/3.
(x) 15 × 3/5
Answer:
To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same.
Therefore, 15 × 3/5 = (15 × 3)/5 = 45/5 = 9.
4. Shade:
(i) 1/2 of the circles in box (a) (ii) 2/3 of the triangles in box (b)
(iii) 3/5 of the squares in the box (c)
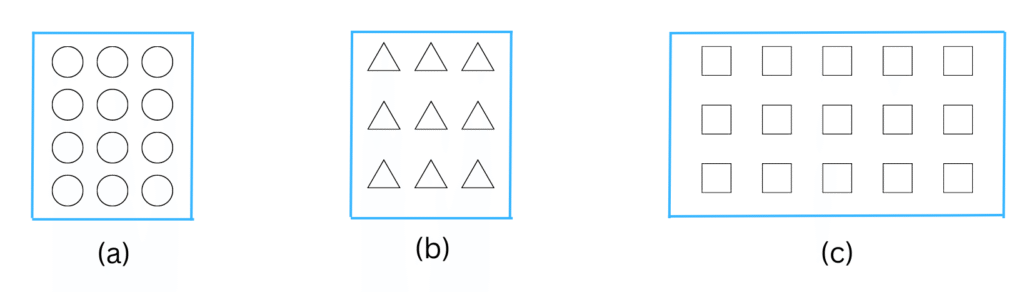
4. (i) 1/2 of the circles in box (a)
Answer:
We count that there are 12 circles in box (a).
We know, 1/2 of 12 = ½× 12 = (1 ×12 )/2 = 6 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
Find the 6 shaded circles below:
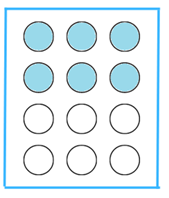
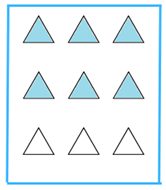
(ii) 2/3 of the triangles in box (b)
Answer:
We count that there are 9 triangles in box (b).
We know, 2/3 of 9 = 2/3× 9 = (2 × 9 )/3 = 6 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
Find the 6 shaded triangles below:
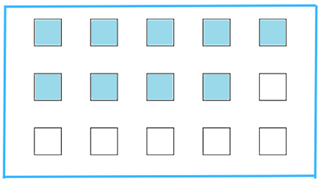
(iii) 3/5 of the squares in the box (c)
Answer:
We count that there are 15 squares in box (c).
We know, 3/5 of 15 = 3/5× 15 = (3 × 15 )/5 = 9 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
Find the 9 shaded squares below:
5. Find:
(a) 1/2 of (i) 24 (ii) 46
Answer:
(i) We know, 1/2 of 24 = ½× 24 = (1 × 24 )/2 = 12 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
(ii) We know, 1/2 of 46 = ½× 46 = (1 × 46 )/2 = 23 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
(b) 2/3 of (i) 18 (ii) 27
Answer:
(i) We know, 2/3 of 18 = 2/3× 18 = (2 × 18 )/3 = 12 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
(ii) We know, 2/3 of 27 = 2/3× 27 = (2 × 27 )/3 = 18 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
(c) 3/4 of (i) 16 (ii) 36
Answer:
(i) We know, 3/4 of 16 = ¾× 16 = (3 × 16 )/4 = 12 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
(ii) We know, 3/4 of 36 = ¾× 36 = (3 × 36 )/4 = 27 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
(d) 4/5 of (i) 20 (ii) 35
Answer:
(i) We know, 4/5 of 20 = 4/5× 20 = (4 × 20 )/5 = 16 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
(ii) We know, 4/5 of 35 = 4/5× 35 = (4 × 35 )/5 = 28 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication).
6. Multiply and express as a mixed fraction:
(a) 3 × 51/5
Answer:
3 × 51/5 = 3 × 26/5 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (3 × 26)/5 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 78/5 = 153/5
(b) 5 × 6 3/4
Answer:
5 × 6 3/4 = 5 × 27/4 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (5 × 27)/4 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 135/4
= 33 3/4
(c) 7 × 2 1/4
Answer:
7 × 2 1/4 = 7 × 9/4 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (7 × 9)/4 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 63/4
= 15 3/4
(d) 4 × 6 1/3
Answer:
4 × 6 1/3 = 4 × 19/3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (4 × 19)/3 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 76/3
= 25 1/3
(e) 3 1/4 × 6
Answer:
3 1/4 × 6 = 13/4 × 6 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (13 × 6 )/4 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 78/4
= (78 ÷ 2)/( 4 ÷ 2)
= 39/2
= 19 1/2
(f) 3 2/5 × 8
Answer:
3 2/5 × 8 = 17/5 × 8 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (17 × 8 )/5 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 136/5
= 27 1/5
7. Find: (a) 1/2 of (i) 2 3/4 (ii) 4 2/9 (b) 5/8 of (i) 3 5/6 (ii) 9 2/3
Answers:
(a) 1/2 of (i) 2 3/4 (ii) 4 2/9
(i) 1/2 of 2 3/4
1/2 of 2 3/4 = 1/2 of 11/4 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
1/2 of 11/4 = ½× 11/4 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 11 )/(2 × 4) (To multiply a fraction with another fraction, we take the product of the numerators and divide it by the product of the denominators)
= 11/8
= 1 3/8
(ii) 1/2 of 4 2/9
1/2 of 4 2/9 = 1/2 × 38/9 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (1 × 38)/(2 × 9) (To multiply a fraction with another fraction, we take the product of the numerators and divide it by the product of the denominators)
= 38/18
= (38 ÷ 2)/(18 ÷ 2)
= 19/9
= 1 1/9
(b) 5/8 of (i) 3 5/6 (ii) 9 2/3
(i) 5/8 of 3 5/6
5/8 of 3 5/6 = 5/8 × 23/6 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (5 × 23)/(8 × 6) (To multiply a fraction with another fraction, we take the product of the numerators and divide it by the product of the denominators)
= 115/48
= 2 19/48
(ii) 5/8 of 9 2/3
5/8 of 9 2/3 = 5/8 × 29/3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (5 × 29)/(8 × 3) (To multiply a fraction with another fraction, we take the product of the numerators and divide it by the product of the denominators)
= 145/24
= 6 1/24
8. Vidya and Pratap went for a picnic. Their mother gave them a water bottle that contained 5 litres of water. Vidya consumed 2/5 of the water. Pratap consumed the remaining water.
(i) How much water did Vidya drink?
Answer:
The amount of water in the bottle = 5 litres.
The amount of water that Vidya consumed
= 2/5 of 5
= 2/5 × 5 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (2 × 5 )/5 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= (10 )/5
= 2 litres
(ii) What fraction of the total quantity of water did Pratap drink?
Answer:
The amount of water in the bottle = 5 litres.
The amount of water that Vidya consumed = 2 litres.
The amount of water that Pratap drank = (5 – 2) litres = 3 litres.
Therefore, the fraction of the total quantity of water that Pratap drank
= ( The amount of water that Pratap drank)/(The amount of water in the bottle)
= (3 litres)/(5 litres)
= 3/5
Solutions to Exercise 2.2 (Page No 29) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals –
1. Find:
(i) 1/4 of (a) 1/4 (b) 3/5 (c) 4/3
(ii) 1/7 of (a) 2/9 (b) 6/5 (c) 3/10
Answer:
(i) 1/4 of (a) 1/4 (b) 3/5 (c) 4/3
(a) 1/4 of 1/4
1/4 of 1/4 = 1/4 × 1/4 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 1)/(4 × 4) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 1/16
(b) 1/4 of 3/5
1/4 of 3/5 = 1/4 × 3/5 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 3)/(4 × 5) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 3/20
(c) 1/4 of 4/3
1/4 of 4/3 = 1/4 × 4/3 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 4)/(4 × 3) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 4/12
= 1/3
(ii) 1/7 of (a) 2/9 (b) 6/5 (c) 3/10
(a) 1/7 of 2/9
1/7 of 2/9 = 1/7 × 2/9 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 2)/(7 × 9) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 2/63
(b) 1/7 of 6/5
1/7 of 6/5 = 1/7 × 6/5 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 6)/(7 × 5) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 6/35
(c) 1/7 of 3/10
1/7 of 3/10 = 1/7 × 3/10 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 3 )/(7 × 10) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 3/70
2. Multiply and reduce to lowest form (if possible):
(i) 2/3 × 22/3
Answer:
2/3 × 22/3
= 2/3 × 8/3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (2 × 8)/(3 × 3) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 16/9
= 17/9
(ii) 2/7 × 7/9
Answer:
2/7 × 7/9
= (2 × 7)/(7 × 9) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 2/9
(iii) 3/8 × 6/4
Answer:
3/8 × 6/4
= (3 × 6)/(8 × 4) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 18/32
= (18 ÷ 2)/(32 ÷ 2)
= 9/16
(iv) 9/5 × 3/5
Answer:
9/5 × 3/5
= (9 × 3)/(5 × 5) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 27/25
= 1 2/25
(v) 1/3 × 15/8
Answer:
1/3 × 15/8
= (1 × 15)/(3 × 8) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 5/8
(vi) 11/2 × 3/10
Answer:
11/2 × 3/10
= (11 × 3)/(2 × 10) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 33/20
= 1 13/20
(vii) 4/5 × 12/7
Answer:
4/5 × 12/7
= (4 × 12)/(5 × 7) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 48/35
= 1 13/35
3. Multiply the following fractions:
(i) 2/5 × 5 1/4
Answer:
2/5 × 5 1/4
= 2/5 × 21/4 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (2 × 21)/(5 × 4) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 42/20
= (42 ÷ 2)/(20 ÷ 2 )
= 21/10
= 2 1/10
(ii) 6 2/5 × 7/9
Answer:
6 2/5 × 7/9
= 32/5 × 7/9 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (32 × 7)/(5 × 9) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 224/45
= 4 44/45
(iii) 3/2 × 5 1/3
Answer:
3/2 × 5 1/3
= 3/2 × 16/3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (3 × 16)/(2 × 3) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 48/6
= (48 ÷ 6)/(6 ÷ 6)
= 8/1
= 8
(iv) 5/6 × 2 3/7
Answer:
5/6 × 2 3/7
= 5/6 × 17/7 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (5 × 17)/(6 × 7) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 85/42
= 2 1/42
(v) 3 2/5 × 4/7
Answer:
= 17/5 × 4/7 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (17 × 4)/(5 × 7) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 68/35
= 1 33/35
(vi) 2 3/5 × 3
Answer:
2 3/5 × 3
= 13/5 × 3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (13 × 3)/5 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 39/5
= 7 4/5
(vi) 3 4/7 × 3/5
Answer:
3 4/7 × 3/5
= 25/7 × 3/5 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (25 × 3)/(7 × 5) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 75/35
= (75 ÷ 5)/(35 ÷ 5)
= 15/7
= 2 1/7
4. Which is greater:
(i) 2/7 of 3/4 or 3/5 of 5/8
Answer:
First, we find 2/7 of 3/4
= 2/7 × 3/4 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (2 × 3)/(7 × 4) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 6/28
= (6 ÷ 2)/(28 ÷ 2)
= 3/14
Then, we find 3/5 of 5/8
= 3/5 × 5/8 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= ( 3 × 5)/(5 × 8) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 15/40
= (15 ÷ 5)/(40 ÷ 5)
= 3/8
Let us convert 3/14 and 3/8 into like fractions (same denominator) to make comparison easier.
The common denominator can be the LCM of 14, 8 = 56.
Therefore, 3/14 = (3 × 4)/(14 × 4) = 12/56
And, 3/8 = (3 × 7)/(8 × 7) = 21/56
Since, 12/56 < 21/56 , we can say that 3/14 < 3/8. Therefore, we can say that: 2/7 of 3/4 < 3/5 of 5/8
(ii) 1/2 of 6/7 or 2/3 of 3/7
Answer:
(ii) 1/2 of 6/7 or 2/3 of 3/7
Answer:
First, we find 1/2 of 6/7
= 1/2 × 6/7 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (1 × 6)/(2 × 7) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 6/14
= (6 ÷ 2)/(14 ÷ 2 )
= 3/7
Then, we find 2/3 of 3/7
= 2/3 × 3/7 (Since the ‘of’ represents multiplication)
= (2 × 3)/(3 × 7) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= 6/21
= (6 ÷ 3)/(21 ÷ 7)
= 2/7
We note that 3/7 and 2/7 are like fractions with common denominator = 7.
Since, 3/7 > 2/7 , we can say that 1/2 of 6/7 > 2/3 of 3/7 .
5. Saili plants 4 saplings, in a row, in her garden. The distance between two adjacent saplings is 3/4 m. Find the distance between the first and the last sapling.
Answer:
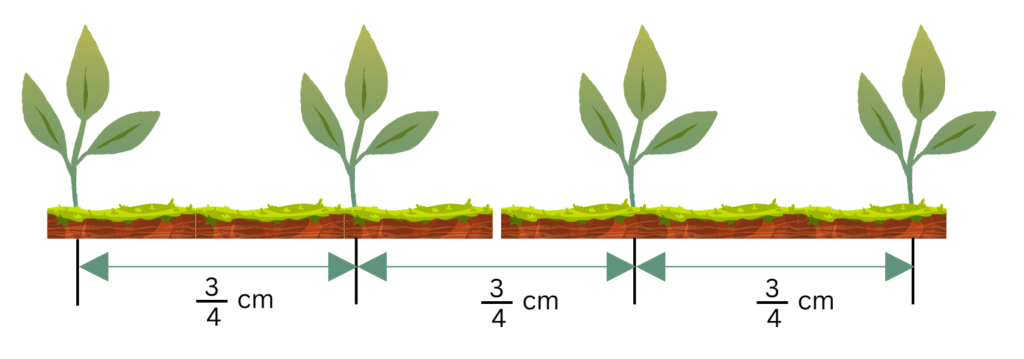
Number of saplings = 4.
The distance between two adjacent saplings = 3/4 m.
Therefore, the distance between the first and last sapling = 3/4 m + 3/4 m + 3/4 m = 3 × 3/4 m = (3 × 3)/4 m = 9/4 m = 2 1/4 m.
6. Lipika reads a book for 1 3/4 hours every day. She reads the entire book in 6 days. How many hours in all were required by her to read the book?
Answer:
Lipika reads the book for 1 3/4 hours/day.
She reads the entire book in 6 days.
Therefore, the number of hours in all required by her to read the book = 1 3/4 hours/day × 6 days = 1 3/4 × 6
= 7/4 × 6 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (7 × 6 )/4 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= 42/4
= (42 ÷ 2)/(4 ÷ 2)
= 21/2
= 10 1/2 hours
7. A car runs 16 km using 1 litre of petrol. How much distance will it cover using 2 3/4 litres of petrol.
Answer:
The car runs 16 km/1 litre of petrol.
Therefore, the total distance covered using 2 3/4 litres of petrol = 2 3/4 litres of petrol × 16 km/1 litre of petrol
= 2 3/4 × 16 km
= 11/4 × 16 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= (11 × 16 )/4 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same)
= (11 × 16 )/4
= (176 )/4
= (176 ÷ 4 )/(4 ÷ 4)
= 44 km
8. (a) (i) provide the number in the box ( ) , such that 2/3 × ( ) = 10/30 .
Answer:
2/3 × ( ) = 10/30
or, 2/3 × ( ) = (2 × 5)/(3 × 10)
or, 2/3 × ( ) = 2/3 × 5/10 (Since, we multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators) we can also separate them as shown)
By comparing we can see that, ( ) = 5/10
Therefore, 2/3 × (5/10) = 10/30
(ii) The simplest form of the number obtained in ( ) is __.
Answer:
( ) = 5/10 = (5 ÷ 5)/(10 ÷ 5) = 1/2 (Reduced to simple form)
Therefore, the simplest form of the number obtained in ( ) is 1/2 .
(b) (i) provide the number in the box ( ), such that 3/5 × ( ) = 24/75
Answer:
3/5 × ( ) = 24/75
or, 3/5 × ( ) = 3/5 × 8/15 (Since, we multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators) we can also separate them as shown)
By comparing we can see that, ( ) = 8/15
Therefore, 3/5 × (8/15) = 24/75
(ii) The simplest form of the number obtained in ( ) is __.
Answer:
( ) = 24/75 = (24 ÷ 3 )/(75 ÷ 3) = 8/25 (Since, we multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators) we can also separate them as shown)
By comparing we can see that, ( ) = 8/25
Therefore, the simplest form of the number obtained in ( ) is 8/25.
Solutions to Exercise 2.3 (Page No 34) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals –
1. Find:
(i) 12 ÷ 3/4
Answer:
We know,
12 ÷ 3/4 = 12 × (Reciprocal of ¾) = 12 × 4/3 = (12 × 4)/3 = 16
(ii) 14 ÷ 5/6
Answer:
14 ÷ 5/6 = 14 × (Reciprocal of 5/6) = 14 × 6/5 = (14 × 6)/5 = 84/5
(iii) 8 ÷ 7/3
Answer:
8 ÷ 7/3 = 8 × (Reciprocal of 7/3) = 8 × 3/7 = (8 × 3)/7 = 24/7
(iv) 4 ÷ 8/3
Answer:
4 ÷ 8/3 = 4 × (Reciprocal of 8/3) = 4 × 3/8 = (4 × 3)/8 = 12/8 = (12 ÷ 4)/(8 ÷ 4) = 3/2
(v) 3 ÷ 21/3
Answer:
3 ÷ 21/3 = 3 ÷ 7/3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 3 × (Reciprocal of 7/3)
= 3 × 3/7 = (3 × 3)/7 = 9/7
(vi) 5 ÷ 34/7
Answer:
5 ÷ 34/7 = 5 ÷ 25/7 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 5 × (Reciprocal of 25/7)
= 5 × 7/25 = (5 × 7)/25 = 35/25 = (35 ÷ 5)/(25 ÷ 5) = 7/5
2. Find the reciprocal of each of the following fractions. Classify the reciprocals as proper fractions, improper fractions and whole numbers.
(i) 3/7
Answer:
The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is 1, are called the reciprocals of each other.
We can see that, 3/7 × 7/3 = (3 × 7)/(7 × 3) = 21/21 = 1.
Therefore, 7/3 is the reciprocal of 3/7.
7/3 is an improper fraction.
(ii) 5/8
Answer:
The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is 1, are called the reciprocals of each other.
We see, 5/8 × 8/5 = (5 × 8)/(8 × 5) = 40/40 = 1.
Therefore, 8/5 is the reciprocal of 5/8.
8/5 is an improper fraction.
(iii) 9/7
Answer:
The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is 1, are called the reciprocals of each other.
We see, 9/7 × 7/9 = (9 × 7)/(7 × 9) = 63/63 = 1.
Therefore, 7/9 is the reciprocal of 7/9.
7/9 is a proper fraction.
(iv) 6/5
Answer:
The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is 1, are called the reciprocals of each other.
We see, 6/5 × 5/6 = (6 × 5)/(5 × 6) = 30/30 = 1.
Therefore, 5/6 is the reciprocal of 6/5.
5/6 is a proper fraction.
(v) 12/7
Answer:
The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is 1, are called the reciprocals of each other.
We see, 12/7 × 7/12 = (12 × 7)/(7 × 12) = 84/84 = 1.
Therefore, 7/12 is the reciprocal of 12/7.
7/12 is a proper fraction.
(vi) 1/8
Answer:
The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is 1, are called the reciprocals of each other.
We see, 1/8 × 8/1 = (1 × 8)/(8 × 1) = 8/8 = 1.
Therefore, 8/1 = 8 is the reciprocal of 1/8 .
8 is a whole number.
(vi) 1/11
Answer:
The non-zero numbers whose product with each other is 1, are called the reciprocals of each other.
We see, 1/11 × 11/1 = (1 × 11)/(11 × 1) = 11/11 = 1.
Therefore, 11/1 = 11 is the reciprocal of 1/11 .
11 is a whole number.
3. Find:
(i) 7/3 ÷ 2
Answer:
7/3 ÷ 2 = 7/3 ÷ 2/1 (We express the whole number 2 as the fraction 2/1)
= 7/3 × (Reciprocal of 2/1) = 7/3 × 1/2 = (7 × 1)/(3 × 2) = 7/6 = 1 1/6
(ii) 4/9 ÷ 5
Answer:
4/9 ÷ 5 = 4/9 ÷ 5 (We express the whole number 5 as the fraction 5/1)
= 4/9 × (Reciprocal of 5/1) = 4/9 × 1/5 = (4 × 1)/(9 × 5) = 4/45
(iii) 6/13 ÷ 7
Answer:
6/13 ÷ 7 = 6/13 ÷ 7/1 (We express the whole number 7 as the fraction 7/1)
= 6/13 × (Reciprocal of 7/1) = 6/13 × 1/7 = (6 × 1)/(13 × 7) = 6/91
(iv) 4 1/3 ÷ 3
Answer:
4 1/3 ÷ 3 = 13/3 ÷ 3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 13/3 × (Reciprocal of 3/1) = 13/3 × 1/3 = (13 × 1)/(3 × 3) = 13/9 = 1 4/9
(v) 3 1/2 ÷ 4
Answer:
3 1/2 ÷ 4 = 7/2 ÷ 4 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 7/2 × (Reciprocal of 4/1) = 7/2 × 1/4 = (7 × 1)/(2 × 4) = 7/8
(vi) 4 3/7 ÷ 7
Answer:
4 3/7 ÷ 7 = 31/7 ÷ 7 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 31/7 × (Reciprocal of 7/1) = 31/7 × 1/7 = (31 × 1)/(7 × 7) = 31/49
4. Find:
(i) 2/5 ÷ 1/2
Answer:
2/5 ÷ 1/2
= 2/5 × (Reciprocal of ½) = 2/5 × 2/1 = (2 × 2)/(5 × 1) = 4/5
(ii) 4/9 ÷ 2/3
Answer:
4/9 ÷ 2/3
= 4/9 × (Reciprocal of 2/3) = 4/9 × 3/2 = (4 × 3)/(9 × 2) = 12/18 = (12 ÷ 6)/(18 ÷ 6) = 2/3
(iii) 3/7 ÷ 8/7
Answer:
3/7 ÷ 8/7
= 3/7 × (Reciprocal of 8/7) = 3/7 × 7/8 = (3 × 7)/(7 × 8) = (21 ÷ 7)/(56 ÷ 7) = 3/8
(iv) 2 1/3 ÷ 3/5
Answer:
2 1/3 ÷ 3/5 = 7/3 ÷ 3/5 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 7/3 × (Reciprocal of 3/5) = 7/3 × 5/3 = (7 × 5)/(3 × 3) = 35/9 = 3 8/9
(v) 3 1/2 ÷ 8/3
Answer:
3 1/2 ÷ 8/3 = 7/2 ÷ 8/3 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 7/2 × (Reciprocal of 8/3) = 7/2 × 3/8 = (7 × 3)/(2 × 8) = 21/16 = 1 5/16
(vi) 2/5 ÷ 1 1/2
Answer:
2/5 ÷ 1 1/2 = 2/5 ÷ 3/2 (Converting the mixed fraction into an improper fraction)
= 2/5 × (Reciprocal of 3/2) = 2/5 × 2/3 = (2 × 2)/(5 × 3) = 4/15 = 4/15
(vii) 3 1/5 ÷ 1 2/3
Answer:
3 1/5 ÷ 1 2/3 = (16 )/5 ÷ 5/3 (Converting the mixed fractions into an improper fractions)
= (16 )/5 × (Reciprocal of 5/3) = 16/5 × 3/5 = 48/25 = 1 23/25
(viii) 2 1/5 ÷ 1 1/5
Answer:
2 1/5 ÷ 1 1/5 = 11/5 ÷ 6/5 (Converting the mixed fractions into an improper fractions)
= (11 )/5 × (Reciprocal of 6/5) = 11/5 × 5/6 = (11 × 5)/(5 × 6) = 55/30 = (55 ÷ 5)/( 30÷ 5) = 11/6 = 1 5/6
Solutions to Exercise 2.4 (Page No 38) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals –
1. Find:
(i) 0.2 × 6
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 2 × 6 = 12
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 1
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 0.2 × 6 = 1.2
(ii) 8 × 4.6
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 8 × 46 = 368
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 1
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 8 × 4.6= 36.8
(iii) 2.71 × 5
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 271 × 5 = 1355
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 2.71 × 5= 13.55
(iv) 20.1 × 4
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 201 × 4= 804
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 1
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 20.1 × 4= 80.4
(v) 0.05 × 7
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 5 × 7= 35
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 0.05 × 7 = 0.35
(vi) 211.02 × 4
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 21102 × 4= 84408
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 211.02 × 4= 844.08
(vii) 2 × 0.86
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 2 × 86 = 172
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 2 × 0.86 = 1.72
2. Find the area of rectangle whose length is 5.7 cm and breadth is 3 cm.
Answer:
The length of the rectangle = 5.7 cm and breadth = 3 cm.
The area of rectangle = (length × breadth)
= (5.7 cm × 3 cm)
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 57 × 3 = 171
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point = 1
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 5.7 × 3 = 17.1
Therefore, the area of the rectangle = 17.1 cm2
3. Find:
(i) 1.3 × 10
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 10 has one zero over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by one place.
1.3 × 10 = 13
(ii) 36.8 × 10
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 10 has one zero over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by one place.
36.8 × 10 = 368
(iii) 153.7 × 10
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 10 has one zero over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by one place.
153.7 × 10 = 1537
(iv) 168.07 × 10
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 10 has one zero over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by one place.
168.07 × 10 = 1680.7 × 10
(v) 31.1 × 100
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 100 has two zeros over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by two places.
31.1 × 100 = 3110
(vi) 156.1 × 100
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 100 has two zeros over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by two places.
156.1 × 100 = 15610
(vii) 3.62 × 100
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 100 has two zeros over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by two places.
3.62 × 100 = 362
(viii) 43.07 × 100
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 100 has two zeros over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by two places.
43.07 × 100 = 4307
(ix) 0.5 × 10
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 10 has one zero over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by one place.
0.5 × 10 = 5
(x) 0.08 × 10
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 10 has one zero over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by one place.
0.08 × 10 = 0.8
(xi) 0.9 × 100
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 100 has two zeros over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by two places.
0.9 × 100 = 0.90 × 100 = 90
(xii) 0.03 × 1000
Answer:
The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 1000 has two zeros over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by two places.
0.03 × 1000 = 0.030 × 1000 = 30
4. A two-wheeler covers a distance of 55.3 km in one litre of petrol. How much distance will it cover in 10 litres of petrol?
Answer:
One litre of petrol takes the two-wheeler a distance of 55.3 km.
Therefore, 10 litres of petrol take the two-wheeler a distance of (10 × 55.3) km
10 × 55.3 = 553 km [The digits in the product will remain the same as in the decimal number. Since 10 has one zero over 1, the decimal point in the product is shifted to the right by one place]
5. Find:
(i) 2.5 × 0.3
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 25 × 3 = 75
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 1 + 1 = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 2.5 × 0.3= 0.75
(ii) 0.1 × 51.7
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 1 × 517 = 517
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 1 + 1 = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 0.1 × 51.7= 5.17
(iii) 0.2 × 316.8
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 02 × 3168= 2 × 3168 = 6336
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 1 + 1 = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get, 0.2 × 316.8 = 63.36
(iv) 1.3 × 3.1
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 13 × 31= 403
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 1 + 1 = 2
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get 1.3 × 3.1 = 4.03
(v) 0.5 × 0.05
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 05 × 005= 5 × 5 = 25
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 1 + 2 = 3
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get 0.5 × 0.05 = 0.025
(vi) 11.2 × 0.15
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 112 × 015= 112 × 15 = 1680
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 1 + 2 = 3
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get 11.2 × 0.15 = 1.680
(vii) 1.07 × 0.02
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 107 × 002= 107 × 2 = 214
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 2 + 2 = 4
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get 1.07 × 0.02 = 0.0214
(viii) 10.05 × 1.05
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 1005 × 105= 105525
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 2 + 2 = 4
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get 10.05 × 1.05 = 10.5525
(ix) 101.01 × 0.01
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 10101 × 001= 10101 × 1 = 10101
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 2 + 2 = 4
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get 101.01 × 0.01 = 1.0101
(x) 100.01 × 1.1
Answer:
First, we multiply them as whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Therefore, we get: 10001 × 11= 110011
Second, we add the digits to the right of the decimal point in the decimal numbers being multiplied.
The number of digits to the right of the decimal point in the two numbers together = 2 + 1 = 3
Third, starting from the rightmost digit of the product, we count the number of digits equal to the sum of the previous addition and move towards the left and place the decimal point there.
Therefore, we get 100.01 × 1.1 = 110.011
Solutions to Exercise 2.5 (Page No 41) of NCERT Class 7 Math Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals –
1. Find:
(i) 0.4 ÷ 2
Answer:
0.4 ÷ 2 = 4/10 ÷ 2
= 4/10 × (Reciprocal of 2/1)
= 4/10 × 1/2
= (4 × 1)/(10 × 2) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 4)/(10 × 2)
= 1/10 × 4/2
= 1/10 × 2
= 2/10
= 0.2 (When dividing a number by 10, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by one place since there is one zero over 1 in 10)
(ii) 0.35 ÷ 5
Answer:
0.35 ÷ 5 = 35/100 ÷ 5
= 35/100 × (Reciprocal of 5/1)
= 35/100 × 1/5
= (35 × 1)/(100 × 5) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 35)/(100 × 5)
= 1/100 × 35/5
= 1/100 × 7
= 7/100
= 0.07 (When dividing a number by 100, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by two places since there are two zeros over 1 in 100)
(iii) 2.48 ÷ 4
Answer:
2.48 ÷ 4 = 248/100 ÷ 4
= 248/100 × (Reciprocal of 4/1)
= 248/100 × 1/4
= (248 × 1)/(100 × 4) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 248)/(100 × 4)
= 1/100 × 248/4
= 1/100 × 62
= 62/100
= 0.62 (When dividing a number by 100, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by two places since there are two zeros over 1 in 100)
(iv) 65.4 ÷ 6
Answer:
65.4 ÷ 6 = 654/10 ÷ 6
= 654/10 × (Reciprocal of 6/1)
= 654/10 × 1/6
= (654 × 1)/(10 × 6) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= ( 1 × 654)/(10 × 6)
= 1/10 × 654/6
= 1/10 × 109
= 109/10
= 10.9 (When dividing a number by 10, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by one place since there is one zero over 1 in 10)
(v) 651.2 ÷ 4
Answer:
651.2 ÷ 4 = 6512/10 ÷ 4
= 6512/10 × (Reciprocal of 4/1)
= 6512/10 × 1/4
= (6512 × 1)/(10 × 4) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= ( 1 × 6512)/(10 × 4)
= 1/10 × 6512/4
= 1/10 × 1628
= 1628/10
= 162.8 (When dividing a number by 10, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by one place since there is one zero over 1 in 10)
(vi) 14.49 ÷ 7
Answer:
14.49 ÷ 7 = 1449/100 ÷ 7
= 1449/100 × (Reciprocal of 7/1)
= 1449/100 × 1/7
= (1449 × 1)/(100 × 7) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 1449)/(100 × 7)
= 1/100 × 1449/7
= 1/100 × 207
= 207/100
= 2.07 (When dividing a number by 100, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by two places since there are two zeros over 1 in 100)
(vii) 3.96 ÷ 4
Answer:
3.96 ÷ 4 = 396/100 ÷ 4
= 396/100 × (Reciprocal of 4/1)
= 396/100 × 1/4
= (396 × 1)/(100 × 4) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 396)/(100 × 4)
= 1/100 × 396/4
= 1/100 × 99
= 99/100 (When dividing a number by 100, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by two places since there are two zeros over 1 in 100)
= 0.99
(viii) 0.80 ÷ 5
Answer:
0.80 ÷ 5 = 80/100 ÷ 5
= 80/100 × (Reciprocal of 5/1)
= 80/100 × 1/5
= (80 × 1)/(100 × 5) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 80)/(100 × 5)
= 1/100 × 80/5
= 1/100 × 16
= 16/100 (When dividing a number by 100, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by two places since there are two zeros over 1 in 100)
= 0.16
2. Find:
(i) 4.8 ÷ 10
Answer:
4.8 ÷ 10
= 48/10 ÷ 10
= 48/10 × 1/10
= (48 × 1)/(10 × 10)
= 48/100
= 0.48
(ii) 52.5 ÷ 10
Answer:
52.5 ÷ 10
= 525/10 ÷ 10
= 525/10 × 1/10
= (525 × 1)/(10 × 10)
= 525/100
= 5.25
(iii) 0.7 ÷ 10
Answer:
0.7 ÷ 10
= 7/10 ÷ 10
= 7/10 × 1/10
= (7 × 1)/(10 × 10)
= 7/100
= 0.07
(iv) 33.1 ÷ 10
Answer:
33.1 ÷ 10
= 331/10 ÷ 10
= 331/10 × 1/10
= (331 × 1)/(10 × 10)
= 331/100
= 3.31
(v) 272.23 ÷ 10
Answer:
272.23 ÷ 10
= 27223/100 ÷ 10
= 27223/100 × 1/10
= (27223 × 1)/(100 × 10)
= 27223/1000
= 27.223
(vi) 0.56 ÷ 10
Answer:
0.56 ÷ 10
= 56/100 ÷ 10
= 56/100 × 1/10
= (56 × 1)/(100 × 10)
= 56/1000
= 0.056
(vii) 3.97 ÷ 10
Answer:
3.97 ÷ 10
= 397/100 ÷ 10
= 397/100 × 1/10
= (397 × 1)/(1000 × 1)
= 397/1000
= 0.397
3. Find:
(i) 2.7 ÷ 100
Answer:
When dividing a number by 100, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are two zeros over 1 in 100).
Therefore,
2.7 ÷ 100 = 0.027
(ii) 0.3 ÷ 100
Answer:
When dividing a number by 100, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are two zeros over 1 in 100).
Therefore,
0.3 ÷ 100 = 0.003
(iii) 0.78 ÷ 100
Answer:
When dividing a number by 100, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are two zeros over 1 in 100).
Therefore,
0.78 ÷ 100 = 0.0078
(iv) 432.6 ÷ 100
Answer:
When dividing a number by 100, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are two zeros over 1 in 100).
Therefore,
432.6 ÷ 100 = 4.326
(v) 23.6 ÷ 100
Answer:
When dividing a number by 100, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are two zeros over 1 in 100).
Therefore,
23.6 ÷ 100 = 0.236
(vi) 98.53 ÷ 100
Answer:
When dividing a number by 100, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are two zeros over 1 in 100).
Therefore,
98.53 ÷ 100 = 0.9853
4. Find:
(i) 7.9 ÷ 1000
Answer:
When dividing a number by 1000, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are three zeros over 1 in 1000).
Therefore,
7.9 ÷ 1000 = 0.0079
(ii) 26.3 ÷ 1000
Answer:
When dividing a number by 1000, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are three zeros over 1 in 1000).
Therefore,
26.3 ÷ 1000 = 0.0263
(iii) 38.53 ÷ 1000
Answer:
When dividing a number by 1000, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are three zeros over 1 in 1000).
Therefore,
38.53 ÷ 1000 = 0.03853
(iv) 128.9 ÷ 1000
Answer:
When dividing a number by 1000, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are three zeros over 1 in 1000).
Therefore,
128.9 ÷ 1000 = 0.1289
(v) 0.5 ÷ 1000
Answer:
When dividing a number by 1000, the digits of the quotient remain the same, but the decimal point in the quotient shifts to the left by two places (since there are three zeros over 1 in 1000).
Therefore,
0.5 ÷ 1000 = 0.0005
5. Find:
(i) 7 ÷ 3.5
Answer:
7 ÷ 3.5 = 7.0/3.5
The decimal point shall be shifted by one place to the right in 3.5 to make it 35. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by one place to the right in 7.0 to make it 70.
Therefore, 7.0/3.5 = 70/35 = 2
(ii) 36 ÷ 0.2
Answer:
36 ÷ 0.2 = 36.0/0.2
The decimal point shall be shifted by one place to the right in 0.2 to make it 2. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by one place to the right in 36.0 to make it 360.
Therefore, 36.0/0.2 = 360/2 = 180
(iii) 3.25 ÷ 0.5
Answer:
3.25 ÷ 0.5 = 3.25/0.5
The decimal point shall be shifted by one place to the right in 0.5 to make it 5. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by one place to the right in 3.25 to make it 32.5
Therefore, 3.25/0.5 = 32.5/5
= 325/10 × (Reciprocal of 5/1)
= 325/10 × 1/5
= (325 × 1)/(10 × 5) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 325)/(10 × 5)
= 1/10 × 325/5
= 1/10 × 65
= 65/10
= 6.5 (When dividing a number by 10, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by one place since there is one zero over 1 in 10)
(iv) 30.94 ÷ 0.7
Answer:
30.94 ÷ 0.7 = 30.94/0.7
The decimal point shall be shifted by one place to the right in 0.7 to make it 7. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by one place to the right in 30.94 to make it 309.4
Therefore, 30.94/0.7 = 309.4/7
= 3094/10 × (Reciprocal of 7/1)
= 3094/10 × 1/7
= (3094 × 1)/(10 × 7) (We multiply two fractions as (Product of Numerators)/(Product of Denominators))
= (1 × 3094)/(10 × 7)
= 1/10 × 3094/7
= 1/10 × 442
= 442/10
= 44.2 (When dividing a number by 10, the decimal point in the quotient will shift to the left by one place since there is one zero over 1 in 10)
(v) 0.5 ÷ 0.25
Answer:
The decimal point shall be shifted by two places to the right in 0.25 to make it 25. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by two places to the right in 0.50 to make it 50
Therefore, 0.5/0.25 = 0.50/0.25 = 50/25 = 2
= 2
(vi) 7.75 ÷ 0.25
Answer:
The decimal point shall be shifted by two places to the right in 0.25 to make it 25. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by two places to the right in 7.75 to make it 775
Therefore, 7.75/0.25 = 775/25 = 31
(vii) 76.5 ÷ 0.15
Answer:
The decimal point shall be shifted by two places to the right in 0.15 to make it 15. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by two places to the right in 76.50 to make it 7650
Therefore, 76.5/0.15 = 76.50/0.15 = 7650/15 = 510
(viii) 37.8 ÷ 1.4
Answer:
The decimal point shall be shifted by one place to the right in 1.4 to make it 14. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by one place to the right in 37.8 to make it 378
Therefore, 37.8/1.4 = 378/14 = 27
(ix) 2.73 ÷ 1.3
Answer:
The decimal point shall be shifted by one place to the right in 1.3 to make it 13. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by one place to the right in 2.73 to make it 27.3
Therefore, 2.73/1.3
= 27.3/13
= 273/10 ÷ 13
= 273/10 × 1/13
= (273 × 1)/(10 × 13)
= (1 × 273)/(10 × 13)
= 1/10 × 273/13
= 21/10
= 2.1
6. A vehicle covers a distance of 43.2 km in 2.4 litres of petrol. How much distance will it cover in one litre of petrol?
Answer:
Using 2.4 litres of petrol a vehicle covers a distance of 43.2 km.
In one litre of petrol a vehicle covers a distance of ( ) km
= (The decimal point shall be shifted by one place to the right in 2.4 to make it 24. Similarly, the decimal point shall also be shifted by one place to the right in 43.2 to make it 432)
= 18
Therefore, it will cover a distance of 18 km in one litre of petrol.
Important Questions from Previous NCERT Textbook:
Exercise 2.1 Page No: 31 (Old Textbook):
1. Solve:
(i) 2 – 3/5
Answer:
We change the fractions into equivalent fractions with common denominators.
Therefore,
2 – 3/5 = 2/1 – 3/5 = (2 × 5)/(1 × 5) – 3/5 = 10/5 – 3/5 = (10 – 3)/5 = 7/5 = 1 2/5
(ii) 4 + 7/8
Answer:
We change the fractions into equivalent fractions with common denominators.
Therefore,
4 + 7/8 = 4/1 + 7/8 = (4 × 8)/(1 × 8) + 7/8 = 32/8 + 7/8 = (32 + 7)/8 = 39/8 = 4 7/8
(iii) 3/5 + 2/7
Answer:
We change the fractions into equivalent fractions with common denominators.
Therefore,
3/5 + 2/7 = (3 × 7)/(5 × 7) + (2 × 5 )/(7 × 5) = 21/35 + 1/35 = (21 + 10)/35 = 31/35
(iv) 9/11 – 4/15
Answer:
We change the fractions into equivalent fractions with common denominators.
Therefore,
9/11 – 4/15 = (9 × 15)/(11 × 15) – (4 × 11 )/(15 × 11) = 135/165 – 44/165 = (135 – 44)/165 = 91/165
(v) 7/10 + 2/5 + 3/2
Answer:
We change the fractions into equivalent fractions with common denominators.
Therefore,
7/10 + 2/5 + 3/2 = (7 × 1)/(10 × 1) + (2 × 2 )/(5 × 2) + (3 × 5 )/(2 × 5) = 7/10 + 4/10 + (15 )/10 = (7 + 4 + 15)/10 = 26/10 = (26 ÷ 2)/(10 ÷ 2) = 13/5 = 2 3/5
(vi) 22/3 + 31/2
Answer:
First, we convert the mixed fractions into improper fractions.
22/3 + 31/2 = 8/3 + 7/2
Therefore,
8/3 + 7/2 = (8 × 2)/(3 × 2) + (7 × 3 )/(2 × 3) = 16/6 + 21/6 = (16 + 21)/6 = 37/6 = 6 1/6
(vii) 81/2 – 35/8
Answer:
First, we convert the mixed fractions into improper fractions.
81/2 – 35/8 = 17/2 – 29/8
Therefore,
17/2 – 29/8 = (17 × 4)/(2 × 4) – (29 × 1 )/(8 × 1) = 68/8 – 29/8 = (68 – 29)/8 = 39/8 = 4 7/8
2. Arrange the following in descending order:
(i) 2/9, 2/3, 8/21
Answer:
Let us convert the above like fractions to like fractions with common denominators.
The common denominator will be the LCM of 9, 3, 21 = 63.
2/9 = (2 × 7)/(9 × 7) = 14/63
2/3 = (2 × 21)/(3 × 21) = 42/63
8/21 = (8 × 3)/(21 × 3) = 24/63
Clearly, 42/63 > 24/63 > 14/63
Therefore, the equivalent fractions arranged in descending order are: 2/3 > 8/21 > 2/9.
(ii) 1/5, 3/7, 7/10
Answer:
Let us convert the above like fractions to like fractions with common denominators.
The common denominator will be the LCM of 5, 7, 10 = 70.
1/5 = (1 × 14)/(5 × 14) = 14/70
3/7 = (3 × 10)/(7 × 10) = 30/70
7/10 = (7 × 7)/(10 × 7) = 49/70
Clearly, 49/70 > 30/70 > 14/70
Therefore, the equivalent fractions arranged in descending order are: 7/10 > 3/7 > 1/5.
3. In a “magic square”, the sum of the numbers in each row, in each column and along the diagonals is the same. Is this a magic square?
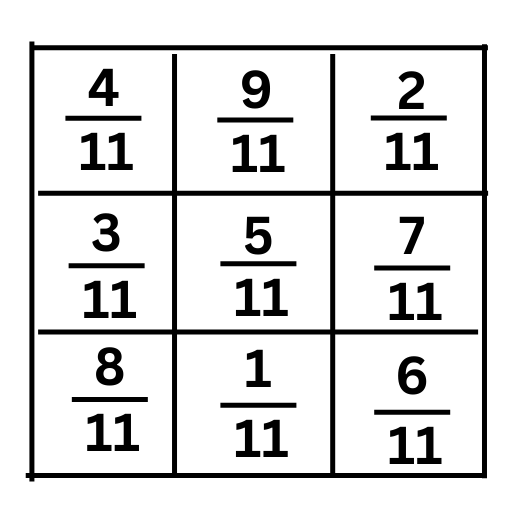
(Along the first row 4/11 + 9/11 + 2/11 = 15/11).
Answer:
The fractions are all like fractions, as they have the same denominator. This makes the additions easier.
The sum of the fractions for each row is shown below:
Row 1:
4/11 + 9/11 + 2/11 = 15/11
Row 2:
3/11 + 5/11 + 7/11 = 15/11
Row 3:
8/11 + 1/11 + 6/11 = 15/11
Column 1:
4/11 + 3/11 + 8/11 = 15/11
Column 2:
9/11 + 5/11 + 1/11 = 15/11
Column 3:
2/11 + 7/11 + 6/11 = 15/11
Diagonal 1:
4/11 + 5/11 + 6/11 = 15/11
Diagonal 2:
2/11 + 5/11 + 8/11 = 15/11
We can see that all the sums are = 15/11, therefore it is a magic square.
4. A rectangular sheet of paper is 12 1/2 cm long and 10 2/3 cm wide. Find its perimeter.
Answer:
We begin by converting the mixed fractions into improper fractions.
The length of the rectangular sheet of paper = 12 1/2 cm = 25/2 cm.
The width of the rectangular sheet of paper = 10 2/3 cm = 32/3 cm.
Perimeter of the rectangular sheet of paper = 2 × (length + breadth) = 2 × (25/2 + 32/3)
Let us convert the above fractions into like fractions (same denominator) to make the addition easier.
25/2 = (25 × 3)/(2 × 3) = 75/6
32/3 = (32 × 2)/(3 × 2) = 64/6
2 × (25/2 + 32/3)
= 2 × (75/6 + 64/6)
= 2 × (75/6 + 64/6)
= 2 × 139/6
= (2 × 139)/6 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same).
= 139/3 cm = 46 1/3 cm.
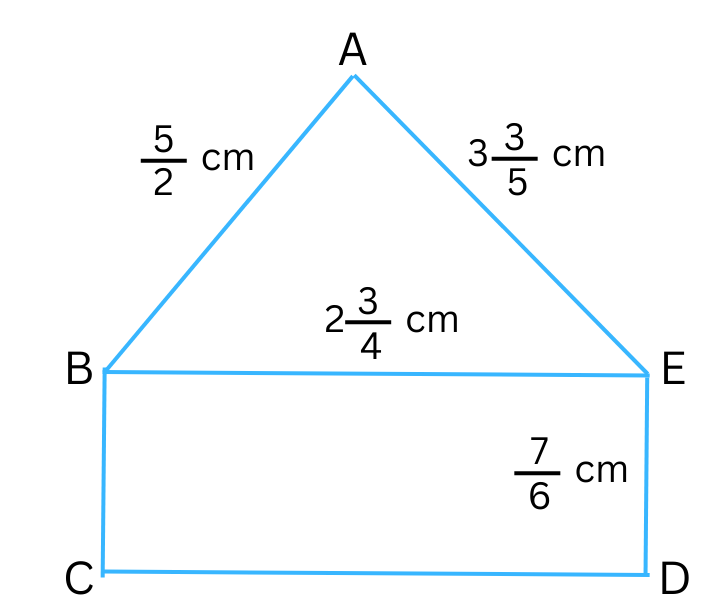
5. Find the perimeters of (i) triangle ABE (ii) the rectangle BCDE in this figure. Whose perimeter is greater?
Answers:
(i) triangle ABE
AB = 5/2 cm
BE = 23/4 cm = 11/4 cm (mixed fraction is converted into an improper fraction)
EA = 33/5 cm = 18/5 cm (mixed fraction is converted into an improper fraction)
The perimeter of the triangle ABE = Sum of the all the sides.
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle ABE = AB + BE + EA
= 5/2 cm + 11/4 cm + 18/5 cm
Let us convert the above fractions into like fractions (same denominator) to make the addition easier.
Common denominator = LCM of 2, 4, 5 = 20.
Therefore, 5/2 cm + 11/4 cm + 18/5 cm
= (5 × 10)/(2 × 10) cm + (11 × 5)/(4 × 5) cm + (18 × 4)/(5 × 4) cm
= 50/20 cm + 55/20 cm + 72/20 cm
= (50 + 55 +72)/20 cm
= 177/20 cm
= 817/20 cm
(ii) the rectangle BCDE
BE = 23/4 cm = 11/4 cm (mixed fraction is converted into an improper fraction)
ED = 7/6 cm
Perimeter of the rectangle BCDE = 2 × (length + breadth)
= 2 × (11/4 + 7/6)
= 2 × [((11 × 3)/(4 × 3)) + ((7 × 2)/(6 × 2))] [Converting the above fractions into like fractions (same denominator) to make the addition easier. Common denominator = LCM of 4, 6 = 12]
= 2 × (33/12 + 14/12)
= 2 × ((33 + 14)/12)
= 2 × 47/12
= (2 × 47)/12 (To multiply a whole number with a proper or an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number with the numerator of the fraction, keeping the denominator same).
= 47/6
= 7 5/6 cm
Perimeter of the triangle ABE = 177/20 cm.
Perimeter of the rectangle BCDE = 47/6 cm.
We convert the above fractions into like fractions (same denominator) to make the addition easier. Common denominator = LCM of 20, 6 = 60.
Therefore,
Perimeter of the triangle ABE = 177/20 = (177 × 3)/(20 ×3) = 531/60
Perimeter of the rectangle BCDE = 47/6 = (47 × 10)/(6 ×10) = 470/60
Since 531/60 > 470/60, therefore Perimeter of the triangle ABE > Perimeter of the rectangle BCDE.
6. Salil wants to put a picture in a frame. The picture is 7 3/5 cm wide. To fit in the frame the picture cannot be more than 7 3/10 cm wide. How much should the picture be trimmed?
Answer:
The width of the picture = 7 3/5 cm = 38/5 cm (converting to a mixed fraction).
To fit in the frame the width of the picture cannot be more than 7 3/10 cm = 73/10 cm (converting to a mixed fraction).
The picture should be trimmed by (38/5 – 73/10 ) cm.
38/5 – 73/10
= (38 × 2)/(5 × 2) – (73 × 1)/(10 × 1) [Converting the above fractions into like fractions (same denominator) to make the subtraction easier. Common denominator = LCM of 5, 10 = 10]
= 76/10 – 73/10
= (76-73)/10
= 3/10 cm
7. Ritu ate 3/5 part of an apple and the remaining apple was eaten by her brother Somu. What part of the apple did Somu eat? Who had the larger share? By how much?
Answer:
The part of the apple that Ritu ate = 3/5.
The remaining apple was eaten by her brother Somu.
The part of the apple that Somu ate
= 1 – 3/5
= (1 × 5)/(1 × 5) – (3 × 1)/(5 × 1) [Converting the above fractions into like fractions (same denominator) to make the subtraction easier. Common denominator = LCM of 1, 5 = 5]
= 5/5 – 3/5
= (5 – 3)/5
= 2/5
So, Ritu ate 3/5 part and Somu ate 2/5 part.
Since, 3/5 > 2/5, we can tell that Ritu had the larger share.
Ritu had the larger share by (3/5 – 2/5) = ((3 – 2)/5) = 1/5 part.
8. Michael finished colouring a picture in 7/12 hour. Vaibhav finished colouring the same picture in 3/4 hour. Who worked longer? By what fraction was it longer?
Answer:
Time taken by Michael to finish colouring the picture = 7/12 hour.
Time taken by Vaibhav to finish colouring the same picture = 3/4 hour.
Let us convert the above fractions into like fractions (same denominator) to make the subtraction easier. Common denominator = LCM of 12, 4 = 12].
7/12 = (7 × 1)/(12 × 1) = 7/12
3/4 = (3 × 3)/(4 × 3) = 9/12
Since, 9/12 > 7/12, Vaibhav worked longer.
Vaibhav worked longer by (9/12 – 7/12) = (9 – 7)/12 = 2/12 = 1/6 hour.
Exercise 2.5 Page No: 47 (Old Textbook):
1. Which is greater?
(i) 0.5 or 0.05
Answer:
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both numbers have the digit 0 to the left of the decimal point.
So, we compare the digits on the right of the decimal point starting from the tenths place. The digit at the tenths place of 0.5 is 5 and the digit at the tenths place of 0.05 is 0. Since 5 > 0, we can say 0.5 > 0.05.
(ii) 0.7 or 0.5
Answer:
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both numbers have the digit 0 to the left of the decimal point.
So, we compare the digits on the right of the decimal point starting from the tenths place. The digit at the tenths place of 0.7 is 7 and the digit at the tenths place of 0.5 is 5. Since 7 > 5, we can say 0.7 > 0.5.
(iii) 7 or 0.7
Answer:
7 can be written as 7.0. Therefore, we compare 7.0 and 0.7.
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here, 7.0 has the digit 7 at the ones place and 0.7 has the digit 0 at the ones place. Since 7 > 0, we can say that 7 > 0.7.
(iv) 1.37 or 1.49
Answer:
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both numbers have the digit 1 to the left of the decimal point.
So, we compare the digits on the right of the decimal point starting from the tenths place. The digit at the tenths place of 1.37 is 3 and the digit at the tenths place of 1.49 is 4. We need not look further. Since 3 < 4, we can say 1.37 < 1.49.
(v) 2.03 or 2.30
Answer:
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both numbers have the digit 2 to the left of the decimal point.
So, we compare the digits on the right of the decimal point starting from the tenths place. The digit at the tenths place of 2.03 is 0 and the digit at the tenths place of 2.30 is 3. We need not look further. Since 0 < 3, we can say 2.03 < 2.30.
(vi) 0.8 or 0.88
Answer:
0.8 can written as 0.80. Therefore, we compare 0.80 and 0.88.
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both numbers have the digit 0 to the left of the decimal point.
So, we compare the digits on the right of the decimal point starting from the tenths place. The digit at the tenths place of 0.80 is 8 and the digit at the tenths place of 0.88 is also 8. So, we continue. The digit at the hundredths place of 0.80 is 0 and the digit at the hundredths place of 0.88 is also 8. Since 0 < 8, we can say 0.8 < 0.88.
2. Express as rupees as decimals:
(i) 7 paise
Answer:
₹ 1 = 100 paise
So, 1 paise = ₹ 1/100
7 paise = ₹ (7 × 1/100) = ₹ ((7 × 1)/100) = ₹ 7/100 = ₹ 0.07
(ii) 7 rupees 7 paise
Answer:
₹ 1 = 100 paise
So, 1 paise = ₹ 1/100
7 paise = ₹ (7 × 1/100) = ₹ ((7 × 1)/100) = ₹ 7/100 = ₹ 0.07
7 rupees 7 paise = 7 rupees + 7 paise = ₹ 7 + ₹ 0.07 = ₹ 7.07
(iii) 77 rupees 77 paise
Answer:
₹ 1 = 100 paise
So, 1 paise = ₹ 1/100
77 paise = ₹ (77 × 1/100) = ₹ ((77 × 1)/100) = ₹ 77/100 = ₹ 0.77
77 rupees 77 paise = 77 rupees + 77 paise = ₹ 77 + ₹ 0.77 = ₹ 77.77
(iv) 50 paise
Answer:
₹ 1 = 100 paise
So, 1 paise = ₹ 1/100
50 paise = ₹ (50 × 1/100) = ₹ ((50 × 1)/100) = ₹ 50/100 = ₹ 0.50
(v) 235 paise
Answer:
₹ 1 = 100 paise
So, 1 paise = ₹ 1/100
235 paise = ₹ (235 × 1/100) = ₹ ((235 × 1)/100) = ₹ 235/100 = ₹ 2.35
3. (i) Express 5 cm in metre and kilometre
Answer:
5 cm in metre:
1 metre = 100 cm
So, 1 cm = 1/100 metre = 0.01 metre
5 cm = (5 × 1/100) metre = ((5 × 1)/100) metre = 5/100 metre = 0.05 metre
5 cm in kilometre:
1 kilometre = 1000 metre
1 metre = 100 cm
So, 1 kilometre = 1000 × 100 cm = 100000 cm
or, 1 cm = 1/100000 kilometre
or, 5 cm = (5 × 1/100000) kilometre = ((5 × 1)/100000) kilometre = 5/100000 kilometre = 0.00005 kilometre
(ii) Express 35 mm in cm, m and km
Answer:
35 mm in cm:
1 cm = 10 mm
So, 1 mm = 1/10 cm
So, 35 mm = (35 × 1/10) cm = ((35 × 1)/10) cm = 35/10 cm = 3.5 cm
35 mm in m:
1 m = 1000 mm
So, 1 mm = 1/1000 m
So, 35 mm = (35 × 1/1000) m = ((35 × 1)/1000) m = 35/1000 m = 0.035 m
35 mm in km:
1 km = 1000 m
So, 1 m = 1/1000 km
We found above that 35 mm = 0.035 m
Therefore, 35 mm = 0.035 m = (0.035 × 1/1000) km = (35/1000 × 1/1000) km = ((35 × 1)/(1000 × 1000)) km = 35/1000000 km = 0.000035 km.
4. Express in kg:
(i) 200 g
Answer:
1 kg = 1000 g
or, 1 g = 1/1000 kg
So, 200 g = (200 × 1/1000) kg = ((200 × 1)/1000) kg = 200/1000 kg = 0.2 kg
(ii) 3470 g
Answer:
1 kg = 1000 g
or, 1 g = 1/1000 kg
So, 3470 g = (3470 × 1/1000) kg = ((3470 × 1)/1000) kg = 3470/1000 kg = 3.47 kg
(iii) 4 kg 8 g
Answer:
1 kg = 1000 g
or, 1 g = 1/1000 kg
or, 8 g = (8 × 1/1000) kg = ((8 × 1)/1000) kg = 8/1000 kg = 0.008 kg
4 kg 8 g = 4 kg + 8 g = 4 kg + 0.008 kg = 4.008 kg
5. Write the following decimal numbers in the expanded form:
(i) 20.03
Answer:
20.03 = 2 × 10 + 0 × 1 + 0 × (1/10) + 3 × (1/100)
(ii) 2.03
Answer:
2.03 = 2 × 1 + 0 × (1/10) + 3 × (1/100)
(iii) 200.03
Answer:
200.03 = 2 × 100 + 0 × 10 + 0 × 1 + 0 × (1/10) + 3 × (1/100)
(iv) 2.034
Answer:
2.034 = 2 × 1 + 0 × (1/10) + 3 × (1/100) + 4 × (1/1000)
6. Write the place value of 2 in the following decimal numbers:
(i) 2.56
Answer:
The place value of 2 in 2.56 is ‘ones’.
(ii) 21.37
Answer:
The place value of 2 in 21.37 is ‘tens’.
(iii) 10.25
Answer:
The place value of 2 in 10.25 is ‘tenths’.
(iv) 9.42
Answer:
The place value of 2 in 9.42 is ‘hundredths’.
(v) 63.352
Answer:
The place value of 2 in 63.352 is ‘thousandths’.
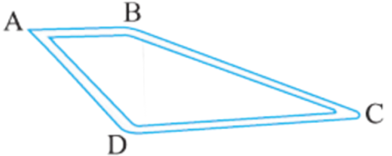
7. Dinesh went from place A to place B and from there to place C. A is 7.5 km from B and B is 12.7 km from C. Ayub went from place A to place D and from there to place C. D is 9.3 km from A and C is 11.8 km from D. Who travelled more and by how much?
Answer:
Dinesh covered the distance AB = 7.5 km and then covered the distance BC = 12.7 km.
Total distance = AB + BC = 7.5 km + 12.7 km = 20.2 km.
Ayub covered the distance AD = 9.3 km and then covered the distance DC = 11.8 km.
Total distance = AD + DC = 9.3 km + 11.8 km = 21.1 km.
To see who travelled more, we compare the two decimal numbers 20.2 km and 21.1 km together.
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both numbers have the digit 0 to the left of the decimal point. The digit at the tens place of both 20.2 and 21.1 is 2. Therefore, we continue. The digit in the ones place of 20.2 km is 0 and the digit in the ones place of 21.1 is 1. Since 1 > 0, we can say that 21.1 > 20.2.
Therefore, we can say that Ayub travelled more distance than Dinesh and by (21.1 km = 20.2 km) = 0.9 km.
8. Shyama bought 5 kg 300 g apples and 3 kg 250 g mangoes. Sarala bought 4 kg 800 g oranges and 4 kg 150 g bananas. Who bought more fruits?
Answer:
1 kg = 1000 g
or, 1 g = 1/1000 kg
So, 300 g = (300 × 1/1000) kg = ((300 × 1)/1000) kg = 300/1000 kg = 0.3 kg
5 kg 300 g = 5 kg + 300 g = 5 kg + 0.3 kg = 5.3 kg
So, the number of apples that Shyama bought = 5 kg 300 g = 5.3 kg.
250 g = (250 × 1/1000) kg = ((250 × 1)/1000) kg = 250/1000 kg = 0.25 kg
3 kg 250 g = 3 kg + 250 g = 3 kg + 0.25 kg = 3.25 kg
So, the number of mangoes that Shyama bought = 3 kg 250 g = 3.25 kg.
Therefore, the total number of fruits that Shyama bought = (number of apples + number of mangoes) = (5.3 kg + 3.25 kg) = 8.55 kg.
800 g = (800 × 1/1000) kg = ((800 × 1)/1000) kg = 800/1000 kg = 0.8 kg
4 kg 800 g = 4 kg + 800 g = 4 kg = 0.8 kg = 4.8 kg
So, the number of oranges that Sarala bought = 4 kg 800 g = 4.8 kg.
150 g = (150 × 1/1000) kg = ((150 × 1)/1000) kg = 150/1000 kg = 0.15 kg
4 kg 150 g = 4 kg + 150 g = 4 kg + 0.15 kg = 4.15 kg
So, the number of bananas that Sarala bought = 4 kg 150 g = 4.15 kg
Therefore, the total number of fruits that Sarala bought = (number of oranges + number of bananas) = (4.8 kg + 4.15 kg) = 8.95 kg.
We compare the decimal numbers 8.55 and 8.95.
We start by comparing the digits on the left of the decimal point, starting from the leftmost digit. Here both numbers have the digit 8 to the
left of the decimal point.
So, we compare the digits on the right of the decimal point starting from the tenths place. The digit at the tenths place of 8.55 is 5 and the digit at the tenths place of 8.95 is 9. Since 9 > 5, we can say that 8.95 > 8.55.
Therefore, Sarala bought more fruits than Shyama.
9. How much less is 28 km than 42.6 km?
Answer:
28 km can be written in the form of a decimal number as: 28.0
Therefore, 28 km is less than 42.6 km by an amount of (42.6 – 28.0) km = 14.6 km.
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals:
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. The area of one half of a square be 20 cm2. What is the area of the whole square?
Answer:
Let the area of the whole square be x.
Therefore, 1/2 × (x) = 20
or, x = 40 cm2 (Answer)
2. A circle of area 12 cm2 is divided into 6 equal parts. What is the area of each part?
Answer:
Area of each part = 1/6 × 12 = 2 cm2.
3. Find the value of (1/2 × 2/3 × 3/4)
Answer:
1/2 × 2/3 × 3/4 = (1 × 2 × 3)/(2 × 3 × 4) = 1/4 (Answer)
4. Find the reciprocal of 4/7.
Answer:
Reciprocal of 4/7 = 1 ÷ 4/7 = 1 × 7/4 = (1 × 7)/4 = 7/4 (Answer)
5. Arrange these decimal numbers in ascending order: 0.35, 0.3, 0.31.
Answer:
The decimal numbers arranged in ascending order are: 0.3, 0.31, 0.35.
6. The length of the side of a square = 0.5 cm and the length of the side of another square = 1/2 cm. Which square has greater area?
Answer:
0.5 cm = 5/10 = 1/2 cm.
Since the lengths of the sides of squares are equal, the areas of the squares= (length)2 are also equal.
7. What is the next term in the series: 0, 1/4, 1/2, 3/4, 1, …..
Answer:
Each term in the series is greater than the previous term by 1/4. The next term in the series = 11/4.
8. Evaluate: 0.7 ÷ 1/10
Answer:
0.7 ÷ 1/10 = 7/10 ÷ 1/10 = 7/10 × 10/1 = 7 (Answer)
9, Between which two integers does the decimal number 1.2 lie on the number line?
Answer:
The decimal number 1.2 lies between 1 and 2 on the number line.
10. When you multiply a fraction by 0.1 does it value increase or decrease?
Answer:
We have, 0.1 = 1/10
Therefore, when a fraction is multiplied by 1/10, its value will decrease.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. Which of the following is a proper fraction?
(a) 4/3
(b) 1/3
(c) 42/3
(d) 2
Answer: (b) 1/3
2. Which is greater among these two expressions:
Expression 1: (634.6 ÷ 100) and Expression 2: (0.6346 × 10)
(a) Expression 1 is greater
(b) Expression 2 is greater
(c) Expression 1 and Expression 2 are equal
(d) They cannot be compared
Answer: (c) Expression 1 and Expression 2 are equal
634.6 ÷ 100
= 634.6/100
= 6.346 (Shifting decimal point to the left by two places)
0.6346 × 10
= 6.346 (Shifting decimal point to the right by one place)
Therefore, Expression 1 = Expression 2.
3. If x = 21/3 and y = 31/2 , then what is the value of (x + y)(x – y)?
(a) – 245/36
(b) 35/6
(c) 245/36
(d) 245/6
Answer: (a) – 245/36
x = 21/3 = 7/3
y = 31/2 = 7/2
(x + y)(x – y)
= (7/3 + 7/2)( 7/3 – 7/2)
= 35/6 × (-7/6)
= – 245/36 (Answer)
4. A number when multiplied by 0.25 gives 0.35. The number is:
(a) 1.5
(b) 1.4
(c) 1.2
(d) 1.6
Answer: (b) 1.4
Let the number be x.
0.25 × x = 0.35 or, x = 1.4
5. Suppose you have three squares and half of a fourth. How many half squares can you obtain from these?
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 31/2
(d) 4
Answer: (b) 7
Number of half squares you can obtain = (31/2 ÷ 1/2) = 7/2 ÷ 1/2 = 7/2 × 2/1 = 7.
Short Answer and Long Answer Type Questions:
1. 2/3 of a number x is 10. What is the number?
Answer:
We have 2/3x = 10
or, x = 10 × 3/2
or, x = 15 (Answer)
2. Evaluate: (1 ÷ 2/3) × (1 ÷ 3/2)
Answer:
(1 ÷ 2/3) × (1 ÷ 3/2)
= (1 × 3/2) × (1 × 2/3)
= 1 × 3/2 × 2/3
= 1 (Answer)
3. You are given a cloth of area 31/4 m2. How many pieces of cloth of area 1/4 m2 can be made from this cloth?
Answer:
Total area of cloth = 31/4 m2 = 13/4 m2.
Number of pieces of cloth of area 1/4 m2 that can be made from this cloth = (13/4 m2 ÷ 1/4 m2) = 13/4 × 4/1 = 13 m2.
4. Which one is greater: 22/3 and 7/4.
Answer:
22/3 = 8/3 = (8 × 4)/(3 × 4) = 32/12
7/4 = (7 × 3)/(4 × 3) = 21/12
Since, 32/12 > 21/12 we can say that 22/3 > 7/4.
5. The length of a rectangle is 10 cm and the breadth is 5 cm. If the length of the rectangle is reduced by half and the breadth is reduced by one-third, by how much would the area decrease?
Answer:
Length of the rectangle = 10 cm and breadth = 5 cm.
Area of the rectangle = length × breadth = 10 × 5 = 50 cm2.
New length of the rectangle = (10 – 1/2 × 10) = 5 cm.
New breadth of the rectangle = (5 – 1/3 × 5) = 10/3 cm.
New area = (5 × 10/3) = 50/3 cm2 = 162/3 cm2.
Therefore, the area decreases by (50 – 162/3) cm2 = 331/3 cm2.
6. Simplify: (5/6 +2/3)/(1/3 ÷1/2)
Answer:
(5/6 +2/3)/(1/3 ÷1/2)
= ((5 + 4 )/6)/(1/3 ×2/1)
= (9/6)/(2/3)
= 9/6 ÷ 2/3
= 9/6 × 3/2
= 9/4 (Answer)
7. Evaluate the following:
(i) 7.8 ÷ 0.039 (ii) 1.6 ÷ 0.004
Answer:
(i) 7.8 ÷ 0.039
7.8/0.039
= 7800/39 (Shifting the decimal point three places to the right in both numerator and denominator)
= 200 (Answer)
(ii) 1.6 ÷ 0.04
1.6/0.04
= 160/4 (Shifting the decimal point two places to the right in both numerator and denominator)
= 40 (Answer)
8. A car needs to travel a certain distance in 3 hours. In the first hour it travelled 1/3rd distance and in the second hour it travelled 1/2 distance. How much distance must it cover in the third hour is the total distance to be covered is 60 km?
Answer:
Fraction of distance it travelled in the first hour = 1/3.
Fraction of distance it travelled in the second hour = 1/2.
Fraction of distance it travelled in the third hour = (1 – 1/3 – 1/2) = 1/6.
Therefore, distance in km that it must cover in the third hour = (1/6 × 60) km = 10 km.
9. A student studied 1/2 of a textbook in 1 hour. Then in the next 1 hour the student studied 1/2 of the fraction studied in the first hour. What fraction should he study in the third hour in order to complete the textbook?
Answer:
Fraction studied in the first 1 hour = 1/2.
In the next 1 hour the fraction the student studied (1/2 × 1/2) = 1/4.
Therefore, the fraction he should study in the third hour to complete the textbook = (1 – 1/2 – 1/4) = 1/4.
10. Simplify:
(i) (0.20 ÷ 0.10 × 0.05)/(0.30 × 0.45 ÷ 0.15) (ii) (1/4 -0.20 +2/3)/(1/4 × 0.20 + 0.5)
Answers:
(i) (0.20 ÷ 0.10 × 0.05)/(0.30 × 0.45 ÷ 0.15)
= (2 × 0.05)/(0.30 × 3)
= 0.1/0.9
= 1/9 (Answer)
(ii) (1/4 -0.20 +2/3)/(1/4 × 0.20 + 0.5)
= (1/4 –20/100 +2/3)/(1/4 ×20/100 +5/10)
= (1/4 –1/5 +2/3)/(1/4 ×1/5 + ½)
= ((5 – 4)/20 +2/3)/(1/4 ×1/5 + ½)
= (1/20 +2/3)/(1/20 + ½)
= ((3 + 40)/60)/((1 + 10)/20)
= (43/60)/(11/20)
= 43/60 ÷ 11/20
= 43/60 × 20/11
= 43/33 (Answer)
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) When two proper fractions are multiplied, the product is _________ than each of the fractions.
(b) If 0.5 is divided by 0.4 the resulting number will be an _________ fraction.
(c) If 0.009 is divided by 0.03 the quotient is __________.
(d) If you divide a number by 100000 the decimal point will shift to the left by ________ zeros. (e) When the fraction is divided by another fraction, we get a whole number. The denominator of the other fraction is a __________ of 2.
(e) When the fraction 1/2 is divided by another fraction, we get a whole number. The denominator of the other fraction is a __________ of 2.
Answer:
(a) When two proper fractions are multiplied, the product is less than each of the fractions.
(b) If 0.5 is divided by 0.4 the resulting number will be an improper fraction.
(c) If 0.009 is divided by 0.03 the quotient is 0.3.
(d) If you divide a number by 100000 the decimal point will shift to the left by 5 zeros.
(e) When the fraction 1/2 is divided by another fraction, we get a whole number. The denominator of the other fraction is a multiple of 2.
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals:
Our team of expert engineers and scientists have taken care to formulate the solutions in a logical manner, with clear explanations wherever possible, to aid your understanding. We assume that you are learning the material for the first time and strive to present the solutions in a manner that will help build your concepts from the ground up. Since our solutions complements the material in Chapter 2 of the Class 7 Maths NCERT textbook, we recommend that you study them together.
Of course, our solutions are all free for you to use and download! We do our best to ensure that we provide you with the best study material and want to provide you plenty more. So make sure you keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list to get the latest updates!
The main topics covered are:
2.1 – Multiplication of Fractions
2.2 – Division of Fractions
2.3 – Multiplication of Decimal Numbers
2.4 – Division of Decimal Numbers
Here are the number of problems by each chapter:
Exercise 2.1 – 8 questions
Exercise 2.2 – 8 questions
Exercise 2.3 – 4 questions
Exercise 2.4 – 5 questions
Exercise 2.5 – 6 questions
Yes, the PDFs of the solutions are available for you to download (please look towards the top of the page) for free!
You must learn multiplication and division of fractions and decimals. When it comes to multiplying and dividing fractions and decimals, there are certain rules. It is essential that you understand the rules and not memorise them. We have shown you how to use these rules to solve problems in this material. We have taken care to show every step of each problem, therefore we advise you to study all the steps in the solutions carefully. Some problems in this chapter can seem tricky to beginners. Therefore, we advise you to solve and re-solve the problems, keeping the solutions by your side for reference, until you are comfortable with the techniques.
And of course, if you need any additional help our expert teacher-mentors are there for you – please feel free to reach out to us anytime!
At educationroundtheworld.com, we believe in guiding students using methods that will be most beneficial for their future. So in addition to top-quality coaching, we mentor them regarding their future academic and professional careers. We have found that this approach boosts students’ confidence and makes them aware of the opportunities that lie ahead. So if that is what you are looking for, feel free to contact us anytime. We provide tailored one-to-one coaching and mentoring, based on your convenience and your needs – have it completely your way! Book an appointment now!


