Hello students and welcome to Class 7 Science! We have prepared top-quality solutions to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants for you, along with extra questions keeping in mind students’ and NCERT’s requirements. We have answered all textbook exercise questions, extended learning – activities and projects, in-text questions and in-text activities in this material. The additional questions cover the entire chapter, are similar to exam questions and will give you additional practice.
Solutions to Exercise (Page No 9) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants:
1. Why do organisms take food?
Answer:
Organisms take food to stay alive and function:
(i) Nutrients in food are necessary for living organisms to build their bodies and to grow.
(ii) It also helps them to guard against diseases and helps repair their bodies in case of damage.
(iii) The energy in food helps to carry out essential life processes.
2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
Answer:
The main difference between parasite and a saprotroph is that a parasite gets its nutrition from a living host, whereas a saprotroph derives its nutrition from dead and decaying matter. An example of a parasite is Cucuta and an example of a saprotroph is fungi.
3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Answer:
You can use the iodine test experiment to test the presence of starch in a leaf. The chlorophyll in the leaf is removed by soaking and heating it in spirit. Then the leaf is washed gently with water and a few drops of iodine solutions is poured over it. The change of colour to blue-black indicates the presence of starch in the leaf.
4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Answer:
Photosynthesis is the process by which food is prepared in plants by the green pigment chlorophyll. This takes place in the leaves of plants using carbon dioxide and in the presence of sunlight. Oxygen is released as a byproduct.
(i) Food is prepared in the leaves of plants and therefore all raw materials have to transported to the leaf for the process to happen.
(ii) The roots absorb water and necessary minerals from the soil which are transported to the leaf through the continuous pipe like vessels.
(iii) The stomata present on the leaf surface take in carbon dioxide from the air.
(iv) Chlorophyll in the leaves capture the energy of the sunlight and synthesize food (carbohydrates) from carbon dioxide and water. They also emit oxygen in the process.
The process can be summarised by the equation shown below:

5. Show with the help of a sketch that plants are the ultimate source of food.
Answer:
It can be seen from the sketch below that humans and animals are directly or indirectly dependent on plants for food:
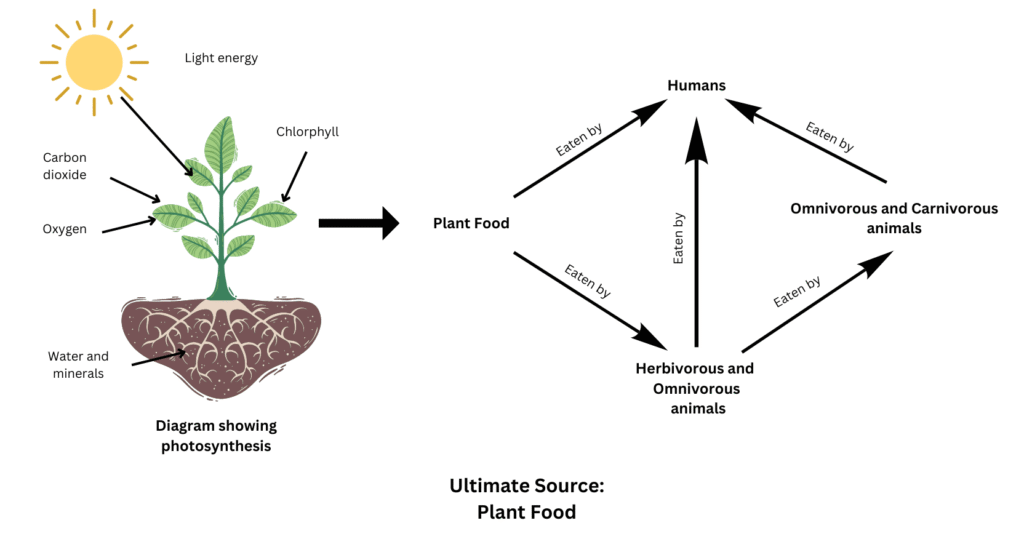
6. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Green plants are called ______________ since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as _______________.
(c) In photosynthesis, solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called ____________.
(d) During photosynthesis, plants take in _____________ and release ______________ gas.
Answers:
a) Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as starch.
(c) In photosynthesis, solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called chlorophyll.
(d) During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen gas.
7. Name the following.
(i) A parasitic plant with a yellow, slender and branched stem.
(ii) A plant that is partially autotrophic.
(iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Answers:
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) Pitcher plant
(iii) Stomata
8. Tick the correct answer.
(a) Cuscuta is an example of:
(i) autotroph (ii) parasite (iii) saprotroph (iv) host
Answer: Cuscuta is an example of a (ii) parasite.
(b) The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(i) Cuscuta (ii) China rose (iii) pitcher plant (iv) rose
Answer: The plant which traps and feeds on insects is: (iii) pitcher plant.
9. Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| Chlorophyll | Rhizobium |
| Nitrogen | Heterotrophs |
| Cuscuta | Pitcher plant |
| Animals | Leaf |
| Insects | Parasite |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| Chlorophyll | Leaf |
| Nitrogen | Rhizobium |
| Cuscuta | Parasite |
| Animals | Heterotrophs |
| Insects | Pitcher plant |
10. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T/F)
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Answers:
(i) False (F). Oxygen is released during photosynthesis.
(ii) False (F). Plants which synthesise their food are called autotrophs.
(iii) True (T). The products of photosynthesis are carbohydrates and water.
(iv) True (T). During photosynthesis the sun’s energy is used to form carbohydrates, which is made up of chemicals. Solar energy gets converted into chemical energy during the process.
11. Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair (ii) Stomata (iii) Leaf veins (iv) Petals
Answer: (ii) Stomata takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis.
12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) roots (ii) stem (iii) flowers (iv) leaves
Answer: (iv) leaves.
13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Answer:
Farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses to:
- Prevent crop damage due to harsh weather conditions.
- Reduce crop damage by keeping out pests.
- Enable different varieties of crops to be grown all year round.
- To grow crops of better and consistent quality and improve yield.
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 10) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants:
1. Project .Take a potted plant with broad leaves. Take two strips of black paper and cut out a small square in the centres. Cover a part of two leaves with these papers and secure them with paper clips (Fig. 1.9). Keep the plant in sunlight for 2–5 days. Observe the difference in the colour of the covered and the uncovered portions on the leaf. Perform iodine test on this leaf. Did the two parts show different results? Now take second leaf. Remove the strip and expose the covered part to the sunlight for 2–3 days and do the iodine test again. Describe your observations.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 1
2. Visit a green house if there is one near your place. Observe how they grow plants. Find out how they regulate the amount of light, water and carbon dioxide to grow the plants.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 2
3. Try growing a sweet potato just in water. Describe your experiment and observations.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 3
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants –
1. (Page 1) Boojho wants to know how plants prepare their own food.
Answer:
Plants prepare food by the process of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll present in leaves uses the energy of the sun to synthesize food from carbon dioxide and water.
2. (Page 1) Paheli wants to know why our body cannot make food from carbon dioxide, water and minerals like plants do.
Answer:
Our body cannot make food from carbon dioxide, water and minerals like plants do because it does not contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Chlorophyll present in plants captures solar energy of the sun which is essential for photosynthesis to occur. Hence due to the absence of chlorophyll photosynthesis cannot occur in the human body.
3. (Page 2) Boojho wants to know how water and minerals absorbed by roots reach the leaves.
Answer:
Water and minerals absorbed by the roots reach the leaves via the pipe-like vessels which connect the roots, stem, branches and the leaves. The vessels provide a continuous path for the nutrients to reach the leaf.
4. (Page 2) Paheli wants to know what is so special about the leaves that they can synthesise food but other parts of the plant cannot.
Answer:
Leaves can synthesise food but other parts of the plant cannot because of the green pigment chlorophyll present in leaves. Chlorophyll present in plants captures solar energy of the sun which is essential for photosynthesis to occur. Other parts of the plant cannot prepare food due to the absence of chlorophyll.
5. (Page 3) Boojho has observed some plants with deep red, violet or brown leaves. He wants to know whether these leaves also carry out photosynthesis.
Answer:
The plants with deep red, violet or brown leaves also contain chlorophyll and can also carry out photosynthesis. The red, violet and brown pigments are present in larger amount which mask the green colour of the chlorophyll pigment. Therefore, the differently coloured leaves are perfectly capable of carrying out photosynthesis.
6. (Page 5) Paheli wants to know whether mosquitoes, bed bugs, lice and leeches that suck our blood are also parasites.
Answer:
Yes, mosquitoes, bed bugs, lice and leeches that suck our blood are also parasites. Although these organisms do not actually live on our body, they can be called parasites because they depend on animals and humans for their nutrition.
7. (Page 5) Boojho is confused. If the pitcher plant is green and carries out photosynthesis, then why does it feed on insects?
Answer:
Even if the pitcher plant is green and carries out photosynthesis, it cannot get its full requirement of nitrogen and other minerals from the soil. Therefore, it depends on insects to fulfil that requirement.
8. (Page 6) Boojho wants to know how these organisms acquire nutrients. They do not have mouths like animals do. They are not like green plants as they lack chlorophyll and cannot make food by photosynthesis.
Answer:
Fungi do not have mouths like animals and lack chlorophyll, but use a different mode of nutrition called saprotrophic nutrition. These organisms take in nutrients from dead and decaying matter.
9. (Page 6) Paheli is keen to know whether her beautiful shoes, which she wore on special occasions, were spoiled by fungi during the rainy season. She wants to know how fungi appear suddenly during the rainy season.
Answer:
Fungiappear suddenly during the rainy season because of the moist conditions. Fungal spores present in the air require wet and warm areas in order to germinate and grow. These wet and warm conditions are prevalent during the rainy season, which is ideal for fungi to grow and spread.
10. (Page 8) Can we say that the insectivorous plants are partial heterotrophs?
Answer:
Yes, insectivorous plants are partial heterotrophs because they derive part of their nutrition from insects.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants:
1. Complete Activity 1.1 (Page 3). Take two potted plants of the same kind. Keep one in the dark (or in a black box) for 72 hours and the other in sunlight. Perform iodine test with the leaves of both the plants as you did in Class VI. Record your results. Now leave the pot which was earlier kept in the dark, in the sunlight for 3 – 4 days and perform the iodine test again on its leaves. Record your observations in your notebook.
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 2 (Page 6). Take a piece of bread and moisten it with water. Leave it in a moist warm place for 2–3 days or until fluffy patches appear on them (Fig. 1.8). What is the colour of these patches? Observe the patches under a microscope or a magnifying glass. Write down your observations in the notebook.
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions
(A) Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Name the process by which plants prepare food.
Answer:
Plants prepare food by the process of photosynthesis.
2. Name the food factory of the plant.
Answer:
The leaf is the food factory of the plant.
3. Do algae contain chlorophyll?
Answer:
Algae contain chlorophyll which gives them the green colour.
4. Do all plants contain chlorophyll?
Answer:
No, all plants do not contain chlorophyll.
5. What are plants which eat insects called?
Answer:
Plants which eat insects are called insectivorous plants.
6. Name two fungi which are useful.
Answer:
Yeast and mushrooms are two fungi which are useful.
7. How can we protect our things from getting spoiled by fungus?
Answer:
We can protect our things from getting spoiled by fungus by keeping them dry.
(B) Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is the source of the food that animals eat?
Answer:
Plants are the ultimate source of food for animals. Plants synthesize food by themselves. Animals get their food from plants, either directly or by eating animals who feed on plants.
2. What are the differences between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Answer:
The organisms which have the ability to make food themselves from simple substances are called autotrophs e.g. plants. Heterotrophs cannot produce food on their own and depend on plants for their food e.g. animals.
3. Why is the sun the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms?Answer: Solar energy is captured by the leaves of plants and stored in the plant in the form of food by the process of photosynthesis. Animals and humans get energy to function by eating food stored in plants or by eating other animals who eat plants. Therefore, the source of all energy that living beings need to survive can be traced back to the sun.
4. Name the different parts of a cell.
Answer:
A cell is enclosed by the thin outer cell membrane. There is a centrally located spherical nucleus inside the cell which is surrounded by the jelly-like cytoplasm.
5. Would life be possible on earth without photosynthesis?
Answer:
Life would not be possible on earth without photosynthesis. Plants would not be able to produce food using photosynthesis. Also, all living organisms depend directly or indirectly on food produced by plants and would not be able to survive due to lack of a food source. The oxygen that we breathe is produced during photosynthesis. If photosynthesis did not happen, we would all die due to a lack of oxygen.
6. We already know that plants can synthesize carbohydrates. How do plants synthesize proteins and vitamins?
Answer:
Proteins containnitrogen and therefore plants need nitrogen to synthesize them. Although plants cannot absorb gaseous nitrogen from the air, a bacterium called Rhizobium converts gaseous nitrogen into a usable form and releases them into the soil. These are then absorbed by the plants along with water and used to synthesize proteins and vitamins.
7. How do plants which do not contain chlorophyll prepare their food?
Answer:
Plants which do not contain chlorophyll and cannot perform photosynthesis obtain their nutrition from other plants (known as the host) using heterotrophic mode of nutrition. These plants are known as parasites. Cuscuta is an example of such a plant.
8. Are humans and animals parasites?
Answer:
No humans and animals are not parasites. Parasites live on the host and get their nutrition from the host. Humans and animals eat plant and animal products separately. Therefore, they cannot be called parasites.
9. Name some places where fungi commonly grow.
Answer:
Fungi grow in moist and warm places. It can grow on moist bread kept in a warm place. They also grow on pickles, leather, clothes etc which are left in hot and humid weather for a long time
10. Do fungi cause diseases?
Answer:
There are some fungi which cause diseases in plants and animals and even humans. Two common diseases cause by fungi in humans are athlete’s foot and jock itch.
11. What is different between heterotrophic nutrition and symbiosis?
Answer:
In heterotrophic nutrition one organism derives its nutrition from the host and not vice versa. In symbiosis, organisms live together and share both shelter and nutrients. It is a two-way relationship. For example, the roots of plants contain certain fungi and both supply nutrients to each other.
12. What is nutrition?
Answer:
The mode of taking food by an organism and its subsequent utilisation by the body to carry our life processes is called nutrition.
(C) Long Answer Type Questions:
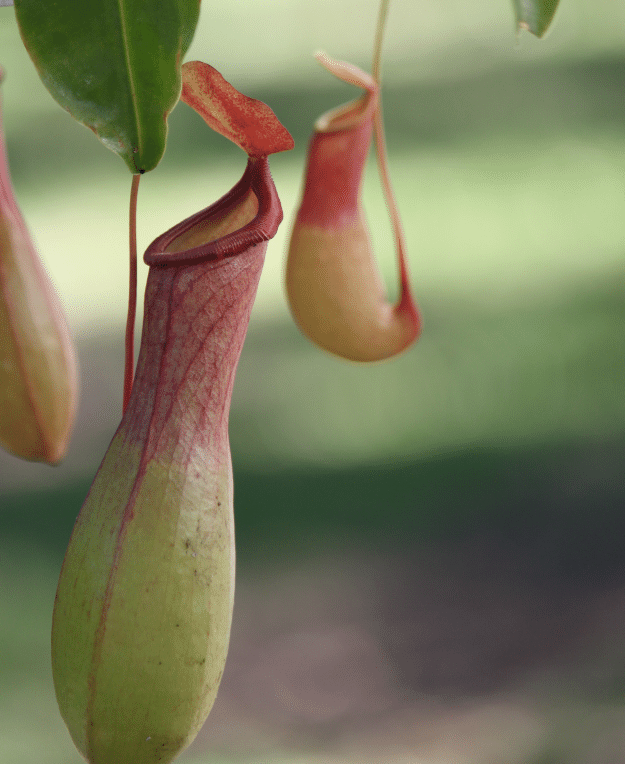
1. How does a pitcher plant trap and consume insects?
Answer:
The pitcher plant has the following characteristics to trap insects:
(i) The leaf of the pitcher plant is modified into a pitcher like or jug-like structure. The apex of the leaf forms a lid which can open or close the mouth of the pitcher as necessary.
(ii) The inside contains hair which are directed downwards to help trap insects.
(iii) When an insect lands in the pitcher, it gets trapped in the downward pointing hairs and the lid closes to prevent it from escaping.
(iv) The digestive juices secreted inside the pitcher helps to digest the insect and absorb the nutrients.

2. Why do farmers spread manure or fertilisers in the fields?
Answer:
Farmers must regularly spread manure or fertilisers in the fields because:
(i) Crop plants absorb a lot of nitrogen and minerals from the soil which depletes the amount of nitrogen and minerals in the soil.
(ii) Plants cannot absorb nitrogen from the air, so it must take in nitrogen and minerals from the soil.
(iii) Fertilisers and manures contain nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus etc.
(iv) These nutrients must be added to the soil regularly to enrich the soil and keep the plants healthy.
3. Why can farmers reduce the use of nitrogenous fertilisers where leguminous plants are grown?
Answer:
Leguminous plants do not need a lot of nitrogenous fertilisers because:
(i) The bacterium Rhizobium lives in the roots of leguminous plants such as grams, peas, moong, beans etc.
(ii) Rhizobium converts atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form.
(iii) In return the plants provide food and shelter to the Rhizobium.
(iv) Thereby the plants and the Rhizobium keep sustaining each other in a symbiotic relationship.
(v) Hence, the use of external nitrogen containing fertilisers can be reduced as the plants also get its supply of nitrogen from the atmosphere through Rhizobium.
(D) Fill in the Blanks:
cells, parasite, medicines, carnivores, starch
(a) _________ is a carbohydrate.
(b) Cuscuta is called a _________.
(c) Fungi cause harmful diseases, but can also be used as _________.
(d) The bodies of living organisms are made up of tiny units called _________.
(e) Insectivorous plants can also be called _________.
Answers:
(a) Starch is a carbohydrate.
(b) Cuscuta is called a parasite.
(c) Fungi cause harmful diseases, but can also be used as medicines.
(d) The bodies of living organisms are made up of tiny units called cells.
(e) Insectivorous plants can also be called carnivores.
(E) Match and pair:
| Column A | Column B |
| Desert plants | Symbiosis between alga and fungus. |
| Fungi | Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen |
| Mushrooms | Photosynthesis happens in stem. |
| Lichens | Saprotrophs |
| Carbohydrates | Fluffy umbrella-like patches |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column A | Column B |
| Desert plants | Photosynthesis happens in stem. |
| Fungi | Saprotrophs |
| Mushrooms | Fluffy umbrella-like patches |
| Lichens | Symbiosis between alga and fungus. |
| Carbohydrates | Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants:
We have experienced scientists on staff who have taken care to explain the concepts to you logically and in an easy-to understand manner. Plenty of additional questions have been provided which cover the chapter in detail and which are similar to exam questions, to help you prepare.
You can also download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime you please! We will keep providing you with plenty of top-quality study material and resources to help you prepare. So, make sure you keep visiting our website and join our email list to take advantage of them!
The following topics are covered:
1.1 – Mode of Nutrition in Plants
1.2 – Photosynthesis – Food Making Process in Plants
1.3 – Other Modes of Nutrition in Plants
1.4 – Saprotrophs
1.5 – How Nutrients are Replenished in the Soil
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 4 Short Answer Questions (Questions 1 – 4)
(ii) 1 Diagram-based Question (Question 5)
(iii) 1 Fill in the Blanks Question (Question 6)
(iv) 1 Name the Following Question (Question 7)
(v) 1 Tick the Correct Answer Question (Question 8)
(vi) 1 Match and Pair Question (Question 9)
(vii) 1 True/False type Question (Question 10)
(viii) 2 Choose the Correct Option Question (Questions 11, 12)
(ix) 1 Long Answer Question (Question 13)
Yes, we have provided a free PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants for you to download! We have also included many formats of additional questions in the PDF which cover the chapter in detail and will give you good practise! Please look towards the top of the page!
Start by understanding how plants prepare food and how the food cycle works. Then study the other modes of nutrition in plants and learn to tell the differences between them. Understand how the different processes work, instead of just memorising the facts. This will help you retain the concepts and easily answer different kinds of questions.
If you study the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants well and practise the additional questions, you will be well prepared for your exams. Study the figures we have included in the solutions materials carefully. This will help you learn and retain the concepts better.
Anytime you need additional coaching beyond what we have provided here – we will be there for you! In addition to top-quality teaching, we provide expert mentoring at no extra cost. Contact us anytime and let us help you out!
Need us to teach you from scratch? Need exam preparation? What about academic and career mentoring? Our expert teacher-mentors provide you will all of this in one complete package at no extra cost. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs- have it completely your way! Reach out to us anytime and let us help you out! Book an appointment now!


