Hello students and welcome to the chapter on Light! We have provided detailed solutions to all Chapter 11 exercise questions, extended learning activities, in-text questions, activities along with extra questions of many formats all in one place. We have also included excellent images which will further help you visualize and understand the concepts. Good luck!
Solutions to Exercises (Page No 138) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light:
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ____________.
(b) Image formed by a convex __________ is always virtual and smaller in size.
(c) An image formed by a __________ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
(d) An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a _________ image.
(e) An image formed by a concave ___________ cannot be obtained on a screen.
Answers:
(a) An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called virtual.
(b) Image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual and smaller in size.
(c) An image formed by a plane mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
(d) An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a real image.
(e) An image formed by a concave lens cannot be obtained on a screen.
2. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a) We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror. (T/F)
(b) A concave lens always forms a virtual image. (T/F)
(c) We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror. (T/F)
(d) A real image cannot be obtained on a screen. (T/F)
(e) A concave mirror always forms a real image. (T/F)
Answers:
(a) We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror. (T/F)
False. The image obtained by a convex mirror is virtual, erect and diminished in size.
(b) A concave lens always forms a virtual image. (T/F)
True. A concave lens always forms a virtual image no matter where the object is located with respect to the lens. You will see that for a convex lens the image cannot be projected onto a screen, it can only be seen through the lens. This proves that the image is virtual.
(c) We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror. (T/F)
True. A concave mirror can form a real, enlarged and inverted image depending on the position of the object with respect to the concave mirror.
(d) A real image cannot be obtained on a screen. (T/F)
False. The image is called real if it can be obtained on a screen.
(e) A concave mirror always forms a real image. (T/F)
False. A concave mirror can form both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object with respect to the concave mirror.
3. Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) A plane mirror | (i) Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) A convex mirror | (ii) Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) A convex lens | (iii) Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) A concave mirror | (iv) The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) A concave lens | (v) The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) A plane mirror | (v) The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (b) A convex mirror | (ii) Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) A convex lens | (i) Used as a magnifying glass |
| (d) A concave mirror | (iii) Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (e) A concave lens | (vi) The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
4. State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Answer:
The characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror is that it is virtual, erect and of the same size as that of the object. The image is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. Lastly, the image is laterally inverted, that is left and right are flipped in the image.
5. Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in which the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings.
Answer:
The letters A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X and Y in the English alphabet form images in a plane mirror which are exactly like the letters themselves. Each letter is symmetric about a vertical line of symmetry drawn through the middle and hence remains the same after lateral inversion.
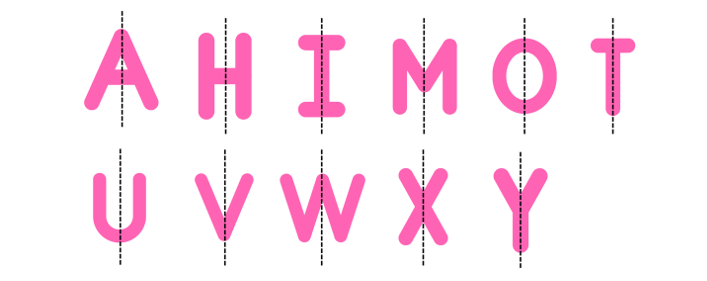
6. What is a virtual image? Give one situation where a virtual image is formed.
Answer:
A virtual image is an image that cannot be projected onto a screen. One situation where a virtual image is formed is in convex mirrors which are used as side mirrors in automobiles. They form diminished virtual images of objects spread over a large area, enabling the driver to see objects behind him properly.
7. State two differences between a convex and a concave lens.
Answer:
A convex lens can form real and virtual images depending on the distance between the object and lens while a concave lens forms only virtual images. A convex lens can form magnified image depending on the distance between the object and lens while a concave lens only forms diminished image.
8. Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Answer:
One use of a concave mirror is that they are used by dentists to see enlarged images of teeth. One use of a convex mirror is that they are used as side mirrors in automobiles because they form diminished images of objects spread over a large area. Thus the driver can see objects behind him.
9. Which type of mirror can form a real image?
Answer:
A concave mirror is capable of forming a real image. Convex and plane mirrors can only form virtual images.
10. Which type of lens always forms a virtual image?
Answer:
Concave lens always forms a virtual image.
Choose the correct option in questions 11–13.
11. A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a
(i) concave lens (ii) concave mirror
(iii) convex mirror (iv) plane mirror
Answer: (ii) concave mirror can produce a virtual image larger than the object.
12. David is observing his image in a plane mirror. The distance between the mirror and his image is 4 m. If he moves 1 m towards the mirror, then the distance between David and his image will be
(i) 3 m (ii) 5 m
(iii) 6 m (iv) 8 m
Answer: (iii) 6 m.
Initially object distance = image distance = 4 m. If he moves 1 m towards the mirror, the new object distance = image distance = (4 – 1) m = 3 m. Therefore, the total distance between David and his image = (image distance + object distance) = (3 + 3) m = 6 m.
Summary: David is observing his image in a plane mirror. The distance between the mirror and his image is 4 m. If he moves 1 m towards the mirror, the total distance between David and his image = 6 m.
13. The rear view mirror of a car is a plane mirror. A driver is reversing his car at a speed of 2 m/s. The driver sees in his rearview mirror the image of a truck parked behind his car. The speed at which the image of the truck appears to approach the driver will be
(i) 1 m/s (ii) 2 m/s
(iii) 4 m/s (iv) 8 m/s
Answer: (iii) 4 m/s
The car is being reversed at a speed of 2 m/s. The image of the truck in the mirror will travel twice the distance travelled by the car in the same time. Therefore, the speed of the image of the truck = 2 × 2 = 4 m/s.
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 139) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light:
1. Play with a mirror. Write your name with a sketch pen on a thin sheet of paper, polythene or glass. Read your name on the sheet while standing in front of a plane mirror. Now look at your image in the mirror.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 1
2. A burning candle in water. Take a shoe box, open on one side. Place a small lighted candle in it. Place a clear glass sheet (roughly 25 cm × 25 cm) in front of this candle (Fig. 11.33). Try to locate the image of the candle behind the glass sheet. Place a glass of water at its position. Ask your friends to look at the image of the candle through the sheet of glass. Ensure that candle is not visible to your friends. Your friends will be surprised to see the candle burning in water. Try to explain the reason.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 2
3. Make a rainbow. Try to make your own rainbow. You can try this project in the morning or in the evening. Stand with your back towards the Sun. Take a hosepipe or a water pipe used in the garden. Make a fine spray in front of you. You can see different colours of rainbow in the spray.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 3
4. View a laughing gallery in some science centre or a science park or a village mela. You will find some large mirrors there. You can see your distorted and funny images in these mirrors. Try to find out the kinds of mirrors used there.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 4
5. Visit a nearby hospital. You can also visit the clinic of an ENT specialist, or a dentist. Request the doctor to show you the mirrors used for examining ear, nose, throat and teeth. Can you recognise the kind of mirror used in these instruments?
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 5
6. Role play. Here is a game that a group of children can play. One child will be chosen to act as the object and another will act as the image of the object. The object and the image will sit opposite to each other. The object will make movements, such as raising a hand, touching an ear etc. The image will have to make the correct movement following the movement of the object. The rest of the group will watch the movements of the image. If the image fails to make the correct movement, she/he will be retired. Another child will take her/his place and the game will continue. A scoring scheme can be introduced. The group that scores the maximum will be declared the winner.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 6
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light:
1. (Page 123) You may have also seen beams of light from the headlamps of scooters, cars and engines of trains. Similarly, a beam of light can be seen from a torch. Some of you may have seen a bream of searchlight from a light house or from an airport tower. What do these experiences suggest?
Answer:
These experiences suggest that light travels in a straight line. You will notice that the beams of light from headlamps of scooters, cars, engines of trains, a torch, the searchlight of a light house and an airport tower are all straight. This means that the light emitted travels in straight lines.
2. (Page 123) Boojho recalls an activity he performed in Class VI. In that activity he looked at a lighted candle first through a straight pipe and then through a bent pipe. Why was Boojho not able to see the candle flame through a bent pipe?
Answer:
Boojho was not able to see the candle flame through a bent pipe because the light from the flame travels in straight lines. The light could not travel through the pipe since it was bent in the middle and hence could not reach Boojho’s eyes.
3. (Page 124) How can we change the path of light?
Answer:
We can change the path of light by letting it fall on a shiny or polished surface which acts as a mirror. For example, a shining stainless steel plate, a shining steel spoon and even the surface of water can change the direction of light.
4. (Page 124) What happens when light falls on a mirror?
Answer:
When light falls on a mirror it gets reflected and changes direction. Since light travels in straight lines the reflected light also travels in straight lines.
5. (Page 125) Paheli wants to know, what makes things visible to us? Boojho thinks that objects are visible only when light reflected from them reaches our eyes. Do you agree with him?
Answer:
Yes, Boojho is right. Objects are visible to us because the light reflected from them reaches our eyes. The brain then processes the information and forms the images that we see.
6. (Page 126) Boojho noted in this notebook: Is it not surprising that my image is of the same size as me whether the mirror is small or large?
Answer:
Yes, the image formed by a plane mirror is of the same size as the object regardless of the size of the mirror. The plane mirror has a flat, smooth surface and hence light reflects from it in a manner which causes no change in the size of the image.
7. (Page 127) Boojho saw an ambulance on the road. He was surprised to see that the word ‘AMBULANCE’ in front was written in a strange manner.
Answer:
The laterally inverted version of the word ‘AMBULANCE’ was deliberately written in front. This enables drivers in front of the ambulance to read the correct version of the word as reflected by the rearview mirror. They would then allow the ambulance to pass freely.
8. (Page 131) Boojho observed his image in the shiny surface of the bell on his new bicycle. He found that his image was erect and smaller in size. He wondered if the bell is also a kind of spherical mirror. Can you recognise the type of mirror?
Answer:
The mirror is a convex mirror. We know this because it forms an image which is erect and smaller in size than the object.
9. (Page 135) Paheli asks: Does this mean that the white light consists of seven colours?
Answer:
Yes,white light consists of the seven colours red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. This is evident because a glass prism splits a narrow beam of sunlight (or white light) into those seven colours. You can even see the seven colours on soap bubbles and Compacts Discs.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light:
1. Complete Activity 11.1 (Page 124). Take a torch. Cover its glass with a chart paper which has three narrow slits as shown in Fig. 11.5. Spread a sheet of chart paper on a smooth wooden board. Fix a plane mirror strip vertically on the chart paper (Fig. 11.5). Now direct the beam of light on the mirror from the torch with slits. Place the torch in such a way that its light is seen along the chart paper on the board. Now adjust its position so that the light from the torch strikes the plane mirror at an angle (Fig. 11.5). Does the mirror change the direction of light that falls on it? Now move the torch slightly to either side. Do you find any change in the direction of reflected light?
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 11.2 (Page 125). Place a lighted candle in front of a plane mirror. Try to see the flame of the candle in the mirror. It appears as if a similar candle is placed behind the mirror. Now move the candle to different positions in front of the mirror. Observe the image in each case. Was the image upright in each case? Did the flame appear on top of the candle as in the object? Now place a vertical screen behind the mirror. Can you get the image on the screen? Now place the screen in front of the mirror. Can you get the image on the screen now?
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 11.3 (Page 126). Take a chess board. If a chess board is not available, draw on a chart paper 64 (8 × 8) squares of equal size. Draw a thick line in the middle of the paper. Fix a plane mirror vertically on this line. Place any small object, such as a pencil sharpener, at the boundary of the third square counting from the mirror. Note the position of the image. Now shift the object to the boundary of the fourth square. Again note the position of the image. Did you find any relation between the distance of the image from the mirror and that of the object in front of it
Answer:
4. Complete Activity 11.4 (Page 127). Stand in front of a plane mirror and look at your image. Raise your left hand. Which hand does your image raise? Now touch your right ear. Which ear does your hand touch in your image? Observe carefully. Now write down your name on a piece of paper and hold it in front of a plane mirror. How does it appear in the mirror?
Answer:
5. Complete Activity 11.5 (Page 128). Take a stainless steel spoon. Bring the outer side of the spoon near your face and look into it. Do you see your image in it? Is this image different from what you see in a plane mirror? Is this image erect? Is the size of the image the same, smaller or larger? Now look at your image using the inner side of the spoon. Make the necessary conclusions.
Answer:
6. Complete Activity 11.6 (Page 129). Take a concave mirror. Hold it facing the Sun. Try to get the light reflected by the mirror on a sheet of paper. Adjust the distance of the paper until you get a sharp bright spot on it. Hold the mirror and the sheet of paper steady for a few minutes. Does the paper start burning? Make the necessary conclusions.
Answer:
7. Complete Activity 11.7 (Page 129). Fix a concave mirror on a stand (any arrangement to keep the mirror steady would do) and place it on a table. Paste a piece of white paper on a cardboard sheet (say about 15 cm × 10 cm). This will act as a screen. Keep a lighted candle on the table at a distance of about 50 cm from the mirror. Try to obtain the image of the flame on the screen. For this, move the screen till a sharp image of the flame is obtained. Make sure that, the screen does not obstruct the light from the candle falling on the mirror. Is this image real or virtual? Is it of the same size as the flame? Now move the candle towards the mirror and place it at different distances from it. In each case try to obtain the image on the screen. Record your observation in Table 11.1. Is it possible to obtain the image on the screen when the candle is too close to the mirror?
Answer:
8. Complete Activity 11.8 (Page 131). Repeat Activity 11.7 now with a convex mirror in place of a concave mirror. Record your observations in a Table similar to Table 11.1
Answer:
9. Complete Activity 11.9 (Page 133). Take a convex lens or magnifying glass. Put it in the path of sunrays. Place a sheet of paper as shown. Adjust the distance between the lens and the paper till you get a bright spot on the paper. Hold the lens and the paper in this position for a few minutes. Does the paper begin to burn?
Now replace the convex lens with a concave lens. Do you see a bright spot on the paper this time too? Why are you now getting a bright spot this time?
Answer:
10. Complete Activity 11.10 (Page 133). Take a convex lens and fix it on a stand as you did with the concave mirror. Place it on a table. Place a lighted candle at a distance of about 50 cm from the lens. Try to obtain the image of the candle on a paper screen placed on the other side of the lens. You may have to move the screen towards or away from the lens to get a sharp image of the flame. What kind of image did you get? Is it real or virtual? Now vary the distance of the candle from the lens. Try to obtain the image of the candle flame every time on the paper screen by moving it. Record your observations as you did in Activity 11.7 for the concave mirror. Did you get in any position of the object an image which was erect and magnified? Could this image be obtained on a screen? Is the image real or virtual?
In a similar fashion study the images formed by a concave lens. You will find that the image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size than the object.
Answer:
11. Complete Activity 11.11 (Page 135). Take a glass prism. Allow narrow beam of sunlight through a small hole in the window of a dark room to fall on one face of the prism. Let the light coming out of the other face of the prism fall on a white sheet of paper or on a white wall. What do you observe? Do you see colours similar to those in a rainbow? Try to identify these colours and write their names in your notebook. Make the necessary conclusions.
Answer:
12. Complete Activity 11.12 (Page 136). Take a circular cardboard disc of about 10 cm diameter. Divide this disc into seven segments. Paint the seven rainbow colours on these segments as shown in Fig. 11.31 (a). You can also paste, coloured papers on these segments. Make a small hole at the centre of the disc. Fix the disc loosely on the tip of a refill of a ball pen. Ensure that the disc rotates freely [Fig. 11.31 (a)]. Rotate the disc in the daylight. When the disc is rotated fast, the colours get mixed together and the disc appears to be whitish [Fig. 11.31 (b)]. Such a disc is popularly known as Newton’s disc.
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light:
Very short answer type questions:
1. How do the sun’s rays reach our eyes?
Answer:
The sun’s rays pass through vacuum of space and then the Earth’s atmosphere in straight lines to reach our eyes.
2. Name a liquid that can behave like a mirror.
Answer:
Water is a liquid that can behave like a mirror.
3. Can a plane mirror form real images?
Answer:
No, a plane mirror forms only virtual images.
4. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. Identify the nature of the lens. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
The lens is a concave lens.
5. If we hold a candle on a front of a mirror and turn the bottom towards the left, which way will the bottom of the image turn?
Answer:
The bottom of the image will turn to the right because of the lateral inversion property of a plane mirror.
6. Name the mirror and the lens which forms an enlarged image of the object.
Answer:
Theconcave mirror and convex lens forms an enlarged image of the object.
7. Which type of mirror Is used in a torch?
Answer:
Torch mirror is used as a concave mirror.
8. Which mirror and lens form inverted images?
Answer:
Concave mirror and convex lens can form inverted images.
9. Which mirror can form images of objects spread over a large area?
Answer:
A convex mirror can form images of objects spread over a large area.
10. Which lens can form an erect and enlarged image of an object on a screen?
Answer:
The convex lens can form an erect and enlarged image of an object on a screen, depending on the distance of the object relative to the lens.
11. Which mirrors always distort images?
Answer:
The curved mirrors in a funny house using concave and convex sections form distorted images.
12. What will be the size of your image in a hand mirror?
Answer:
The hand mirror is a plane mirror so the size of your image will be the same as your actual size.
Short answer type questions:
1. When light falls on a mirror it gets reflected. So is it right to say that light travels in straight lines?
Answer:
Yes, it is right to say that light travels in straight lines because the incoming light rays travel in straight lines and even after reflection from the mirror it travels in straight lines. Only the direction in which light travels after reflection changes.
2. When can we not see an object?
Answer:
We cannot see an object in darkness. We see an object when the light reflected by it reaches our eyes. In a dark room there is no light and so we cannot see anything.
3. Name some surfaces which do not reflect light.
Answer:
Surfaces which are uneven or rough such as paper and wood do not reflect light. Surfaces which are black in colour also do not reflect any light.
4. If a mirror is broken will you still see your reflection?
Answer:
Yes, if the mirror shatters into many pieces you will see still reflections on each piece because each individual piece is flat. However, you will see something different on each piece. This is because each piece is angled differently and so light is reflected back to you in many different directions.
5. Name two factors that the type of image formed by spherical mirrors depend on.
Answer:
The type of image formed by spherical mirrors depends on:
- Type of spherical mirror: convex or concave.
- Position of the object relative to the mirror.
6. Which spherical mirror gives images which are erect and of the same size?
Answer:
No spherical mirror gives images which are erect and of the same size as the object. Only a plane mirror forms images like that.
7. A beam of light is reflected almost horizontally from the surface of a plane mirror. What can you say about the incoming light beam?
Answer:
The almost horizontal direction of the reflected light beam indicates that the incoming light beam was also almost horizontal. Place mirrors ensure that there is symmetry between the incoming and reflected light rays.
8. Look at the image formed on the sheet of paper which is being held to the ground below. What can you say about the lens used to form the image?
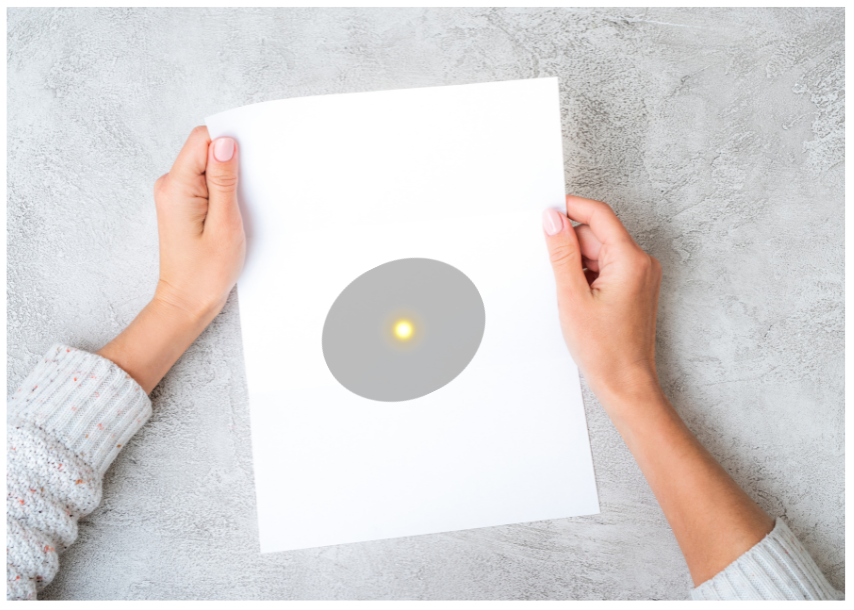

Answer:
The bright spot in the image formed is actually a small image of the Sun and is surrounded by the grey shadow of the lens. Hence, we can conclude that the image has been formed by a converging convex lens held in the path of sunrays.
Long Answer Type Questions:
1. Name the main differences between convex and concave mirrors.
Answer: The main differences between convex and concave mirrors are:
| Convex Mirror | Concave Mirror |
| (i) Convex mirrors have an outward curved reflective surface. | (i) Concave mirrors have an inward curved reflective surface. |
| (ii) Convex mirrors reflect light outwards and are called ‘diverging’ mirrors. | (ii) Concave mirrors reflect light inwards and are called ‘converging’ mirrors. |
| (iii) Convex mirrors always form virtual images, regardless on the object’s distance from it. | (iii) Concave mirrors form both real and virtual images, depending on the object’s distance from it. |
| (iv) Convex mirrors always form erect images, regardless of the object’s distance from it. | (iv) Concave mirrors can form erect or inverted images, depending on the object’s distance from it. |
| (v) Convex mirrors always form diminished images, regardless of the object’s distance from it. | (v) Concave mirrors form images which can be both smaller or larger than the object, depending on the object’s distance from it. |
| (vi) Convex mirrors can form images of objects spread over a large area. | (vi) Concave mirrors have a narrower field of view but the images can be larger and more magnified. |
| (vii) Used as sideview mirrors in vehicles to observe objects located behind over a large area. | (vii) Used by dentists and ENT doctors to view enlarged images of teeth and ear, nose, throat. |
2. You are given three mirrors of different types. How will you identify each one of them? (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer: We can identify the three mirrors using the characteristics of the images formed by them:
Plane mirror: If the image formed by the mirror is virtual, erect, of the same size as the object and the same distance away from the mirror then it is a plane mirror.
Convex Mirror: If the images formed by a convex mirror are always virtual, erect and diminished regardless of the object’s distance from it, then it is a convex mirror.
Concave Mirror: If the image formed when the object is placed very close to mirror is virtual and erect and the image formed when the object is moved further away from the mirror is real and inverted, then it is called a concave mirror.
Fill in the Blanks:
convex, inverted, seven, lens, concave
(a) An ENT head mirror is always ___________ in nature.
(b) A magnifying glass is actually a type of ___________.
(c) A ___________ lens is a converging lens.
(d) A prism can separate light into its ___________ different colours.
(e) Convex and plant mirrors cannot form ___________ images of objects.
Answers:
(a) An ENT head mirror is always concave in nature.
(b) A magnifying glass is actually a type of lens.
(c) A convex lens is a converging lens.
(d) A prism can separate light into its seven different colours.
(e) Convex and plane mirrors cannot form inverted images of objects.
Match and Pair:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Compact Disc | (i) Change in direction |
| (b) Reflection of light | (ii) Object and image distances from the mirror are equal |
| (c) Convex mirror | (iii) Burnt ships using mirrors |
| (d) Archimedes | (iv) Colours of rainbow |
| (e) Plane mirror | (v) Virtual image |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Compact Disc | (iv) Colours of rainbow |
| (b) Reflection of light | (i) Change in direction |
| (c) Convex mirror | (v) Virtual image |
| (d) Archimedes | (iii) Burnt ships using mirrors |
| (e) Plane mirror | (ii) Object and image distances from the mirror are equal |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light:
Light can be a confusing chapter to beginners. Our expert team of Indian and foreign-educated teachers, engineers and scientists have taken care to present the material such that all details are covered and all your questions are answered. All the exercise questions, extended learning activities, in-text questions, activities and the self-designed extra questions have been accurately answered and attractive images have been included wherever possible to help clear your concepts. We advise you to look at the images properly while studying the material to extract maximum benefit.
Also feel free to download the free PDFs of the solutions anytime! Did you find our study material helpful? We will be providing you with plenty more study material and other resources to help you prepare. So keep visiting our website and subscribe to our email list with one click to be among the first to receive the free goodies!
The following topics are covered:
11.1 – Light Travels Along a Straight Line
11.2 – Reflection of Light
11.3 – Right or Left!
11.4 – Playing With Spherical Mirrors
11.5 – Images Formed By Lenses
11.6 – Sunlight – White or Coloured?
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 1 Fill in the Blanks Type Question (Question 1)
(ii) 1 True/False Type Question (Question 2)
(iii) 1 Match and Pair Type Question (Question 3)
(iv) Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 4 – 10)
(v) 3 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (Questions 11 – 13)
The key is to understand and remember how images are formed by plane and spherical mirrors, and convex and concave lenses. For this purpose we recommend that you study this material thoroughly and pay attention to every single detail. All the different cases have been explained in various different ways and excellent figures have been included which will further clear your concepts and help in retention.
If you need additional help, we are there for you! Our expert teachers believe in a structured and rigorous approach to training and will prepare you to succeed in any exam. Feel free to contact us anytime with your requirements and let us help you out! (Insert hyperlink)
We understand that every student’s preparation needs are unique and our methods ensure that your unique needs are met every step of the way. Our expert teachers will only train you but also mentor you and help you discover your inherent talents, which will be of tremendous help to you.
We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs – have it completely your way! Contact us with your anytime requirements and let us help you out! Book any number of appointments now!


