Welcome students! Feel free to go through our solutions material to NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals where we have answered all textbook exercise questions, extended learning – activities and projects, in-text questions and in-text activities. We have also included extra questions of many formats to further bolster your preparation. Attractive figures have also been included which will help you learn visually.
Solutions to Exercise (Page No 20) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals:
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The main steps of nutrition in humans are _________, __________, __________, _________ and __________.
(b) The largest gland in the human body is __________.
(c) The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and ___________ juices which act on food.
(d) The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger-like outgrowths called _________.
(e) Amoeba digests its food in the ____________.
Answers:
(a) The main steps of nutrition in humans are ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion.
(b) The largest gland in the human body is liver.
(c) The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and digestive juices which act on food.
(d) The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger-like outgrowths called villi.
(e) Amoeba digests its food in the food vacuole.
2. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a) Digestion of starch starts in the stomach. (T/F)
(b) The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. (T/F)
(c) The gall bladder temporarily stores bile. (T/F)
(d) The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time. (T/F)
Answers:
(a) Digestion of starch starts in the stomach. (T/F)
False. Digestion of starch starts in the mouth. Saliva helps to break down carbohydrates like starch into simpler units which helps in digestion.
(b) The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. (T/F)
True. The muscular organ tongue present inside the buccal cavity moves the food around and mixes it with saliva while chewing.
(c) The gall bladder temporarily stores bile. (T/F)
True. Bile juice is secreted by the liver and temporarily stored in the sac-shaped gall bladder.
(d) The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time. (T/F)
True. Ruminants swallow grass and store it in the stomach where it gets partially digested. Later this partially digested grass returns to the mouth and the ruminant chews it for some time.
3. Tick (✓) mark the correct answer in each of the following:
(a) Fat is completely digested in the
(i) stomach (ii) mouth (iii) small intestine (iv) large intestine
(b) Water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the
(i) stomach (ii) food pipe (iii) small intestine (iv) large intestine
Answers:
(a) Fat is completely digested in the (iii) small intestine.
(b)Water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the (iv) large intestine.
4. Match the items of Column I with those given in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| Food components | Product(s) of digestion |
| Carbohydrates | Fatty acids and glycerol |
| Proteins | Sugar |
| Fats | Amino acids |
Answer: The correct table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| Food components | Product(s) of digestion |
| Carbohydrates | Sugar |
| Proteins | Amino acids |
| Fats | Fatty acids and glycerol |
5. What are villi? What is their location and function?
Answer:
Villi are tiny finger-like outgrowths present along the inner walls of the small intestine of the human body. The villi provide increased surface area for the absorption of digested food by blood vessels close to the surface.
6. Where is the bile produced? Which component of the food does it help to digest?
Answer:
Bile is produced in the liver which is a reddish-brown gland situated in the upper right part of the abdomen. It helps to digest fats.
7. Name the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Give the reason also.
Answer:
Cellulose is the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. The cellulose is stored in the part of the stomach called the rumen. The rumen contains certain bacteria which digest cellulose. Humans do not contain bacteria and therefore cannot digest cellulose.
8. Why do we get instant energy from glucose?
Answer:
We get instant energy from glucose because it is the simplest sugar and is easily absorbed into the bloodstream. Complex carbohydrates first need to be broken down into glucose for absorption to take place. However, glucose gets absorbed directly and we thus get instant energy from it.
9. Which part of the digestive canal is involved in:
(i) absorption of food ________________.
(ii) chewing of food ________________.
(iii) killing of bacteria ________________.
(iv) complete digestion of food ________________.
(v) formation of faeces ________________.
Answers:
(i) absorption of food Small intestine.
(ii) chewing of food Buccal cavity.
(iii) killing of bacteria Stomach.
(iv) complete digestion of food Small intestine.
(v) formation of faeces Large intestine.
10. Write one similarity and one difference between nutrition in amoeba and human beings.
Answer:
Similarity between nutrition in amoeba and human beings is that both human beings and amoeba digest food using digestive juices.
Difference between nutrition in amoeba and human beings is that human beings ingest food using the buccal cavity, but amoeba takes in food by engulfing it with pseudopodia and false feet.
11. Match the items of Column I with suitable items in Column II
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Salivary gland | (i) Bile juice secretion |
| (b) Stomach | (ii) Storage of undigested food |
| (c) Liver | (iii) Saliva secretion |
| (d) Rectum | (iv) Acid release |
| (e) Small intestine | (v) Digestion is completed |
| (f) Large intestine | (vi) Absorption of water |
| (vii) Release of faeces |
Answer:
The completed table is shown below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Salivary gland | (iii) Saliva secretion |
| (b) Stomach | (iv) Acid release |
| (c) Liver | (i) Bile juice secretion |
| (d) Rectum | (ii) Storage of undigested food |
| (e) Small intestine | (v) Digestion is completed |
| (f) Large intestine | (vi) Absorption of water |
12. Label Fig. 2.11 of the digestive system.
Answer:
Find the labelled diagram below:
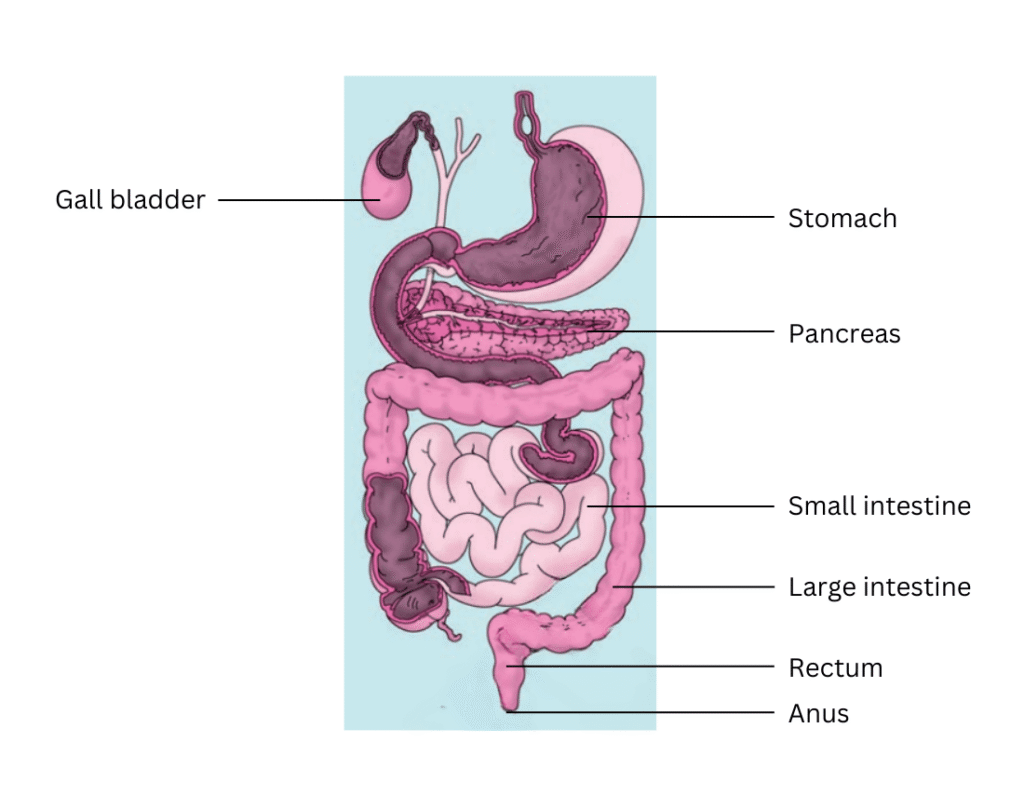
13. Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass? Discuss.
Answer:
We cannot survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass because they are rich in cellulose and the stomach of humans are not able to digest it. Also, raw, leafy vegetables/grass do not provide us with essential carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Thus, we cannot have a balanced diet.
Solutions to Extended Learning – Activities and Projects (Page No 22) of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals:
1. Visit a doctor and find out:
(i) Under what conditions does a patient need to be on a drip of glucose?
(ii) Till when does a patient need to be given glucose?
(iii) How does glucose help the patient recover? Write the answers in your notebook.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 1
2. Find out what vitamins are and get the following information.
(i) Why are vitamins necessary in the diet?
(ii) Which fruits or vegetables should be eaten regularly to get vitamins?
Write a one-page note on the information collected by you. You may take help of a doctor, a dietician, your teacher or any other person, or from any other source.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 2
3. Collect data from your friends, neighbours and classmates to know more about “milk teeth”. Tabulate your data. One way of doing it is given below:
| S. No | Age at which first tooth fell | Age at which last tooth fell | No. of tooth lost | No of tooth replaced. |
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
| 4. | ||||
| 5. |
Find out from at least twenty children and find the average age at which children lose the milk teeth. You may take help of your friends.
Answer:
Solution to Extended Learning Problem 3
Solutions to In Text Questions of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals –
1. (Page 13) Boojho is fascinated by the highly coiled small intestine seen in Fig. 2.2. He wants to know its length. Would you like to make a wild guess? We have given its approximate length on page 16. Just imagine how such a long structure is accommodated in a small space within our body!
Answer:
The small intestine is highly coiled and is about 7.5 metres long. Such a long structure is accommodated in a small space within our body due to its high coiled nature.
2. (Page 15) Paheli wants to know how food moves in the opposite direction during vomiting.
Answer:
Food moves in the opposite direction during vomiting due to the movement of the walls of the oesophagus. When food in not accepted by the stomach, the stomach repels it causing a movement in the oesophagus in the reverse direction. This results in vomiting.
3. (Page 18) Paheli wants to know why these animals cannot chew food properly at the time they take it in?
Answer:
These animals cannot chew food properly because they eat grass which contains high amounts of cellulose. Therefore, the food must be converted into a form that is easier to chew. The food is quickly swallowed and partially digested in the rumen and then returns to the mouth so it can be chewed easily.
4. (Page 18) Boojho wants to know why we cannot digest cellulose like the cattle do.
Answer:
We cannot digest cellulose like cattle do because we do not contain special bacteria in our stomach which digest cellulose. Cattle have special bacteria present in the part of the stomach called rumen which can digest cellulose.
Solutions to All Activities of NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals:
1. Complete Activity 2.1 (Page 11). What is the type of food and mode of feeding of the following animals? Write down your observations in the given Table. You may find the list of modes of feeding given below the Table helpful.
Table 2.1 Various modes of feeding
| Name of animal | Kind of food | Mode of feeding |
| Snail | ||
| Ant | ||
| Eagle | ||
| Humming-bird | ||
| Lice | ||
| Mosquito | ||
| Butterfly | ||
| House fly |
(Scraping, chewing, siphoning, capturing and swallowing, sponging, sucking etc.)
Answer:
2. Complete Activity 2.2 (Page 13). Wash your hands. Look into the mirror and count your teeth. Use your index finger to feel the teeth. How many kinds of teeth could you find? Take a piece of an apple or bread and eat it. Which teeth do you use for biting and cutting, and which ones for piercing and tearing? Also find out the ones that are used for chewing and grinding? Record your observations in Table 2.2.
Table 2.2
| Type of Teeth | Number of teeth | Total | |
| Lower jaw | Upper jaw | ||
| Cutting and biting teeth (Incisors) | |||
| Piercing and tearing Teeth (Canines) | |||
| Chewing and grinding teeth (Premolars and molars) | |||
Answer:
3. Complete Activity 2.3 (Page 14). Take two test tubes. Label them ‘A’ and ‘B’. In test tube ‘A’ put one teaspoonful of boiled rice; in test tube ‘B’ keep one teaspoonful of boiled rice after chewing it for 3 to 5 minutes. Add 3–4 mL of water in both the test tubes (Fig. 2.4). Now pour 2–3 drops of iodine solution in each test tube and observe. Why is there a change in colour in the test tubes? Discuss the results with your classmates and your teacher.
Answer:
4. Complete Activity 2.4. (Page 15)
1. Prepare a separate sample each of (i) sugar solution, (ii) common salt solution, (iii) lemon juice and (iv) juice of crushed neem leaf or bitter gourd.
2. Blindfold one of your classmates and ask her/him to take out the tongue and keep it in straight and flat position.
3. Use a clean toothpick to put the above samples one by one on different areas of the tongue as shown in Fig. 2.6. Use a new toothpick for each sample.
4. Ask the classmate which areas of the tongue could detect the sweet, salty, sour and bitter substances.
5. Now write down your observations and label Fig. 2.6. Repeat this activity with other classmates.
Answer:
Extra Questions to Complement Solutions:
(A) Very Short Answer Type Questions:
1. What is another name for the alimentary canal?
Answer:
Another name for the alimentary canal is the digestive tract.
2. What is the process of intake of food called?
Answer:
The process of intake of food is called ingestion.
3. Which one is the widest part of the alimentary canal?
Answer:
The widest part of the alimentary canal is the stomach.
4. What is the length of the small intestine?
Answer:
The small intestine is about 7.5 metres long.
5. Where is the liver located?
Answer:
The liver is located on the upper right part of the abdomen.
6. Where is the stomach located?
Answer:
The stomach is located on the upper left part of the abdomen.
7. Where is the pancreas located?
Answer:
The pancreas is located just below the stomach.
8. Where does absorption take place?
Answer:
Absorption takes place in the small intestine.
9. What kind of food causes tooth decay?
Answer:
Tooth decay is caused by sugary foods such as chocolates, sweets, soft drinks.
10. Name one difference between milk teeth and permanent teeth.
Answer:
Milk teeth are replaceable, permanent teeth are not.
11. Is the number of teeth in children and adults the same?
Answer:
No, children have 28 teeth and adults have 32 teeth.
12. Where does the digestion of food in an amoeba take place?
Answer:
The digestion of food in an amoeba takes place in a food vacuole.
13. Name the simplest carbohydrate.
Answer:
Glucose is the simplest carbohydrate.
(B) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ):
1. The false feet of Amoeba are used for (NCERT Exemplar)
(a) movement only.
(b) capture of food only.
(c) capture of food and movement.
(d) exchange of gases only.
Answer: The false feet of Amoeba are used for (c) capture of food and movement.
2. Which of the following pair of teeth differ in structure but are similar in function? (NCERT Exemplar)
(a) canines and incisors.
(b) molars and premolars.
(c) incisors and molars.
(d) premolars and canines
Answer: (b) molars and premolars differ in structure but are similar in function.
3. Given below from (i) to (iv) are some food items. (NCERT Exemplar)
(i) Boiled and mashed potato
(ii) Glucose solution
(iii) A slice of bread
(iv) Mustard oil
Which of the above will give blue-black colour when tested with iodine?
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer: The right answer is(b) (i) and (iii). Boiled and mashed potatoes and bread contain starch, so they will give blue-black colour when tested with iodine.
4. Choose the odd one out from each group and give reasons. (NCERT Exemplar)
(i) liver, salivary gland, starch, gall bladder
(ii) stomach, liver, pancreas, salivary gland
(iii) tongue, absorption, taste, swallow
(iv) oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine, rectum
Answer: The odd one out is (i) liver, salivary gland, starch, gall bladder. Starch is a component of food while the others are glands and organs.
5. Which of the following does an amoeba does not have?
(i) Cell Membrane
(ii) Nucleus
(iii) Vacuoles
(iv) Stomach
(v) Cytoplasm
Answer: The amoeba does not have a (iv) Stomach.
(C) Short Answer Type Questions:
1. Name the main components of food.
Answer:
Food contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Food also consists of dietary fibres and water.2. Why is digestion important for our body?
Answer:
Digestion helps to break down complex components of food such as carbohydrates into simpler substances, which the body can then absorb and utilise.
3. How does a starfish feed?
Answer:
Starfish feed by opening the shells of animals and extending the stomach through its mouth to eat the soft animal living inside. The stomach then retracts inside the body and the food is slowly digested.
4. What is the action of saliva on food?
Answer:
Saliva helps in mastication to make food soft and breaks down the starch into sugars.
5. Give two examples where food is not taken through the mouth.
Answer:
Food is not taken through the mouth in case of:
(i) Aquatic animals which filter food particles and feed on them.
(ii) The amoeba which uses pseudopodia to surround the food particle and then digests it.
6. Describe the functions of the tongue.
Answer:
The tongue is a fleshy muscular organ in our mouth used for:
(i) Talking
(ii) Mixing saliva with food with helps in mastication and swallowing.
(iii) Tasting food with the help of taste buds.
7. Why is it important to clean your mouth with a toothbrush or datun?
Answer:
If you do not clean mouth many harmful bacteria will start to grow in it. These bacteria break down the sugars present in leftover food particles and release acids. These acids can damage your teeth and cause tooth decay. This can result in extreme pain and even tooth loss. Therefore, it is important to clean your mouth with a toothbrush to remove leftover food particles.
8. What are the different secretions in the stomach and what are their functions?
Answer:
The different secretions in the stomach and their functions are as follows:
(i) The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucous which gives protection to the inner lining.
(ii) The inner lining also secretes hydrochloric acid that kills harmful bacteria in food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic so the digestive juices can act.
(iii) The digestive juices (also secreted from the inner lining) breaks down the proteins into simpler substances.
9. What is assimilation?
Answer:
After absorption by the blood vessels in the small intestine, the absorbed nutrients are carried by the blood vessels to the different organs of the body where they are used to build complex proteins and other essential substances required by the body. This process is called assimilation.
10. Why can diarrhoea be fatal and what can be done to fight it?
Answer:
Diarrhoea is caused by infection or food poisoning and can be fatal if excessive water and salt are lost from the body, thereby causing dehydration. Therefore, we need to replenish the lost water and salt in the patient’s body. This can be done by preparing Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) by dissolving sugar and salt in the right proportion in boiled and cooled water and administering it to the patient.
11. Why should not we inhale suddenly from the mouth while eating?
Answer:
When we swallow food, there is a flap-like valve inside the throat which closes and the food is guided into the foodpipe and prevented from entering the windpipe. When we inhale suddenly through the mouth while eating, the valve might not close in time and food might be sucked into the windpipe. This results in choking.
12. Why is the digestion of fat difficult as compare to the other nutrients?
Answer:
Fat exists as large globules and is insoluble in water. Therefore, they have to be broken down into smaller droplets to make digestion easier.
13. Where is the Caecum located in certain animals? What is its function?
Answer:
The Caecum is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. Certain bacteria present in the Caecum helps to digest cellulose.
(D) Long Answer Type Questions:
1. Briefly describe each part of the alimentary canal and how they help in digestion.
Answer:
The alimentary canal is continuous and food components gradually get digested as it passes through the following parts:
(i) Mouth and Buccal Cavity: The teeth present in the mouth helps to break down the food into small pieces and the saliva helps in mastication and to break down the starch into sugars.
(ii) Foodpipe/oesophagus: The movement of the wall of the foodpipe helps to push the swallowed food downwards into the stomach.
(iii) Stomach: The stomach acids help the digestive juices break down the proteins into simpler substances.
(iv) Small Intestine: The small intestine receives bile and pancreatic juice from the liver and pancreas respectively. These along with the intestinal juice completes the digestion of all food components. The undigested food passes into the large intestine.
(v) Large Intestine: The large intestine absorbs water and some salts from the undigested food material.
(vi) Rectum: The remaining waste is collected in the rectum from the large intestine as faeces.
(vii) Anus: The faeces are ejected from the anus by the process of egestion.
2. Describe the process of how digestion takes place in the small intestine.
Answer:
The small intestine receives bile and pancreatic juice from the liver and the pancreas respectively and also secretes its own intestinal juice.
(i) The bile helps to digest fats.
(ii) The pancreatic juice converts carbohydrates, fats and proteins to simpler forms.
(iii) The remaining undigested food is digested in the lower part of the small intestine by the intestinal juice. All components of food namely carbohydrates, fats and proteins are broken down into glucose, fatty acids and glycerol and amino acids respectively.
(E) Fill in the Blanks:
wider, J-shaped, digestive system, defecated, shorter, liver
(a) Food that is not used by the body is _________.
(b) The digestive tract and the associated glands together form the _________.
(c) The _________ is the largest gland in the body.
(d) The large intestine is _________ and _________ than the small intestine.
(e) The shape of the stomach is _________.
Answers:
(a) Food that is not used by the body is defecated.
(b) The digestive tract and the associated glands together form the digestive system.
(c) The liver is the largest gland in the body.
(d) The large intestine is shorter and wider than the small intestine.
(e) The shape of the stomach is J-shaped.
(F) Match and Pair:
1. Match the items of Column I with suitable items in Column II:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Milk teeth | (i) Buccal cavity |
| (b) William Beaumont | (ii) 1.5 metre |
| (c) Tongue | (iii) Infancy |
| (d) Large intestine | (iv) Gall bladder |
| (e) Bile | (v) Working of stomach |
Answer:
The correct table is shown below:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a)Milk teeth | (iii) Infancy |
| (b) William Beaumont | (v) Working of stomach |
| (d)Tongue | (i) Buccal cavity |
| (e) Large intestine | (ii) 1.5 metre |
| (f) Bile | (iv) Gall bladder |
++++++++++++++
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on NCERT Solutions to Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals:
The solutions to the exercises, extended learning, in-text questions and activities have been designed by experienced teachers and scientists and comprehensively cover the chapter. We have also included many typical questions that you will see in your exams along with selected questions from NCERT Exemplar. The concepts have been explained simply and logically with attractive figures to help you easily understand and retain the material.
The free PDFs of the solutions are available for download anytime! We will keep supplying you with plenty of top-quality study material and resources to support your preparation. So, keep visiting our website and join our email list to be among the first to receive them!
The following topics are covered:
2.1 – Different Ways of Taking Food
2.2 – Digestion in Humans
2.3 – Digestion in Grass-Eating Animals
2.4 – Feeding and Digestion in Amoeba
Here are the number of problems for the chapter:
(i) 1 Fill in the Blanks Question (Question 1)
(ii) 1 True/False Type Question (Question 2)
(iii) 1 Tick the Correct Answer Question (Question 3)
(iv) 2 Match and Pair Questions (Questions 3, 11)
(v) 6 Short Answer Type Questions (Questions 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 13)
(vi) 1 Name the Following Question (Question 9)
(vii) 1 Label the Diagram Type Question (Question 12)
Of course! Feel free to download the PDF versions of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals anytime! All the different types of additional questions are also included in the PDF version! Please look towards the top of the page!
The most important part of this chapter is to understand how the human digestive system works and the functions of the different organs, glands etc. Once you know the human digestive system, make sure you are able to understand how it is different from the digestive system of certain animals, amoeba etc. Please try to understand how the process works, instead of just memorising. This will help you answer different types of questions in your exams with relative ease.
Need extra help? Need us to prepare you for your exams? Need academic and career guidance? Our expert teacher-mentors will be there for you anytime you need them! Reach out to us anytime with your requirements and let us help you out!
Expert guidance can make a world of difference! Our experienced teacher-mentors understand your needs and will prepare you in the right way to help you excel in any exam. They will also provide you with expert advice regarding your future academic and professional careers at no extra cost. If that is what you are looking for, feel free to contact us anytime. We provide expert one-on-one coaching and mentoring to you depending on your convenience and needs- have it completely your way! Reach out to us anytime and let us help you out! Book any number of appointments now!


