7. Complete Activity 1.7 (Page 9).
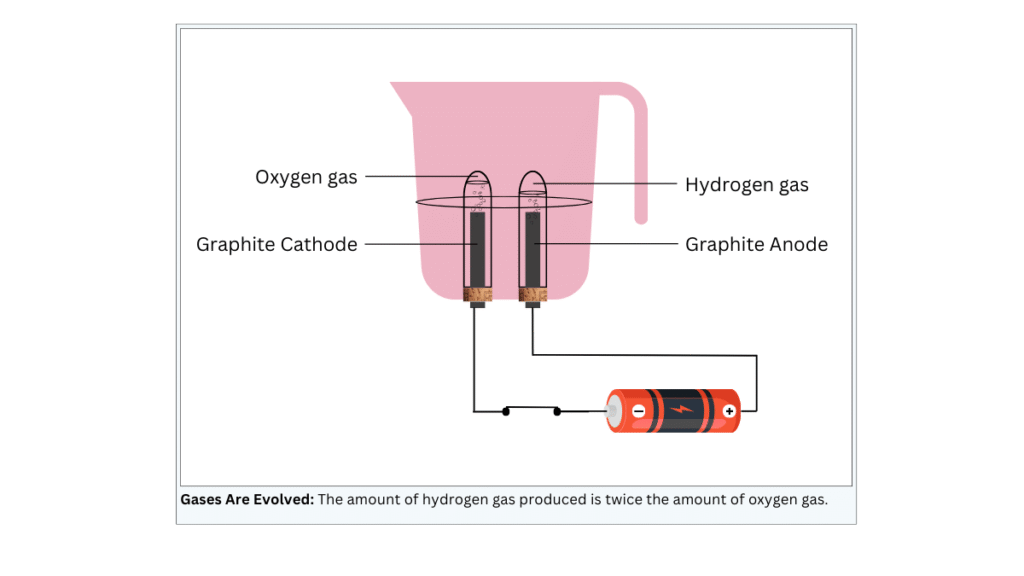
- Take a plastic mug. Drill two holes at its base and fit rubber stoppers in these holes. Insert carbon electrodes in these rubber stoppers as shown in Fig. 1.6.
- Connect these electrodes to a 6 volt battery.
- Fill the mug with water such that the electrodes are immersed. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the water.
- Take two test tubes filled with water and invert them over the two carbon electrodes.
- Switch on the current and leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
- You will observe the formation of bubbles at both the electrodes. These bubbles displace water in the test tubes.
- Is the volume of the gas collected the same in both the test tubes?
- Once the test tubes are filled with the respective gases, remove them carefully.
- Test these gases one by one by bringing a burning candle close to the mouth of the test tubes. CAUTION: This step must be performed carefully by the teacher.
- What happens in each case?
- Which gas is present in each test tube?
Answer:
Aim: To observe if the volume of the gas collected in both test tubes is the same, test the gases one by one using a burning candle and make the necessary conclusions.
Materials Required: Plastic mug, two rubber stoppers, two carbon electrodes, 6 V battery, water, dilute sulphuric acid, candle.
Procedure:
(i) Two equal sized holes are drilled at the bottom of the plastic mug and the rubber stoppers are fitted in these holes.
(ii) The carbon electrodes are inserted in the rubber stoppers.
(iii) The electrodes are connected to the terminals of a 6 V battery.
(iv) Now, fill the mug with water taking care that the electrodes are immersed.
(v) Few drops of sulphuric acid are added to the water.
(vi) Two test tubes are filled with water and inverted over the two carbon electrodes.
(vii) The current is switched on and the apparatus is left undisturbed for some time. The observations are noted.
(viii) Once the test tubes are filled with gas they are removed carefully.
(ix) The gases are tested using a burning candle held close to the mouth of each test tube. CAUTION: This step must be performed carefully by the teacher. Note the observations.
Observations:
- Gas bubbles form at both electrodes and displace water in the test tubes.
- The volume of gas collected in one test tube is twice the volume of gas collected in the other test tube.
- One of the gases burns with a popping sound when the burning candle near the out of the test tube. No such sound is heard for the other gas.
Conclusions:
- On passage of electric current, water decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- One molecule of water forms 2 molecules of hydrogen and 1 molecule of oxygen, hence the volume of hydrogen collected is twice that of oxygen collected. The decomposition reaction is shown below:
2H2O (l) —> 2H2(g) + O2(g) - The gas which burns with a popping sound is hydrogen while the other gas is oxygen.
- The electrode at which hydrogen gas is produced is called cathode and the electrode at which oxygen gas is produced is called anode.
- This specific decomposition reaction is known as electrolysis of water.
“7. Complete Activity 1.7 (Page 9).
Which gas is present in each test tube?
Take a plastic mug. Drill two holes at its base and fit rubber stoppers in these holes. Insert carbon electrodes in these rubber stoppers as shown in Fig. 1.6.
Connect these electrodes to a 6 volt battery.
Fill the mug with water such that the electrodes are immersed. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the water.
Take two test tubes filled with water and invert them over the two carbon electrodes.
Switch on the current and leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
You will observe the formation of bubbles at both the electrodes. These bubbles displace water in the test tubes.
Is the volume of the gas collected the same in both the test tubes?
Once the test tubes are filled with the respective gases, remove them carefully.
Test these gases one by one by bringing a burning candle close to the mouth of the test tubes. CAUTION: This step must be performed carefully by the teacher.
What happens in each case?” – Solved.
Related Links:
Solution to Group Activity
Solution to Activity 1.1
Solution to Activity 1.2
Solution to Activity 1.3
Solution to Activity 1.4
Solution to Activity 1.5
Solution to Activity 1.6
Solution to Activity 1.7
Solution to Activity 1.8
Solution to Activity
Solution to Activity 1.9
Solution to Activity 1.10
Solution to Activity 1.11


