6. Complete Activity 2.6 (Page 21).
- Take about 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube and add two drops of phenolphthalein solution.
- What is the colour of the solution?
- Add dilute HCl solution to the above solution drop by drop.
- Is there any colour change for the reaction mixture?
- Why did the colour of phenolphthalein change after the addition of an acid?
- Now add a few drops of NaOH to the above mixture.
- Does the pink colour of phenolphthalein reappear?
- Why do you think this has happened?
Answer:
Aim: To observe how the colour of phenolphthalein solutionchanges by alternately addingNaOH and HCl solutions and conclude based on that.
Materials Required: 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution, dilute HCl solution, phenolphthalein solution, test tube, two droppers.
Procedure:
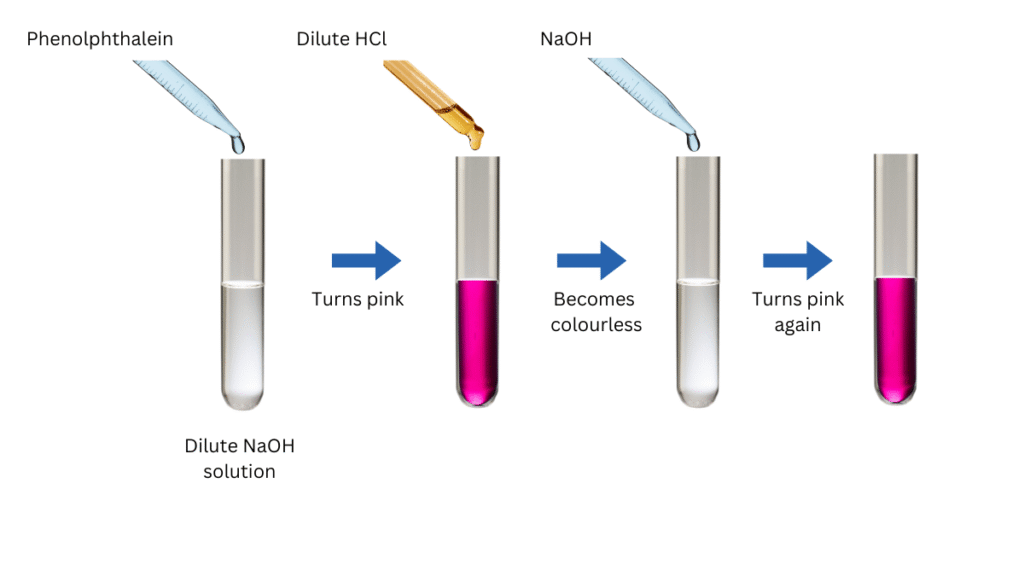
(i) Take about 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution in the test tube.
(ii) Add two drops of the phenolphthalein solution to the test tube. Note the colour of the solution.
(iii) Using the first dropper add dilute HCl solution to the above solution drop by drop. Note the colour change for the reaction mixture.
(iv) Now using the second dropper add a few drops of NaOH to the above mixture. Note the colour change for the reaction mixture.
Observations:
- After adding phenolphthalein solution to NaOH the solution turns pink.
- When dilute HCl solution is added, the pink colour gradually fades and the solution becomes colourless.
- When NaOH is added to the above mixture, the solution turns pink again.
Conclusions:
- Phenolphthalein indicator shows pink colour in basic solutions and is colourless in acidic solutions.
- Initially the basic NaOH solution gave the pink colour.
- When acid was added a neutralisation rection took place which nullified the effect of the base and gradually the solution became acidic. Hence the solution became colourless.
- When NaOH was added it nullified the effect of the acid and the solution became pink again.
- The reaction is shown below:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) –> NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) - In general, the reaction between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is known as a neutralisation reaction. In general, a neutralisation reaction can be written as: Base + Acid → Salt + Water.
“6. Complete Activity 2.6 (Page 21).
Why do you think this has happened?
Take about 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube and add two drops of phenolphthalein solution.
What is the colour of the solution?
Add dilute HCl solution to the above solution drop by drop.
Is there any colour change for the reaction mixture?
Why did the colour of phenolphthalein change after the addition of an acid?
Now add a few drops of NaOH to the above mixture.
Does the pink colour of phenolphthalein reappear?” – Solved.
Related Links:
Solution to Group Activity
Solution to Activity 2.1
Solution to Activity 2.2
Solution to Activity 2.3
Solution to Activity 2.4
Solution to Activity 2.5
Solution to Activity 2.6
Solution to Activity 2.7
Solution to Activity 2.8
Solution to Activity 2.9
Solution to Activity 2.10
Solution to Activity 2.11
Solution to Activity 2.12
Solution to Activity 2.13
Solution to Activity 2.14
Solution to Activity 2.15


