8. Complete Activity 2.8 (Page 22).
- Take solutions of glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, etc.
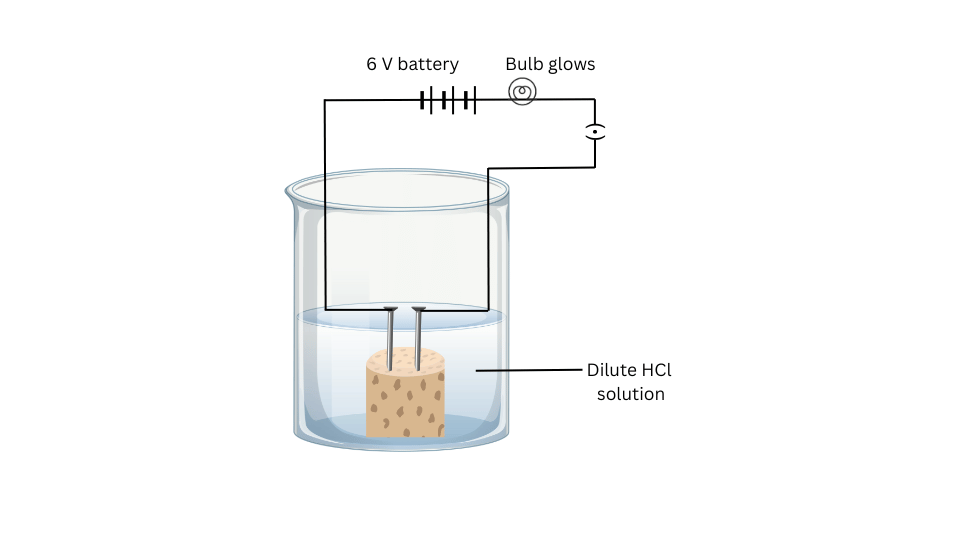
- Fix two nails on a cork, and place the cork in a 100 mL beaker.
- Connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6 volt battery through a bulb and a switch, as shown in Fig. 2.3.
- Now pour some dilute HCl in the beaker and switch on the current.
- Repeat with dilute sulphuric acid.
- What do you observe?
- Repeat the experiment separately with glucose and alcohol solutions. What do you observe now?
- Does the bulb glow in all cases?
Answer:
Aim: To pass current through dilute HCl, dilute sulphuric acid, glucose and alcohol solutionsand conclude based on the observations.
Materials Required: Glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nails, cork, 100 mL beaker. 6 V battery, bulb, switch.
Procedure:
(i) Attach the two nails to the cork and place the cork in the 100 mL beaker.
(ii) Connect the nails to the two terminals of the 6 volt battery through the bulb and switch to complete the circuit.
(iii) Pour dilute HCl solution and switch on the current. Note the observations.
(iv) Repeat the activity with dilute sulphuric acid solution. Note the observations.
(v) Repeat the activity with glucose and alcohol solutions. Note the observations.
(vi) Repeat the same activity with sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide. Note the observations.
Observations:
- The bulb glows in case of the dilute HCl and dilute sulphuric acid solutions.
- The bulb does not glow in case of the glucose and alcohol solutions.
- The bulb glows in case of sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide solutions.
Conclusions:
- HCl forms H+ and Cl– ions in aqueous solution. These ions conduct electricity.
- H2SO4 forms H+ and SO42- ions in aqueous solution. These ions conduct electricity.
- Glucose and alcohol do not form ions in aqueous solution. Hence, they do not conduct electricity.
- NaOH forms Na+ and OH– ions in aqueous solution. These ions conduct electricity.
- Ca(OH)2 forms Ca2+ and ions in aqueous solution. These ions conduct electricity.
- We conclude that acids and bases form ions in aqueous solution.
“8. Complete Activity 2.8 (Page 22).
Does the bulb glow in all cases?
Take solutions of glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, etc.
Fix two nails on a cork, and place the cork in a 100 mL beaker.
Connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6 volt battery through a bulb and a switch, as shown in Fig. 2.3.
Now pour some dilute HCl in the beaker and switch on the current.
Repeat with dilute sulphuric acid.
What do you observe?
Repeat the experiment separately with glucose and alcohol solutions. What do you observe now?” – Solved.
Related Links:
Solution to Group Activity
Solution to Activity 2.1
Solution to Activity 2.2
Solution to Activity 2.3
Solution to Activity 2.4
Solution to Activity 2.5
Solution to Activity 2.6
Solution to Activity 2.7
Solution to Activity 2.8
Solution to Activity 2.9
Solution to Activity 2.10
Solution to Activity 2.11
Solution to Activity 2.12
Solution to Activity 2.13
Solution to Activity 2.14
Solution to Activity 2.15


